FedEx Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
FedEx Bundle
What is included in the product
Tailored exclusively for FedEx, analyzing its position within its competitive landscape.
Swap in your own data to identify threats & opportunities, leading to competitive advantages.
Full Version Awaits
FedEx Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases FedEx's Porter's Five Forces Analysis. The document explores competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, threat of substitutes, and threat of new entrants. It presents a thorough examination of these forces within the industry. Upon purchase, you receive this exact, detailed analysis file.
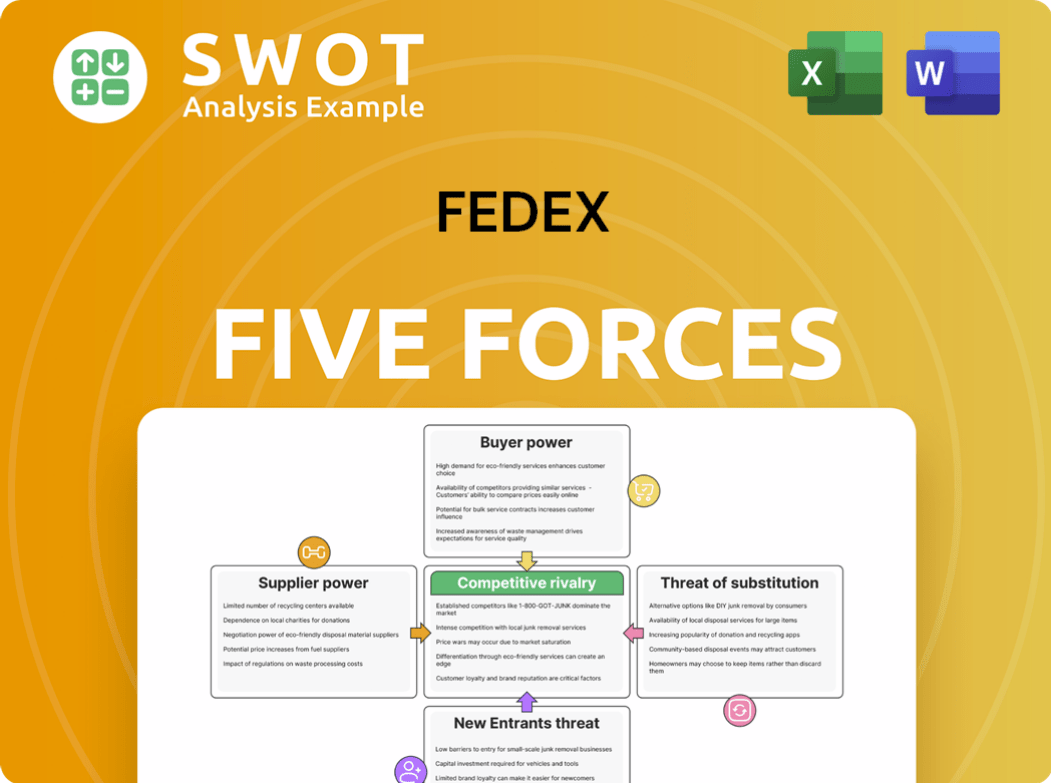
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Template
FedEx faces intense competition from rivals like UPS and regional players, significantly impacting its pricing and market share. Bargaining power of buyers is moderate due to the availability of alternative shipping services. Supplier power, particularly from fuel providers and aircraft manufacturers, can squeeze profit margins. The threat of new entrants is moderate, given high capital requirements and established brand loyalty. However, the threat of substitutes, such as digital information transfer, is a growing concern.
Our full Porter's Five Forces report goes deeper—offering a data-driven framework to understand FedEx's real business risks and market opportunities.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
FedEx depends on key suppliers for aircraft, vehicles, and fuel. Limited alternatives give suppliers power. This can elevate operational costs. In 2024, fuel costs rose, impacting profitability.
Fuel price volatility heavily influences FedEx's costs. Suppliers of jet fuel and diesel hold substantial power. In 2024, fuel expenses comprised a significant portion of operational spending. FedEx actively manages these costs using hedging strategies and fuel surcharges to mitigate risks. For instance, in Q3 2024, fuel prices led to a 4.5% increase in operating expenses.
