Equity Bank Bundle
How Did Equity Bank Rise to Become an African Banking Powerhouse?
From its humble beginnings as a mortgage financier, Equity Bank has become a leading financial services group. This Equity Bank SWOT Analysis reveals the strategic maneuvers that propelled this Kenyan bank to the forefront of African banking. Discover the compelling story of resilience, strategic pivots, and a commitment to financial inclusion.
Equity Bank's journey, starting in 1984 as Equity Building Society, is a testament to its adaptability. Initially serving low-income Kenyans, the bank faced challenges but transformed through visionary leadership. Today, Equity Group Holdings serves millions across East and Central Africa, highlighting its profound impact on financial inclusion and its place as a significant African financial institution.
What is the Equity Bank Founding Story?
The story of Equity Bank, a prominent player in the African financial landscape, began in October 1984. It was initially established as Equity Building Society (EBS). This Kenyan bank was founded with a clear vision: to provide mortgage financing to low-income Kenyans, aiming to make homeownership accessible to a wider population.
The founders of EBS sought to address a gap in the market, capitalizing on a more relaxed regulatory environment in the early 1980s. This allowed Kenyans to establish licensed financial institutions. The initial goal was to serve an underserved market segment, focusing on financial inclusion. The founders pooled their resources to get the institution off the ground.
Despite its noble intentions, EBS faced significant challenges. Poor management and issues with its mortgage business model led to the Central Bank of Kenya declaring it technically insolvent in 1993. This early struggle highlights the difficulties faced by the institution in its formative years.
Equity Bank's early days were marked by a focus on providing financial services to those often excluded from traditional banking. The original mission was to offer mortgage financing to low-income individuals.
- Founded in October 1984 as Equity Building Society (EBS).
- The initial focus was on mortgage financing for low-income Kenyans.
- EBS faced challenges and was declared technically insolvent in 1993.
- The founding of Equity Bank was influenced by a relaxed regulatory environment in the early 1980s.
The Marketing Strategy of Equity Bank has played a crucial role in its growth. Equity Bank's journey from a building society to a major financial institution is a testament to its resilience and adaptability.
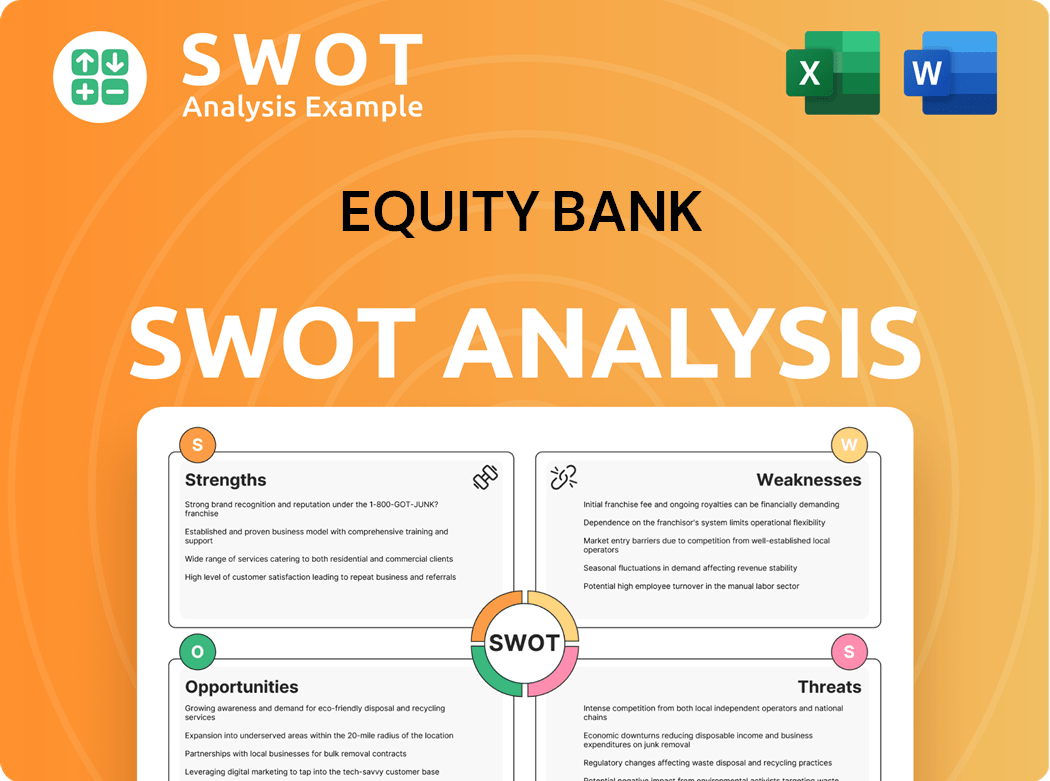
Equity Bank SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
What Drove the Early Growth of Equity Bank?
