23andMe Bundle
How Did 23andMe Revolutionize Personal Genomics?
From its inception in 2006, 23andMe, a pioneering company in direct-to-consumer genetic testing, has fundamentally reshaped how we understand our DNA. Initially offering saliva-based DNA testing, the company quickly gained recognition, even earning a 'Invention of the Year' title. Today, with millions genotyped, 23andMe's impact on both healthcare and the biotechnology industry is undeniable.
The 23andMe SWOT Analysis provides a comprehensive look at the company's strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Exploring the 23andMe history reveals a fascinating journey, from its early days with its 23andMe founder to navigating challenges like FDA approval and privacy concerns. Understanding the evolution of 23andMe company is crucial for anyone interested in the future of genetic testing and its implications for individuals and the healthcare industry.
What is the 23andMe Founding Story?
The story of 23andMe, a pioneer in the direct-to-consumer genetic testing space, began in April 2006. Founded in Mountain View, California, the company emerged with a vision to make genetic information accessible to everyone. This would empower individuals to understand their health and ancestry.
The founders, Anne Wojcicki, Linda Avey, and Paul Cusenza, brought diverse expertise to the table. Wojcicki, with a background in healthcare investment, saw an opportunity to shift the focus of healthcare towards prevention. Avey and Cusenza, coming from a DNA micro-array company, provided technical knowledge. Their combined efforts laid the foundation for 23andMe's innovative approach.
The name '23andMe' itself reflects the company's core mission, representing the 23 pairs of chromosomes in human cells. This symbolizes the personal and intimate nature of the genetic information they provide. The company's initial business model revolved around offering direct-to-consumer genetic testing services, starting with a saliva-based DNA test.
23andMe was founded in April 2006 by Anne Wojcicki, Linda Avey, and Paul Cusenza in Mountain View, California.
- The initial product, a saliva-based DNA test, launched in November 2007, priced at $999.
- Early funding included venture capital, with Google investing $3.9 million in 2007.
- Paul Cusenza left the company in 2007, followed by Linda Avey in 2009.
- The company aimed to revolutionize healthcare through accessible genetic information.
The launch of 23andMe's first product in November 2007 marked a significant milestone. The at-home DNA test, priced at $999, offered customers insights into their genetic makeup. Initial funding came from various sources, including a $3.9 million investment from Google in 2007. This early support helped fuel the company's growth and expansion.
As the company evolved, it faced various challenges and changes. Paul Cusenza left the company in 2007, followed by Linda Avey in 2009. Despite these transitions, 23andMe continued to advance its mission. The company's journey is a testament to its pioneering spirit and commitment to providing valuable genetic information to its customers. To understand more about the company's financial aspects, you can explore the Revenue Streams & Business Model of 23andMe.
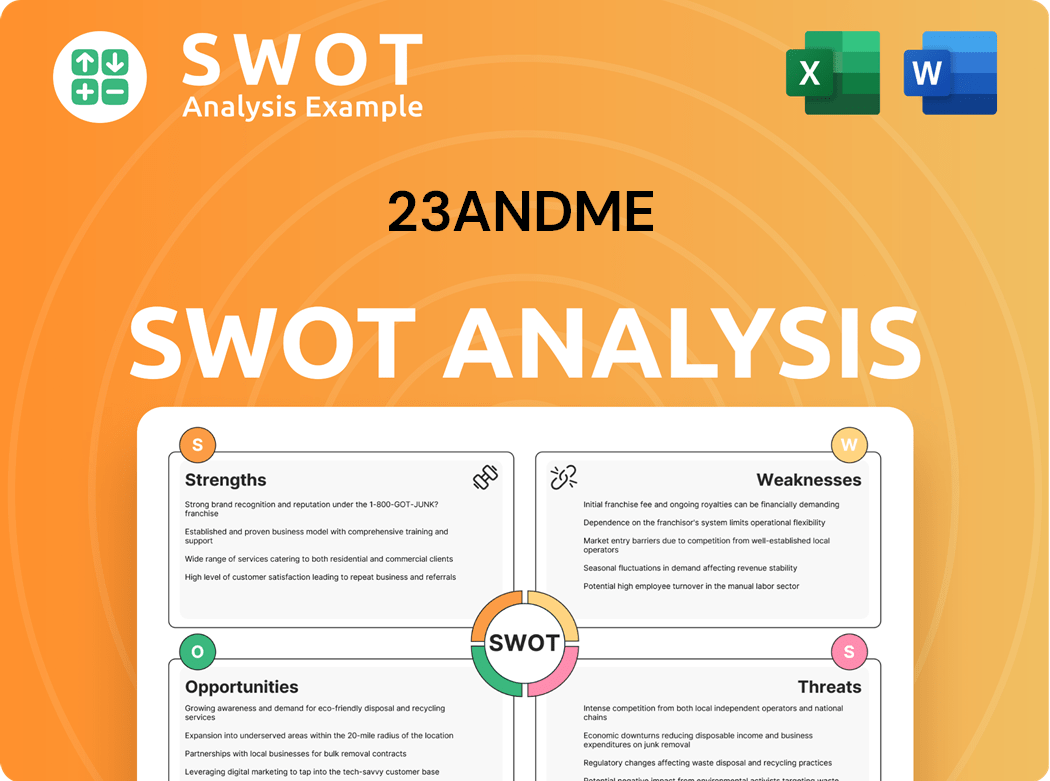
23andMe SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
