CLP Holdings Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
CLP Holdings Bundle
What is included in the product
Analyzes CLP Holdings' position in the power industry, evaluating competitive forces.
Instantly understand strategic pressure with a powerful spider/radar chart.
Full Version Awaits
CLP Holdings Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases CLP Holdings' Porter's Five Forces Analysis in its entirety. The document displayed here is the same analysis you’ll download instantly after purchase.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Template
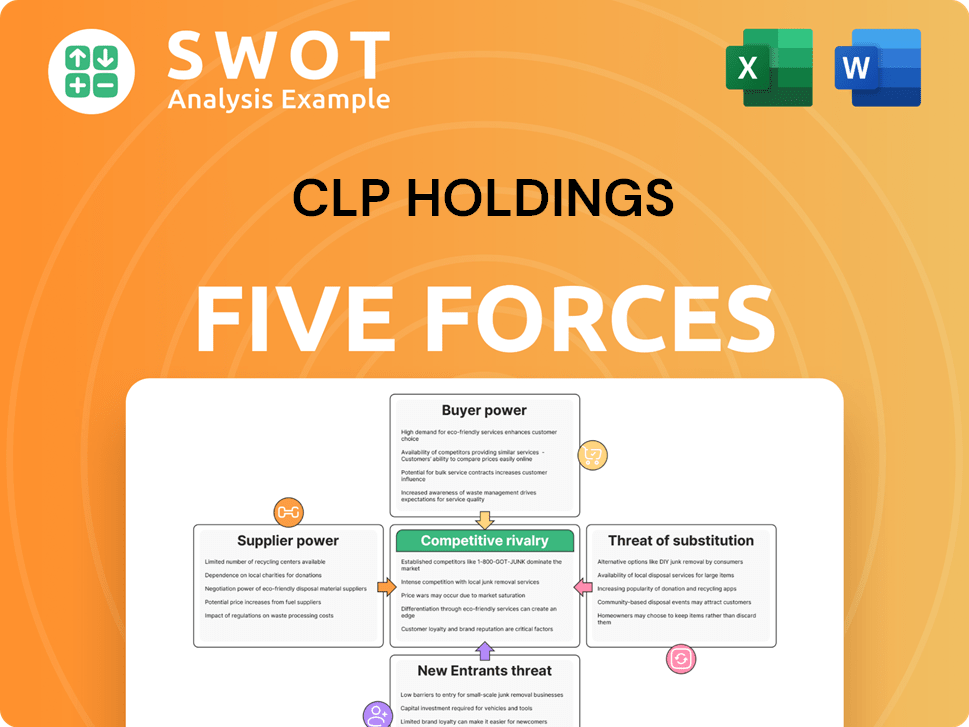
CLP Holdings faces moderate rivalry due to its established position, balanced by high capital costs. Buyer power is relatively low, with stable demand and regulated pricing. Supplier power is limited due to diversified energy sources. The threat of new entrants is low due to high barriers and regulations. Substitutes pose a moderate threat, with renewable energy trends.
Unlock key insights into CLP Holdings’s industry forces—from buyer power to substitute threats—and use this knowledge to inform strategy or investment decisions.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
High supplier concentration can significantly increase suppliers' bargaining power. If CLP depends on few suppliers for essential resources, they hold more leverage. For example, in 2024, the price of key fuel components rose, impacting energy firms. CLP's dependence on specific tech suppliers can make it vulnerable to price hikes.
Fluctuations in fuel costs, especially coal and gas, heavily influence CLP's profitability. The removal of the coal price cap at Mt Piper has driven up fuel expenses, impacting the company's financial outcomes. In 2024, coal prices saw volatility, affecting operational costs. Effective fuel cost management is vital for competitive tariffs. The company's 2024 reports reflect these challenges.
CLP Holdings heavily depends on suppliers for specialized equipment and technology crucial for its operations. The bargaining power of these suppliers is significant, especially if they hold proprietary technology. For example, in 2024, CLP invested heavily in smart grid technologies, increasing its reliance on specific tech providers. Switching costs are high due to the complexity of power infrastructure.
Regulatory Compliance Costs
Stringent environmental regulations significantly impact CLP Holdings' supplier relationships. Compliance costs, driven by the need for emissions control technologies and cleaner fuel mixes, can increase supplier pricing for essential equipment and services. For example, in 2024, CLP invested heavily in technologies to reduce emissions, affecting supplier contracts. The company's decarbonization and renewable energy goals further shape these relationships, influencing supplier capabilities and costs.