Boeing and Airbus, as the dominant aircraft manufacturers, wield significant supplier power over FedEx. FedEx's fleet, crucial for its operations, relies heavily on these manufacturers. In 2024, Boeing delivered 528 aircraft, while Airbus delivered 735. Any price hikes or delays impact FedEx's capital spending and strategic plans.
Technology and software providers
FedEx's reliance on technology and software is growing. Suppliers of these vital components, like specialized logistics software, have considerable bargaining power. FedEx must continuously invest in technology to stay competitive, highlighting the importance of these supplier relationships. For instance, in fiscal year 2024, FedEx's capital expenditures were around $5.7 billion, a significant portion of which went to technology. This spending underscores the influence of tech suppliers.
- Tech and software suppliers can exert influence due to FedEx's dependence.
- Ongoing tech investment is essential for maintaining a competitive edge.
- FedEx's 2024 capital expenditures included substantial tech-related spending.
- These supplier relationships are thus critical.
Labor union strength
The bargaining power of labor unions, like the Air Line Pilots Association (ALPA) representing some FedEx pilots, affects FedEx's operational costs and flexibility. Negotiations on wages, benefits, and working conditions directly influence the company's financial results. For example, in 2024, labor costs accounted for a significant portion of FedEx's expenses. Managing labor relations is essential for maintaining smooth operations and controlling costs.
- In 2024, FedEx's operating expenses included substantial labor costs.
- Negotiations with unions impact financial performance.
- Effective labor relations are crucial for cost management.
Fuel and aircraft suppliers significantly influence FedEx. Fluctuating fuel costs and limited aircraft options affect expenses. In 2024, fuel prices and Boeing/Airbus deliveries shaped operational finances.
| Factor | Impact | 2024 Data |
|---|---|---|
| Fuel Costs | High operational costs | Fuel expenses up 4.5% in Q3 2024 |
| Aircraft Suppliers | Capital spending, delays | Boeing delivered 528, Airbus 735 aircraft |
| Tech Suppliers | Competitive edge and expenses | $5.7B in CapEx, including tech |
Customers Bargaining Power
Large customers, like Amazon, wield considerable bargaining power due to their high shipping volumes, which can constitute a significant portion of FedEx's revenue; for instance, Amazon accounted for 10% of FedEx's total revenue in 2023. These key accounts, with their substantial shipping needs, can negotiate favorable rates, putting pressure on FedEx's profit margins. Retaining these corporations demands competitive pricing and tailored service offerings, like the FedEx's $1.5 billion investment in its ground network in 2024.
The rise of e-commerce has significantly amplified customer expectations for rapid, cost-effective shipping. Online retailers now possess considerable leverage, influencing both pricing and service standards within the shipping industry. FedEx faces the challenge of adjusting to these elevated demands to preserve its competitive position. In 2024, e-commerce sales in the US reached approximately $1.1 trillion, underscoring the customer's enhanced bargaining power.
Individual consumers are typically price-sensitive, particularly for non-urgent shipments, which enhances their bargaining power. The presence of competitors like UPS and USPS provides consumers with alternative shipping choices, increasing their leverage. FedEx must carefully balance its pricing strategies with service quality to attract and retain individual customers. In 2024, FedEx reported an average daily package volume of about 16.6 million.
Service customization demands
Customers are increasingly demanding customized logistics solutions, enhancing their bargaining power. This shift requires FedEx to invest in flexible and scalable services to meet diverse needs. Tailoring services to specific requirements strengthens customer influence over pricing and service terms. In 2024, FedEx's revenue was $87.5 billion, with a significant portion driven by customized services.
- Increased demand for personalized logistics solutions.
- Customers' ability to dictate service terms.
- Need for scalable, flexible infrastructure investment.
- Impact on pricing and service negotiations.
Transparency and tracking expectations
Customers in the shipping industry now demand real-time tracking and transparent pricing. Companies excelling in these areas often gain a competitive edge. For example, FedEx has invested heavily in its tracking technology, providing detailed updates to its customers. This commitment to transparency and customer service is vital for building loyalty and a positive brand image. In 2024, FedEx's revenue was approximately $90 billion, demonstrating the importance of meeting customer expectations.
- Real-time tracking is now a standard expectation for customers.
- Transparent pricing helps build trust and loyalty.
- Superior customer service enhances brand perception.
- FedEx's revenue in 2024 was around $90 billion.
