Fuji Electric Bundle
What's the Story Behind Fuji Electric's Global Reach?
Ever wondered how a Japanese company became a global powerhouse in energy and thermal technology? Fuji Electric's journey began in 1923, born from a strategic partnership that would reshape the industrial landscape. From its roots in Tokyo, this Fuji Electric SWOT Analysis delves into the fascinating history of a company that has consistently adapted and innovated.

This brief history of Fuji Electric reveals a company that started by introducing Siemens-style electrical technology to Japan. Over the years, Fuji Electric has played a significant role in industrial automation and power electronics. Today, it stands as a testament to innovation and sustainability, contributing to industrial and social infrastructure worldwide.
What is the Fuji Electric Founding Story?
The story of the Fuji Electric Company began in August 1923. It was born from a collaborative venture between Japan's Furukawa Electric Co., Ltd. and Germany's Siemens AG.
The company's name, 'Fuji,' cleverly combined 'Fu' from Furukawa and 'Si' (pronounced 'ji' in Japanese) from Siemens, paying homage to Japan's Mount Fuji. The establishment took place in Tokyo, Japan, where the Head Office and sales offices in Tokyo and Osaka opened in the same year.
The founders saw an opportunity to bring advanced electrical technology to Japan, which was rapidly industrializing but dependent on imports. Their initial focus was on manufacturing and supplying essential electrical machinery and equipment. This included motors, transformers, generators, and circuit breakers to support mechanization in key sectors like mining, steel, and chemicals, and to stabilize electric power supply.
Early products included transformers, with production starting in 1925 at the Kawasaki factory.
- Electric fan production began in 1927.
- Mercury-vapor rectifier production started in 1930, quickly gaining a high market share and contributing to transportation infrastructure.
- During this period, Fuji Electric introduced approximately 3,400 patents from Siemens and developed around 1,100 of its own patents.
- This demonstrated a strong commitment to technological integration and independent innovation, laying the groundwork for its future in industrial automation and power electronics.
The company's early successes were pivotal in establishing its presence in the Japanese market. For more insights into the company's strategic positioning, consider exploring the Target Market of Fuji Electric.
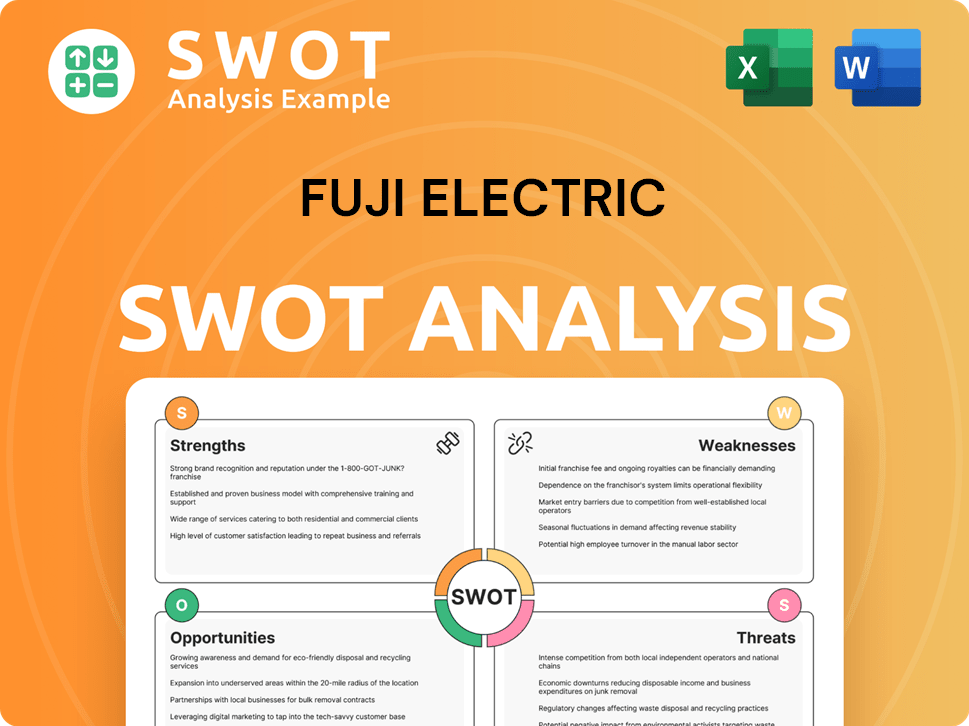
Fuji Electric SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
What Drove the Early Growth of Fuji Electric?