Following 1994, the Equity Bank history experienced a significant transformation, shifting from mortgages to microfinance, which fueled rapid growth. This strategic pivot led to its evolution from a building society to a fully-fledged commercial bank, Equity Bank Limited (EBL), in 2004. The transition, guided by James Mwangi, concluded on January 1, 2005, marking a crucial milestone for the Kenyan bank.
The bank aggressively expanded its branch network, increasing from 13 in 2002 to 42 by 2006, with plans for 70 by 2008. This rapid expansion was notable, especially when compared to larger institutions like Barclays Bank of Kenya, which had 58 branches in 2006. The growth strategy included diversifying branch types to cater to various customer segments.
In the U.S., Equity Bancshares, Inc., founded in November 2002, began operations in 2003 with the acquisition of the National Bank of Andover. By June 2007, Equity Bank (US) had assets of $226.9 million, a substantial increase from $52.8 million in December 2004. Mergers and acquisitions were key to its growth, with the merger with Signature Bancshares in 2007 and the acquisition of Ellis State Bank in 2008.
To serve different customer segments, Equity Bank diversified its branch formats. This included 'regular' branches for core clients, 'mobile' branches for rural customers, and 'prestige' branches for emerging affluent clients. This strategic approach enhanced the bank's ability to reach a broader customer base and support its mission of financial inclusion.
The early expansion phase of Equity Bank was marked by significant financial milestones. The growth in assets and customer base reflected the success of its microfinance model and strategic branch network expansion. For more details on the ownership and structure of the company, you can read about the Owners & Shareholders of Equity Bank.
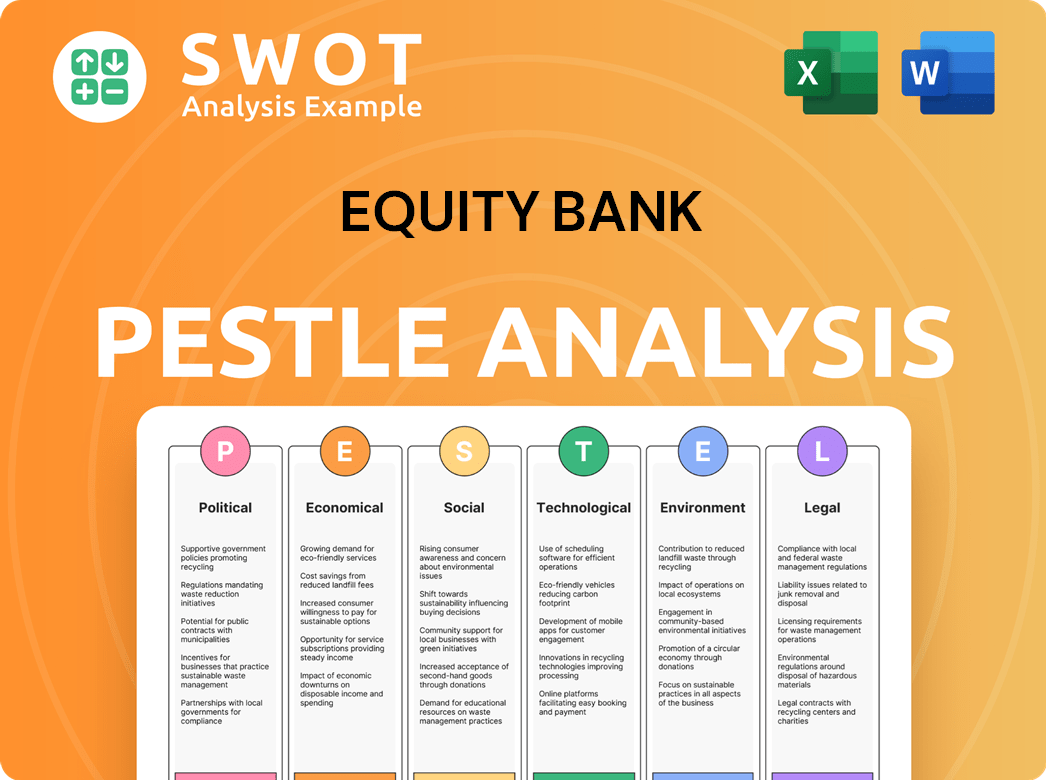
Equity Bank PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
What are the key Milestones in Equity Bank history?
