Telstra Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Telstra Bundle
What is included in the product
Tailored exclusively for Telstra, analyzing its position within its competitive landscape.
Quickly identify Telstra's vulnerabilities by visualizing strategic pressure with a clear spider/radar chart.
Preview Before You Purchase
Telstra Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This is the full Telstra Porter's Five Forces Analysis. The document displayed presents the complete analysis you'll receive. It's fully formatted and ready for download. The instant-access file is identical. This is the final version.
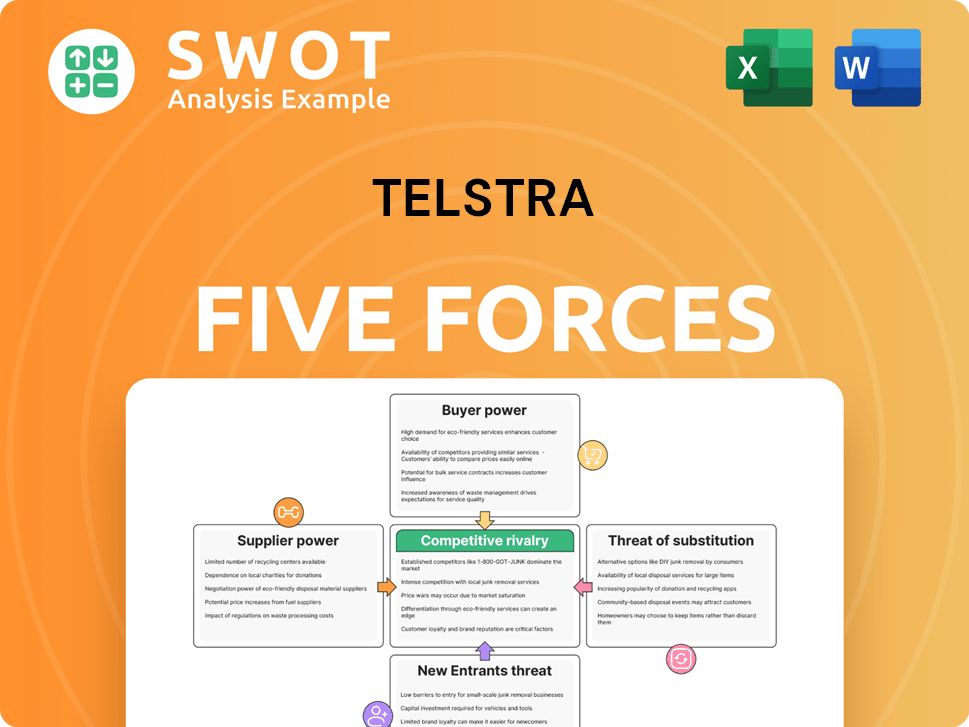
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Template
Telstra faces dynamic market pressures, as assessed through Porter's Five Forces. Rivalry is high due to strong competitors. Bargaining power of buyers is moderate. Supplier power is manageable. The threat of new entrants is a factor. Substitutes pose a moderate challenge.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Telstra’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Telstra's dependence on key suppliers like Ericsson and Nokia grants these suppliers considerable bargaining power. In 2023, Telstra's capital expenditures on network equipment reached roughly AUD 2.5 billion. This reliance limits Telstra's ability to negotiate favorable prices and contract terms. The industry's structure concentrates supply, strengthening supplier influence.
Telstra's operational efficiency heavily depends on tech suppliers, including Microsoft and AWS. In 2024, Telstra allocated around AUD 1.1 billion to cloud services. The reliance on these providers boosts their bargaining power. Switching suppliers is difficult due to service quality and compatibility needs.
Telstra faces potential price hikes from suppliers due to surging demand for high-speed networks. The global telecom equipment market, valued at USD 150 billion in 2023, fuels this. Growth is expected with a 5.5% CAGR through 2030. Increased demand puts pressure on Telstra, potentially increasing their costs.
