General Electric Bundle
Who Really Owns General Electric After Its Transformation?
Following a massive restructuring, General Electric (GE) has emerged as a focused aerospace powerhouse, but who exactly holds the reins? Understanding the intricacies of General Electric SWOT Analysis is crucial. This exploration delves into the evolution of
The recent spin-offs of GE Vernova and GE Aerospace have fundamentally altered the
Who Founded General Electric?
The formation of the General Electric Company, or GE, in 1892, was the result of a merger, not a conventional founding. The merger brought together the Edison Electric Light Company, founded by Thomas Edison, and the Thomson-Houston Electric Company, spearheaded by Charles A. Coffin and Edwin J. Houston. This consolidation aimed to create a dominant force in the emerging electrical industry.
Early ownership of the GE company was a blend of shareholders from the two merging entities. The capital came from the existing investors and financiers of Edison Electric and Thomson-Houston. These early backers were primarily industrialists and financiers who recognized the immense potential of electricity. The merger was designed to reduce competition and establish a strong presence in the rapidly growing electrical sector.
The merger agreements focused on integrating the corporate structures and shareholding bases of both companies. This likely involved share exchanges and the establishment of a unified board of directors. The founding vision was to create a comprehensive electrical company capable of developing, manufacturing, and distributing a wide range of electrical products and services. This reflected the distribution of control among the combined entities.
Thomas Edison brought his innovations in lighting and power distribution to the merger. His contributions were crucial to establishing the company's early technological foundation.
Thomson-Houston contributed a strong commercial and manufacturing base. This helped in the company's ability to scale up production and distribution.
Early investors were primarily industrialists and financiers. They recognized the growth potential of the electrical industry. These investors played a key role in the initial capitalization of the company.
The merger strategy aimed to reduce competition and create a dominant market player. This consolidation was a strategic move to gain a competitive edge in the electrical market.
Early agreements focused on integrating the two corporate structures and shareholding bases. This integration was critical for the operational and financial alignment of the merged entity.
The shared vision was to create a comprehensive electrical company. This vision guided the development of a wide range of electrical products and services.
Understanding the early ownership of GE provides insights into the company's foundational structure and strategic goals. The merger of Edison Electric Light Company and Thomson-Houston Electric Company formed the basis of the company. If you're interested in learning more about the company's target market, you can read this article: Target Market of General Electric.
- The initial capital came from existing investors of the merging companies, not traditional angel investors.
- The goal was to create a dominant force in the electrical industry by reducing competition.
- Early agreements focused on integrating the corporate structures and shareholding bases.
- The founding vision was to create a comprehensive electrical company.
General Electric SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
How Has General Electric’s Ownership Changed Over Time?
The evolution of General Electric (GE) ownership reflects its transformation from a merged private entity in 1892 to a publicly traded giant. The initial public offering (IPO) solidified its status on the New York Stock Exchange, and over time, GE's market capitalization soared, peaking at over $600 billion in the early 2000s. This growth was accompanied by a shift in ownership towards institutional investors, mutual funds, and index funds, mirroring broader market trends.
The ownership structure of GE has been significantly reshaped by strategic decisions, including the spin-off of GE Vernova in April 2024. This move, alongside the focus on GE Aerospace, altered the company's asset base and shareholder composition. The restructuring aimed to unlock shareholder value by creating more focused businesses, influencing long-term strategy towards specialized growth in aviation.
| Ownership Aspect | Details | Data (Early 2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Ownership | Institutional Investors | Majority of shares |
| Top Institutional Holders | Vanguard, BlackRock, State Street, Capital World Investors | Vanguard (~9.39%), BlackRock (~7.74%), State Street (~4.41%) |
| Individual Insiders | Current and former executives, board members | Smaller percentages |
As of early 2024, institutional investors are the primary holders of GE Aerospace shares, with Vanguard Group Inc., BlackRock Inc., and State Street Corp. among the top shareholders. The significant holdings by these institutional investors highlight the influence of passive and active funds in GE's ownership. Individual insiders, including current and former executives, hold smaller percentages of shares. This structure reflects the company's evolution and the impact of strategic decisions on its shareholder base. The spin-off of GE Vernova and the focus on GE Aerospace have further refined the ownership landscape.
The ownership of General Electric has evolved significantly since its inception, with a shift towards institutional investors. Major shareholders include Vanguard, BlackRock, and State Street. The strategic spin-off of GE Vernova and focus on GE Aerospace have reshaped the shareholder composition.
- Institutional investors hold the majority of GE Aerospace shares.
- Vanguard, BlackRock, and State Street are among the top institutional holders.
- Strategic decisions, like spin-offs, impact the ownership structure.
- GE is a publicly traded company.
General Electric PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
Who Sits on General Electric’s Board?
As of early 2025, the Board of Directors of GE Aerospace, the remaining entity of the former General Electric, is central to its governance, representing the interests of GE shareholders and steering its strategic direction. The board typically consists of a mix of independent and executive directors. Larry Culp serves as the Chairman and CEO of GE Aerospace. The board also includes independent directors with diverse backgrounds in finance, technology, and industry, ensuring a broad range of expertise.
