General Electric Bundle
How has General Electric Shaped the Modern World?
Journey back in time to explore the General Electric SWOT Analysis and the captivating GE history, a story of innovation that spans over a century. From its roots in the Industrial Revolution to its current transformation, General Electric has consistently redefined the boundaries of technology and business. Discover how Thomas Edison and other visionary GE founder figures laid the groundwork for a global powerhouse.

The GE company story is more than just a corporate timeline; it's a reflection of the evolution of technology, from pioneering electrical systems to advanced aviation engines. Understanding the brief history of General Electric provides crucial context for analyzing its current strategic direction and future prospects. Explore the early years of GE and its impact on technology, offering insights into how this industrial giant continues to shape our world.
What is the General Electric Founding Story?
The story of General Electric (GE) begins with a pivotal merger in the late 19th century, marking the birth of one of the world's most influential companies. This union brought together two giants of the electrical industry, setting the stage for GE's future innovations and its profound impact on technology and the economy. Understanding the founding story of GE provides insights into its early strategies and the vision that drove its initial success.
General Electric was officially established on April 15, 1892. This formation was the result of a merger between the Edison General Electric Company and the Thomson-Houston Electric Company. This strategic consolidation was a crucial step in the early years of GE, combining the strengths of both entities to capitalize on the burgeoning demand for electricity.
The early years of GE were shaped by the vision of its founders and the opportunities presented by the Industrial Revolution. Thomas Edison, a key figure in the company's origins, had already made significant contributions to the electrification of homes and industries. His work laid the groundwork for GE's initial focus on developing and commercializing electrical products.
General Electric was formed on April 15, 1892, through the merger of Edison General Electric Company and Thomson-Houston Electric Company. Key figures included Thomas Edison and Charles A. Coffin, with J.P. Morgan playing a crucial role.
- The initial problem/opportunity was the potential of electricity to transform daily life and industry.
- GE's first products included electrical components like generators, motors, and light bulbs.
- Early funding came from financiers like J.P. Morgan and the Vanderbilt family.
- The competitive landscape included Westinghouse Electric Company, leading to a patent pool agreement in 1896.
The Mission, Vision & Core Values of General Electric were rooted in the early goals of the company. The primary goal was to provide comprehensive electrical equipment and systems. GE's initial business model focused on supplying all the necessary components for electrification, including generators, transmission equipment, electric motors, and light bulbs. This comprehensive approach allowed GE to establish a strong foothold in the market.
An interesting aspect of GE's history is the origin of its iconic logo, the Monogram, which dates back to its founding. While the exact origins are debated, an employee named Arthur L. Rich is credited with an early design. The early financial backing for Edison's ventures came from prominent financiers such as J.P. Morgan and members of the Vanderbilt family. The competitive landscape, particularly with Westinghouse Electric Company, presented challenges. This competition eventually led to a patent pool agreement in 1896. This agreement cleared the way for GE's dominance in the electrification industry.
The cultural and economic context of the late 19th century, often referred to as the Gilded Age, provided a fertile ground for the growth of innovative companies like GE. Rapid industrialization and the increasing demand for electrical power fueled the company's expansion. The company's early success was built on a foundation of innovation, strategic partnerships, and a keen understanding of the market's needs.
