Sony Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Sony Bundle
What is included in the product
Analyzes Sony's competitive position through Porter's Five Forces, highlighting its challenges and opportunities.
Quickly identify competitive threats by easily visualizing Sony's external market factors.
What You See Is What You Get
Sony Porter's Five Forces Analysis
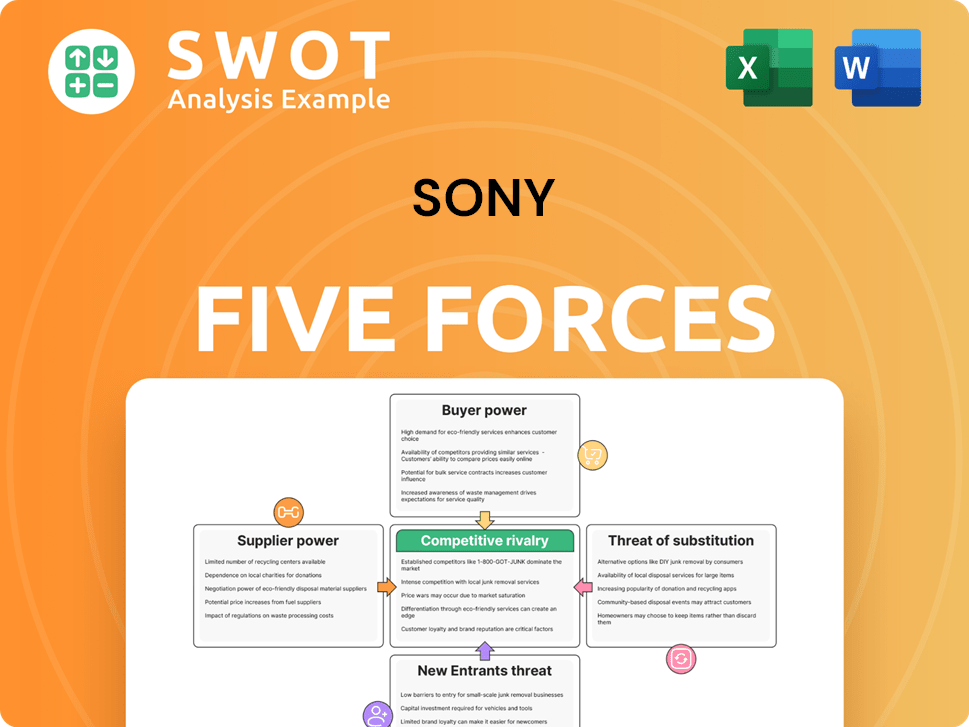
This preview details Sony's Five Forces analysis, covering competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, threat of substitutes, and threat of new entrants. The document dissects each force, providing a comprehensive look at Sony's market position. This is the complete, ready-to-use analysis file. What you're previewing is what you get—professionally formatted and ready for your needs.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Template
Sony's success is shaped by industry forces. Rivalry among existing competitors, like Microsoft and Samsung, is fierce. Buyer power varies, influenced by product diversity. The threat of new entrants, especially in gaming and entertainment, remains constant. Substitute products, such as streaming services, pose a risk. Suppliers, from component makers to content creators, also exert their influence.
This preview is just the starting point. Dive into a complete, consultant-grade breakdown of Sony’s industry competitiveness—ready for immediate use.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Sony's reliance on a few key suppliers, like TSMC and Samsung Display, boosts supplier bargaining power. These suppliers provide crucial components such as semiconductor chips and display panels. This dependency gives suppliers leverage to negotiate prices and terms. For example, in 2024, TSMC's revenue reached $69.3 billion, reflecting its strong market position and influence.
Sony's substantial annual component procurement, reaching $8.9 billion in 2024, provides significant leverage over suppliers. This buying power enables Sony to negotiate advantageous terms, including pricing. With a high supplier negotiation leverage of 92.3%, Sony effectively controls pricing and supply conditions. Long-term contracts, lasting 6 to 15 years, further stabilize the supply chain.