Vertical Integration Efforts
Telstra has taken steps to vertically integrate its operations, a strategy designed to lessen the influence of its suppliers. A prime example is the 2022 acquisition of Digicel Pacific, aimed at potentially saving AUD 200 million annually. Vertical integration strengthens Telstra's position in the supply chain, creating more control. This approach reduces reliance on external suppliers, bolstering Telstra's bargaining power.
- Digicel Pacific acquisition aimed for AUD 200 million in annual savings.
- Vertical integration enhances supply chain control.
- Reduces dependency on external suppliers.
- Improves negotiating power.
Shift to Renewable Energy
Telstra's move to renewable energy reshapes supplier dynamics. By 2025, aiming for 100% renewable energy, Telstra is reducing reliance on traditional energy suppliers. This strategic shift, costing between AUD 100M and AUD 150M initially, enhances long-term sustainability. The switch provides cost-effective energy options.
- Telstra's 100% renewable energy target by 2025 impacts energy suppliers.
- Initial investment in renewables: AUD 100M to AUD 150M.
- Reduced dependency on coal and gas suppliers.
- Focus on sustainable, cost-effective energy solutions.
Telstra’s reliance on suppliers, like Ericsson and Nokia, gives them significant bargaining power, especially with equipment costs around AUD 2.5 billion in 2023. This includes cloud service spending of approximately AUD 1.1 billion in 2024. However, vertical integration and renewable energy shifts, with initial costs between AUD 100M-AUD 150M, are strategies to counteract this.
| Aspect | Details | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Dependence | Network equipment: AUD 2.5B (2023), Cloud services: AUD 1.1B (2024) | Higher costs, limited negotiation |
| Mitigation | Vertical integration (Digicel), renewable energy | Increased control, cost savings |
| Renewable Energy Costs | AUD 100M-AUD 150M (initial) | Reduced reliance on traditional suppliers |
Customers Bargaining Power
Switching costs in telecommunications are generally low, enabling customers to switch providers easily, thereby boosting their bargaining power. With the rise of competitors, Telstra faces intense pressure to provide competitive offerings to retain its customer base. For instance, in 2024, the Australian Communications and Media Authority (ACMA) reported a high churn rate in the mobile market. This ease of switching compels Telstra to prioritize customer satisfaction and offer attractive service packages to remain competitive. The low switching costs significantly impact Telstra's pricing and service strategies.
Customers show price sensitivity, impacting Telstra's pricing strategies. In 2024, Telstra adopted a value-based pricing model. This change aims to boost customer retention. The move away from CPI-linked pricing reflects a focus on user experience. This approach helps retain customers.
Informed customers, aware of market options, can drive better prices. Telstra's customer experience focus, with personalized solutions, is key. This strategy helped it achieve a 49% market share in mobile services in 2024. By prioritizing customer needs, Telstra aims to sustain its competitive advantage.
Service Customization
Telstra's customers wield significant bargaining power due to their expectation of customized services. This necessitates Telstra to provide personalized solutions, directly impacting its operational strategies. The company's emphasis on customer satisfaction, offering tailored services, is a core strategy to build loyalty. This customer-centric approach is vital in a competitive market.
- Telstra reported a customer service Net Promoter Score (NPS) of +20 in the first half of FY24.
- In 2024, Telstra invested significantly in digital channels to enhance customer experience.
- Telstra's focus is on offering personalized plans and services.
Customer Churn
High churn rates in telecom boost customer power, forcing companies to compete fiercely for retention. Telstra faces this, yet has seen solid consumer handheld user growth. Price increases help Telstra fund network improvements and customer service.
- Telstra's consumer branded churn remained broadly stable.
- The company implements price rises.
- Ongoing investments in network coverage.
Customers have strong bargaining power due to easy switching, intensified by competitive pressures in 2024. This forces Telstra to prioritize competitive pricing and customer satisfaction to retain its market share. The high churn rates reported by ACMA highlight the impact on Telstra's strategies.
| Factor | Impact | Data (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Switching Costs | Low | High mobile churn rate |
| Price Sensitivity | High | Value-based pricing model adopted |
| Customer Information | High | 49% market share in mobile |
Rivalry Among Competitors
Telstra dominates the Australian telecommunications market. In 2023, Telstra held over 22.5 million retail mobile accounts, showcasing significant market share. This leadership position is critical in the highly competitive telecom landscape. Telstra’s 5G rollout and network infrastructure contribute to its ability to command premium pricing.