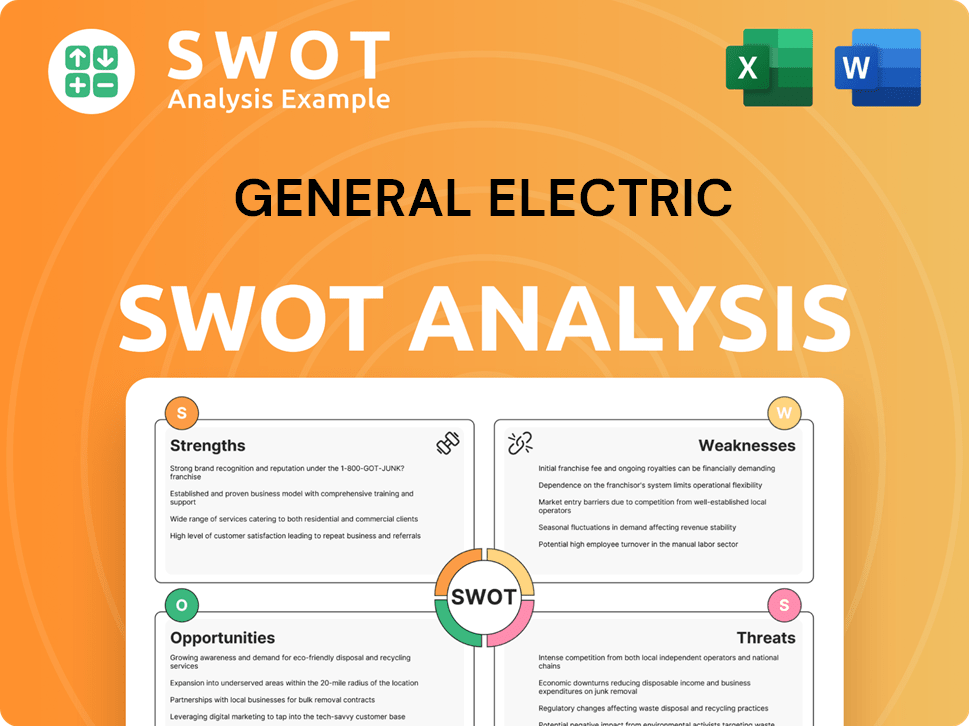
General Electric SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
What Drove the Early Growth of General Electric?
The early phase of the GE company saw rapid expansion beyond its initial lighting focus. This expansion was fueled by continuous innovation and strategic market entries. The company's commitment to innovation was solidified with the establishment of the first industrial laboratory in the United States in 1900, which became a hub for developing groundbreaking technologies. Early product launches also included X-ray machines, electric fans, and various household appliances.
General Electric quickly diversified its product offerings. By 1906, the company introduced its first major appliance, an electric range. This move marked the beginning of its expansion into various consumer and industrial sectors.
The establishment of the first industrial laboratory in the United States in 1900 was a pivotal moment. This lab became a center for developing groundbreaking technologies, including X-ray machines and electric fans. The company's commitment to innovation was solidified with the establishment of the first industrial laboratory in the United States in 1900, which became a hub for developing groundbreaking technologies.
GE rapidly entered new markets, becoming the primary supplier of electrified railway systems in the U.S. and securing contracts in industries like steel, cement, and paper. The company also ventured into power transmission, laying down lines at Niagara Falls by 1894.
Key acquisitions and mergers marked this period of growth. In 1903, GE acquired Stanley Electric Manufacturing Company. A significant merger in 1918 saw GE's heating-device division merge with Pacific Electric Heating Company (maker of the Hotpoint iron) and Hughes Electric Heating Company, forming the Edison Electric Appliance Company.
Leadership transitions were also crucial; after Thomas Edison sold his shares in 1894, remaining as a consultant, Charles Coffin, the head of Thomson-Houston, assumed control and led GE through its promising beginnings. The company's stock began trading on the New York Stock Exchange in 1892. Market reception was largely positive, as GE effectively integrated its products into the consumer market and faced minimal competition after the patent pool agreement with Westinghouse. For more insights, explore the Marketing Strategy of General Electric.
