Microsoft Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Microsoft Bundle
What is included in the product
Identifies disruptive forces, emerging threats, and substitutes that challenge market share.
Quickly identify the most pressing strategic threats with color-coded force ratings.
Preview Before You Purchase
Microsoft Porter's Five Forces Analysis
The Porter's Five Forces analysis previewed here is the same comprehensive document available immediately after purchase. This analysis explores Microsoft's competitive landscape, detailing its strengths and weaknesses.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Template
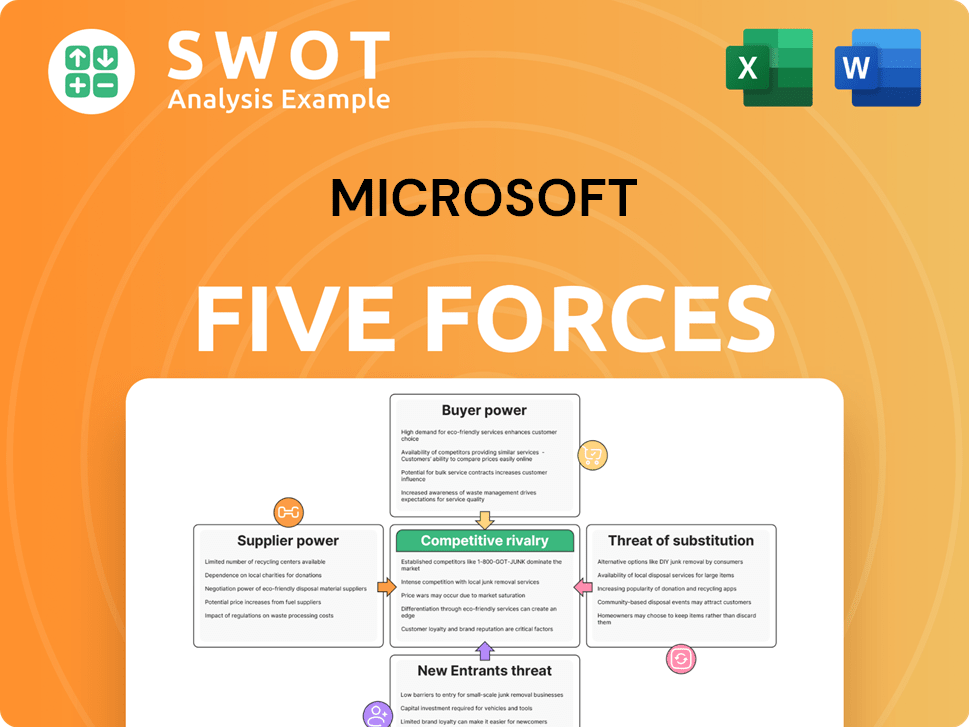
Microsoft faces complex competitive pressures, significantly shaped by Porter's Five Forces. The tech giant contends with powerful buyers, particularly enterprise clients, influencing pricing. Intense rivalry with competitors like Apple and Google is another key factor. The threat of new entrants, while moderate, remains a consideration. Substitute products, such as cloud-based alternatives, pose a persistent challenge. Finally, supplier power, especially of critical components, can impact Microsoft.
Unlock key insights into Microsoft’s industry forces—from buyer power to substitute threats—and use this knowledge to inform strategy or investment decisions.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Microsoft's supplier concentration is moderate, depending on the specific components and services. The company sources from a broad range of suppliers, reducing its vulnerability to any single entity. Microsoft's substantial purchasing power enables favorable negotiation of prices and terms. For example, in 2024, Microsoft's cost of revenue was approximately $80 billion, reflecting the significance of supply chain costs.
Microsoft often faces low switching costs, especially for common components; this limits supplier power. For instance, Microsoft can easily switch cloud service providers. However, for unique tech, like custom chips, costs rise, giving suppliers more leverage. Microsoft's 2024 revenue was $211.9 billion, showing its ability to negotiate with suppliers. This encourages competition, keeping supplier power in check.
Suppliers' ability to forward integrate into Microsoft's markets is limited. Hardware suppliers might compete, but lack Microsoft's software ecosystem and brand recognition. This asymmetry constrains suppliers' direct market challenge. Microsoft's 2024 revenue was about $230 billion, showcasing its strong market position. This dominance limits suppliers' leverage.
