23andMe Bundle
Who Really Owns 23andMe?
Unraveling the 23andMe ownership structure is key to understanding its future. This innovative company, offering direct-to-consumer genetic testing, has evolved significantly since its founding in 2006. From its early days as a private entity to its current status as a public company, the ownership landscape of 23andMe has undergone a fascinating transformation.
Understanding the 23andMe company ownership is crucial, especially given its handling of sensitive genetic data and its dual focus on consumer services and pharmaceutical research. The company's journey, from its initial funding rounds to its 23andMe SWOT Analysis and public listing, has shaped its current ownership profile. This exploration will delve into the key players, including 23andMe investors and the 23andMe founder, to provide a comprehensive view of who controls this influential genomics company. We'll also investigate the 23andMe stock and its major shareholders.
Who Founded 23andMe?
The company, 23andMe, was co-founded in 2006 by Linda Avey, Paul Cusenza, and Anne Wojcicki. Anne Wojcicki has been a key figure, serving as CEO from the beginning and significantly shaping the company's direction. Early on, Wojcicki's connections, including her former marriage to Google co-founder Sergey Brin, helped attract initial investments and set the company's course.
Sergey Brin was among the early investors in 23andMe. The company's early funding rounds drew significant attention from venture capital firms, reflecting the growing interest in personalized genomics. Google was an early strategic investor. Other notable early backers included New Enterprise Associates (NEA) and MPM Capital, which provided crucial capital to fuel research and development and expand direct-to-consumer services.
These early investments were crucial for establishing 23andMe's market position and funding its scientific endeavors. The initial ownership structure likely involved preferred stock allocations to these venture capital firms in exchange for their substantial capital injections, a common practice in early-stage biotechnology startups. Agreements such as vesting schedules for founder shares would have been in place to ensure long-term commitment and align incentives with the company's growth.
23andMe was co-founded by Anne Wojcicki, Linda Avey, and Paul Cusenza. Anne Wojcicki has been a key figure, serving as CEO from the beginning. The founders' vision was to make genetic information accessible and understandable to everyone.
Early investors included Sergey Brin, Google, New Enterprise Associates (NEA), and MPM Capital. These investments were crucial for the company's early growth and expansion. The early funding rounds reflected a strong interest in personalized genomics.
The initial ownership structure likely involved preferred stock for venture capital firms. Founder shares were subject to vesting schedules to ensure long-term commitment. This structure is typical for early-stage biotech companies.
Anne Wojcicki's leadership was instrumental in attracting early investment. Her strategic connections, including her relationship with Sergey Brin, played a key role. She shaped the company's vision and direction from its inception.
The early funding rounds were critical for research and development efforts. These rounds helped 23andMe expand its direct-to-consumer services. The investments enabled 23andMe to establish its market position.
Venture capital firms played a significant role in the early success of 23andMe. These firms provided crucial capital for growth and expansion. Their investments reflect the growing interest in the genomics field.
Understanding the 23andMe ownership structure involves looking at its founders and early investors. The company's journey began with Anne Wojcicki, Linda Avey, and Paul Cusenza. Early investments from Google and venture capital firms like NEA and MPM Capital were vital. The initial ownership structure included preferred stock for investors and vesting schedules for founders. For more insights into the company's market, consider reading about the Target Market of 23andMe.
- The founders' vision shaped the company's direction.
- Early investors provided crucial capital for growth.
- The ownership structure evolved with subsequent funding rounds.
- Anne Wojcicki's leadership was key to attracting investment.
