SVB Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
SVB Bundle
What is included in the product
Evaluates control held by suppliers and buyers, and their influence on pricing and profitability.
A dynamic analysis template that updates automatically with real-time industry data.
What You See Is What You Get
SVB Porter's Five Forces Analysis
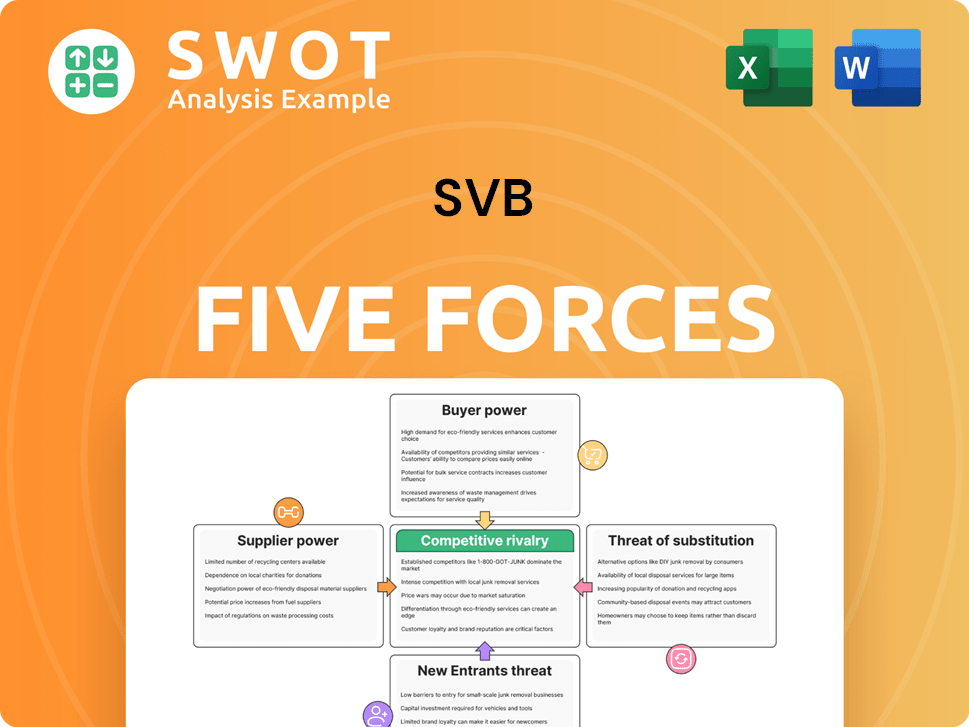
This preview shows the complete SVB Porter's Five Forces analysis. It examines competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, threat of substitutes, and threat of new entrants. The analysis is professionally formatted and ready for your immediate use. You'll receive the same, comprehensive document instantly after purchase.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Template
SVB faced intense competition, especially from established banks and fintech startups. The threat of new entrants was high, fueled by relatively low barriers to entry in some segments. Buyer power, particularly from venture capital-backed companies, significantly impacted SVB's pricing. Substitute services, like specialized financial products, posed a threat. Supplier power (e.g., talent) also influenced SVB’s operations.
Our full Porter's Five Forces report goes deeper—offering a data-driven framework to understand SVB's real business risks and market opportunities.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
SVB, like other banks, depended on specialized providers for core banking and software. These vendors, often limited in number, wielded significant bargaining power. Switching costs for tech platforms could range from $5 million to $20 million, as seen in 2024. This high cost made SVB less likely to switch vendors frequently.
Switching banking tech is costly; solutions can cost $5M-$20M. SVB hesitates to switch, boosting supplier power. Technology upgrades, like SVB's $12M in 2022, highlight the investment. This financial commitment strengthens suppliers' leverage in negotiations.
SVB's operational efficiency was heavily reliant on a select group of financial software vendors. In 2022, these key software providers constituted 75% of SVB's software spending. This concentration amplified the suppliers' influence. Dependence on these vendors for essential banking, analytics, and fund management software further strengthened their bargaining position.
