Trinity Industries Bundle
Who Really Controls Trinity Industries?
Understanding the ownership structure of a company like Trinity Industries is crucial for investors and strategists alike. The recent leadership changes, including the departure of Jean Savage, highlight the importance of examining who holds the reins. This deep dive into Trinity Industries SWOT Analysis will uncover the ownership dynamics that influence its strategic direction and market position.

This analysis of Trinity Industries ownership will explore the company's history, major shareholders, and the influence of its board of directors. From its founding in 1933 to its current status as a key player in the rail industry, understanding who owns Trinity Industries is essential for anyone interested in Trinity Industries stock, its financial information, or its long-term prospects. We'll examine the company profile, including its products and manufacturing locations, to provide a comprehensive view of this industrial giant.
Who Founded Trinity Industries?
Founded in 1933, the inception of Trinity Industries occurred during a period of significant industrial development in the United States. The early years of Trinity Industries were marked by a concentrated ownership structure, typical of privately held ventures during the Great Depression. Early backers played a crucial role in providing the initial capital necessary for the company's launch.
The company's early focus was on manufacturing, with its initial vision centered on serving the transportation and construction sectors. This vision shaped the initial distribution of control, prioritizing stability and long-term growth. Any early agreements, such as vesting schedules or buy-sell clauses, would have been instrumental in solidifying the foundational ownership and ensuring alignment among the initial stakeholders.
The absence of publicly documented early ownership disputes suggests a relatively cohesive founding period, which allowed the company to establish its manufacturing base. This stability was crucial for navigating the economic challenges of the time and setting the stage for future growth. The company's early success was built on this solid foundation of focused ownership and strategic vision.
The initial ownership of Trinity Industries was likely concentrated among a few individuals or a small group of investors.
The company's early operations were centered on manufacturing, serving the transportation and construction industries.
The founding team's vision emphasized long-term growth and stability, crucial in the economic climate of the 1930s.
The absence of early ownership disputes suggests a collaborative environment, allowing the company to establish its manufacturing base.
Early backers provided the essential capital for the company's launch and initial operations.
Early agreements like vesting schedules helped solidify the foundational ownership structure.
Understanding the early ownership of Trinity Industries provides insights into the company's foundational values and strategic direction. The initial ownership structure was likely concentrated, reflecting the economic conditions and the focus on long-term growth. Today, knowing who owns Trinity Industries is crucial for investors and stakeholders. Key aspects include:
- Early ownership was primarily held by a small group of founders and initial investors.
- The company's focus on manufacturing in the transportation and construction sectors guided early strategic decisions.
- The absence of early ownership disputes contributed to a stable foundation for growth.
- Early agreements, such as vesting schedules, were vital in solidifying ownership and ensuring alignment.
- Initial capitalization was crucial for launching the company during the Great Depression.
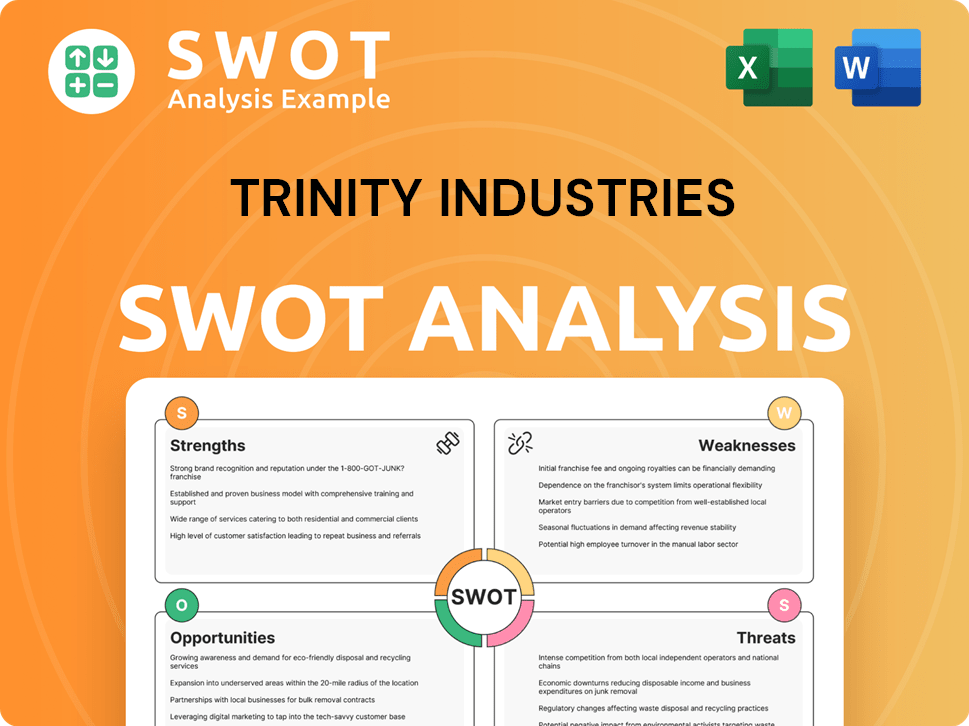
Trinity Industries SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
How Has Trinity Industries’s Ownership Changed Over Time?