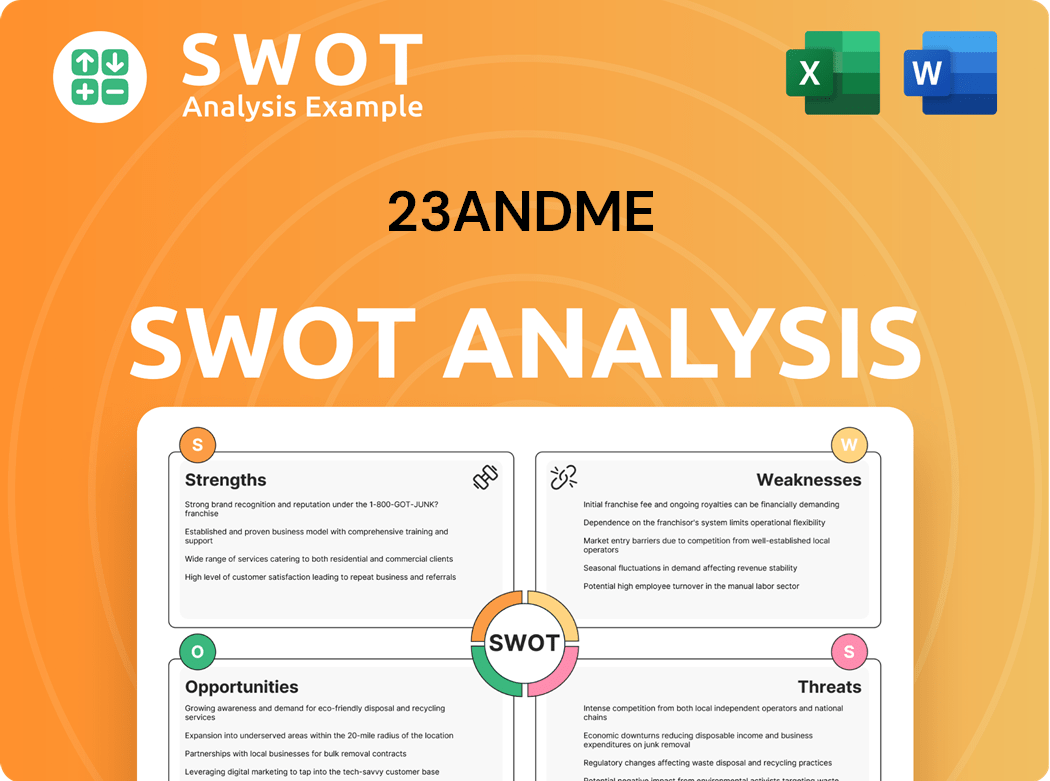
23andMe SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
How Has 23andMe’s Ownership Changed Over Time?
The 23andMe company's ownership structure has evolved significantly, especially with its move to become a publicly traded entity. A major shift occurred on June 17, 2021, when 23andMe completed a business combination with VG Acquisition Corp. (VGAC), a Special Purpose Acquisition Company (SPAC) backed by Virgin Group. This strategic move led to the company's listing on the Nasdaq under the ticker symbol 'ME', valuing the company at approximately $3.5 billion at the time of its initial public offering (IPO).
This transition to a public company has brought about changes in the shareholder base and increased the company's access to capital. The IPO marked a pivotal moment in 23andMe's history, impacting its strategic direction and operational dynamics. The shift also introduced greater public scrutiny and enhanced governance requirements, influencing the company's approach to research and development, particularly within its therapeutics division.
| Shareholder | Stake as of March 30, 2024 | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| The Vanguard Group, Inc. | 10.45% | A major institutional investor, common in many public companies. |
| Anne Wojcicki | 10.4% | Co-founder and CEO, maintaining significant individual ownership. |
| BlackRock Inc. | 6.10% | Another key institutional investor, reflecting broad market holdings. |
| Richard Branson/Virgin Group | Notable stake | Retained ownership from the SPAC merger. |
The ownership structure of 23andMe has seen a transformation, particularly with its shift to being a public company. As of early 2024, institutional investors like Vanguard and BlackRock hold significant portions of the company's shares, reflecting the typical landscape of publicly traded entities. The company's founder and CEO, Anne Wojcicki, remains a key individual shareholder, demonstrating her ongoing commitment to the company's vision. Richard Branson, through Virgin Group, also maintains a notable stake following the SPAC merger. These changes have influenced the company's strategy, facilitating greater investment in research and development, especially in its therapeutics arm, and increasing the demands of public oversight and governance.