- Emission control technology costs increased by 15% in 2024.
- Expenditures on cleaner fuel mixes rose by 10% in 2024.
- CLP's renewable energy investments totaled $2.5 billion in 2024.
Long-Term Contracts
CLP Holdings' long-term contracts with suppliers, such as those for fuel, can lessen supplier bargaining power. These agreements can offer price stability, shielding CLP from sudden cost increases. However, these contracts can also limit flexibility if market conditions change, potentially leading to higher costs. Managing these contracts requires balancing security and adaptability to navigate supplier dynamics effectively. For instance, in 2024, CLP's fuel costs were a significant portion of its operating expenses.
- Long-term contracts provide price stability and reduce the impact of fluctuating fuel costs.
- These contracts may restrict CLP's ability to take advantage of lower spot prices if available.
- Careful contract management is crucial to balance cost certainty and market responsiveness.
- In 2024, fuel costs represented a substantial portion of CLP's overall expenditures.
CLP faces supplier bargaining power challenges, especially from concentrated suppliers and those with proprietary tech. Fuel cost fluctuations, like 2024's coal price volatility, impact profitability. Environmental regulations and high switching costs also affect supplier dynamics. Long-term contracts offer stability but may limit flexibility, influencing overall costs.
| Aspect | Impact | 2024 Data |
|---|---|---|
| Emission Control Tech | Increased Costs | Up 15% |
| Cleaner Fuel Mix | Higher Expenses | Up 10% |
| Renewable Energy Investment | Strategic Shift | $2.5B |
Customers Bargaining Power
Customer bargaining power varies; in some regions, limited choices exist, weakening customer influence. Increased competition and deregulation, however, boost customer power, enabling provider switching. CLP Holdings must compete effectively, focusing on efficiency gains and improvements to business support and technology systems. For example, in 2024, CLP's customer base grew, indicating a need for strategic adaptation. The company's ability to retain customers is crucial.
Customers' sensitivity to electricity prices significantly impacts their bargaining power. Rising living costs and economic slowdowns heighten price consciousness. For example, in 2024, many households in Hong Kong sought cheaper energy options due to economic pressures. Offering competitive tariffs and energy-efficient solutions is key to customer retention. CLP Holdings' financial reports from 2024 show that customer satisfaction is directly linked to the ability to provide affordable and sustainable energy plans.
Customers with demand response capabilities can shape CLP's pricing. Smart grids and time-of-use tariffs give customers control over energy expenses. CLP is connecting customers and corporates to zero-carbon solutions, including cooling, solar, and batteries. This includes electrification and data center development. In 2023, CLP's customer base totaled over 2.6 million, highlighting the scope of this influence.
Government and Regulatory Influence
Government policies significantly affect customer bargaining power in the energy sector. Subsidies for energy efficiency and mandates for renewable energy sources can empower customers. CLP Power actively supports the government's initiatives for green transport and electric vehicle development. This collaboration aims to transform Hong Kong into a low-carbon, smart city.
- Hong Kong's government plans to increase renewable energy's share to 7.5% by 2035.
- CLP invested HK$1.8 billion in renewable energy projects in 2024.
- The government offers tax incentives for electric vehicle purchases.
Large Industrial Customers
Large industrial customers, like data centers, wield substantial bargaining power because of their high electricity needs. Securing these customers involves negotiating long-term power purchase agreements (PPAs) and providing tailored energy solutions. Data centers were a significant growth driver, contributing 5.6% to CLP's total Hong Kong sales during the first nine months of 2024. This highlights the importance of customer retention strategies.
- Data centers are a key customer segment.
- PPAs and customized solutions are crucial.
- Data centers represent a significant portion of sales.
- Customer retention strategies are vital.
