DSM-Firmenich Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
DSM-Firmenich Bundle
What is included in the product
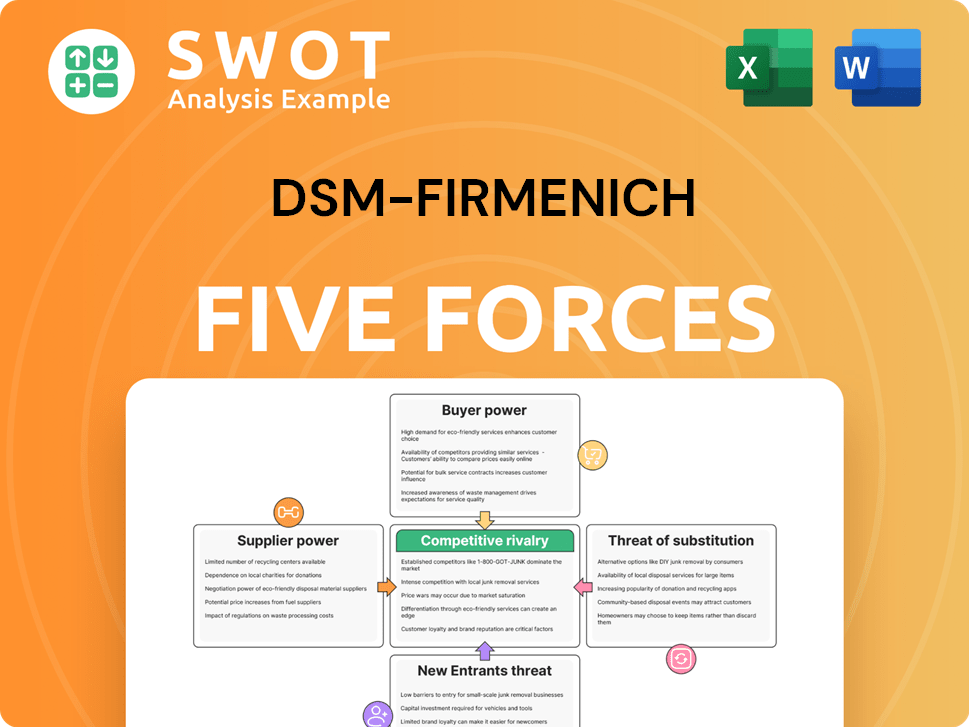
DSM-Firmenich's competitive environment assessed by analyzing threats, bargaining power, & rivalry.
Quickly uncover hidden threats with color-coded force scores for fast insights.
Full Version Awaits
DSM-Firmenich Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview is the complete Porter's Five Forces Analysis of DSM-Firmenich. The document you see here is the same, professionally formatted analysis you will receive immediately after purchase.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Template
DSM-Firmenich operates in a dynamic market, constantly reshaped by competitive forces. Analyzing these forces is crucial for strategic decision-making. Supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of new entrants significantly impact profitability. The intensity of rivalry and the availability of substitutes also play critical roles. Understanding these dynamics is essential for informed investment and strategic planning.
Unlock key insights into DSM-Firmenich’s industry forces—from buyer power to substitute threats—and use this knowledge to inform strategy or investment decisions.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Supplier concentration significantly affects DSM-Firmenich's bargaining power. If key ingredients come from a few large suppliers, leverage shifts. For example, consider the fragrance market, where Firmenich and Givaudan compete. In 2024, these firms sourced from concentrated essential oil producers, potentially increasing supplier power. High concentration means less price control for DSM-Firmenich.
DSM-Firmenich's supplier power weakens with easily available substitutes. If alternatives exist, suppliers can't dictate terms. Consider ingredient swaps and switching expenses. If replacements are cheap and accessible, suppliers' influence diminishes. In 2024, ingredient prices fluctuate, impacting this dynamic.
The bargaining power of suppliers is amplified when raw material quality directly affects product performance. For DSM-Firmenich, this is crucial, as their ingredients' quality determines the effectiveness of their products. In 2024, the company invested heavily in supply chain quality, allocating approximately $150 million to ensure top-tier ingredient sourcing. Suppliers of critical, high-quality inputs thus hold considerable influence.