Impact of supplier inputs on Microsoft's differentiation is high
Microsoft's reliance on suppliers is crucial for its product differentiation, directly impacting its ability to offer cutting-edge features and performance. The quality and innovation provided by suppliers of components and technologies are essential for Microsoft's competitive edge. Effective management of these supplier relationships is key to maintaining a strong market position. In 2024, Microsoft's R&D spending was approximately $26.8 billion, reflecting its commitment to innovation heavily reliant on supplier contributions.
- Supplier innovation is critical for Microsoft's product features.
- High-quality components directly influence product performance.
- Effective supplier management is essential for market competitiveness.
- Microsoft's R&D spending in 2024 was about $26.8B.
Microsoft's influence on supplier profitability is significant
Microsoft's substantial purchasing power, driven by its large order volumes, significantly impacts supplier profitability. Suppliers frequently rely on Microsoft's business, making them vulnerable to pricing and term pressures. This leverage allows Microsoft to negotiate favorable deals. For instance, in 2024, Microsoft's hardware revenue reached $20 billion, demonstrating its market influence.
- Large Order Volumes: Microsoft's massive scale gives it considerable bargaining power.
- Supplier Dependence: Many suppliers rely heavily on Microsoft for revenue.
- Pricing Pressure: Microsoft can negotiate lower prices and favorable terms.
- Market Dominance: Microsoft's influence is amplified by its strong market position.
Microsoft's supplier power is moderate, due to its broad supplier base and high switching ability. Its immense purchasing power enables advantageous negotiations, especially for standard components. The ability of suppliers to directly challenge Microsoft is limited by its strong market position and integrated ecosystem.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | Moderate; Diverse supplier base |
| Switching Costs | Generally low for standard components |
| Forward Integration | Limited threat from suppliers |
| Purchasing Power | Strong due to large scale |
Customers Bargaining Power
Microsoft's expansive customer base spans individuals and corporations, diminishing the influence of any single entity. This broad reach, serving diverse needs, weakens individual customer demands. For instance, in 2024, Microsoft's cloud revenue grew significantly, showing reduced reliance on specific customer segments. This diversification strategy bolsters Microsoft's market position.
Switching costs for Microsoft's customers hinge on the product. Consumers face moderate costs when changing operating systems or productivity software, considering familiarity and data transfer. For businesses deeply embedded in Microsoft's ecosystem, these costs are notably higher. In 2024, Microsoft's commercial revenue grew, indicating strong customer lock-in. This lock-in strengthens Microsoft's position in the market, thanks to the high switching costs.
Customer price sensitivity is moderate for Microsoft. In the enterprise sector, value and integration are key, not just cost. Microsoft's brand, reliability, and support justify premium pricing, easing price pressure. Microsoft's Q1 2024 revenue was $56.5 billion, showing customer willingness to pay.
Availability of substitute products is high
The availability of substitute products significantly impacts Microsoft's customer bargaining power. Customers can choose from open-source software, alternative operating systems, and rival cloud platforms. This readily available competition gives customers leverage. In 2024, the global cloud computing market, where Microsoft Azure competes, was valued at over $670 billion, highlighting the vastness of alternatives.
- Open-source software provides free alternatives to Microsoft's applications.
- Competing cloud services like AWS and Google Cloud offer similar functionalities.
- Customers can switch providers easily, increasing their bargaining power.
- This forces Microsoft to maintain competitive pricing and innovation.
Customer access to information is extensive
Customers wield considerable power due to vast information access regarding Microsoft's offerings. They can easily find reviews, compare prices, and explore alternatives online, increasing their leverage. This transparency necessitates that Microsoft constantly provides value and competitive pricing to maintain customer loyalty. For instance, in 2024, Microsoft's customer satisfaction scores influenced its pricing strategies.
- Online reviews and comparisons directly impact customer choices.
- Microsoft's pricing must remain competitive against rivals like Google and Amazon.
- Customer communities provide feedback that shapes product development.
- Negotiating power is higher for enterprise clients with substantial IT budgets.