Customer bargaining power varies based on competition and regulations; increased options boost customer influence. Economic factors and price sensitivity shape demand; competitive tariffs and energy efficiency are crucial for retention. Smart grids and government policies also affect customer bargaining, particularly for large consumers like data centers.
| Factor | Impact | 2024 Data |
|---|---|---|
| Competition | Higher competition increases customer choice | CLP's customer base grew, indicating adaptation is needed. |
| Price Sensitivity | Rising costs increase price consciousness | Many households in Hong Kong sought cheaper energy options. |
| Government Policies | Subsidies and mandates empower customers | HK plans 7.5% renewable energy by 2035; CLP invested HK$1.8B in renewables in 2024. |
Rivalry Among Competitors
CLP Holdings contends with rivals in diverse energy markets. To retain and expand its market share, it needs ongoing innovation, competitive pricing, and dependable service. Intense rivalry is present, amid higher living costs. In 2024, the energy sector saw significant competition, with market share fluctuations across providers.
The renewable energy sector is heating up competition for CLP Holdings. Firms are pouring funds into green projects to meet decarbonization goals. Investment in renewables surged, with global spending expected to reach $2 trillion in 2024. Delivering cleaner, reliable power is crucial, with solar and wind energy costs falling 10-20% in 2024.
Rapid technological advancements in energy generation, storage, and distribution intensify rivalry. Companies must invest in new tech to stay competitive. For instance, CLP is exploring models like a clean energy fund. In 2024, CLP invested HK$10.5 billion in renewable energy projects. Partnerships are crucial to navigate these changes.
Regulatory Changes
Regulatory changes and government policies dramatically influence competition. CLP Holdings must anticipate intensified competition over time. Government support for renewables and stricter emissions standards reshape the market. For example, in 2024, Hong Kong's government increased its focus on green energy, impacting CLP's investment strategy. This shift necessitates strategic adjustments to remain competitive.
- Increased focus on renewable energy projects.
- Stricter emissions standards.
- Government policies impacting investment strategy.
- Need for strategic adjustments to stay competitive.
Geographic Diversification
CLP's geographic diversification, spanning across Asia-Pacific, helps to buffer against intense competition in any single market. This strategy, however, places CLP in varied competitive environments. In 2024, CLP's operations in Hong Kong and Mainland China generated significant revenue, but also faced unique challenges. Focusing on markets with stable designs and competitive advantages is a key strategy.
- Revenue from Hong Kong operations in 2024: approximately HK$28.6 billion.
- Revenue from Mainland China operations in 2024: approximately HK$12.8 billion.
- CLP's strategic focus includes markets offering long-term growth potential.
- The company aims to leverage its core competencies across different regions.
CLP Holdings faces intense competition, fueled by renewable energy growth, technological advancements, and regulatory changes. The company navigates this through geographic diversification and strategic investments.
CLP's revenue from Hong Kong operations was approximately HK$28.6 billion in 2024, while Mainland China contributed around HK$12.8 billion.
Strategic focus is on markets with long-term growth potential.
| Aspect | 2024 Data | Strategic Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Renewable Energy Investment | HK$10.5 billion | Leveraging core competencies |
| Hong Kong Revenue | HK$28.6 billion | Stable design |
| Mainland China Revenue | HK$12.8 billion | Competitive advantages |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The rise of energy-efficient measures, like smart grids and improved appliances, presents a threat to CLP Holdings. These innovations decrease the need for traditional electricity, impacting demand. To counter this, CLP Holdings focuses on energy management solutions, aiming to meet evolving customer needs. In 2024, the global smart grid market was valued at $35.15 billion, showing strong growth. By adapting, CLP Holdings aims to navigate the shift towards a lower-carbon economy.
The increasing adoption of distributed generation, like rooftop solar, poses a threat to CLP Holdings. Customers generating their own power reduces demand for electricity from the company's grid. CLP is connecting customers and corporates to zero carbon energy solutions. In 2024, the distributed generation market expanded, with solar panel installations increasing by 25%.
Alternative energy sources present a threat to CLP Holdings. Natural gas, biofuels, and hydrogen can replace electricity in some uses. The rise in green maritime fuel and electric transport is also a factor. In 2024, renewable energy accounted for roughly 30% of global electricity generation.
Demand Response Programs
Demand response programs pose a threat to CLP Holdings by potentially reducing demand for its electricity. Effective programs can lower peak demand, minimizing the need for new power plants. Smart grids and time-of-use tariffs help customers manage energy costs, impacting CLP's revenue. This shift could lead to lower electricity sales for CLP if customers reduce consumption during peak times. The company must adapt to these changes to remain competitive.
- In 2024, global demand response capacity reached approximately 200 GW.
- Smart meter penetration has increased, with over 80% of US households having them.
