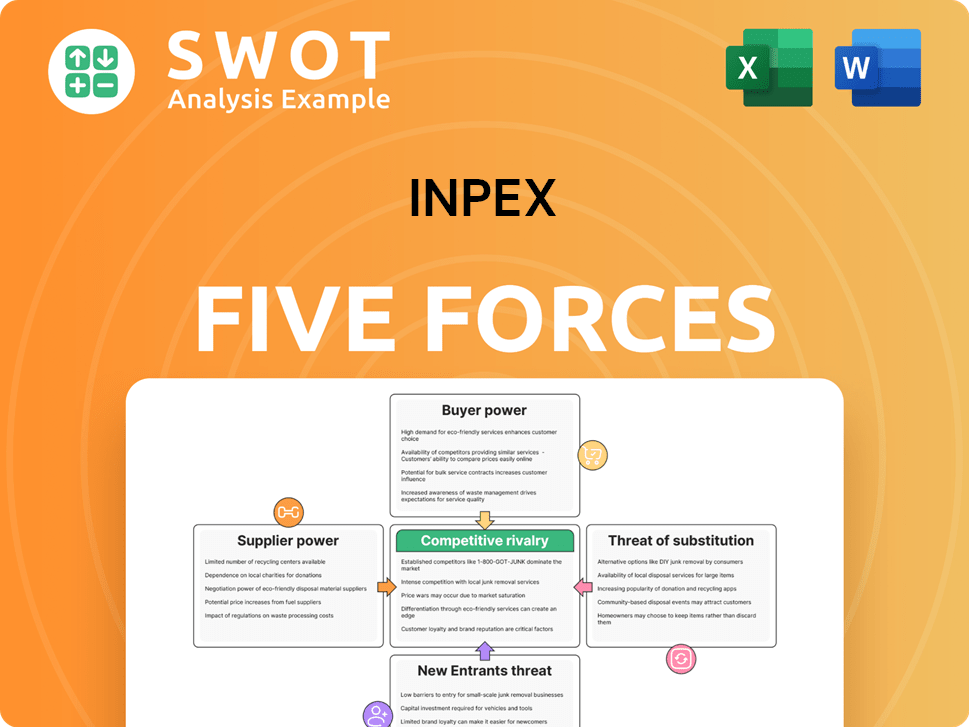
Inpex Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Inpex Bundle
What is included in the product
Evaluates control held by suppliers & buyers, and their influence on pricing and profitability.
Instantly visualize strategic pressure with a powerful spider/radar chart for quick insights.
Preview Before You Purchase
Inpex Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This is the complete Inpex Porter's Five Forces analysis. You're seeing the fully-formed document. After your purchase, you'll get immediate access to this comprehensive report, ready for your review and use. It's a complete, professionally written analysis. No hidden extras.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Template
Inpex faces moderate competitive rivalry in the oil & gas sector, influenced by major players. Buyer power is somewhat limited, as demand for energy is relatively inelastic. Suppliers, including equipment manufacturers, exert moderate influence. The threat of new entrants is low, given high capital requirements. Substitute products, like renewables, pose a growing but manageable threat.
Our full Porter's Five Forces report goes deeper—offering a data-driven framework to understand Inpex's real business risks and market opportunities.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
INPEX faces suppliers with strong bargaining power, especially for specialized equipment and services. The industry's reliance on a few key providers, like those offering advanced drilling tech, gives them leverage. This can lead to higher costs for INPEX, impacting profitability. For example, the cost of offshore drilling equipment rose by 15% in 2024, squeezing margins.
Switching suppliers in the oil and gas industry, like INPEX, is expensive due to specialized equipment and regulatory hurdles. These high switching costs significantly boost supplier bargaining power, potentially leading to less favorable terms for INPEX. For example, in 2024, the average cost to switch a major oil pipeline supplier could exceed $50 million. Long-term relationships and proven performance records further strengthen supplier leverage.
Suppliers with control over crucial resources like drilling rigs or specialized tech hold considerable power. INPEX relies on these resources, making it susceptible to supplier terms. For example, in 2024, the cost of offshore drilling rigs increased by approximately 15% due to limited availability. Scarcity, influenced by market dynamics or geopolitics, boosts supplier influence, as seen with fluctuating shipping costs in 2024 impacting project timelines and budgets.
Influence of OPEC+ nations
The bargaining power of suppliers for companies like INPEX is heavily influenced by OPEC+ nations, particularly concerning crude oil and natural gas. Their control over production levels and strategic decisions directly impacts resource availability and pricing. INPEX faces potential cost increases and supply disruptions due to these actions, affecting its operational efficiency and profitability.