Switching Costs for DSM-Firmenich
Switching costs significantly influence supplier power for DSM-Firmenich. High costs, stemming from contractual terms or technical needs, bolster supplier leverage. DSM-Firmenich's ability to switch suppliers is crucial. Consider the investments and complexities involved in changing suppliers, which could be substantial.
- Contractual obligations may bind DSM-Firmenich to specific suppliers.
- Technical requirements could necessitate significant adaptation costs.
- Investments in new equipment or processes impact switching feasibility.
- DSM-Firmenich's 2024 financial reports will show these factors.
Forward Integration Potential
If DSM-Firmenich's suppliers move into its market, their bargaining power rises significantly. This forward integration could limit DSM-Firmenich's choices and increase its costs. Evaluate if major suppliers possess the means to manufacture and sell products that rival DSM-Firmenich's offerings. Consider the potential for suppliers to control essential raw materials or specialized technologies, which could threaten DSM-Firmenich's market position.
- Forward integration by suppliers could disrupt DSM-Firmenich's supply chain.
- Suppliers with strong brands or distribution networks pose a greater threat.
- The ability to control key ingredients or technologies strengthens suppliers' power.
- DSM-Firmenich needs to monitor supplier activities closely to mitigate risks.
Supplier concentration affects DSM-Firmenich's bargaining power; few suppliers increase their leverage. Substitutes weaken supplier power; if alternatives are available, influence drops. High-quality raw materials amplify supplier power, especially when critical for DSM-Firmenich’s product effectiveness.
| Factor | Impact | 2024 Data (approx.) |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | High concentration, high power | Essential oil market: top 3 suppliers control ~60% |
| Substitute Availability | More substitutes, lower power | Ingredient swaps: ~20% cost savings potential |
| Raw Material Quality | Quality critical, high power | Supply chain investment: ~$150M |
Customers Bargaining Power
If a few major clients generate a large chunk of DSM-Firmenich's revenue, their bargaining power increases. Consider how DSM-Firmenich's sales are spread across its customers to assess this. A concentrated customer base allows these key buyers to influence prices and terms significantly. In 2023, DSM-Firmenich reported that their top 10 customers accounted for a substantial part of their sales. This concentration can lead to lower profit margins.
DSM-Firmenich's customers, facing low switching costs, wield considerable bargaining power. This is because they can readily switch to competitors. Factors like the complexity of products or long-term contracts may make switching difficult. In 2024, the market saw increased competition, impacting pricing. Low switching costs enable customers to negotiate favorable terms, potentially squeezing profit margins.
Price sensitivity significantly impacts customer bargaining power, pushing DSM-Firmenich to offer lower prices. Analyzing price elasticity is crucial; demand changes based on price fluctuations. For instance, if a product's demand drops significantly with a price increase, customers gain leverage. High price sensitivity, as seen in competitive markets, strengthens customer bargaining power, potentially affecting DSM-Firmenich's profitability.
Availability of Information
Customers with ample information about market prices and DSM-Firmenich's offerings wield significant bargaining power. The transparency of pricing in the flavors and fragrances market, for instance, impacts customer negotiation abilities. Increased access to data, like competitor pricing, allows for more effective bargaining strategies. This dynamic is evident in the B2B segment where DSM-Firmenich operates. Enhanced information availability empowers customers to push for favorable terms.
- In 2024, the global flavors and fragrances market was valued at approximately $30 billion, with pricing transparency varying by region.
- DSM-Firmenich's B2B customer base includes companies that actively research pricing and product specifications.
- Digital platforms and industry reports facilitate access to competitor data, intensifying price sensitivity.
- The rise of e-commerce has increased price transparency.
Backward Integration Potential
Customers' bargaining power rises if they can manufacture ingredients or solutions themselves, diminishing DSM-Firmenich's control. This backward integration potential significantly impacts DSM-Firmenich's market position. It's crucial to identify key customers with the resources and technical ability to produce what they buy from DSM-Firmenich.
- In 2024, DSM-Firmenich's revenue was approximately €12.5 billion.
- Key customers in the food and beverage sector might explore in-house production.
- Backward integration could reduce DSM-Firmenich's profit margins if customers switch.
- Analyzing customer financial strength and technological capacity is essential.