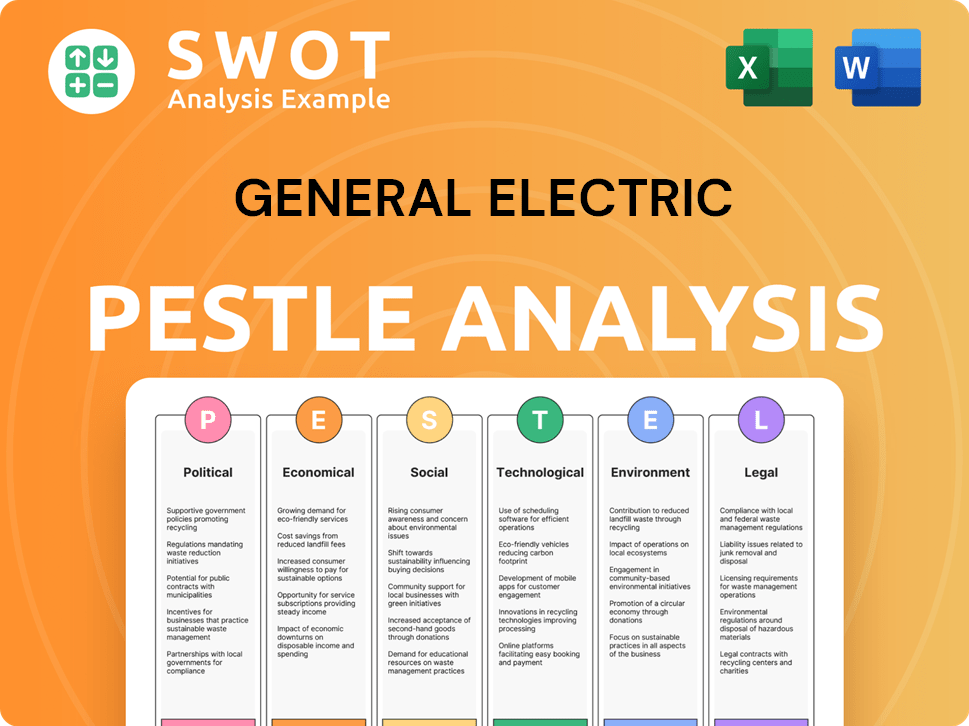
General Electric PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
What are the key Milestones in General Electric history?
The GE history is marked by significant milestones, from its inception to its modern restructuring. The GE company has consistently adapted to technological advancements and market shifts, playing a pivotal role in shaping industries. The journey of General Electric reflects a long history of innovation and strategic adaptation.
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 1878 | GE founder, Thomas Edison, establishes the Edison Electric Light Company, a precursor to GE. |
| 1892 | The Edison General Electric Company merges with the Thomson-Houston Electric Company to form General Electric. |
| 1900 | GE establishes the first industrial research laboratory in the United States, fostering future innovations. |
| 1938 | GE introduces the fluorescent lamp, significantly improving lighting efficiency. |
| 1947 | GE develops silicone production, expanding into new materials. |
| 1950s | GE supplies nuclear reactors for naval vessels, entering the nuclear power industry. |
| 2018 | Larry Culp becomes CEO and initiates significant restructuring, including the split into focused entities. |
| 2023 | GE's share price surges by 95.8%, reflecting positive outcomes from restructuring. |
General Electric's innovations have consistently pushed technological boundaries, significantly impacting various sectors. From early advancements in lighting to pioneering work in aviation and healthcare, GE has consistently been at the forefront of technological progress.
GE's impact on technology began with Thomas Edison's development of the incandescent light bulb, revolutionizing lighting. The company's continuous advancements in lighting technology, including the fluorescent lamp, improved energy efficiency and expanded applications.
GE's role in the Industrial Revolution was significant through its development of power generation equipment. The company provided essential infrastructure for the electrification of cities and industries, powering economic growth.
GE has been a leader in aviation, developing advanced jet engines for both commercial and military aircraft. These engines have improved fuel efficiency and performance, contributing to advancements in air travel.
GE Healthcare has developed cutting-edge medical imaging and diagnostic equipment. These innovations have improved patient care and diagnostic accuracy, playing a crucial role in modern healthcare.
The company's work in materials science, including the development of silicones, has led to new applications across various industries. These materials have enhanced product performance and expanded the possibilities of design and manufacturing.
GE has integrated digital solutions into its operations, enhancing efficiency and data analysis. These technologies have improved operational performance and provided insights for better decision-making.
Despite its successes, GE history has faced numerous challenges, including antitrust issues and financial setbacks. These obstacles have necessitated strategic shifts and restructuring efforts to maintain competitiveness. The company's ability to adapt and innovate has been crucial to its longevity.
Early in its history, General Electric faced antitrust actions that affected its business structure. These actions led to divestitures and forced the company to adapt its market strategies.
In 1961, GE pleaded guilty to price fixing, which damaged its reputation and led to legal consequences. This event highlighted the importance of ethical business practices.