- OPEC+ holds around 40% of global crude oil production.
- In 2024, OPEC+ production cuts influenced oil prices, impacting supply costs.
- Natural gas prices are also affected by OPEC+ decisions, particularly through LNG.
- INPEX's operational costs and profitability are thus sensitive to OPEC+ strategies.
Impact of geopolitical instability
Geopolitical instability significantly impacts supplier power, especially for a company like INPEX, which relies on global supply chains. Conflicts and sanctions can disrupt the flow of essential resources and services, thereby increasing supplier leverage. For example, the Russia-Ukraine war caused sharp increases in energy prices and supply chain disruptions. These disruptions can lead to higher procurement costs and operational planning challenges for INPEX.
- The price of Brent crude oil, a key benchmark for INPEX's products, fluctuated significantly in 2024 due to geopolitical events.
- Supply chain disruptions in 2024, particularly in regions like the Middle East, increased the costs for INPEX’s procurement.
- INPEX's operational planning in 2024 had to account for potential disruptions from various geopolitical sources.
INPEX faces strong supplier power due to specialized tech and limited providers. Switching costs are high, like the $50M average to change a pipeline supplier in 2024. OPEC+ controls 40% of global oil, impacting supply costs. Geopolitical events caused significant oil price fluctuations in 2024.
| Factor | Impact on INPEX | 2024 Data |
|---|---|---|
| Specialized Equipment Costs | Higher Costs, Reduced Margins | Offshore drilling equipment +15% |
| Switching Costs | Supplier Leverage | Pipeline supplier switch cost $50M+ |
| OPEC+ Influence | Price & Supply Disruptions | OPEC+ holds ~40% crude oil |
| Geopolitical Instability | Supply Chain Disruptions | Brent crude fluctuated significantly |
Customers Bargaining Power
INPEX's customer base concentration significantly influences its pricing power. If a few major buyers dominate, they can pressure INPEX for discounts. In 2024, LNG contract prices fluctuated, indicating buyer leverage. For instance, a small group of Asian utilities often negotiate LNG deals, affecting INPEX’s revenue. This dynamic necessitates INPEX to maintain strong relationships.
INPEX's customer bargaining power is affected by price sensitivity. If customers are price-sensitive, they might switch suppliers or cut consumption if prices rise. This sensitivity increases with economic pressures or access to cheaper energy. In 2024, global oil prices saw fluctuations, impacting customer decisions. Data from the EIA shows that in 2024, the average U.S. gasoline price was around $3.50 per gallon, reflecting this sensitivity.
The availability of alternative energy sources is increasing, which weakens the bargaining power of oil and gas customers. Renewable energy sources are becoming more affordable. In 2024, global renewable energy capacity increased significantly, with solar and wind leading the growth. Customers can switch to these alternatives if oil and gas prices are too high.
Influence of government policies
Government policies significantly shape customer bargaining power in the energy sector. Subsidies for renewables and carbon taxes directly influence demand dynamics. These policies can shift customer preferences towards alternatives, reducing demand for traditional oil and gas. Regulatory interventions and clean energy mandates further drive adoption of low-carbon fuels. This impacts long-term demand for conventional energy sources.
- In 2024, global renewable energy capacity is expected to grow by 50%
- Carbon taxes are implemented in over 40 countries and 30 subnational jurisdictions.
- The U.S. Inflation Reduction Act includes significant clean energy investments.
- The EU's Fit for 55 package aims to reduce emissions by at least 55% by 2030.
Shifting global energy trade dynamics
Shifting global energy trade dynamics significantly influence customer bargaining power, a key aspect of Inpex's Porter's Five Forces analysis. Geopolitical events and trade agreements affect the ability of customers to negotiate prices for LNG and crude oil. The availability of alternative supply sources empowers buyers, reducing their reliance on specific suppliers.
- In 2024, the global LNG trade volume is projected to reach approximately 410 million metric tons.
- The US, Qatar, and Australia are major LNG exporters, providing buyers with diverse options.
- Diversification of supply routes, including through the Suez Canal and Panama Canal, further enhances buyer leverage.
INPEX faces customer bargaining power influenced by market dynamics. Concentration among buyers enables negotiation leverage, as seen in 2024 LNG contract fluctuations. Price sensitivity and access to alternatives further amplify customer influence.