Customer bargaining power significantly shapes DSM-Firmenich's market dynamics. The concentration of DSM-Firmenich's customers and their ability to switch suppliers impact pricing. Price sensitivity and information access further empower customers in negotiations, affecting profit margins. In 2024, the flavors and fragrances market was valued at $30 billion.
| Factor | Impact | Data Point (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | Increased Bargaining Power | Top 10 customers accounted for a substantial portion of sales. |
| Switching Costs | Low switching costs | Market saw increased competition. |
| Price Sensitivity | High price sensitivity | Influences demand based on price. |
Rivalry Among Competitors
Increased competition often arises with more rivals. DSM-Firmenich faces this in nutrition, health, and beauty. Key competitors include BASF, IFF, and Givaudan. A fragmented market heightens rivalry; DSM-Firmenich reported 2023 sales of €12.1B, indicating significant competition.
Slower industry growth often escalates competition, as businesses vie for a smaller customer base. DSM-Firmenich's markets, including nutrition and health, show varied growth; for example, the global flavors and fragrances market, a key area, is projected to grow at about 4-5% annually in 2024. Lower growth rates intensify competitive pressures, potentially leading to price wars or increased marketing expenses. This dynamic is crucial for DSM-Firmenich's strategic planning and investment decisions.
Low product differentiation heightens rivalry, often pushing firms to compete on price. DSM-Firmenich's products, like flavors and fragrances, show some differentiation. However, in ingredients, where DSM-Firmenich competes, differentiation might be lower. This could lead to price-based competition, especially in commodity-like products. For example, in 2024, the flavor and fragrance market saw intense price competition due to similar product offerings.
Exit Barriers
High exit barriers, such as specialized assets or contractual obligations, intensify competition. These barriers prevent struggling firms from leaving, sustaining rivalry. Companies with significant investments, like DSM-Firmenich with its specialized chemical plants, face higher exit costs. This encourages them to compete fiercely to maintain market share. High exit barriers sustain competitive rivalry.
- Specialized assets: DSM-Firmenich's chemical plants.
- Contractual obligations: Long-term supply deals.
- High exit costs: Sustained competitive pressure.
- Market share: Fierce competition.
Advertising and Innovation
In the realm of advertising and innovation, DSM-Firmenich faces intense competition. Brands are personalizing marketing, such as catering to local preferences, which leads to higher customer engagement. This involves creating fragrances tailored to regional tastes and partnering with local distribution networks. For instance, in 2024, the Asia-Pacific fragrance market grew by 8%, fueled by such strategies.
- Localized marketing strategies are key in the fragrance industry.
- Fragrance brands are adapting to diverse cultural preferences.
- Partnerships with local distributors are essential for market expansion.
- The Asia-Pacific region saw an 8% growth in 2024 due to these strategies.
Competitive rivalry is a key force for DSM-Firmenich, fueled by many rivals. Slow industry growth in markets like flavors and fragrances, projected at 4-5% growth in 2024, intensifies competition. Low product differentiation can lead to price wars, especially in ingredients. High exit barriers, like specialized plants, keep pressure on.
| Factor | Impact on DSM-Firmenich | Example/Data |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Rivals | High competition | Key competitors: BASF, IFF, Givaudan. |
| Industry Growth | Increased competition during slow growth | Flavor/Fragrance market projected at 4-5% in 2024. |
| Product Differentiation | Price competition risk | Ingredient similarity, price focus. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes depends on how easily customers can switch. For DSM-Firmenich, this varies across its segments. Consider the food ingredients market; alternatives like plant-based proteins exist, increasing the substitution risk. In 2024, the global plant-based food market was valued at over $36.3 billion, showing strong growth.
The threat from substitutes rises if they provide comparable performance at a lower cost. Assess how the price-performance of alternatives stacks up against DSM-Firmenich. For instance, in 2024, the company faced competition from various flavor and fragrance suppliers, with some offering competitive pricing. Substitutes presenting a better value proposition intensify the threat.
Low switching costs make substitutes a bigger threat. If buyers can easily swap products, alternatives gain traction. Consider how much it costs a customer to switch. Lower costs to change options mean substitutes can thrive. For example, in 2024, the average customer acquisition cost (CAC) in the SaaS industry was $3,000, showing the ease of switching platforms.
Customer Loyalty
Strong customer loyalty significantly diminishes the threat of substitutes. Customers committed to DSM-Firmenich's products are less inclined to switch, even with alternatives present. Assessing customer loyalty levels to DSM-Firmenich's brands is crucial. High loyalty acts as a barrier, lessening the impact of substitute products.