- Time-of-use rates can cut peak demand by 10-15% in some regions.
- CLP's revenue could be affected as consumers adopt these programs.
Energy Storage Solutions
Advancements in energy storage solutions pose a threat to CLP Holdings. Technologies like batteries allow customers to reduce their reliance on the grid. Customers can store electricity from renewables for later usage, potentially diminishing demand from CLP. Invest in flexible capacity leveraging business models and partnerships, including Hallett BESS.
- The global energy storage market is projected to reach $23.5 billion by 2024.
- CLP is involved in projects like the 500 MW/1,000 MWh Lake Lyell pumped hydro project.
- The Mt Piper BESS is another key project for CLP.
CLP Holdings faces threats from various substitutes impacting electricity demand. Energy-efficient measures and smart grids reduce the need for traditional electricity. Distributed generation and alternative energy sources like solar and natural gas further challenge CLP.
Demand response programs and energy storage solutions like batteries also pose risks, potentially lowering electricity sales. CLP must adapt by focusing on energy management and renewable projects.
| Substitute | Impact | 2024 Data |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency | Decreased Demand | Smart grid market: $35.15B |
| Distributed Generation | Reduced Grid Reliance | Solar panel installs +25% |
| Alternative Energy | Demand Shift | Renewables: ~30% of gen. |
| Demand Response | Reduced Peak Demand | Global capacity: 200 GW |
| Energy Storage | Reduced Grid Use | Market: $23.5B projection |
Entrants Threaten
High capital costs pose a significant threat due to the electricity industry's infrastructure demands. New entrants face substantial investment needs for power generation and distribution. This financial barrier is exemplified by CLP's 2023 capital expenditure of HK$13.5 billion. Economies of scale also favor established players, like CLP, who can leverage bulk contracts.
The electricity sector faces significant barriers to entry due to stringent regulations. New entrants must navigate complex licensing and permit procedures, slowing market entry. CLP Holdings, like other established players, benefits from these hurdles. GFR registration renewals, such as the 3-year cycle, highlight the ongoing regulatory burden. These regulatory requirements limit the threat of new competitors.
CLP Holdings, as an established entity, enjoys significant economies of scale, making it difficult for new entrants to match its cost structure. This advantage is particularly relevant in the energy sector, where large-scale operations lead to lower per-unit production costs. Supply-side economies of scale are evident; starting large is crucial for new entrants. In 2024, CLP reported a revenue of HK$97.8 billion, underscoring its operational efficiency.
Access to Transmission and Distribution Networks
New entrants face significant hurdles due to the control incumbent firms, like CLP Holdings, have over transmission and distribution networks. This control acts as a major barrier, limiting market access. The Hong Kong government is actively working to enhance the power transmission system with the Mainland to address this.
This initiative aims to increase electricity imports, changing the market dynamics. The goal is to raise the import share from 27% to 35% by 2025.
- Network Control: Incumbents like CLP control essential infrastructure.
- Government Initiatives: Plans to enhance transmission with the Mainland are in place.
- Import Target: The goal is to increase electricity imports to 35% by 2025.
Technological Expertise
The electricity sector demands substantial technological expertise, creating a barrier for new entrants. This includes specialized knowledge in power generation, transmission, and distribution systems. New companies face the challenge of acquiring and retaining skilled personnel proficient in these advanced technologies. The energy sector's rapid technological advancements, driven by innovation, further increase the complexity for new entrants.
- Expertise in smart grid technologies and renewable energy systems is crucial.
- Investment in R&D and continuous technology upgrades is essential.
- Cybersecurity measures to protect grid infrastructure are vital.
- Need for advanced data analytics for operational efficiency.
New entrants face substantial barriers due to high capital costs and regulatory hurdles, limiting market access. CLP's established economies of scale and control over transmission networks further deter new competition. Technological expertise requirements add another layer of complexity for potential entrants. The Hong Kong government is working to enhance the power transmission system with the Mainland.
| Barrier | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Costs | High infrastructure investment needs. | Significant barrier to entry. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Complex licensing and permits. | Slows down market entry. |
| Economies of Scale | CLP's operational efficiency. | Difficult for new firms to compete. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
The analysis leverages CLP Holdings' annual reports, industry publications, and market data to assess competitive forces. Regulatory filings and financial news contribute further.