Suppliers' forward integration moderately impacts Sony's material access. Moderate size and overall supply keep supplier power at a moderate level. Strategic moves in Sony's operations help manage supplier concerns. In 2024, Sony's supply chain resilience initiatives aim to diversify sourcing, mitigating risks. Sony’s 2023 annual report shows a 3% increase in supply chain diversification efforts.
Supplier Power 4
Sony's substantial investments in vertical integration significantly curb supplier power. For instance, the company allocated $5.6 billion to semiconductor manufacturing and $1.3 billion to image sensor R&D, reducing dependence on outside vendors. Sony's internal component production, reaching 24.7%, further diminishes the leverage suppliers hold. This strategic move ensures greater control over costs and supply chains.
- Vertical integration investments: $6.9 billion
- Internal component production: 24.7%
Supplier Power 5
Sony's shift to mass logistics and sourcing from cheaper countries like China and Taiwan significantly reduces supplier power. The electronics market's competitive landscape, with numerous companies, further dilutes the influence of individual suppliers. Sony's strategy leverages this by accessing components at lower costs, enhancing its profit margins. This approach is reflected in Sony's financial reports, with cost of sales decreasing by 3.7% in the fiscal year 2024.
- Cost of Sales Reduction: 3.7% decrease in fiscal year 2024.
- Global Sourcing: Utilizes suppliers in China and Taiwan.
- Market Competition: Operates in a highly competitive electronics market.
- Logistics: Employs mass logistics to cut production costs.
Sony manages supplier power through a mix of strategies. Key suppliers like TSMC have significant leverage, but Sony's large procurement volume, reaching $8.9B in 2024, balances this. Vertical integration, with investments of $6.9B, and global sourcing also curb supplier influence.
| Factor | Impact | Data |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Reliance | High initial impact | TSMC's $69.3B revenue (2024) |
| Procurement Power | Mitigating influence | $8.9B Component spend (2024) |
| Vertical Integration | Reducing supplier power | $6.9B investment |
Customers Bargaining Power
Buyers wield considerable influence over Sony, thanks to readily available information that facilitates product comparisons and brand switching. Low switching costs amplify this buyer power, impacting Sony's pricing and product strategies. Sony must intensify its marketing efforts to attract and retain customers, as competition is high. In 2024, Sony's market share in gaming consoles faced pressure from competitors, highlighting the need for customer-centric strategies.
Sony's buyer power varies; in gaming (44.5% share, $25.4B revenue in 2023), customers have less power due to brand loyalty. Consumer Electronics (12.3% global share, $18.7B revenue in 2023) sees higher buyer power from retail giants. Entertainment/Media (8.6% share, $15.2B revenue in 2023) faces fluctuating buyer power based on content demand. Retailers like Argos and Currys, built long-term relationships with Sony.
Buyer power significantly impacts Sony. Consumer electronics price sensitivity hovers around 65-75%, varying by product. This challenges Sony to balance innovation with affordability. Sony must offer quality service at competitive prices to retain customers. In 2024, Sony's focus remains on value to combat buyer power.
Buyer Power 4
Sony's strong brand loyalty, especially with PlayStation, tempers buyer power. A 72% customer retention rate for PlayStation and a 58.4% repeat purchase rate for Sony electronics showcase this. The company's high average customer lifetime value (CLTV) of $1,247 per consumer reinforces the value of these relationships. Sony's brand image and quality products foster consumer preference, reducing buyer influence.
- High customer retention rates provide a buffer.
- Repeat purchases indicate brand loyalty.
- CLTV highlights the importance of customer relationships.
- Brand image and quality boost customer preference.
Buyer Power 5
Buyer power significantly shapes Sony's market dynamics. Distribution channels heavily influence this power, with online retail capturing 37.6% of sales. Physical stores contribute a substantial 42.3%, and direct sales account for 20.1%. Customers' demand for advanced features within 18-24 month cycles further amplifies buyer power.
- Online retail's 37.6% share offers global reach, increasing buyer options.
- Physical stores' 42.3% contribution highlights the importance of in-person experiences.
- Direct sales at 20.1% provide Sony with direct customer interaction.
- Eighty-four percent of consumers want cutting-edge features fast.