The 2010s brought significant financial challenges, leading to the sale of major business units. These setbacks prompted a major restructuring effort.
In June 2018, General Electric was removed from the Dow Jones Industrial Average after a long tenure. This removal reflected the company's declining performance.
Under CEO Larry Culp, GE initiated a significant overhaul, including the split into focused entities. This restructuring aimed to improve efficiency and drive growth.
The company has navigated market volatility and changing economic conditions, requiring continuous adaptation. These challenges have tested the resilience of General Electric's business model.
For more insights into GE's evolution over time and its strategic shifts, consider reading about the Growth Strategy of General Electric.
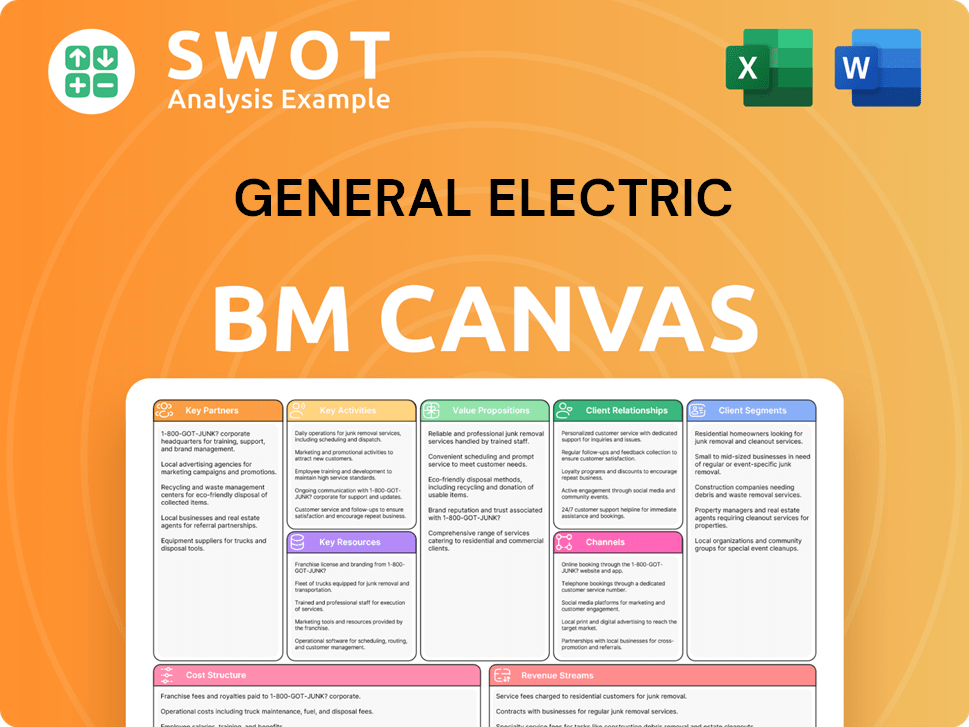
General Electric Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What is the Timeline of Key Events for General Electric?
The Owners & Shareholders of General Electric have witnessed a remarkable journey. From its roots in the late 19th century, General Electric (GE) has been a pivotal force in the Industrial Revolution and beyond. Founded by Thomas Edison, GE's evolution reflects significant technological advancements and strategic shifts, shaping its trajectory through mergers, innovations, and market adaptations.
| Year | Key Event |
|---|---|
| 1878 | Thomas Edison establishes the Edison Electric Light Company, which laid the groundwork for GE. |
| 1892 | General Electric Company is formed, marking the official beginning of the GE company and its listing on the NYSE. |
| 1900 | GE establishes the first industrial research laboratory in the United States, fostering innovation. |
| 1906 | GE introduced its first major appliance, an electric range, expanding its product offerings. |
| 1919 | GE, along with AT&T and Westinghouse, forms the Radio Corporation of America (RCA), entering the broadcasting industry. |
| 1938 | GE introduces the fluorescent lamp, a significant advancement in lighting technology. |
| 1943 | General Electric Capital Corporation is established, diversifying the company's financial services. |
| 1955 | The U.S. Navy launches the submarine Seawolf, powered by a GE nuclear reactor, showcasing GE's technological capabilities. |
| 1981 | Jack Welch becomes chairman and CEO, initiating a period of significant growth and diversification for GE. |
| 1986 | GE acquires RCA, including NBC, expanding its media and entertainment portfolio. |
| 1998 | Revenues surpass $100 billion, highlighting GE's substantial financial growth. |
| 2018 | GE is removed from the Dow Jones Industrial Average, reflecting shifts in the company's structure and market position. |
| 2023 (Early) | GE HealthCare Technologies Inc. (GEHC) is spun off as an independent company. |
| 2024 (April 2) | GE Vernova Ltd. (GEV) is spun off, and the remaining company is renamed GE Aerospace. |
GE Aerospace is positioned for considerable expansion, driven by increasing demand for aftermarket services. The company is targeting an operating profit of roughly $10 billion by 2028. This strategic focus is expected to boost the company's financial performance in the coming years.