Customer bargaining power significantly affects FedEx due to e-commerce and large accounts. Customers, like Amazon (10% of FedEx's 2023 revenue), negotiate favorable rates. This pressure demands competitive pricing and tailored services. In 2024, e-commerce sales hit $1.1 trillion, amplifying customer leverage.
| Aspect | Impact | Data (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| E-commerce Influence | Elevated customer expectations | US e-commerce sales: $1.1T |
| Pricing Pressure | Negotiated rates | FedEx Revenue: ~$90B |
| Service Demands | Customized logistics | Avg. daily packages: 16.6M |
Rivalry Among Competitors
The express delivery market is fiercely competitive, with giants like FedEx, UPS, and DHL battling for dominance. These companies aggressively compete on price, service speed, and expansive global networks. This intense rivalry, highlighted by strategies like UPS's 2024 investments in automation, squeezes profit margins. The pressure to capture market share remains high, influencing strategic decisions.
Focusing on service differentiation is key in competitive rivalry. Companies like FedEx specialize, offering services like cold chain logistics. Innovation in service offerings gives a competitive edge. FedEx invests in tech and enhancements. In 2024, FedEx's revenue was about $90 billion.
Geographic expansion is a key strategy for competitive advantage. FedEx actively expands its global footprint to reach new customer segments. In 2024, FedEx Express saw international revenue grow, reflecting successful expansion. This includes growth in Asia-Pacific and Europe. These efforts aim to bolster FedEx's position in vital growth markets.
Technological innovation investment
Technological innovation is crucial, with FedEx investing heavily in technology to gain an edge. Automation, AI, and data analytics boost efficiency and elevate service quality. These advancements enhance FedEx's capacity to handle rising package volumes. Its tech investments support its long-term competitiveness in the market.
- FedEx's capital expenditure in fiscal year 2024 was approximately $5.7 billion.
- The company is deploying AI and machine learning to optimize its delivery networks.
- Investments in automation have improved sorting and handling processes.
- FedEx continues to focus on data analytics to enhance customer service and predict demand.
Brand reputation importance
Brand reputation is vital for FedEx to attract and keep customers. It impacts customer decisions and builds loyalty, making them choose FedEx. FedEx spends significantly on marketing and customer service to boost its brand image. A strong reputation helps FedEx compete effectively in the market.
- FedEx's brand value was estimated at $33.7 billion in 2024.
- Customer satisfaction scores are carefully monitored to maintain the brand's positive image.
- FedEx spends billions annually on marketing and advertising.
- Positive reviews and consistent service quality are key.
Competitive rivalry in the express delivery sector is intense, with FedEx facing strong competition from UPS and DHL. FedEx focuses on service differentiation, geographic expansion, and technological innovation to stay competitive. Brand reputation is also crucial; in 2024, FedEx's brand value was estimated at $33.7 billion.
| Aspect | Details | 2024 Data |
|---|---|---|
| Revenue | Total Revenue | Approx. $90 Billion |
| Capital Expenditure | Fiscal Year Spend | Approx. $5.7 Billion |
| Brand Value | Estimated Value | $33.7 Billion |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The rise of digital document delivery significantly threatens traditional shipping methods. Email and cloud services diminish the demand for physical document transport. In 2024, the global digital document market was valued at approximately $25 billion, showing strong growth. FedEx faces pressure to diversify its services, such as offering digital solutions. This shift demands that FedEx adapts to maintain relevance.
Local and regional carriers pose a threat to FedEx by offering competitive pricing, especially on specific routes. These smaller carriers can be a cost-effective alternative, making them attractive to price-sensitive customers. FedEx must differentiate its services, perhaps through speed or reliability, to justify its premium pricing strategy. In 2024, the shipping industry saw regional carriers capturing a growing market share, with some increasing volumes by up to 15%.
Some companies might create their own delivery systems, cutting down on using services like FedEx. Building internal logistics can be a smart move for big businesses. FedEx needs to show its services are worth the cost to keep these customers. In 2024, Amazon Logistics handled about 70% of Amazon's deliveries, showcasing this trend. This shift highlights the importance of FedEx's service quality.
Alternative transportation modes
Rail and sea freight pose a threat to FedEx, especially for less urgent deliveries. These alternatives are generally cheaper for large quantities of goods. For example, in 2024, sea freight costs were significantly lower per ton-mile than air freight. FedEx counters this by emphasizing the speed and dependability of its express services.