Specialized Data Analytics Tools
SVB's reliance on specialized data analytics and customer relationship management tools, sourced from a limited vendor pool, significantly impacts its operations. These tools are essential for SVB's functionalities, increasing vendor leverage. In 2022, SVB engaged approximately 10 specialized software vendors. This concentration of crucial services gives vendors substantial bargaining power.
- SVB's dependency on a few key vendors enhances their bargaining power.
- The specialized tools are critical for SVB's operational efficiency and client management.
- By 2022, SVB had around 10 key software vendors.
- Limited vendor options mean SVB is vulnerable to vendor pricing and service terms.
Influence of Premium Investment Firms
SVB's relationships with premium investment firms significantly influence its operations. These firms, managing SVB's assets, levy management fees. Historically, these fees have ranged from 1.0% to 2.0% of assets under management. This pricing structure gives substantial power to these firms, especially considering SVB's sizable asset base.
- In 2022, SVB collaborated with 5 premium investment firms.
- Management fees were around 1.0% to 2.0% of assets managed.
- SVB's managed assets were approximately $20 billion.
- Fees accumulated to a considerable amount, impacting SVB's profitability.
SVB's dependence on a few critical tech and investment service vendors enhanced their power. Switching tech providers was costly, with expenses of $5M-$20M in 2024. This reliance enabled vendors to exert influence over pricing and service terms.
| Key Area | Details | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Tech Vendor Concentration | Approx. 10 specialized software vendors in 2022. | Increased vendor bargaining power. |
| Switching Costs | $5M-$20M to change core banking platforms (2024). | Reduced SVB's negotiation leverage. |
| Investment Firm Fees | 1.0%-2.0% of assets under management. | Significant impact on SVB's profitability. |
Customers Bargaining Power
SVB benefited from established brand loyalty, particularly in tech and life sciences. Its reputation for top-tier service and customized financial products helped retain clients. In 2022, SVB's net income reached $678 million, showcasing profits from a dedicated customer base.
SVB's clients were mainly venture capital-backed startups in tech and healthcare. This concentration exposed SVB to industry-specific risks. During the COVID-19 pandemic, the tech sector's loan portfolio decreased significantly. In 2024, the tech industry saw a 10% drop in funding. This highlighted SVB's vulnerability.
SVB faced high customer bargaining power due to a significant portion of uninsured deposits. A staggering 94% of its deposits surpassed the $250,000 FDIC insurance limit. These institutional clients, highly sensitive to risk, swiftly withdrew funds. This rapid withdrawal triggered a liquidity crisis, highlighting their substantial influence.
Influence of Large Institutional Investors
Large institutional investors significantly influence SVB's fund management. These investors can negotiate fees and demand specific investment strategies. SVB's ability to retain these clients impacts its revenue and asset base. The concentration of assets among institutional clients amplifies their power. In 2024, institutional clients accounted for roughly 60% of SVB's assets under management, highlighting their substantial leverage.
- Fee Negotiation: Institutional clients can negotiate lower fees.
- Strategic Influence: They can demand specific investment strategies.
- Asset Concentration: A large portion of assets are linked to institutions.
- Revenue Impact: Client decisions directly impact revenue.
Demand for Competitive Rates
Customers' bargaining power is amplified by interest rate changes, pushing them to seek better deals. Businesses are shifting from banks to money market funds for higher returns, intensifying the competition. Criticism of regulations, especially post-2018 Dodd-Frank rollbacks, highlights the impact of rules on SVB's stability. This environment underscores how customer choices and regulatory landscapes shape financial institutions.
- In 2024, money market funds saw significant inflows as rates rose.
- The Dodd-Frank Act's modifications in 2018 are still debated for their effect on bank risk.
- Customers' search for higher yields intensified with rising interest rates.