Government policies, like renewable energy subsidies, shift customer preferences, decreasing demand for traditional oil and gas. Trade dynamics, geopolitical events, and supply diversification also affect buyer power.
| Factor | Impact on Bargaining Power | 2024 Data/Example |
|---|---|---|
| Buyer Concentration | High concentration increases leverage | LNG deals often involve few major buyers |
| Price Sensitivity | High sensitivity enhances switching | Average U.S. gasoline price ~$3.50/gallon |
| Alternative Sources | Availability reduces dependence | 50% growth in renewable energy capacity |
Rivalry Among Competitors
The oil and gas sector sees fierce rivalry. Major international companies like Shell and ExxonMobil, alongside national entities such as Saudi Aramco, battle for exploration and market dominance. This competition results in aggressive pricing and strategic investments. In 2024, ExxonMobil's revenue was around $330 billion, showing the scale of competition. INPEX must navigate this landscape to maintain its position.
The oil and gas sector's capital-intensive nature intensifies rivalry. In 2024, exploration costs alone averaged $30-$50 per barrel. Large investments in rigs, pipelines, and refining infrastructure are essential for any player. This drives companies to maximize efficiency and aggressively compete for market share, as shown by Inpex's $9.8 billion capital expenditure in the financial year 2023.
Mergers and acquisitions (M&A) in the oil and gas sector significantly alter competition. Consolidation creates stronger rivals, increasing market share and resources. INPEX needs to track and adapt to these shifts to maintain its competitive edge and explore growth opportunities. In 2024, Chevron's acquisition of Hess for $53 billion exemplifies industry consolidation, impacting market dynamics. The Permian Basin has seen substantial M&A activity.
Geopolitical factors and market volatility
Geopolitical factors and market volatility heavily influence competitive rivalry. Conflicts, sanctions, and trade disputes disrupt supply chains and create uncertainty, fostering intense competition. Companies must adjust strategies to stay competitive amidst these challenges. For example, Russia's pivot to Asia has amplified competition in the Asian energy market.
- The Ukraine conflict caused significant oil and gas price volatility in 2022 and 2023.
- Trade disputes between the US and China continue to affect global markets.
- Sanctions against Russia have reshaped energy markets.
- Geopolitical risks are expected to persist in 2024.
Focus on cost of supply and access to capital
Competitive rivalry in the oil and gas sector is heating up, driven by the need for lower costs and better financing. Companies are buying each other to boost reserves and cut expenses. This trend is making competition fiercer as firms fight for financial strength [9].
- In 2024, the oil and gas M&A market saw significant activity, with deals focused on strategic cost reductions.
- Access to capital remains crucial, especially with the shift towards renewable energy.
- Companies are using M&A to improve operational efficiency, vital for cost competitiveness.
- Enhanced financial positions are key in this competitive landscape.
Competitive rivalry within the oil and gas industry is extremely fierce, marked by a continuous battle for market share and dominance.
Companies aggressively compete on pricing, strategic investments, and operational efficiency to stay ahead. Mergers and acquisitions further intensify this rivalry, creating stronger competitors, as seen in the $53 billion Chevron-Hess deal in 2024.
Geopolitical instability and market volatility significantly influence competition, demanding quick strategic adaptations to stay competitive.
| Aspect | Details | Impact on INPEX |
|---|---|---|
| Revenue | ExxonMobil (2024): ~$330B | Pressure to maintain profitability |
| M&A Activity | Chevron-Hess (2024): ~$53B | Need for strategic adaptation |
| Exploration Costs | Average (2024): $30-$50/barrel | Focus on cost management |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The rise of renewable energy presents a substantial threat to INPEX. Solar and wind power costs have plummeted, making them viable alternatives to fossil fuels. In 2024, renewable energy capacity additions globally reached record levels, signaling a strong shift. INPEX must diversify to stay competitive, potentially investing in renewables or related technologies [2, 5, 8].
The rise of electric vehicles (EVs) poses a significant threat to INPEX. EVs diminish the need for gasoline and diesel, impacting oil demand. In 2024, EV sales continued to climb, with EVs making up a larger share of new car registrations globally. Governments are pushing EV adoption, which could further cut into the market for oil-based fuels. INPEX must plan for this shift to maintain future profitability. [5, 15]
Biofuels and alternative fuels pose a threat to oil and gas companies like INPEX, as they offer potential substitutes. Hydrogen and ammonia are emerging as viable alternatives in transportation and industrial sectors. The competitiveness of these fuels could increase with technological advancements. INPEX is actively exploring opportunities in hydrogen and ammonia to diversify its portfolio and mitigate risks. In 2024, the global biofuel market was valued at approximately $100 billion.