- Sea freight costs are approximately 10-20% of air freight costs.
- Rail transport is 20-30% cheaper compared to trucking.
- FedEx's on-time delivery rate is a key differentiator.
3D printing potential
The rise of 3D printing presents a long-term threat to FedEx. On-demand manufacturing could lessen reliance on shipping finished goods. FedEx is actively assessing 3D printing's impact on its business model. This shift could alter package volume and service demand. FedEx's strategic planning includes adapting to this technological disruption.
- 3D printing market is projected to reach $55.8 billion by 2027.
- FedEx has invested in automation and technology to improve efficiency.
- The company has explored partnerships to adapt to changing market dynamics.
- FedEx's revenue in 2024 was approximately $87.6 billion.
Digital document delivery continues to impact FedEx, with the global market valued around $25 billion in 2024. Regional carriers' increased market share, up to 15% volume growth, also poses a threat. In-house logistics, like Amazon handling about 70% of its deliveries, reduces FedEx's customer base.
Rail and sea freight offer cheaper alternatives; sea freight costs are approximately 10-20% of air freight. 3D printing's growth, projected to $55.8 billion by 2027, presents a future challenge.
| Substitute | Impact | 2024 Data |
|---|---|---|
| Digital Documents | Reduces Physical Shipping | $25B Market |
| Regional Carriers | Cost-Effective | Up to 15% Volume Growth |
| In-House Logistics | Customer Reduction | Amazon: 70% Deliveries |
| Rail/Sea Freight | Cheaper Transport | Sea 10-20% of Air |
| 3D Printing | On-Demand Mfg | $55.8B by 2027 |
Entrants Threaten
The express delivery sector demands substantial capital for infrastructure and tech. Startup costs are high, creating barriers. FedEx profits from its established infrastructure. In 2024, FedEx's capital expenditures were approximately $5.7 billion, showcasing the scale of investment needed. This deters smaller firms.
Established brand loyalty poses a significant threat to new entrants in the shipping industry. FedEx, with its decades-long presence, benefits from strong customer trust and recognition. New companies struggle to replicate this, requiring substantial marketing investments to build brand awareness. For instance, FedEx's revenue in 2024 was approximately $90 billion, reflecting its established market position and customer loyalty.
The shipping industry faces intricate regulatory hurdles. New entrants struggle with customs, security, and transport rules. FedEx's established compliance expertise acts as a significant barrier. In 2024, regulatory costs for logistics firms rose by about 7%, increasing entry difficulty.
Network effects advantage
Network effects give FedEx a strong edge because its value grows with each new customer. As of 2024, FedEx has a massive global network, serving over 220 countries and territories. This extensive reach, built over decades, is hard for newcomers to match. The more customers using FedEx, the more valuable its network becomes, creating a barrier to entry.
- FedEx's global network handles millions of packages daily.
- Replicating such a network requires massive investment and time.
- Established brand recognition builds customer trust.
- New entrants face high initial costs and operational hurdles.
Technological expertise requirements
The logistics industry demands advanced technology for smooth operations, creating a significant barrier for new entrants. FedEx's established technological infrastructure, including its tracking systems and delivery networks, requires substantial investment to replicate. This technological edge supports FedEx's strong competitive position in the market. New companies face high initial costs and the challenge of matching FedEx's scale and efficiency.
- FedEx's revenue for fiscal year 2023 was approximately $87.5 billion.
- The company has made continuous investments in technology to enhance its services.
- New entrants need significant capital to compete effectively.
- FedEx's tech investments increase the entry barriers.
New shipping companies struggle due to high startup costs and regulatory hurdles. FedEx benefits from its established infrastructure and brand. In 2024, regulatory costs rose about 7% for logistics firms.
| Factor | Impact on New Entrants | FedEx's Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Needs | High initial investments in infrastructure and technology. | Established network and tech, with 2024 capex of $5.7B. |
| Brand Loyalty | Requires major marketing to build trust. | Decades of established recognition and customer loyalty. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Complex customs and security rules. | Expertise in compliance; regulatory costs increased. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
The analysis utilizes data from FedEx annual reports, industry publications, and market research. It incorporates financial statements and competitor analyses for insights.