Vodafone Group Bundle
Who Really Calls the Shots at Vodafone Group?
Unraveling the Vodafone ownership structure is key to understanding its strategic moves and market influence. From its roots as Racal Telecomms to its global presence today, Vodafone's journey has been shaped by a dynamic mix of investors. Knowing who owns Vodafone Group is crucial for anyone looking to understand its future direction and potential.
The Vodafone Group SWOT Analysis is essential for investors. This analysis will explore the Vodafone shareholders, the Vodafone parent company, and the broader Vodafone structure. We'll examine the evolution of Vodafone's ownership, from early investors to the current major players, revealing how these shifts have shaped the company's governance and strategic decisions. This comprehensive overview will answer questions like "Who are Vodafone's major shareholders?" and "Is Vodafone a publicly traded company?"
Who Founded Vodafone Group?
The story of Vodafone Group begins with Racal Telecomms, a division of Racal Electronics. Ernest Harrison, then chairman of Racal Electronics, played a crucial role in recognizing the potential of mobile telecommunications, setting the stage for what Vodafone would become. While not a traditional founder, Harrison's vision was instrumental in the company's early development.
Initially, Vodafone's ownership was entirely within Racal Electronics. The company's structure evolved significantly when Racal Telecomms was spun off and listed on the London Stock Exchange in 1991 as Vodafone Group Plc. This initial public offering (IPO) marked a shift from a wholly-owned subsidiary to a publicly traded entity.
The IPO introduced a broader shareholder base, transforming the ownership landscape. Specific details about individual equity splits or initial shareholding percentages at the inception of Racal Telecomms are not publicly available due to its internal division status. Early backers were essentially the shareholders of Racal Electronics, who subsequently received shares in Vodafone upon its demerger. The demerger agreement effectively distributed control to a wider set of investors through the public offering, paving the way for its future growth as an independent company.
Understanding the early structure of Vodafone Group is key to understanding its current marketing strategy. The company's journey from a subsidiary to a publicly traded entity shaped its Vodafone ownership and investor relations. Key points include:
- Racal Electronics was the Vodafone parent company at the outset.
- The IPO in 1991 marked a significant change in the Vodafone structure.
- Early Vodafone investors were the shareholders of Racal Electronics.
- The demerger facilitated a broader distribution of shares.
Vodafone Group SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
How Has Vodafone Group’s Ownership Changed Over Time?
The ownership structure of Vodafone Group has seen significant changes since its initial public offering (IPO) in 1991. As a publicly traded entity, its shares are broadly distributed among various investors, including institutional investors, mutual funds, and individual shareholders. Key events, such as mergers, acquisitions, and divestitures, have reshaped the company's ownership. The acquisition of Mannesmann in 2000 was a pivotal moment, substantially altering Vodafone's scale and integrating Mannesmann's shareholders into the Vodafone ownership framework.
The evolution of Vodafone's ownership reflects its strategic moves in the telecommunications market. The company's structure has been influenced by its growth strategy, which has involved both expanding its global footprint and streamlining its operations through asset sales. Understanding the Vodafone structure is essential for investors tracking the company's performance and strategic direction. The shifts in ownership have also driven Vodafone to focus on shareholder returns, including divesting non-core assets and optimizing operations.
| Event | Impact | Year |
|---|---|---|
| IPO | Initial public offering, shares available to the public | 1991 |
| Acquisition of Mannesmann | Significant increase in scale and shareholder base | 2000 |
| Strategic Divestitures | Streamlining operations and refocusing on core markets | Ongoing |
As of early 2025, major institutional shareholders play a crucial role in Vodafone's ownership. While specific percentages fluctuate, prominent institutional investors such as BlackRock, Inc. and The Vanguard Group are consistently among the top holders of Vodafone shares, reflecting a common trend in large-cap public companies. These institutional holdings often give them substantial voting power and influence over company strategy and governance. For detailed breakdowns, one can consult recent SEC filings or annual reports, which show the distribution between institutional and retail ownership. For more insights, consider exploring the Competitors Landscape of Vodafone Group.