SVB faced high customer bargaining power, especially with uninsured deposits. Rapid fund withdrawals by risk-sensitive clients triggered liquidity issues. Institutional investors influenced fees and strategies.
Rising interest rates pushed customers toward better deals. Money market funds attracted significant inflows in 2024. Regulatory changes impacted SVB’s stability.
| Metric | Data | Year |
|---|---|---|
| Uninsured Deposits | 94% | 2023 |
| Tech Funding Drop | 10% | 2024 |
| Institutional Assets | 60% | 2024 |
Rivalry Among Competitors
The financial services sector faces fierce competition, dominated by giants like JPMorgan Chase, Bank of America, and Citi. These top 25 U.S. banks manage over $17 trillion in assets. In Q2 2023, SVB Financial Group held approximately $118 billion in assets. This disparity highlights the intense competitive pressure SVB faced from larger institutions.
The financial sector is experiencing increased competition due to fintech companies. The global fintech market was valued at around $309 billion in 2023. These companies, like Stripe, Robinhood, and Square, are challenging traditional banks. They offer innovative services and attract customers, changing the competitive landscape.
SVB distinguishes itself by focusing on tech and life sciences. They offer high-quality service and customized financial solutions. A survey showed 80% of SVB's clients prefer them, a strong competitive advantage. This client loyalty makes it difficult for new competitors to gain traction. SVB's strategy creates a robust barrier against rivalry.
Market Share Battles in Niche Segments
Competitive rivalry was fierce, especially in venture capital. SVB contended with various banks and financial institutions. Established players, like JPMorgan Chase and Wells Fargo, targeted the tech sector, challenging SVB's dominance. Competition intensified, impacting SVB's market position.
- JPMorgan Chase's assets: $3.9 trillion in 2024.
- Wells Fargo's assets: $1.9 trillion in 2024.
- Venture capital investments in 2023: $136.5 billion.
Brand Loyalty Influencing Client Retention
Strong brand loyalty significantly impacts client retention within SVB's competitive landscape. SVB has cultivated a reputation for excellent customer service and specialized financial products. This focus helped SVB achieve a net income of $678 million in 2022, reflecting the value of its loyal customer base.
- High client retention is a key factor in maintaining profitability.
- Loyalty reduces the risk of client churn.
- SVB's tailored financial solutions enhance client stickiness.
Competitive rivalry in SVB's market was substantial. Established banks like JPMorgan Chase ($3.9T assets in 2024) and Wells Fargo ($1.9T in 2024) aggressively pursued the same tech and life sciences clients. This created intense pressure on SVB's market share and profitability.
| Factor | Impact on SVB | Data |
|---|---|---|
| Rivalry Intensity | High | Venture capital investments in 2023: $136.5B |
| Key Competitors | Strong | JPMorgan Chase, Wells Fargo |
| Strategic Focus | Specialized | Tech & Life Sciences |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Fintech solutions pose a significant threat to traditional banks by offering alternatives. These include online lending platforms and digital payment systems. The global fintech market was valued at about $309 billion in 2023. It is projected to grow at a CAGR of 23.58% through 2030, indicating strong market substitution potential.
Non-bank financial institutions, like credit unions and investment firms, offer banking services. They can lure customers with specialized products and attractive rates. As interest rates fluctuate, customers might seek better returns elsewhere. In 2024, the assets of U.S. credit unions totaled over $2 trillion, showing significant market presence.
The threat of substitutes in air travel varies; options like cars, trains, and boats exist, but time is crucial. Air travel remains dominant for speed. This force is low to medium. For example, in 2024, the US saw over 800 million air passengers, showing its importance despite alternatives.
Money Market Funds
Money market funds pose a threat to SVB due to their function as a substitute for traditional bank deposits. These funds provide a liquid and relatively safe option for businesses to park their cash, offering competitive yields. Concerns following SVB's collapse have heightened the appeal of money market funds. Businesses are now more inclined to shift funds for better returns and perceived safety.
- In 2024, money market funds saw significant inflows, reflecting investor caution.