Microsoft's customer base is diverse, reducing individual influence. Switching costs and brand loyalty moderate customer power. Availability of alternatives and price sensitivity also affect customer bargaining power, alongside the easy access to information.
| Aspect | Impact | Data |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Diversity | Reduces individual leverage | Microsoft serves millions of users globally in 2024 |
| Switching Costs | Influence customer decisions | Commercial revenue grew in 2024 |
| Alternatives | Increase customer leverage | Cloud market valued over $670B in 2024 |
Rivalry Among Competitors
Microsoft's software and cloud services face fierce competition. Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Google Cloud Platform (GCP) aggressively pursue market share. This rivalry pushes Microsoft to innovate, as seen with its Azure cloud revenue, which grew 28% in Q1 2024. Continuous improvement is crucial to stay ahead.
Microsoft leverages ecosystem integration to stand out, offering a cohesive suite of products. This approach creates a strong value proposition, making it difficult for rivals to match the seamless experience. For instance, Microsoft's cloud revenue hit $35.1 billion in Q1 2024, a 23% increase. Competitors, however, target specialized solutions and niche markets to compete.
Microsoft faces intense competition, necessitating substantial investments in advertising and marketing. In 2024, Microsoft's marketing expenses reached billions, a reflection of the competitive pressures. Rivals like Google and Amazon also dedicate massive budgets to marketing, fueling a constant struggle for customer attention. This high spending underscores the fierce competitive rivalry in the tech industry.
Consolidation trends in the industry
The tech industry sees constant consolidation, where firms buy others to grow. Microsoft, a key player, has acquired LinkedIn and GitHub. This reduces rivals but strengthens survivors. In 2024, tech M&A reached $600 billion globally. This includes deals like Synopsys buying Ansys.
- Microsoft's LinkedIn acquisition: $26.2 billion.
- 2024 global tech M&A: $600 billion.
- Synopsys-Ansys deal value: $35 billion.
- GitHub acquisition by Microsoft: $7.5 billion.
Aggressive pricing strategies
Aggressive pricing is a standard practice in software and cloud services, fueled by competition for budget-conscious clients. Microsoft strategically uses promotional pricing and bundling to draw in and keep customers. This price competition can squeeze profit margins, demanding strong cost management. This strategy is evident in Microsoft's cloud services, where they frequently offer competitive rates to gain market share.
- Microsoft's cloud revenue grew 23% in fiscal year 2024, showing its pricing strategies' impact.
- The company's gross margin for cloud services is approximately 70%, reflecting the need for cost efficiency.
- Promotional offers and discounts are regularly used to counter competitors like Amazon and Google.
Microsoft's competitive landscape is intense. Amazon and Google challenge Microsoft in cloud services, spurring innovation. Strategic acquisitions and pricing strategies are crucial for market dominance.
| Aspect | Details | 2024 Data |
|---|---|---|
| Cloud Revenue Growth | Azure's growth reflects competitive pressures. | 28% Q1 2024 |
| Marketing Expenses | Microsoft invests heavily in marketing to compete. | Billions in 2024 |
| M&A Activity | Tech acquisitions reshape the market. | $600B globally |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Open-source software significantly threatens Microsoft. Alternatives like Linux and LibreOffice offer cost-effective, customizable solutions. Adoption of open-source is rising, especially in servers, challenging Microsoft. In 2024, the open-source market grew to $48.8 billion. This growth impacts Microsoft's proprietary software dominance.
Cloud-based services from competitors like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud Platform, and Salesforce pose a significant threat to Microsoft. These alternatives offer similar cloud functionalities, intensifying price and feature competition. For example, AWS held around 32% of the cloud infrastructure market share in Q4 2023. The ease of switching increases the risk of substitution, impacting Microsoft's market position.
Alternative operating systems like macOS and Linux present a substitution threat. Windows, though dominant, faces competition. macOS is popular with creative professionals. Linux gains traction among developers. In 2024, Windows held roughly 73% of the desktop OS market, while macOS held about 15% and Linux around 3%.
Virtualization and containerization technologies
Virtualization and containerization technologies pose a threat to Microsoft by enabling customers to run applications across various platforms. This flexibility diminishes reliance on specific Microsoft operating systems and hardware, increasing the likelihood of substitution. The market for containerization, for instance, is projected to reach $12.9 billion by 2024. Organizations can now more easily switch between environments, potentially reducing their dependence on Microsoft products.