The early growth of the Fuji Electric Company was marked by significant expansion and diversification, solidifying its position as a key player in the Japanese industrial landscape. From its inception in 1923, the company quickly broadened its product range, venturing into new technologies and markets. This period laid the foundation for its future growth and its contributions to power electronics and industrial automation.
Following the start of electrical machinery manufacturing in 1924, the company began producing transformers in 1925. It quickly diversified, introducing electric fans in 1927 and mercury-vapor rectifiers in 1930. The rectifiers achieved a high market share in Japan, contributing to the development of transportation infrastructure. This early diversification demonstrated the company's ability to adapt and innovate.
In 1935, the telephone department was spun off, eventually becoming Fujitsu Limited. This strategic move allowed the company to focus on its core strengths. Further expansion included building its first hydraulic turbine in 1936 and watt-hour meters in 1937. By 1938, it completed Asia's first 230 kV extra-high voltage expansion circuit breaker.
The company expanded its manufacturing footprint with the opening of the Matsumoto factory in 1942, followed by the Fukiage and Toyoda factories in 1943, and the Mie factory in 1944. Post-war, in 1954, mass production of selenium rectifiers began, capturing 80-90% of the domestic market in response to the demand for televisions and radios. This period also saw the company entering the vending machine market.
A significant merger with Kawasaki Denki Seizo Co., Ltd. in 1968 added the Kobe and Suzuka factories. The company began manufacturing silicon diodes in 1959 and bipolar transistors in 1975, signaling a shift towards electronic components. The establishment of Fuji Electric Corporation of America in 1970, for sales in North and Latin America, reflects its efforts to expand its market reach. For more insights, check out the Marketing Strategy of Fuji Electric.
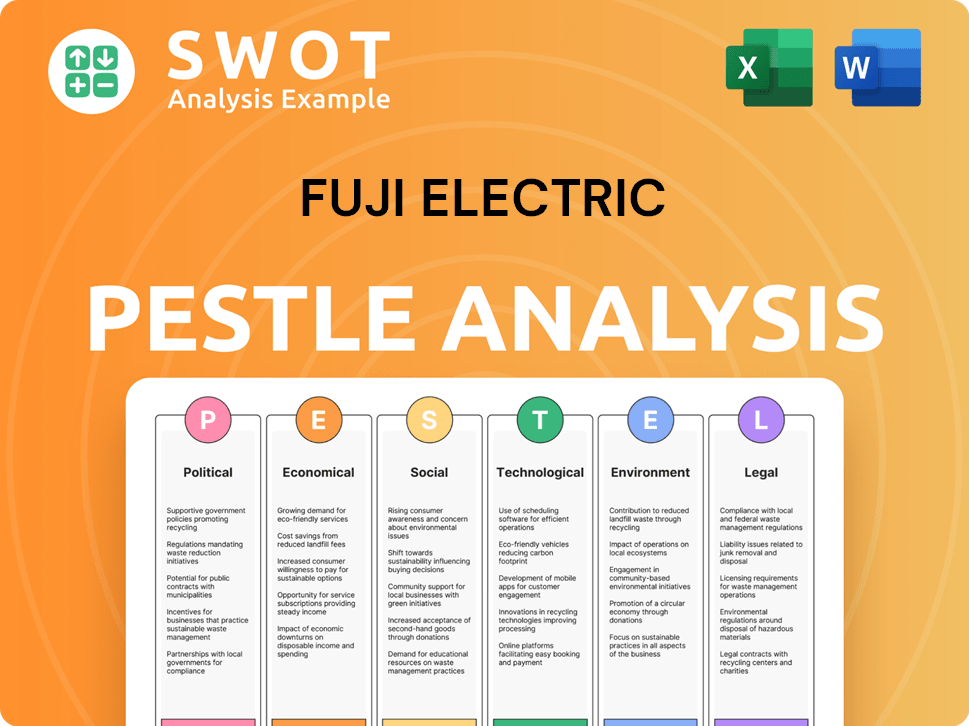
Fuji Electric PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
What are the key Milestones in Fuji Electric history?