What Drove the Early Growth of 23andMe?
Following its launch, the 23andMe company quickly expanded its reach and refined its product offerings. The company's early growth and expansion were marked by strategic moves to increase accessibility and build a substantial customer base. This period saw significant developments in pricing, geographic reach, and funding, laying the groundwork for its future success.
In January 2008, 23andMe expanded its services to Canada and 49 European countries, broadening its market reach. This expansion was a key step in making its DNA testing services available to a wider international audience. The company's ability to navigate international regulations and consumer preferences was crucial for this early growth.
23andMe adjusted its pricing strategy to increase accessibility. In September 2008, the cost of the test was lowered to $399. Later, they offered options as low as $99. These price reductions played a significant role in attracting a larger customer base and making genetic testing more affordable for many.
The company secured several funding rounds to support its growth. After the initial Series A funding in 2007, 23andMe received $50 million in Series B funding in 2009. In 2012, Google invested $25 million, further fueling its expansion and research initiatives. These investments were crucial for scaling operations and expanding its capabilities.
By June 2011, 23andMe had tested approximately 75,000 individuals. By August 2020, the company had over 12 million customers. 23andMe focused on building a large genetic database from customer data, with their consent, to use for research. This strategy is further explored in the Marketing Strategy of 23andMe.
23andMe PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable

What are the key Milestones in 23andMe history?
The 23andMe company has experienced a dynamic journey, marked by significant achievements and considerable obstacles. From its inception, the company has navigated the evolving landscape of genetic testing, leaving a notable impact on the industry. The 23andMe history is full of ups and downs.
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 2007 | 23andMe launched its direct-to-consumer DNA testing service, offering ancestry and health information. |
| 2008 | Time magazine named 23andMe's service 'Invention of the Year', recognizing its innovative approach. |
| 2013 | The FDA ordered 23andMe to halt the marketing of its health-related genetic tests due to regulatory concerns. |
| 2015 | 23andMe received FDA clearance to market certain health risk reports, marking a return to health testing. |
| 2018 | A strategic partnership with GlaxoSmithKline (GSK) was established, involving a $300 million investment for drug discovery. |
| 2020 | 23andMe acquired Lemonaid Health for $400 million, expanding into telehealth services. |
23andMe pioneered the direct-to-consumer DNA testing market, making genetic information accessible to the general public. They were also early adopters of using customer data for scientific research, contributing to advancements in the field of genetics.
23andMe was among the first to offer autosomal DNA testing directly to consumers, simplifying the process of accessing genetic information. This innovation removed the need for a doctor's visit, making genetic testing more convenient and accessible.