Vodafone's ownership structure is primarily shaped by institutional investors, with significant stakes held by major asset management firms.
- Institutional investors hold a considerable portion of Vodafone shares, influencing strategic decisions.
- Mergers and acquisitions, such as the Mannesmann acquisition, have significantly impacted the shareholder base.
- Understanding the Vodafone ownership breakdown is crucial for investors to assess the company's direction.
- Recent strategic moves include asset sales and a focus on shareholder returns.
Vodafone Group PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
Who Sits on Vodafone Group’s Board?
The Board of Directors of Vodafone Group, as of early 2025, includes a mix of executive and non-executive directors. Key figures include Jean-François van Boxmeer as Chairman and Margherita Della Valle as Chief Executive. The board's composition reflects a balance designed to ensure robust governance and oversight, aligning with the interests of the broader shareholder base. This structure helps in making decisions that consider shareholder value, reflecting the distributed yet influential nature of its ownership.
The governance structure of Vodafone Group is designed to ensure accountability and strategic direction. The board's decisions, including those related to divestments or strategic partnerships, are made with consideration of shareholder value. This approach is crucial in a company with a diverse shareholder base, ensuring that the interests of all stakeholders are taken into account. The Brief History of Vodafone Group provides additional context on the company's evolution and its governance practices.
| Board Member | Role | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Jean-François van Boxmeer | Chairman | Oversees the board's activities and ensures effective governance. |
| Margherita Della Valle | Chief Executive | Leads the company's operations and strategic direction. |
| Non-Executive Directors | Various | Provide independent oversight and expertise in areas such as finance, technology, and risk management. |
Vodafone operates on a one-share-one-vote principle for its ordinary shares. This means voting power is directly proportional to the number of shares owned. There are no known dual-class shares or similar mechanisms that would grant disproportionate voting rights. This structure ensures that all Vodafone shareholders have voting rights based on their share ownership, promoting a fair and transparent governance model. Recent years have seen a focus on corporate governance, with activist investors occasionally engaging with the company on issues such as strategy and executive compensation. These engagements underscore the influence of significant institutional Vodafone shareholders in shaping decision-making processes.
Voting power at Vodafone is directly proportional to share ownership, with no special voting rights. The board includes executive and non-executive directors, ensuring robust governance. The board's decisions consider shareholder value, reflecting the distributed nature of Vodafone shareholders.
- One-share-one-vote principle.
- Focus on corporate governance.
- Board decisions consider shareholder value.
- Influenced by institutional Vodafone investors.
Vodafone Group Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What Recent Changes Have Shaped Vodafone Group’s Ownership Landscape?
Over the past few years (2022-2025), the ownership landscape of Vodafone Group has seen notable shifts, primarily driven by strategic divestitures and a focus on streamlining operations. A key development has been the ongoing process of selling off its stake in Vantage Towers, a move designed to reduce debt and concentrate on core connectivity services. For example, in late 2022 and early 2023, Vodafone completed the sale of a portion of its Vantage Towers stake to a consortium led by KKR and Global Infrastructure Partners. This transaction brought in significant capital and adjusted the composition of its assets and, indirectly, its shareholder appeal. This is part of a broader strategy to enhance shareholder value and reshape the Growth Strategy of Vodafone Group.