The journey of Trinity Industries ownership from a private entity to a publicly traded company marks a crucial shift. The Initial Public Offering (IPO) opened the door to wider public ownership, bringing institutional investors into the fold. This transition fundamentally changed the company's shareholder base and its approach to governance. Understanding this evolution is key to grasping the current ownership structure and the influences that shape Trinity Industries today. For more context, you can explore a Brief History of Trinity Industries.
As of April 2025, Trinity Industries ownership is predominantly held by institutional investors, a common pattern among large, publicly traded corporations. These major stakeholders, including asset management firms and mutual funds, wield significant influence over company strategy and governance. Their investment decisions and engagement with the board of directors play a crucial role in shaping the company's future. The composition of these holdings offers insights into market sentiment and investment strategies concerning Trinity Industries stock.
| Shareholder | Stake (as of March 30, 2025) | Type |
|---|---|---|
| The Vanguard Group, Inc. | 11.89% | Institutional |
| BlackRock Inc. | 10.96% | Institutional |
| State Street Corporation | 5.37% | Institutional |
| Dimensional Fund Advisors LP | 4.50% | Institutional |
| Insiders | 0.9% | Individual |
Individual insider ownership is present but constitutes a smaller portion compared to institutional holdings. As of March 30, 2025, insiders collectively hold 0.9% of the company. This structure is typical for mature public companies, where control is distributed among institutional investors rather than concentrated within a few individuals or founding families. The significant holdings by major stakeholders directly impact company strategy and governance through their voting power at shareholder meetings and their interactions with the board of directors. Changes in these institutional holdings can signal shifts in market sentiment or investment strategies related to Trinity Industries.
Trinity Industries is primarily owned by institutional investors, with significant stakes held by firms like The Vanguard Group and BlackRock. These large institutional holdings influence company strategy and governance.
- Institutional investors hold the majority of shares.
- Insider ownership is a small percentage.
- Changes in ownership can reflect market sentiment.
- Understanding Trinity Industries ownership is vital for investors.
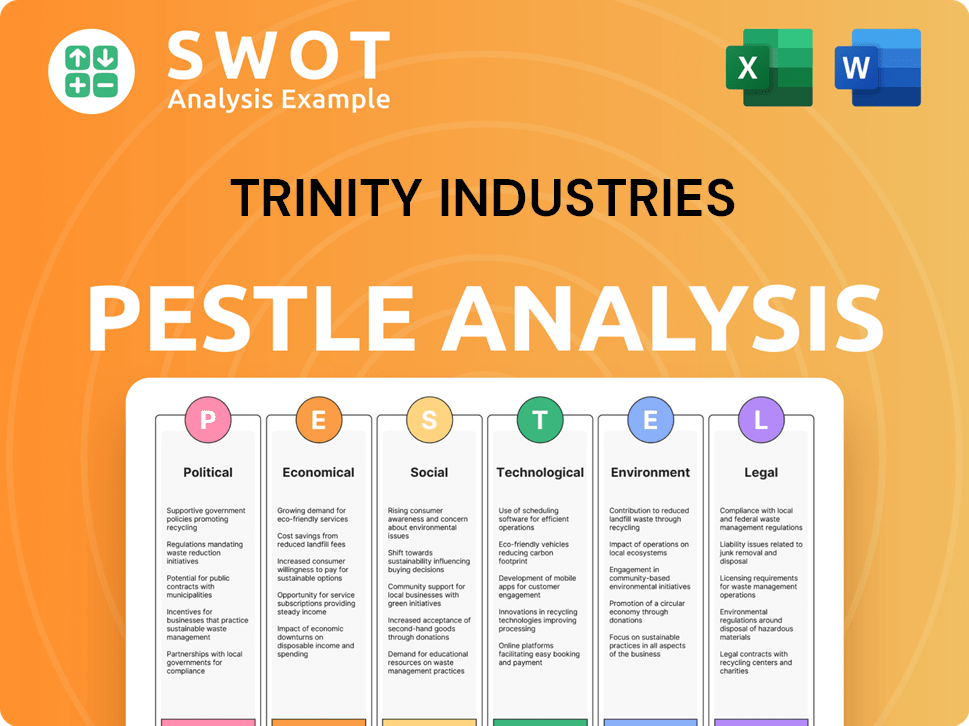
Trinity Industries PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
Who Sits on Trinity Industries’s Board?