- Yields on money market funds have generally outpaced those on traditional bank deposits.
- The shift to money market funds can reduce SVB's deposit base, impacting its ability to lend.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) poses a threat to SVB by offering substitutes via blockchain. DeFi provides alternative platforms for lending and investment, potentially diverting customers. In 2024, DeFi's total value locked (TVL) fluctuated, showcasing adoption volatility. VC investors' ESG focus could shift funds away from traditional banks.
- Blockchain and DeFi offer substitutes for traditional banking.
- Alternative means for lending, borrowing, and investing are available.
- VC investors increasingly prioritize ESG factors.
- DeFi's TVL showed fluctuating adoption.
SVB faces substitute threats from fintech, non-bank institutions, and money market funds. Fintech offers digital alternatives; the global market was worth ~$309B in 2023. Money market funds attracted significant 2024 inflows due to investor caution.
| Substitute | Impact | 2024 Data |
|---|---|---|
| Fintech | Alternative banking services | Market grows at 23.58% CAGR |
| Money Market Funds | Deposit Substitution | Significant Inflows |
| Non-bank institutions | Competitive products & rates | US Credit Unions: $2T+ in assets |
Entrants Threaten
The financial services sector faces significant barriers due to high regulatory standards. SVB, like other banks, must adhere to strict federal and state laws, including the Dodd-Frank Act and the Bank Holding Company Act. Compliance with Dodd-Frank can cost over $500 million annually for large financial institutions.
Capital requirements pose a significant threat, especially for new banks. The Federal Reserve mandates a minimum tier 1 capital ratio of 4% of risk-weighted assets. This requirement demands substantial upfront investment. In 2024, the average capital ratio for US banks was around 12%, highlighting the high financial bar. Capital adequacy is a major hurdle for new entrants.
Achieving economies of scale is challenging in banking, favoring larger institutions with cost advantages. SVB Financial Group faced this reality, with established banks leveraging size for lower operational costs. In 2024, the top 10 U.S. banks held over 50% of total banking assets, showcasing scale's impact. This concentration made it tough for new entrants.
Established Brand Loyalty
Established brand loyalty poses a significant threat to new entrants. SVB Financial Group, before its collapse in 2023, had strong brand loyalty within the tech and life sciences sectors. Data from 2022 indicated that about 80% of SVB's clients were likely to stick with them. This loyalty presented a major hurdle for competitors trying to enter the market and take away existing customers.
- Client retention rates were consistently high, reflecting strong relationships.
- Specialized services and industry knowledge deepened client ties.
- The established reputation offered a competitive advantage.
Need for Trust and Reputation
New banks face a significant hurdle in establishing trust and a solid reputation, crucial in the financial services industry. Building this trust is time-consuming and resource-intensive, presenting a barrier to entry. SVB Financial Group, for instance, cultivated strong brand loyalty within specialized sectors like technology and life sciences. This existing loyalty makes it harder for new entrants to compete.
- Trust is paramount in finance; it takes years to build and can be lost quickly.
- SVB had a strong brand reputation in tech and life sciences, offering specialized services.
- New banks must overcome the established trust and reputation of existing players to succeed.
- Building a reputation requires consistent performance and customer satisfaction.
Threat of new entrants is high due to stringent regulations and capital needs.
The Federal Reserve mandates a minimum tier 1 capital ratio. Compliance costs can exceed $500M annually.
New entrants face brand loyalty hurdles. In 2024, top 10 US banks controlled over 50% of assets.
| Barrier | Impact | 2024 Data |
|---|---|---|
| Regulations | High compliance costs | Dodd-Frank compliance costs >$500M |
| Capital | Significant investment needed | Average US bank capital ratio ~12% |
| Brand Loyalty | Hard to gain customers | Top 10 banks held >50% assets |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
The SVB analysis utilizes SEC filings, market research reports, and financial news outlets. This combination provides crucial information on competitive dynamics and market positioning.