Price competition in the telecom sector can be fierce, pressuring margins. Telstra's 2024 shift to value-based pricing aims to improve user experience. This strategy moves away from CPI-linked pricing models. In 2024, Telstra's revenue decreased, highlighting the impact of pricing dynamics.
Telstra holds a significant competitive edge due to its expansive network coverage. Its infrastructure supports fixed-line, mobile, and broadband services, ensuring reliable cash flow. Telstra's mobile network reaches over 99.6% of the Australian population, with 5G available to over 85% as of late 2024. This broad coverage attracts customers seeking dependable mobile connectivity and high speeds.
Innovation and Technology
Telstra aggressively pursues innovation and technology to maintain its competitive edge. The company's commitment is evident in its substantial investments in research and development. A prime example is the ongoing construction of a 14,000-kilometer high-speed fiber network throughout Australia, supported by a $1.6 billion investment. Furthermore, Telstra's collaboration with Microsoft to implement Copilot for M365 across its workforce showcases its strategy to integrate AI.
- Telstra invested $1.6 billion in a high-speed fiber network.
- Telstra partners with Microsoft to use Copilot for M365.
- Telstra employs 21,000 staff.
Cost Reduction
Telstra's dedication to cost reduction is crucial for staying competitive. The T22 program successfully delivered AUD 2.7 billion in cost savings, and the company is now targeting an additional AUD 500 million under the T25 plan. Telstra, while not the cheapest, aims to be the lowest-cost provider. This strategy supports healthy EBITDA margins, exceeding 30%.
- T22 program delivered AUD 2.7 billion in cost savings.
- T25 plan targets AUD 500 million in further reductions.
- Telstra's EBITDA margins are over 30%.
Telstra faces intense competition from Optus and Vodafone in Australia's telecom market. These rivals compete aggressively on pricing and service offerings, impacting Telstra’s margins. Telstra’s competitive advantage stems from its established network and innovative services, yet it is consistently challenged to defend its market share.
| Metric | Telstra | Competitors |
|---|---|---|
| Market Share (Mobile, 2024) | ~40% | ~60% (Optus, Vodafone, etc.) |
| 2024 Revenue Change | Decrease | Varies |
| Cost Savings (T22) | AUD 2.7B | N/A |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for Telstra is notably high due to the proliferation of VoIP, messaging apps, and social media. These alternatives offer voice and data services, which can be adopted by customers easily. For example, in 2024, the global VoIP market reached approximately $35 billion, reflecting its growing popularity, and this growth impacts traditional telecom revenues. To mitigate this threat, Telstra must focus on unique services and bundled offerings.
Fixed wireless presents a notable threat to Telstra as a substitute for fixed-line broadband. These solutions offer high-speed internet, particularly in areas lacking robust infrastructure. The quick installation of fixed wireless makes it an attractive alternative for consumers. In 2024, the fixed wireless market expanded, with approximately 1.8 million subscribers in Australia. Telstra must innovate to compete effectively.
Over-the-top (OTT) services pose a significant threat to Telstra, with streaming video and audio acting as substitutes for traditional services. This impacts Telstra's media and fixed-line revenues. In 2024, the Australian streaming market is estimated to be worth over $3 billion. Telstra can integrate OTT services into bundles and offer attractive data packages.
Free Wi-Fi
Free Wi-Fi poses a threat to Telstra by offering a substitute for mobile data. This substitution can lead to a decrease in Telstra's mobile data revenue, as users opt for free Wi-Fi in public spaces. To counter this, Telstra can offer superior Wi-Fi services. Integrating Wi-Fi into mobile plans provides seamless connectivity and additional value for customers. In 2024, the average cost of mobile data in Australia was around $10 per GB, making free Wi-Fi an attractive alternative.