The 23andMe ownership structure has changed considerably, especially after it became a public company. The Vanguard Group, BlackRock, and Anne Wojcicki are among the major shareholders. The company's journey from a private entity to a publicly traded one has reshaped its financial strategies and operational frameworks.
- The company went public through a SPAC merger.
- Institutional investors now hold a significant portion of shares.
- Anne Wojcicki, the 23andMe founder, remains a key shareholder.
- The company's access to capital has increased.
23andMe PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable

Who Sits on 23andMe’s Board?
The current 23andMe board of directors includes a mix of representatives from major shareholders, founders, and independent members. As of early 2024, the board includes Anne Wojcicki, the co-founder and CEO. Other board members bring expertise in areas like finance, healthcare, and technology. For example, Richard Branson, founder of the Virgin Group, serves on the board, representing the interests of VG Acquisition Corp., which merged with 23andMe. The board's composition is designed to provide diverse perspectives and ensure robust governance, which is crucial for navigating the company's dual focus on consumer genetics and pharmaceutical development.
The board's structure reflects the company's evolution from a private startup to a publicly traded entity. The presence of independent directors helps to balance the interests of various stakeholders, including individual investors and institutional shareholders. This balance is important for making strategic decisions and ensuring accountability. The board's oversight is particularly important given the sensitive nature of the data handled by 23andMe and the potential for significant growth in the pharmaceutical sector.
| Board Member | Title | Affiliation |
|---|---|---|
| Anne Wojcicki | Co-founder and CEO | 23andMe |
| Richard Branson | Director | VG Acquisition Corp. |
| Other Directors | Various | Seasoned Executives and Independent Members |
The voting structure of 23andMe is generally based on a one-share, one-vote principle for its common stock. However, specific details regarding any dual-class share structures or special voting rights for founders or early investors would be detailed in the company's SEC filings, such as the S-1 registration statement or subsequent 10-K and 10-Q reports. Major institutional investors like Vanguard and BlackRock, along with the continued significant stake held by Anne Wojcicki and Richard Branson, collectively exert substantial influence over strategic decisions and board appointments. Understanding the Growth Strategy of 23andMe is also helpful in understanding the company's direction.
The 23andMe company's ownership structure involves a board of directors with diverse expertise and major shareholders. The voting rights are typically one-share, one-vote, but key stakeholders have significant influence.
- The board includes the CEO and representatives from major investors.
- Institutional investors like Vanguard and BlackRock hold considerable influence.
- Richard Branson, through VG Acquisition Corp., is a significant shareholder.
- The company's governance structure is designed to balance various interests.
23andMe Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout

What Recent Changes Have Shaped 23andMe’s Ownership Landscape?
In the past few years, significant shifts have occurred in the 23andMe ownership landscape. The most impactful event was its public listing in June 2021 through a SPAC merger. This transition fundamentally changed the shareholder base, expanding it from a concentrated group of private 23andMe investors to a more diverse pool of public shareholders. This move provided substantial capital but also subjected the 23andMe company to increased market scrutiny and regulatory requirements.
Recent trends in 23andMe's ownership reflect broader industry patterns, including increased institutional ownership. Anne Wojcicki, the 23andMe founder, remains a significant shareholder, but the public listing has led to a dispersion of ownership. In April 2024, 23andMe announced a reverse stock split to comply with Nasdaq's minimum bid price rule, which consolidated shares. The company has also been exploring strategic alternatives for its therapeutics business, potentially leading to further ownership changes or partnerships. As of late May 2024, the company's market capitalization was approximately $150 million.
| Ownership Aspect | Details | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Public Listing | June 2021 via SPAC merger | Expanded shareholder base, increased market scrutiny |
| Institutional Ownership | Increasing | Reflects industry trends |
| Reverse Stock Split | April 8, 2024 | Complies with Nasdaq rules |
Understanding the evolution of 23andMe ownership is crucial for investors and stakeholders. The shift from private to public ownership has brought about changes in the company's financial structure and strategic direction. For more insights into the company's marketing approach, you can explore the Marketing Strategy of 23andMe.