The board's composition reflects the company's focus on operational efficiency and shareholder value. Major institutional investors, such as Vanguard and BlackRock, hold significant stakes in GE. While they don't have designated board seats, their substantial voting power influences decisions on director elections, executive compensation, and significant corporate actions. This influence is a key aspect of how GE is managed, ensuring accountability to its shareholders and driving strategic decisions that aim to enhance long-term value. The recent strategic moves, including the spin-off of GE Vernova, have been partly influenced by ongoing dialogue with its large institutional investor base.
| Board Member | Title | Affiliation |
|---|---|---|
| Larry Culp | Chairman and CEO | GE Aerospace |
| Carolina Dybeck Happe | CFO | GE Aerospace |
| Other Independent Directors | Various | Diverse backgrounds in finance, technology, and industry |
GE Aerospace operates under a one-share-one-vote structure, meaning each common share typically carries one vote. This structure ensures that voting power is proportional to shareholding. There are no known dual-class shares or special voting rights that would grant outsized control to specific individuals or entities. This structure supports the principle of equal voting rights for all shareholders. For those interested in understanding the financial aspects of the company, you can learn more about the Revenue Streams & Business Model of General Electric.
Understanding who owns GE, or more precisely, GE Aerospace, is crucial for investors and stakeholders.
- The board of directors oversees strategic direction and represents shareholder interests.
- Major institutional investors like Vanguard and BlackRock hold significant influence.
- GE operates under a one-share-one-vote structure, ensuring proportional voting power.
- The company's structure is designed to enhance shareholder value and operational efficiency.
General Electric Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What Recent Changes Have Shaped General Electric’s Ownership Landscape?
Over the past few years, the ownership structure of General Electric has undergone significant changes. The company has strategically spun off major business units, reshaping its shareholder base. In January 2023, GE HealthCare was spun off, with GE shareholders receiving the majority of the shares. More recently, in April 2024, GE Vernova, encompassing the energy businesses, was also spun off, transforming GE into a standalone aviation-focused company, now known as GE Aerospace. These moves have dramatically altered who owns GE, leading to a more focused ownership structure across the resulting independent companies.
These spin-offs have created three separate publicly traded entities: GE HealthCare, GE Vernova, and GE Aerospace. This shift allows investors to choose specific industry exposures. The changes reflect a broader trend toward corporate simplification and specialization, potentially unlocking value. While there haven't been immediate major share buybacks by GE Aerospace post-spin, the company's financial strategy is now tailored to the aviation sector. The aim is to create more agile, growth-oriented businesses, attracting investors interested in the aerospace industry. There are no immediate plans for further significant ownership changes like privatization for GE Aerospace, as the focus is on maximizing its performance as a standalone entity.
| Metric | Details | Data |
|---|---|---|
| Spin-off of GE HealthCare | Date | January 2023 |
| GE HealthCare Shares Distributed to GE Shareholders | Percentage | 80.1% |
| Spin-off of GE Vernova | Date | April 2024 |
| Current Focus of GE Aerospace | Industry | Aviation |
The transformation of GE's ownership structure, including the spin-offs of GE HealthCare and GE Vernova, has created three distinct publicly traded companies, impacting who owns GE and how investors can engage with these businesses. This strategic shift aligns with industry trends toward specialization and is designed to enhance shareholder value.
The spin-off of GE HealthCare in January 2023, distributing the majority of shares to existing GE shareholders.
The April 2024 spin-off of GE Vernova, resulting in GE Aerospace as a standalone aviation company.
Shareholders now hold shares in three separate public companies: GE HealthCare, GE Vernova, and GE Aerospace.
GE Aerospace is focused on maximizing performance as a standalone entity, with no immediate plans for major ownership changes.
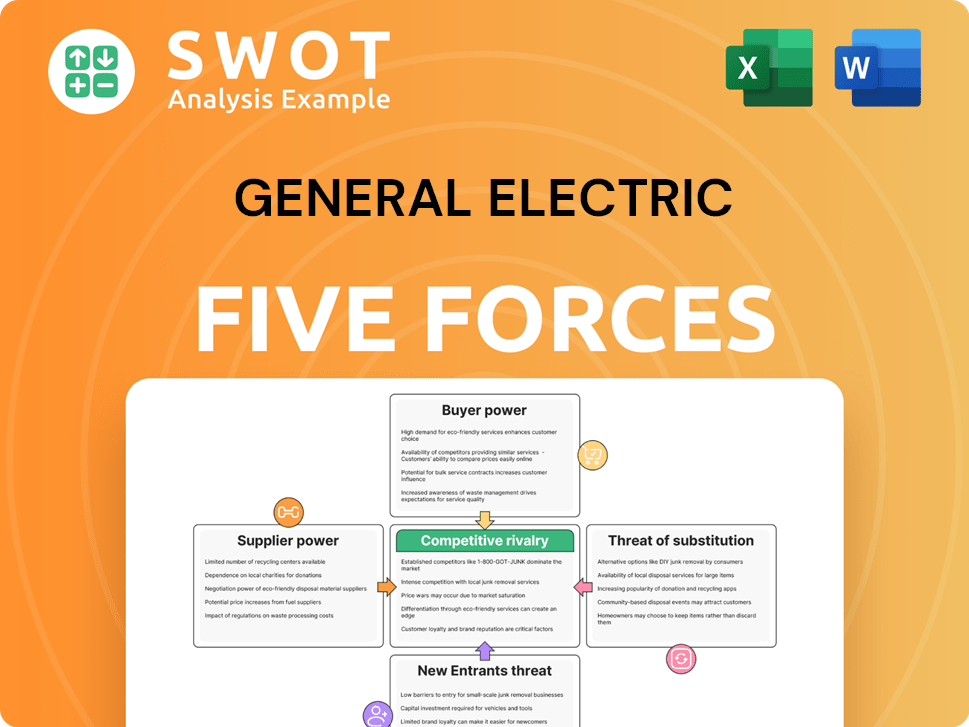
General Electric Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of General Electric Company?
- What is Competitive Landscape of General Electric Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of General Electric Company?
- How Does General Electric Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of General Electric Company?
- What is Brief History of General Electric Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of General Electric Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.