The Fuji Electric Company has a rich Fuji Electric history marked by significant milestones. From its early ventures into integrated circuits to becoming a key player in industrial automation and power electronics, the company has consistently evolved.
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 1970s | Ventured into integrated circuits and inverters, and initiated research into solar cell technology. |
| 1984 | Name changed from 'Fuji Electric Manufacturing Co., Ltd.' to 'Fuji Electric Co., Ltd.' |
| 1985 | Launched the first generation of UPS 'M-UPS Series' utilizing MOSFETs. |
| 1987 | Introduced the first IGBT module. |
| 1988 | Began manufacturing 1st-generation IGBTs. |
| 2015 | Introduced heat pumps for steam generation. |
| 2019 | Released an on-site diagnostic system using analytics and AI. |
| 2021 | Released the UPS7500WX Series high-capacity UPS. |
Fuji Electric has consistently pushed the boundaries of technological innovation, developing groundbreaking products and solutions. These innovations have not only advanced its own capabilities but have also contributed significantly to the broader fields of energy management and industrial efficiency.
Developed Japan's first fuel cell cogeneration system powered by digested sewage sludge gas. This system highlights the company's commitment to sustainable energy solutions.
Created the world's first three-level module integrating a new RB-IGBT and an existing IGBT, achieving a world-highest efficiency of 98.5% for DC 1,000 V products. This innovation set a new standard in power electronics efficiency.
Commercialized power conditioning systems for mega solar power generation, supporting the growth of renewable energy. This move underscored the company's strategic focus on sustainable energy solutions.
Released an on-site diagnostic system using analytics and AI in 2019, showcasing its commitment to digital transformation. This system enhanced operational efficiency and predictive maintenance capabilities.
Introduced heat pumps for steam generation in 2015, contributing to energy saving through the utilization of low-temperature factory waste heat. This innovation improved energy efficiency in industrial processes.
Released the UPS7500WX Series high-capacity UPS in 2021, enhancing power backup solutions for critical infrastructure. This new series improved reliability and efficiency in power management.
Despite these achievements, Fuji Electric has faced various challenges in its journey. The company has focused on strengthening its business structure and enhancing profitability, particularly in its FA Components business.
The ED&C components sector faced a downturn due to decreased demand from machinery manufacturers and semiconductor production equipment. This impacted overall performance, requiring strategic adjustments.
The energy segment's operating profit saw a slight decline, attributed to the absence of large-scale renewable energy projects recorded in the previous period. This highlighted the cyclical nature of some project-based revenues.
Fuji Electric emphasizes improving corporate value through management focusing on profit and generating cash for investments in growth areas. This strategy aims to ensure long-term sustainability and competitiveness.
The company actively manages its intellectual property, with a focus on patent applications related to new energy sources and efficiency improvements in power electronics. This protects its technological advancements.
The semiconductor and automotive sectors have shown significant growth, with semiconductor automotive sales increasing by 36% in the recent period. This highlights the importance of these sectors for future revenue.
Establishing guidelines for overseas intellectual property rights and anti-counterfeiting measures is crucial. This protects the company's innovations and market position globally.