The Equity Bank history is marked by remarkable growth and strategic pivots. From overcoming technical insolvency in 1993 to becoming a leading African financial institution, the bank's journey highlights its resilience and adaptability. Key milestones include the transition from a building society to a commercial bank and significant expansions across Africa and beyond.
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 1993 | The bank restructured its management and shifted from mortgage financing to microfinance, marking a turning point. |
| 2000 | Launched 'Bank 2000', a rapid computerization process, improving efficiency in data collection and service delivery. |
| 2004 | Equity Building Society converted into Equity Bank Limited, a fully-fledged commercial bank. |
| 2006 | Listed on the Nairobi Securities Exchange, becoming the largest bank by market capitalization. |
| 2007 | Helios invested USD 185 million, attracting strategic investors. |
| 2015 | Equity Group commenced operations in the Democratic Republic of Congo through the acquisition of Pro-credit Bank. |
| 2015 | Equity Bank (US) held its Initial Public Offering. |
| 2023 | Common stock began trading on the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) under the ticker symbol 'EQBK' in May. |
Innovation has been central to Equity Bank's strategy, especially in enhancing financial inclusion and customer service. The bank has consistently adopted technological advancements to improve access, convenience, and affordability of its services. This has included mobile banking solutions and digital payment platforms.
The 'Bank 2000' project, launched in June 2000, involved a rapid computerization process within four months. This significantly improved data collection and service delivery, laying the groundwork for future technological advancements.
Equitel, a mobile virtual network operator (MVNO) launched by Equity Group Holdings, provided mobile banking services. It allowed customers to access banking services through their mobile phones, expanding financial inclusion.
Equity Bank integrated innovative payment solutions like Bebapay and PayPal. These integrations enhanced the bank's digital payment capabilities, offering customers more convenient and versatile transaction options.
Despite its successes, Equity Bank has faced several challenges. Competitive pressures in the dynamic banking sector and difficulties replicating its business model in some African countries have tested its resilience. The bank has also had to navigate regulatory changes and economic fluctuations.
The Kenyan bank has faced increasing competition from both local and international financial institutions. This has required continuous innovation and strategic adjustments to maintain market share and profitability.
Replicating the successful microfinance model in other African countries has presented challenges. Variations in economic conditions, regulatory frameworks, and customer behavior have impacted returns on equity in certain markets.
The banking sector is subject to evolving regulations, which require Equity Bank to adapt its operations and strategies. Compliance with new regulatory requirements can be costly and time-consuming.
Economic downturns and fluctuations in currency exchange rates can impact the bank's financial performance. These external factors require careful risk management and strategic planning.