The company has published numerous scientific papers using de-identified customer data, contributing valuable insights to genetic research. This approach has helped advance the understanding of various diseases and traits.
23andMe has developed health reports that provide information on genetic predispositions to certain diseases and conditions. These reports help individuals understand their health risks and make informed decisions.
23andMe's ancestry reports offer detailed information about an individual's ethnic origins and family history. These reports provide insights into a person's ancestral background.
The acquisition of Lemonaid Health allowed 23andMe to integrate telehealth services into its offerings. This integration expanded the company's healthcare services, providing more comprehensive support to its customers.
Strategic partnerships, such as the one with GSK, have enabled 23andMe to leverage its genetic data for drug discovery. These collaborations accelerate the development of new treatments.
23andMe has faced significant challenges, including regulatory hurdles and data privacy concerns. The company's valuation has fluctuated, reflecting the competitive pressures and financial difficulties it has encountered. For more information about the company's ownership and stakeholders, you can read the article Owners & Shareholders of 23andMe.
The FDA's initial restrictions on health-related genetic tests significantly impacted 23andMe's business. Navigating these regulatory challenges has been a continuous effort.
Data privacy is a major concern for 23andMe, as it handles sensitive genetic information. The company must continually address these concerns to maintain customer trust.
The market for DNA testing is competitive, with companies like AncestryDNA vying for market share. 23andMe must differentiate itself to maintain its position.
The company has faced financial difficulties, including layoffs and a decline in valuation. In fiscal year 2024, the company reported a decrease in revenue.
The stock price of 23andMe has experienced fluctuations, reflecting the market's perception of the company's performance and future prospects. This volatility impacts investor confidence.
Building and maintaining customer trust is crucial for 23andMe, particularly given the sensitivity of the data they handle. This requires robust data security measures and transparent communication.
23andMe Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout

What is the Timeline of Key Events for 23andMe?
The 23andMe company, a pioneer in direct-to-consumer genetic testing, has experienced a dynamic journey marked by innovation, regulatory hurdles, and strategic shifts. From its inception in April 2006, 23andMe quickly gained recognition, launching its first at-home DNA test in November 2007 and being named 'Invention of the Year' by Time in 2008. However, the company faced challenges, including an FDA order in 2013 to halt health-related genetic tests, later reintroducing them with authorization. Strategic partnerships, such as the one with GlaxoSmithKline (GSK) in 2018, aimed to leverage its extensive genetic database for drug discovery. Despite these advancements, 23andMe encountered financial difficulties, leading to a business restructuring in November 2024, including significant layoffs, and ultimately, a Chapter 11 filing in March 2025. The company's acquisition by Regeneron in May 2025 represents a pivotal moment, potentially reshaping its future in the genetic testing landscape. Read more about the Target Market of 23andMe.
| Year | Key Event |
|---|---|
| April 2006 | 23andMe is founded. |
| November 2007 | Launches its first direct-to-consumer genetic test in the US. |
| 2008 | Service named 'Invention of the Year' by Time. |
| 2013 | FDA orders 23andMe to stop marketing health-related genetic tests. |
| October 2015 | Reintroduces some health reports with FDA authorization. |
| 2017 | Receives FDA clearance for specific genetic health risk reports. |
| 2018 | Forms a major partnership with GlaxoSmithKline (GSK). |
| July 2020 | Announces first clinical trial with GSK partnership. |
| December 2020 | Raises $82.5 million in Series F funding. |
| February 2021 | Announces merger with SPAC VG Acquisition Corp. |
| June 2021 | Becomes a publicly traded company (NASDAQ: ME). |
| October 2021 | Acquires Lemonaid Health. |
| 2023 | Notifies customers of a data breach affecting 6.9 million users. |
| November 2024 | Announces business restructuring, including layoffs of approximately 40% of staff and discontinuation of therapeutics development. |
| March 2025 | Initiates voluntary Chapter 11 process and explores strategic alternatives, including a sale. |
| May 2025 | Announces acquisition by Regeneron in a court-supervised sale. |
The acquisition by Regeneron in May 2025 marks a significant shift for 23andMe. This deal provides a potential financial lifeline and strategic direction, allowing the company to leverage its genetic database for research and development. The acquisition is expected to be finalized in the near future, pending regulatory approvals and court proceedings.