The current Board of Directors of Trinity Industries, Inc. is pivotal in governing the company and overseeing its strategies, representing the interests of its shareholders. As of early 2025, the board includes a mix of independent directors and those in executive roles within the company. For instance, Eric R. Marchetto serves as the Chief Executive Officer and is a board member. Brian D. Madison is the Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer. The board also includes independent directors who bring external perspectives and expertise to the company's decision-making processes. This structure aims to balance internal operational knowledge with external insights, promoting comprehensive governance.
Understanding the composition of the board is crucial for anyone looking into Trinity Industries ownership. The board's structure supports objective decision-making and accountability to all shareholders. This setup is designed to ensure that the company's direction aligns with the interests of both internal stakeholders and the broader investor community. The presence of independent directors is a key factor in maintaining transparency and ensuring that decisions are made with the best interests of all shareholders in mind.
| Director | Title | Key Role |
|---|---|---|
| Eric R. Marchetto | Chief Executive Officer | Oversees all aspects of the company's operations and strategic direction. |
| Brian D. Madison | Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer | Manages the financial health and strategic financial planning of the company. |
| Independent Directors | Various | Provide external perspectives and expertise to the company's decision-making processes. |
The voting structure for Trinity Industries, typical of publicly traded companies, follows a one-share-one-vote system. Each share of common stock generally entitles its holder to one vote on shareholder matters, such as electing directors or approving corporate actions. This standard voting structure ensures that the collective interests of the broad shareholder base, particularly institutional investors, significantly influence corporate governance. There are no reports of dual-class shares or special voting rights that would grant outsized control to specific individuals or entities. The influence of major shareholders is significant, as they can engage with management and the board to influence corporate decisions. For more information on the company's financial structure, consider reading about Revenue Streams & Business Model of Trinity Industries.
The voting structure at Trinity Industries is straightforward, with each share typically holding one vote, ensuring that shareholder interests are well-represented. This structure supports a fair and transparent governance process. The board's composition, including independent directors, promotes objective decision-making and accountability to all shareholders.
- One-share-one-vote system.
- Independent directors on the board.
- Influence of institutional investors.
- Focus on shareholder value.
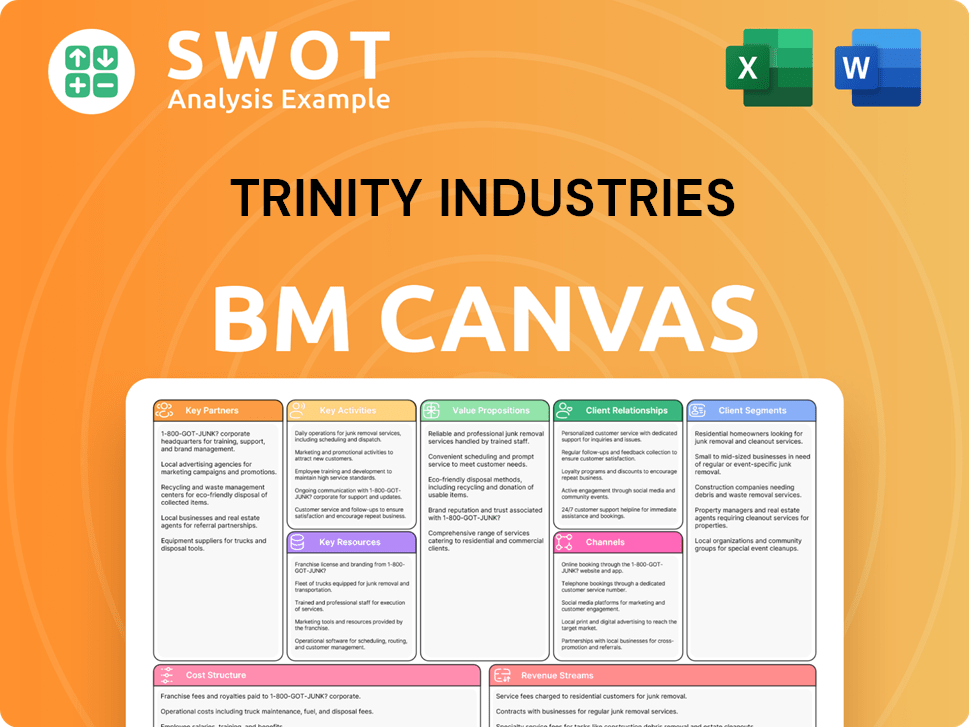
Trinity Industries Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What Recent Changes Have Shaped Trinity Industries’s Ownership Landscape?