The SPAC merger in June 2021 broadened the shareholder base. This transition provided capital but also increased market scrutiny. The change affected the company's financial and strategic decisions.
Anne Wojcicki remains a significant shareholder. Institutional ownership is on the rise. The public listing has naturally led to a dispersion of ownership.
The reverse stock split aimed to meet Nasdaq's requirements. The company is exploring options for its therapeutics business. These moves could lead to ownership changes.
As of late May 2024, the market capitalization was around $150 million. This figure reflects the company's current valuation. It is an important metric for investors.
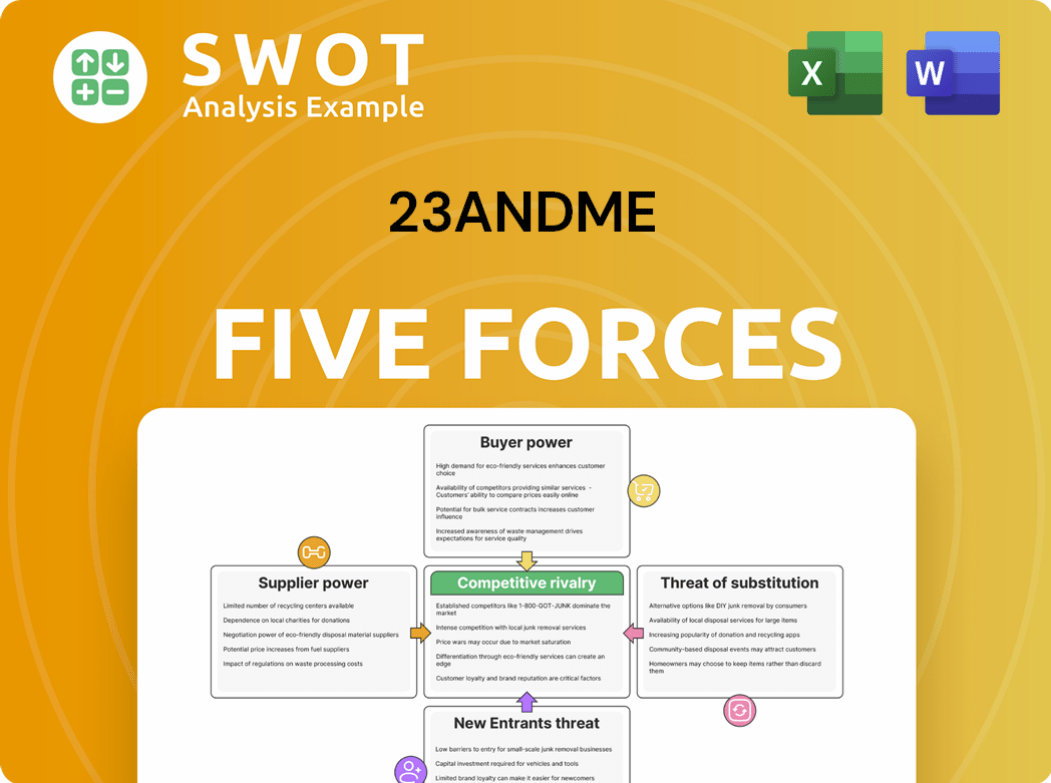
23andMe Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of 23andMe Company?
- What is Competitive Landscape of 23andMe Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of 23andMe Company?
- How Does 23andMe Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of 23andMe Company?
- What is Brief History of 23andMe Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of 23andMe Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.