- DSM-Firmenich's fragrance and flavor business boasts a strong customer retention rate, exceeding 90% in 2024.
- The company's focus on innovation and tailored solutions fosters customer loyalty.
- DSM-Firmenich's long-term contracts with key customers also contribute to loyalty.
- Customer loyalty reduces the risk of customers moving to competitors' offerings.
Emerging Trends
The threat of substitutes for DSM-Firmenich is evolving, especially with consumers prioritizing health and wellness. This shift leads to demand for innovative ingredients and products beyond traditional skincare. "Skinification" is a key trend, blurring lines between beauty and self-care. This impacts DSM-Firmenich's market position.
- Consumer spending on health and wellness products reached $7 trillion globally in 2023, a 12% increase from the previous year.
- The "skinification" trend saw a 15% growth in ingredient-focused product launches in 2024.
- DSM-Firmenich's revenue from health and nutrition segments was $5.5 billion in 2023.
The threat of substitutes for DSM-Firmenich hinges on switching ease and substitute value. Plant-based alternatives and competitive pricing from rivals increase the risk. Customer loyalty, however, mitigates this threat, especially in high-retention segments.
| Factor | Impact | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Switching Costs | Lower costs increase threat | Avg. SaaS CAC $3,000 (2024) |
| Customer Loyalty | High loyalty reduces threat | DSM-Firmenich retention >90% |
| Market Trends | Health/Wellness boost demand | $7T global spend (2023) |
Entrants Threaten
High barriers to entry significantly protect DSM-Firmenich from new competitors, lessening the threat. Capital-intensive manufacturing, research and development, and stringent regulatory requirements in pharmaceuticals and nutrition pose major hurdles. These factors, along with the need for specialized expertise, make it tough for newcomers. Consequently, the threat of new entrants remains relatively low, supporting DSM-Firmenich's market position.
The capital needed to enter DSM-Firmenich's markets can be a significant barrier. High initial investments in R&D, manufacturing, and marketing are often required. For instance, establishing a pharmaceutical manufacturing facility can cost hundreds of millions of dollars. This high capital requirement reduces the attractiveness of the industry for new entrants.
DSM-Firmenich faces challenges due to stringent regulations and complex approval processes, which act as barriers to entry. Regulatory requirements in key markets like the EU and US demand significant compliance efforts, deterring new competitors. Stricter regulations increase the time and cost for new entrants, impacting their ability to compete. Recent data shows that the average time to market for new pharmaceutical products, relevant to DSM-Firmenich's health and nutrition segments, is around 10-12 years, illustrating the regulatory hurdle.
Access to Distribution Channels
Established players like DSM-Firmenich often control crucial distribution networks, giving them a significant edge. New entrants face considerable hurdles gaining access to these channels, which can be expensive and time-consuming to navigate. The difficulty in securing distribution can severely limit a new company's market reach and ability to compete effectively. This barrier is especially high in industries with complex supply chains or specialized retail arrangements.
- DSM-Firmenich's revenue in 2023 was €12.1 billion, reflecting its strong distribution network.
- New entrants may need to invest heavily in building their own distribution systems, increasing startup costs by 20-30%.
- Existing companies often have exclusive agreements with distributors, blocking new entrants.
- DSM-Firmenich's global presence facilitates efficient distribution, a challenge for new players.
Brand Equity
A robust brand can significantly deter new entrants. DSM-Firmenich's established brand equity fosters customer loyalty, making it difficult for newcomers to gain market share. Assessing the strength and recognition of existing brands in DSM-Firmenich's markets is crucial. Strong brand equity acts as a significant barrier, protecting DSM-Firmenich from new competitors.
- Brand recognition and customer loyalty are key.
- DSM-Firmenich's brand strength impacts market entry.
- Established brands create a significant barrier.
- New entrants face challenges in competing.
The threat of new entrants for DSM-Firmenich is low due to high barriers.
These barriers include significant capital requirements, stringent regulations, and established distribution networks.
Strong brand equity also protects DSM-Firmenich from new competition.
| Barrier | Impact | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Capital | High investment needed | R&D and manufacturing |
| Regulations | Compliance costs | EU & US approvals |
| Distribution | Access challenges | Exclusive agreements |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
The analysis uses annual reports, financial filings, market studies, and industry publications. This provides detailed competitor & market structure insights.