Energy efficiency measures
Energy efficiency measures pose a significant threat to Inpex. Improvements, such as better insulation and efficient appliances, decrease overall energy consumption. Consumer preferences for energy-efficient products further drive this trend. In 2024, the global market for energy-efficient appliances was valued at approximately $300 billion.
- Market growth is projected to reach $450 billion by 2028.
- Government policies promoting energy efficiency, such as tax credits and rebates, also boost the adoption of alternatives.
- The declining cost of renewable energy is another factor.
- Investments in energy efficiency increased by 15% in 2024.
Technological advancements and carbon capture
Technological advancements in carbon capture, utilization, and storage (CCUS) present a double-edged sword for INPEX. While CCUS could mitigate emissions from fossil fuels, potentially reducing the need for substitutes, its economic viability is still uncertain. INPEX is strategically investing in CCS projects to reduce the risk of stranded assets, showing a proactive stance in 2024. The success of these projects will greatly affect the future of fossil fuels.
- INPEX is involved in multiple CCS projects globally.
- The International Energy Agency (IEA) estimates that CCUS capacity needs to grow significantly to meet global climate goals.
- The cost of CCUS can vary widely, impacting its competitiveness.
The threat of substitutes for INPEX includes renewables, EVs, biofuels, and energy efficiency. These alternatives challenge traditional oil and gas demand, impacting INPEX's profitability. Investment in renewables and CCS is crucial for INPEX's future. The global energy efficiency market was valued at $300B in 2024.
| Substitute | Impact on INPEX | 2024 Data |
|---|---|---|
| Renewable Energy | Reduced demand for fossil fuels | Record renewable capacity additions |
| Electric Vehicles (EVs) | Lower gasoline/diesel demand | EV sales continued to climb |
| Biofuels | Alternative transportation fuel | Biofuel market valued at $100B |
Entrants Threaten
The oil and gas sector demands massive initial investments for exploration and production, acting as a significant hurdle for newcomers. INPEX, with its robust infrastructure and financial backing, holds a competitive edge due to these high capital needs. For instance, in 2024, the average cost to develop a new oil field could range from $500 million to several billion dollars, severely limiting new entries [14]. This financial barrier shields INPEX from smaller, less-capitalized competitors.
The oil and gas sector faces a tough regulatory landscape, including environmental rules, safety benchmarks, and operational permits. This complexity can be a major hurdle for newcomers. INPEX's established expertise in compliance gives it an edge. For example, in 2024, compliance costs for new projects were about $50 million.
The oil and gas sector demands advanced technology and expertise, making it difficult for new companies to enter. New entrants often face challenges acquiring the necessary skills and resources to compete. INPEX has a competitive edge due to its investments in technology and a skilled workforce. In 2024, INPEX's R&D spending was approximately ¥10 billion. This strengthens its position against new entrants.
Economies of scale
Established oil and gas giants, like INPEX, have a significant advantage due to economies of scale. They can produce and distribute oil and gas at lower costs than new entrants. This cost advantage makes it tough for new companies to compete effectively. INPEX uses its large operations to cut costs and stay competitive in the market. In 2024, INPEX's revenue was approximately $16 billion, reflecting its operational scale [14].
- Lower production costs due to large-scale operations.
- Established distribution networks provide cost advantages.
- INPEX's significant revenue in 2024 showcases its scale.
Long lead times and project risks
Oil and gas ventures usually demand protracted lead times, often spanning several years to over a decade, alongside substantial project risks, including geological uncertainties and political instability. These elements act as a barrier, deterring potential new entrants. INPEX's expertise in handling complex, long-term projects provides a competitive advantage. These projects are capital-intensive and require significant upfront investment before any returns are realized [1, 2, 3].
- Long lead times, often 5-10+ years.
- Project risks include geological and political factors.
- Capital-intensive, requiring huge upfront investments.
- INPEX's experience offers a competitive edge.
New oil and gas companies face major challenges entering the market. High initial investments and complex regulations create significant barriers. INPEX, with its resources, has a competitive edge [14].
| Barrier | Impact | INPEX Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| High Capital Costs | New oil field development costs $500M-$2B [14] | Established infrastructure and finances |
| Regulatory Complexity | Compliance costs about $50M in 2024 | Expertise in compliance |
| Technology and Expertise | Requires advanced skills and tech | ¥10B R&D in 2024 |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
The Inpex Porter's Five Forces analysis uses financial reports, industry benchmarks, market share data, and trade publications.