The future of 23andMe will likely center on its core direct-to-consumer testing services and strategic partnerships. Despite discontinuing in-house therapeutics development, the company's database remains a valuable asset for collaborations. This includes potential partnerships with pharmaceutical companies and research institutions for drug discovery and development.
Data privacy and security remain paramount for 23andMe, especially after the 2023 data breach. Potential buyers, like Regeneron, must adhere to the company's privacy policies and applicable laws regarding customer data. This focus is essential for maintaining customer trust and complying with evolving regulatory standards in the genetic testing industry.
The 23andMe company operates in a competitive market alongside other DNA testing and genetic testing providers. The company must navigate this landscape by differentiating its services, ensuring data security, and adapting to the changing regulatory environment. The company's success will depend on its ability to innovate and respond to market demands.
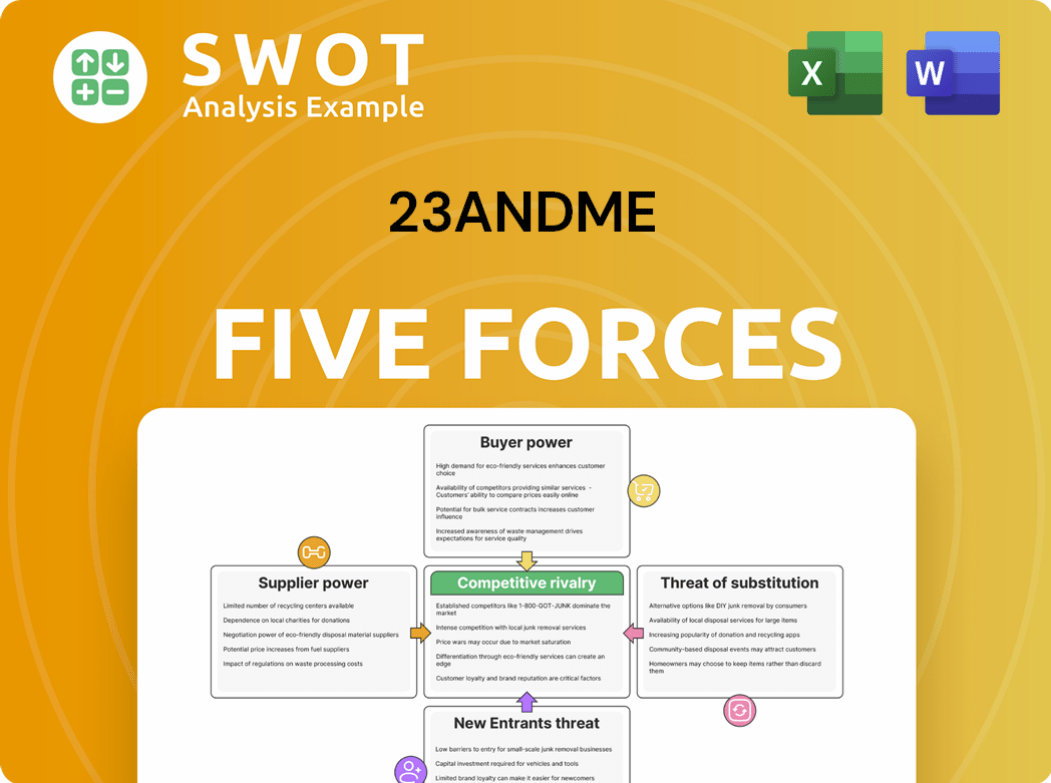
23andMe Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What is Competitive Landscape of 23andMe Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of 23andMe Company?
- How Does 23andMe Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of 23andMe Company?
- What is Brief History of 23andMe Company?
- Who Owns 23andMe Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of 23andMe Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.