Industry trends, such as the rise of institutional ownership and a focus on shareholder returns, continue to influence Vodafone. The company has engaged in share buyback programs aimed at returning value to shareholders, potentially increasing the percentage ownership of existing shareholders. Discussions and speculation regarding potential mergers or acquisitions in certain markets could significantly impact the ownership structure. Public statements from Vodafone's leadership often emphasize a commitment to simplifying operations and exploring strategic partnerships, which could lead to further shifts in ownership or the introduction of new strategic investors in specific regional operations. The company's recent focus on simplifying its structure and improving operational efficiency aligns with broader industry trends and investor expectations for improved returns.
| Metric | Details | Data (Approximate) |
|---|---|---|
| Market Capitalization (as of May 2024) | Reflects the total value of outstanding shares. | Around $25 billion USD |
| Share Buyback Program (Announced 2023) | Amount allocated for repurchasing shares. | £500 million |
| Institutional Ownership | Percentage of shares held by institutional investors. | Approximately 50-60% |
Vodafone Group's ownership structure is primarily influenced by institutional investors and public shareholders. Key players include large investment firms and pension funds. The company’s focus on strategic partnerships and streamlining operations continues to shape its ownership profile, with ongoing efforts to enhance shareholder value and adapt to market dynamics. The company's stock symbol is VOD.
Vodafone Group is a publicly traded company, with a diverse shareholder base. Major shareholders include institutional investors and a significant portion of shares held by the public.
Divestitures, like the sale of Vantage Towers stake, have brought in capital and reshaped the company's asset composition. These moves are part of a broader strategy to reduce debt and focus on core services.
Vodafone is actively pursuing share buyback programs to return value to shareholders. This can incrementally increase the ownership percentage of remaining shareholders.
The company is exploring strategic partnerships, which could lead to further shifts in ownership and the introduction of new strategic investors in specific regional operations.
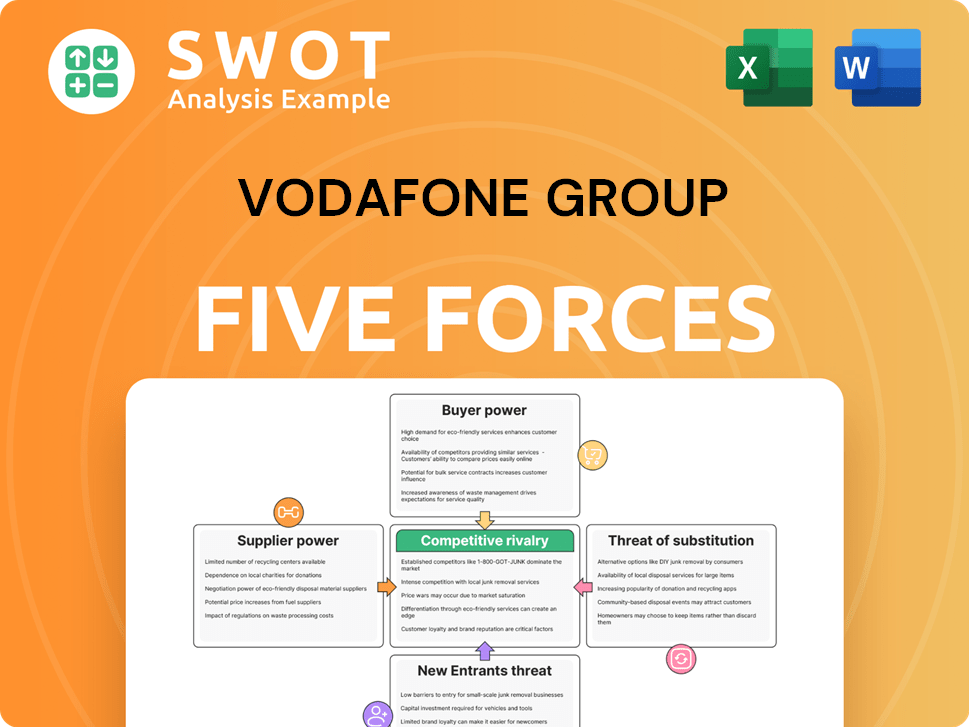
Vodafone Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of Vodafone Group Company?
- What is Competitive Landscape of Vodafone Group Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Vodafone Group Company?
- How Does Vodafone Group Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Vodafone Group Company?
- What is Brief History of Vodafone Group Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Vodafone Group Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.