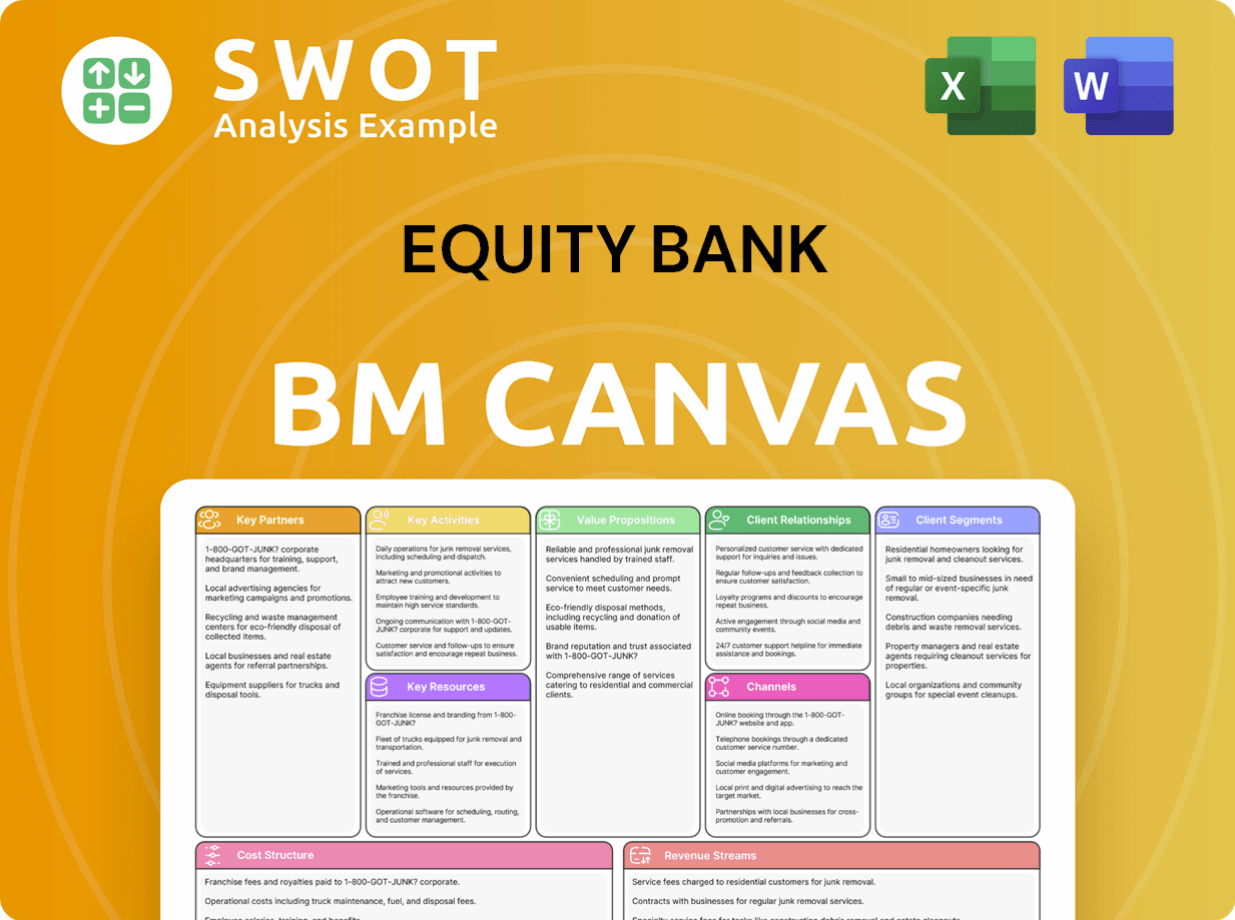
Equity Bank Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What is the Timeline of Key Events for Equity Bank?
The Equity Bank history is marked by significant transformations and strategic expansions. Founded in October 1984 as Equity Building Society (EBS) in Kenya, it initially targeted low-income populations with mortgage financing. Facing challenges, including technical insolvency in 1993, the institution underwent a turnaround led by James Mwangi, who joined in 1994. The bank then embraced technological advancements, launching 'Bank 2000' in June 2000. In 2004, EBS transitioned into a commercial bank, Equity Bank Limited (EBL), and listed on the Nairobi Securities Exchange in 2006. Strategic investments and acquisitions further fueled its growth, including Helios's investment in 2007 and the establishment of the Equity Group Foundation in 2010. Equity Group Holdings Limited was formed in 2014, and the company expanded internationally with the acquisition of Pro-credit Bank in the Democratic Republic of Congo in 2015. In May 2023, Equity Bank (US) moved its common stock to the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE).
| Year | Key Event |
|---|---|
| October 1984 | Founded as Equity Building Society (EBS) in Kenya, focusing on mortgage financing. |
| 2004 | EBS converted to a fully-fledged commercial bank, Equity Bank Limited (EBL). |
| 2006 | Listed on the Nairobi Securities Exchange, becoming the largest bank by market capitalization. |
Looking ahead, Equity Bank (US) plans for continued strategic growth, both organically and through acquisitions. Richard Sems, the current CEO, emphasized the pursuit of M&A opportunities. The bank aims to enhance customer financial well-being by introducing new products and services, including a robo-advisor launched in 2024.