Sony faces significant customer bargaining power due to easy product comparisons and low switching costs. Gaming, with its 44.5% market share and brand loyalty, sees lower buyer power than consumer electronics. In 2024, price sensitivity and online retail's influence (37.6% of sales) continue to shape Sony's market strategies.
| Aspect | Details | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Market Share | Gaming: 44.5%, Consumer Electronics: 12.3% | Buyer power varies by segment |
| Online Sales | 37.6% of total sales | Increases customer choice, heightens bargaining power |
| Customer Retention | PlayStation: 72% | Mitigates buyer power through loyalty |
Rivalry Among Competitors
Sony's competitive landscape is crowded with giants like Samsung, Apple, and Microsoft. The tech market is fiercely contested, driving intense rivalry. Consumer switching costs are low, increasing the pressure on Sony. In 2024, Samsung's revenue reached $260 billion, highlighting the scale of competition.
Sony faces fierce rivalry, especially in consumer electronics, gaming, and entertainment. Its $5.78 billion R&D spending in fiscal 2023 shows its response to competition. However, sales in India have declined for three years. This suggests challenges in maintaining market share against rivals.
Sony faces intense competition, particularly in gaming. PlayStation dominates the console market with 68% share. The video game market is saturated, and new entry barriers are high. Sony's diverse portfolio, including consumer electronics (12.4%) and cameras (20.1% professional), offers some protection.
Competitive Rivalry 4
Competitive rivalry in Sony's market is fierce due to tech and entertainment convergence. Streaming services and digital platforms fiercely compete for consumer attention, driving up the competition. This leads to short product life cycles and lower profitability, particularly given high R&D investments. To combat this, Sony focuses on product innovation and enhanced features.
- Sony's R&D spending in FY2024 was approximately ¥1.2 trillion.
- The global streaming market is projected to reach $1.2 trillion by 2028.
- Sony's PlayStation 5 sales reached over 50 million units by late 2023.
- High exit barriers make it hard for firms to leave the market.
Competitive Rivalry 5
Sony's competitive landscape is dynamic. It battles rivals in audio (Bose) and gaming (Nintendo). Sony must innovate constantly to stay ahead. The company's success hinges on product differentiation.
- Sony's PS5 sales reached 50 million units by December 2023.
- Bose held a 14% market share in the U.S. headphone market in 2023.
- Nintendo's Switch sold over 139 million units globally by December 2023.
- Sony's revenue for the fiscal year 2023 was approximately $88.3 billion.
Competitive rivalry significantly shapes Sony's market position. Intense competition from giants like Samsung, Apple, and Nintendo forces constant innovation. Sony's R&D spending reached ¥1.2 trillion in FY2024. To stay competitive, Sony focuses on product differentiation.
| Key Competitors | Market Share (Approx. 2024) | Strategic Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Samsung | Varies by product | Innovation and cost leadership |
| Apple | Varies by product | Premium branding & ecosystem |
| Nintendo | Gaming console market share (significant) | Unique gaming experiences |
| Bose | Headphone market (14% in 2023) | Audio quality & brand loyalty |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Substitutes pose a moderate threat to Sony, affecting its diverse offerings. Competitors like Samsung in TVs or Apple in music players can attract customers. The availability of cheaper alternatives, like generic electronics, pressures Sony. In 2024, Sony's electronics revenue was impacted by these choices. This can influence pricing and profitability.
The threat of substitutes for Sony is moderate. Easy substitution is a concern because buyers face low switching costs. Sony competes with many entertainment options; streaming services and gaming consoles are viable alternatives. In 2024, the global video game market was valued at around $282.6 billion, highlighting the constant competition.
Smartphones and mobile gaming platforms are significant substitutes for Sony's cameras and consoles. Competition from these platforms is intensifying, impacting Sony's market share. In 2024, global smartphone gaming revenue reached approximately $92 billion, highlighting the shift. Augmented and virtual reality technologies further pose a threat, potentially reshaping entertainment consumption.
Threat of Substitution 4
The threat of substitutes for Sony is increasing, especially with the rise of cloud-based entertainment and streaming services. Consumers are shifting away from traditional media, demanding on-demand content. Streaming platforms pose a direct challenge, and social media further diversifies entertainment options. For example, TikTok boasts 1.5 billion monthly active users, and YouTube has 2.5 billion.