Analysts anticipate that GE (now GE Aerospace) will achieve an EPS of $5.42 in 2025, with a further increase to $6.40 in 2026. This represents an impressive 18% increase from 2025 levels. These projections reflect confidence in the company's growth trajectory.
GE Vernova aims to generate between $36–$37 billion in revenue in 2025. This growth is supported by strong order volumes in electrification and renewable energy sectors. The company is strategically positioned to capitalize on the increasing demand for sustainable energy solutions.
GE HealthCare is focused on driving innovation in diagnostics and imaging, backed by a 2025 cash flow of $2–$2.5 billion from its healthcare business. This investment underscores the company's commitment to advancing healthcare technologies and solutions. The company is strategically positioned to capitalize on the increasing demand for sustainable energy solutions.
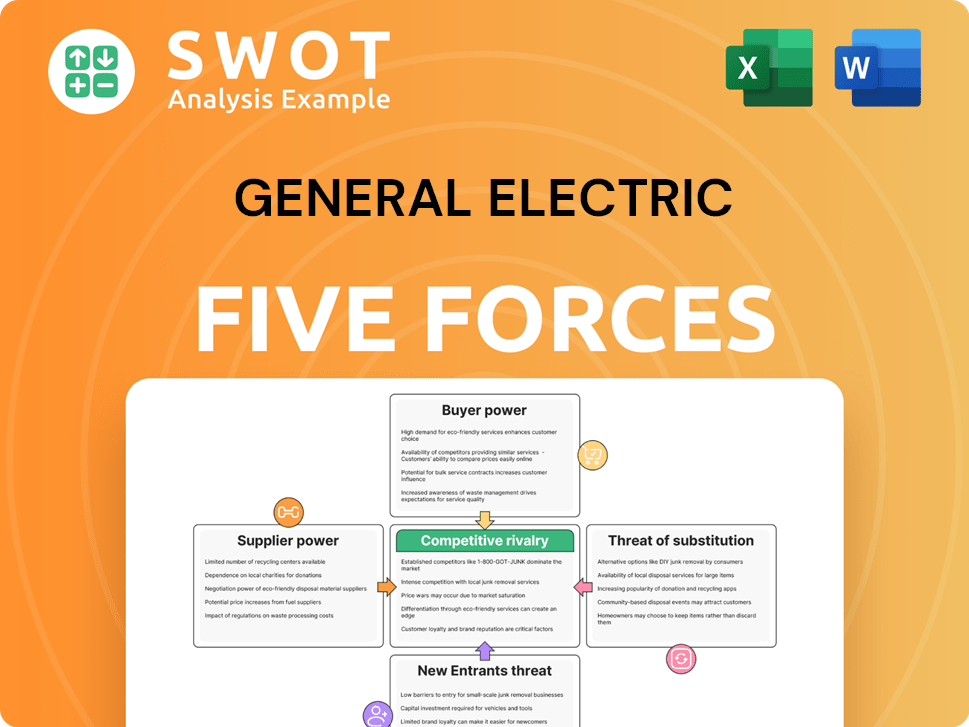
General Electric Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What is Competitive Landscape of General Electric Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of General Electric Company?
- How Does General Electric Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of General Electric Company?
- What is Brief History of General Electric Company?
- Who Owns General Electric Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of General Electric Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.