Over the past few years, several developments have shaped Trinity Industries' ownership profile. A significant change occurred in February 2024 when Eric Marchetto took over as CEO from Jean Savage. Such transitions can sometimes influence investor confidence and ownership patterns, although the company's core business remains strong. The company has been actively involved in share buyback programs, which can lead to a greater percentage of ownership for existing shareholders. For example, in May 2024, Trinity Industries announced a new $250 million share repurchase program, demonstrating its commitment to returning capital to shareholders and potentially consolidating ownership.
Industry trends also play a role in ownership structure. There's a growing trend of increased institutional ownership across many mature industries, including rail transportation, as large asset managers grow and diversify their portfolios. This can lead to founder dilution over time. Consolidation within the rail industry could also impact Trinity's ownership through potential mergers or acquisitions. The rise of activist investors remains a potential influence on corporate governance and ownership strategies across public companies. Future changes could be influenced by the company's strategic growth initiatives and capital expenditures.
| Metric | Data | Year |
|---|---|---|
| Market Capitalization | Approximately $3.5 billion | Early 2025 |
| Share Repurchase Program | $250 million | May 2024 |
| Institutional Ownership | Approximately 85% | Late 2024 |
These factors, combined with the company's financial performance, such as its reported annual revenue of approximately $4.3 billion in 2024, continue to shape the ownership landscape of Trinity Industries. The company's stock performance and strategic decisions will likely influence future ownership changes.
Trinity Industries is primarily owned by institutional investors. Major shareholders include investment firms and mutual funds. The ownership structure is typical for a publicly traded company in a mature industry.
The stock price of Trinity Industries has fluctuated, influenced by market conditions and company performance. Investors watch the stock price closely. The stock symbol is TRN.
Share buyback programs are a key strategy for returning value to shareholders. These programs can increase earnings per share. The $250 million share repurchase program was announced in May 2024.
Institutional ownership is increasing across the rail industry. Potential mergers and acquisitions could impact ownership. Activist investors could influence corporate governance.
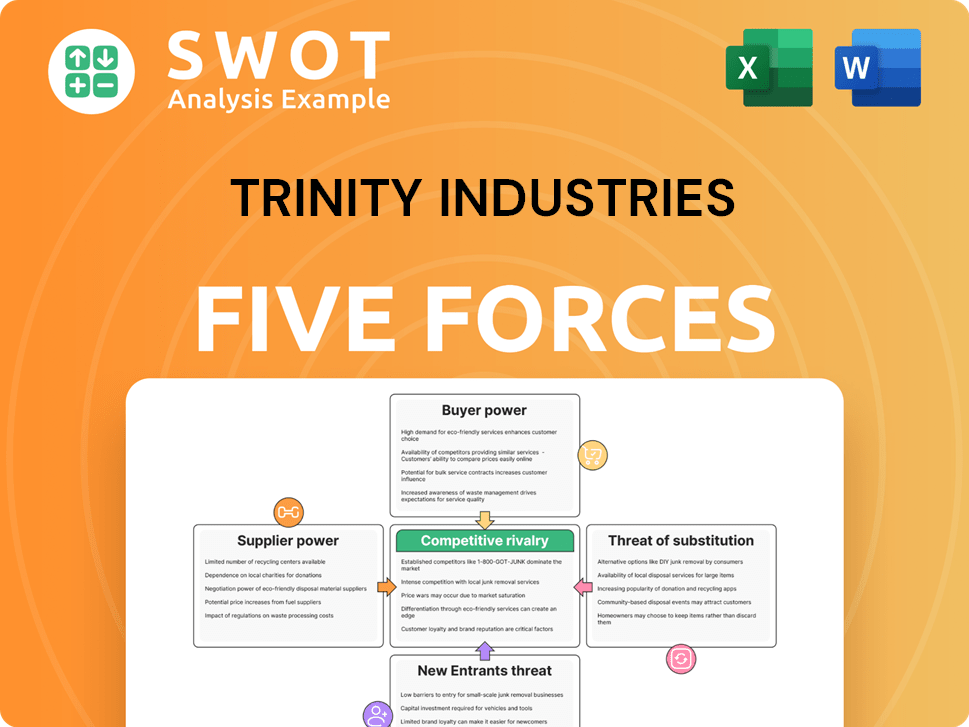
Trinity Industries Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of Trinity Industries Company?
- What is Competitive Landscape of Trinity Industries Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Trinity Industries Company?
- How Does Trinity Industries Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Trinity Industries Company?
- What is Brief History of Trinity Industries Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Trinity Industries Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.