For more insights into the company's strategies, consider exploring the Growth Strategy of Fuji Electric.
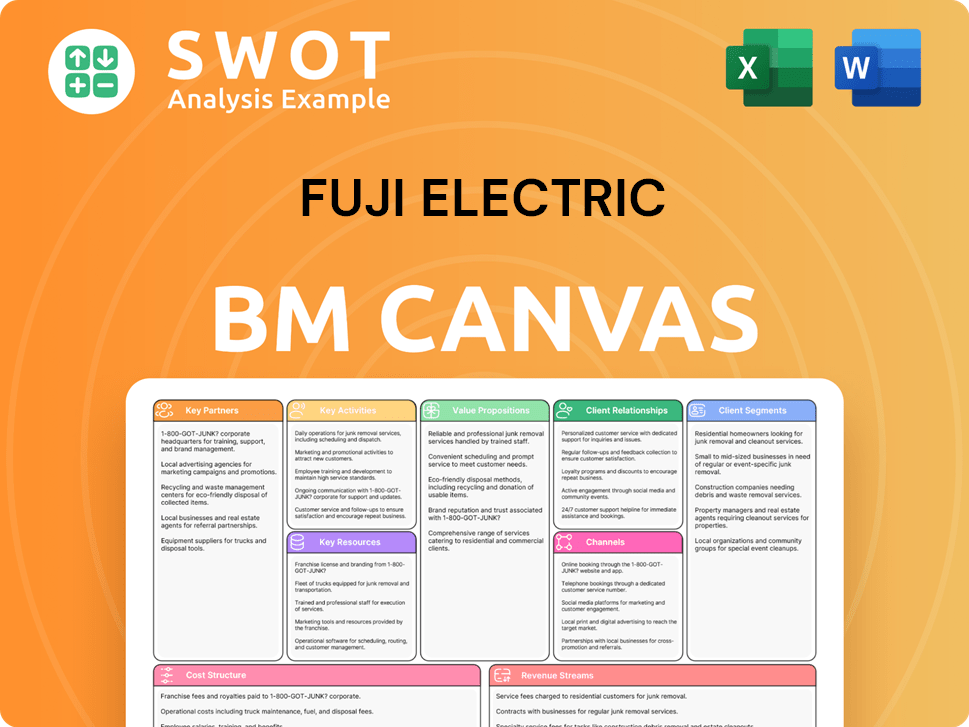
Fuji Electric Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What is the Timeline of Key Events for Fuji Electric?
The Fuji Electric Company, a prominent Japanese company, has a rich history of innovation and adaptation. Founded in 1923, the company has evolved significantly, from its early days in transformer production to its current focus on industrial automation and power electronics. The journey reflects a commitment to technological advancement and strategic expansion, positioning it as a key player in the global market.
| Year | Key Event |
|---|---|
| 1923 | Fuji Electric Manufacturing Co., Ltd. was established in Tokyo. |
| 1925 | Transformer production commenced at the Kawasaki factory. |
| 1935 | The telephone department was spun off, later becoming Fujitsu Limited. |
| 1954 | Mass production of selenium rectifiers began, dominating the domestic market. |
| 1968 | Merged with Kawasaki Denki Seizo Co., Ltd., expanding manufacturing capabilities. |
| 1970 | Delivered beverage vending machines to the Osaka World Exposition. |
| 1984 | The company's name changed to Fuji Electric Co., Ltd. |
| 1987 | Introduced the first IGBT module. |
| 1997 | Supplied large-capacity flat IGBT main converters for Shinkansen trains. |
| 2003 | The company's name changed to Fuji Electric Holdings Co., Ltd. |
| 2011 | Merged with Fuji Electric Device Technology Co., Ltd. |
| 2012 | Launched coffee machines for convenience stores. |
| 2015 | Completed a new power semiconductor research and development building. |
| 2019 | Released an on-site diagnostic system using analytics and AI. |
| 2021 | Released the UPS7500WX Series high-capacity UPS. |
Fuji Electric is prioritizing a 'green transformation' to contribute to a decarbonized society. This involves strategic initiatives and investments in sustainable technologies. The company aims to align its business practices with environmental goals, fostering a circular economy.