- Containerization market size is expected to reach $12.9 billion in 2024.
- Virtualization allows for easier migration between different platforms.
- This reduces vendor lock-in for customers.
- Microsoft faces increased competition from platforms offering virtualization.
Web-based applications
Web-based applications pose a significant threat to Microsoft's desktop software dominance. These applications offer accessible alternatives, reducing the need for locally installed software. Google Workspace and similar tools provide comparable features to Microsoft Office, thus decreasing dependence on Microsoft's products. The expansion of web-based applications intensifies the substitution threat, particularly in the productivity space.
- Google Workspace holds a substantial market share, with over 3 billion users globally as of late 2024, directly competing with Microsoft Office.
- Microsoft's cloud revenue grew 22% in the last quarter of 2024, a testament to the need to adapt to the web-based market.
- The shift towards web-based solutions is evident, with a 15% increase in cloud application usage among businesses in 2024.
The threat of substitutes significantly impacts Microsoft's market position. Open-source software, cloud services, and alternative operating systems challenge its dominance. Web-based applications also offer accessible alternatives. These substitutes increase competition and potentially erode Microsoft's market share.
| Substitute | Impact | 2024 Data |
|---|---|---|
| Open-Source Software | Cost-effective, customizable alternatives | Market grew to $48.8B in 2024 |
| Cloud Services | Intensified price and feature competition | AWS ~32% cloud infrastructure share in Q4 |
| Alternative OS | Competition to Windows | Windows ~73%, macOS ~15%, Linux ~3% desktop OS share |
| Web-Based Apps | Accessibility, feature parity | Google Workspace has over 3B users |
Entrants Threaten
High capital requirements are a significant barrier. The software and cloud services sectors demand substantial investments in R&D, infrastructure, and marketing. New entrants face steep costs to compete with Microsoft. Building cloud infrastructure can cost billions. In 2024, Microsoft's R&D spending was over $25 billion.
Microsoft's robust brand recognition and customer loyalty act as a significant hurdle for new entrants. Established brands like Microsoft enjoy a competitive edge due to existing customer trust and preference. In 2024, Microsoft's brand value reached approximately $340 billion, underscoring its powerful market position. New companies face considerable challenges in replicating this level of brand equity and customer retention.
Microsoft's vast scale provides substantial economies, particularly in software, cloud services, and hardware. This advantage enables competitive pricing, hindering new entrants' ability to match costs. In 2024, Microsoft's cloud revenue alone reached $120 billion, showcasing its massive operational scale. This size fuels innovation, creating a formidable barrier.
Proprietary technology and intellectual property
Microsoft's vast array of proprietary technology and intellectual property forms a formidable barrier. Patents, copyrights, and trade secrets safeguard its innovations, making replication difficult. This protection is particularly evident in its cloud services, where Microsoft Azure holds a significant market share. The company's R&D spending, reaching $27.5 billion in fiscal year 2023, continuously fuels this advantage.
- Microsoft's R&D investment in 2023 was $27.5 billion.
- Azure has a significant market share in the cloud services sector.
- Patents and copyrights protect Microsoft's innovations.
Stringent regulations and compliance requirements
The software and cloud services sectors face strict regulations, especially regarding data privacy and security. New companies must comply with these complex rules, which can be expensive and time-intensive. These compliance demands create significant hurdles for new entrants, potentially limiting competition. Microsoft's commitment to compliance is evident in its investments in cybersecurity and data protection. This regulatory burden can be a major barrier to entry, impacting the competitive landscape.
- Data privacy laws like GDPR and CCPA require significant investments.
- Cybersecurity standards and certifications add to operational costs.
- Compliance teams and legal expertise are essential for new entrants.
- Failure to comply can result in hefty fines and reputational damage.
The threat of new entrants to Microsoft is moderate, due to existing barriers. High capital needs, including significant R&D investments, pose a challenge. Microsoft's strong brand, valued at $340 billion in 2024, provides a competitive edge.
| Barrier | Impact | 2024 Data |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High investment needed | R&D: $25B+ |
| Brand Recognition | Customer loyalty | Brand Value: $340B |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Compliance costs | GDPR, CCPA compliance |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our analysis leverages annual reports, market research, and competitor filings, coupled with economic indicators for a data-driven view.