Equity Group Holdings (Africa) is focused on its Africa Recovery and Resilience Plan (ARRP), a private sector-led development plan. This plan emphasizes investments in technology, human resources, and platforms, with a focus on regional consolidation and digital transformation, as 86% of transactions are now processed digitally. The group's regional subsidiaries are significant contributors, accounting for 49% of total assets and 54% of profit before tax in 2024.
Equity Group aims to grow its deposit book by 7.5%-12.5% in the coming years. The bank's long-term vision remains to champion socio-economic prosperity for the people of Africa. The bank's focus on digital transformation and regional consolidation, along with its commitment to financial inclusion, positions it for continued success in the African market.
The regional subsidiaries of Equity Group Holdings are significant contributors, accounting for 49% of total assets and 54% of profit before tax in 2024. This highlights the importance of its expansion strategy. The bank's focus on digital transactions, with 86% processed digitally, demonstrates its commitment to technological advancements.
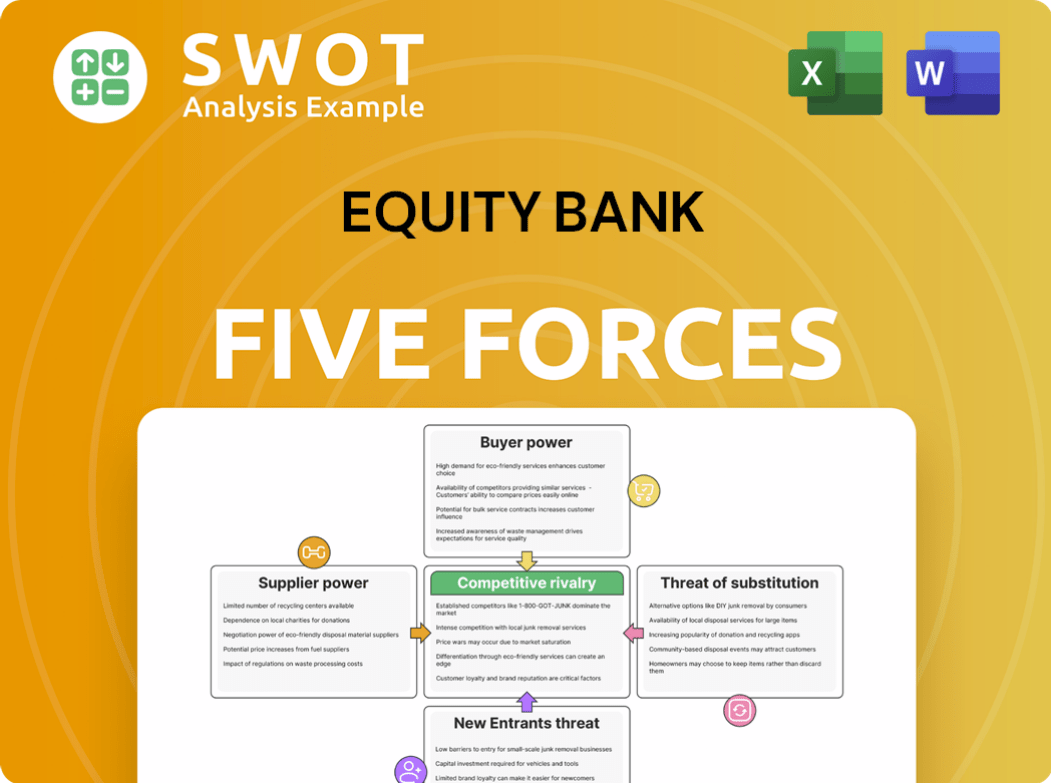
Equity Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What is Competitive Landscape of Equity Bank Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Equity Bank Company?
- How Does Equity Bank Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Equity Bank Company?
- What is Brief History of Equity Bank Company?
- Who Owns Equity Bank Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Equity Bank Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.