- Availability of free Wi-Fi in public spaces reduces Telstra's mobile data revenue.
- Telstra can leverage its network to offer superior Wi-Fi services.
- Integration of Wi-Fi into mobile plans enhances customer value.
- The average cost of mobile data in Australia was around $10 per GB in 2024.
Emerging Technologies
Emerging technologies pose a threat to Telstra. Satellite internet and LEO satellite capabilities could become substitutes. Telstra invests in LEO to connect remote areas. The company aims to mitigate threats and expand its market reach.
- Telstra's capital expenditure for FY24 was $3.9 billion.
- In FY24, Telstra added 472,000 new services.
- Telstra's market capitalization as of May 2024 was approximately $48 billion.
Substitutes significantly threaten Telstra's revenues. The rise of VoIP and messaging apps like WhatsApp, which had over 2.5 billion users in 2024, directly impacts voice service demand. Fixed wireless, growing with approximately 1.8 million subscribers in Australia in 2024, offers a broadband alternative. Streaming, a $3 billion market in Australia in 2024, and free Wi-Fi further intensify this pressure.
| Substitute | Impact | 2024 Data |
|---|---|---|
| VoIP & Messaging Apps | Voice service decline | WhatsApp users: 2.5B+ |
| Fixed Wireless | Broadband competition | 1.8M subscribers in Australia |
| Streaming Services | Fixed-line & media revenue drop | $3B Australian market |
Entrants Threaten
High capital expenditure is a major hurdle in the telecommunications sector. New entrants face huge costs to build infrastructure. Telstra's existing network, valued at billions, gives it a strong advantage. In 2024, infrastructure spending in the sector remained high, at roughly $6 billion.
Stringent regulatory hurdles significantly deter new entrants. The Australian Communications and Media Authority (ACMA) enforces rigorous standards, increasing market entry costs. Compliance with consumer protection laws adds complexity and time. New players face substantial challenges navigating these regulations. In 2024, ACMA imposed $1.5 million in penalties for non-compliance.
Telstra's strong brand recognition, built over decades, presents a significant barrier to new entrants. The company's brand is synonymous with reliability. Telstra's customer-centric approach has fostered loyalty; its mobile subscriber base reached 24.1 million in FY23. New competitors face a tough challenge.
Economies of Scale
Telstra, as the dominant player in Australia's telecom market, benefits significantly from economies of scale, presenting a formidable barrier to new entrants. Its vast network infrastructure and customer base allow for cost efficiencies that smaller competitors struggle to match. This advantage is crucial in a capital-intensive industry where price competition is fierce. For example, Telstra's revenue in the financial year 2024 was $21.7 billion.
- Telstra's market capitalization in 2024 was approximately $48 billion, reflecting its strong market position.
- The company's investments in 5G infrastructure enhance its competitive edge.
- New entrants face high capital expenditure requirements.
- Telstra's existing customer loyalty further supports its scale.
Technological Expertise
The telecommunications sector demands substantial technological expertise, posing a significant hurdle for new competitors. Telstra continuously invests in innovation, allocating significant resources to research and development. This dedication allows Telstra to introduce new products and services, meeting evolving customer demands effectively. Telstra's strategic focus strengthens its market position against potential entrants.
- Telstra's capital expenditure for FY23 was $3.9 billion, demonstrating its investment in technology.
- Telstra's innovation strategy focuses on 5G and network advancements.
- The company's focus on innovation has helped it launch new products and services that meet the evolving needs of customers.
- Telstra's investments in technology enhance customer experience.
The threat of new entrants to Telstra is moderate due to high barriers. Substantial capital expenditure, regulatory hurdles, and Telstra's brand strength limit new competition. However, ongoing technological advancements create opportunities.
| Barrier | Impact | 2024 Data |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Expenditure | High Costs | Sector infrastructure spending: $6B |
| Regulations | Compliance Costs | ACMA penalties: $1.5M |
| Brand Recognition | Customer Loyalty | Telstra revenue: $21.7B |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
This Porter's Five Forces assessment draws data from Telstra's financial reports, competitor analyses, and industry-specific research.