- Streaming services compete directly with traditional media formats.
- Social media platforms offer alternative entertainment sources.
- Consumer preferences are evolving towards digital content.
- Sony needs to innovate to stay relevant.
Threat of Substitution 5
The threat of substitution is significant for Sony Porter, particularly due to the rise of alternative entertainment platforms. Consumers increasingly choose social media and online streaming services over traditional offerings. The shift towards online entertainment, like music downloads (both legal and illegal), presents a challenge. The bargaining power of substitute products is currently high in the telecommunication industry. For instance, customers can use email services or platforms like Skype for communication.
- Streaming services like Netflix and Spotify have significantly increased their user base in 2024, showcasing the appeal of substitutes.
- The global music streaming market was valued at over $26 billion in 2023, highlighting the impact of digital alternatives.
- Email usage continues to grow, with over 4.5 billion email users worldwide in 2024, underscoring the prevalence of communication substitutes.
- The shift from physical media to digital downloads and streaming is evident in the decline of CD sales, which dropped significantly in the last decade.
The threat of substitutes significantly impacts Sony. Streaming and social media offer alternative entertainment, challenging Sony's traditional media. In 2024, global streaming revenues reached ~$85 billion, illustrating this shift. Sony must innovate to remain competitive against these substitutes.
| Category | Substitute | 2024 Data |
|---|---|---|
| Entertainment | Streaming Services | Global Streaming Revenue: ~$85B |
| Gaming | Mobile Gaming | Global Smartphone Gaming Revenue: ~$92B |
| Communication | Email/VoIP | Worldwide Email Users: ~4.5B |
Entrants Threaten
The threat of new entrants for Sony is typically low. High barriers, like substantial capital, deter newcomers. Sony's need for innovation and economies of scale also limit new competition. The gaming industry, for example, requires huge investments; in 2024, game development costs surged.
The threat of new entrants to Sony's music business is moderate. High initial costs, including brand building and operational expenses, create barriers. Newcomers face challenges establishing supplier relationships and competing with established firms like Sony. Building a competitive catalog, like Sony's "largest...in the world," demands significant capital and time.
The threat of new entrants for Sony is moderate. Low switching costs for consumers slightly open the door for new competitors. Brand loyalty and Sony's tech expertise act as strong defenses. A significant hurdle is the enormous cost of building a recognizable brand. In 2024, Sony's marketing expenses were substantial, reflecting the high investment required to establish a new brand in the market.
Threat of New Entrants 4
The threat of new entrants in the music industry is significant. Stringent regulations and policies globally pose a challenge for new firms. Existing industry giants, like the Big Four record labels, offer considerable competition, making survival difficult for smaller entities. New entrants face substantial marketing costs due to high competition.
- Regulatory hurdles: New music ventures must navigate complex licensing and compliance requirements, varying by country.
- Market dominance: The Big Four control a large portion of the market share, creating a barrier for smaller labels.
- Marketing expenses: Launching a successful music venture requires substantial investments in marketing and promotion to reach target audiences.
- Market share: The top 10 music labels hold approximately 70% of the global market share.
Threat of New Entrants 5
The threat of new entrants is moderate for Sony. The cellular phone market is highly saturated, which can deter new companies. Sony's well-established brand and market presence provide a significant competitive advantage. However, constant technological advancements mean new entrants might disrupt the market. Sony must keep innovating to maintain its edge.
- Market saturation in the cellular phone industry limits new entrants.
- Sony's strong brand and market position offer a competitive barrier.
- Technological innovation could create opportunities for new competitors.
For Sony, the threat of new entrants varies. High capital needs and brand strength deter new competitors in some sectors. However, in other areas like the music industry, moderate threats exist. The cellular phone market sees moderate entry barriers.
| Sector | Threat Level | Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Gaming | Low | High capital, innovation need |
| Music | Moderate | Brand building, market share |
| Cell Phones | Moderate | Market saturation, tech disruption |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
This analysis is built upon Sony's annual reports, market research, industry publications, and financial data from credible sources.