For FY2025 (ending March 31, 2026), Fuji Electric projects net sales of 1.14 trillion yen. The company anticipates an operating profit of 118 billion yen, with an operating profit ratio of 10.4%. These figures reflect the company's growth strategy and market expectations.
Future investments include production equipment for mobility-related products and smart meters. Test equipment for heat products and enhanced forward-looking development activities are also planned. These investments support innovation in key business areas.
While the Chinese real estate market poses challenges, recovery in Asia and India is expected. Fuji Electric is accelerating initiatives in India, where infrastructure investment is rising. The company's international expansion is a key component of its growth strategy.
Fuji Electric is working towards sustainability-focused business practices by fiscal 2025, with material issues set for fiscal year 2030. This commitment underscores its dedication to environmental stewardship and long-term value creation. The company is committed to a virtuous cycle in its innovation process.
Analysts predict a positive trend for Fuji Electric's stock, with long-term growth expected. The company's focus on energy and environment technology remains central. Fuji Electric continues to create products that support a sustainable society, driving innovation in industrial automation and power electronics.
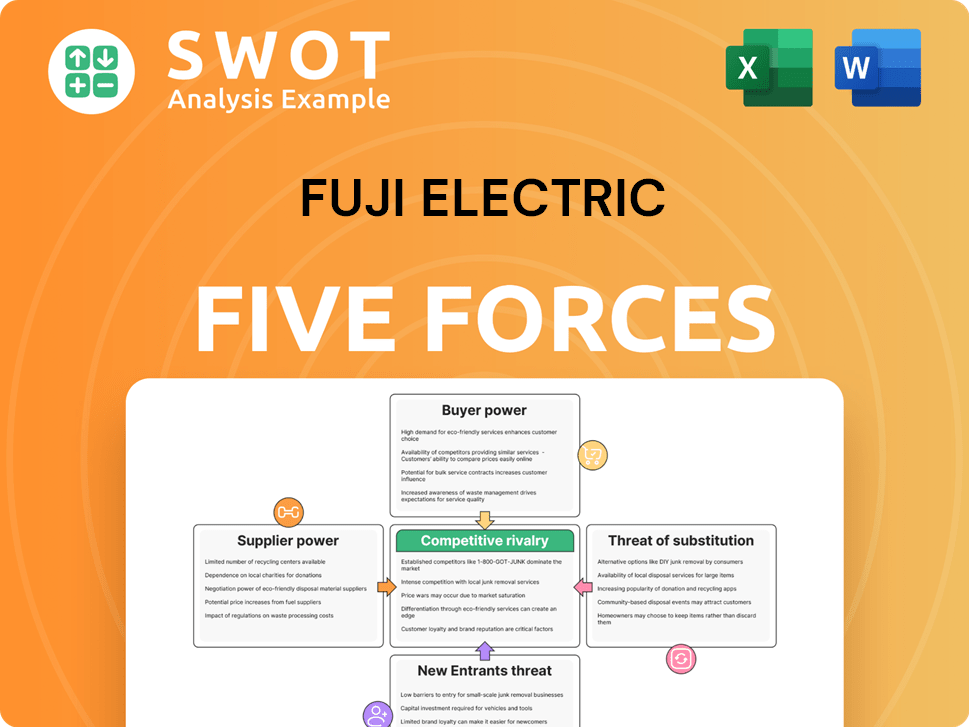
Fuji Electric Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What is Competitive Landscape of Fuji Electric Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Fuji Electric Company?
- How Does Fuji Electric Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Fuji Electric Company?
- What is Brief History of Fuji Electric Company?
- Who Owns Fuji Electric Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Fuji Electric Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.