Legrand Bundle
How did a porcelain workshop evolve into a global leader like Legrand?
Uncover the fascinating Legrand SWOT Analysis, a journey that began in 1865 in Limoges, France, with a porcelain tableware workshop. From its humble beginnings, the Legrand company has transformed into a global specialist in electrical and digital building infrastructures. Explore the key milestones that shaped this French company's remarkable evolution.
The Legrand company's history is a testament to strategic adaptation and innovation. Its evolution from porcelain to electrical equipment mirrors the broader technological advancements of the last century. Understanding the Legrand company timeline reveals a commitment to anticipating market needs and expanding its global presence. This brief history of Legrand highlights its enduring legacy in the electrical solutions sector.
What is the Legrand Founding Story?
The story of the Legrand history begins in 1865 with a porcelain tableware workshop in Limoges, France. This workshop, founded by Henri Barjaud de Lafond and Léonard Clidasson, was strategically located to utilize the Vienne river for transporting wood, essential for firing kilns. The company's evolution from its initial focus to its current status as a leader in electrical equipment is a significant part of its history.
The company's identity took shape in 1904 when Frédéric Legrand, Charles Alary, and Jean Joquel acquired the business, renaming it 'Legrand, Alary & Joquel Company'. This marked a crucial turning point, setting the stage for future developments. The early years were focused on porcelain products, but a pivotal shift was on the horizon.
In 1919, Legrand partnered with Jean Mondot, an artisan specializing in electric switches made from porcelain and boxwood. This collaboration marked the company's entry into electrical equipment, utilizing porcelain's insulating properties. This strategic move positioned Legrand to capitalize on the growing demand for electrical installations. The company's focus became exclusively electrical after a factory fire in 1949, leading to the complete abandonment of the porcelain business by 1950. Jean Verspieren and Edouard Decoster, who took over management in 1944, steered the company through this transformative period.
Legrand's early days were rooted in porcelain tableware, evolving into a major player in electrical equipment.
- Founded in 1865 as a porcelain workshop.
- Entered the electrical equipment market in 1919.
- Shifted focus entirely to electrical products after a factory fire in 1949.
- Management transitioned under Jean Verspieren and Edouard Decoster in 1944.
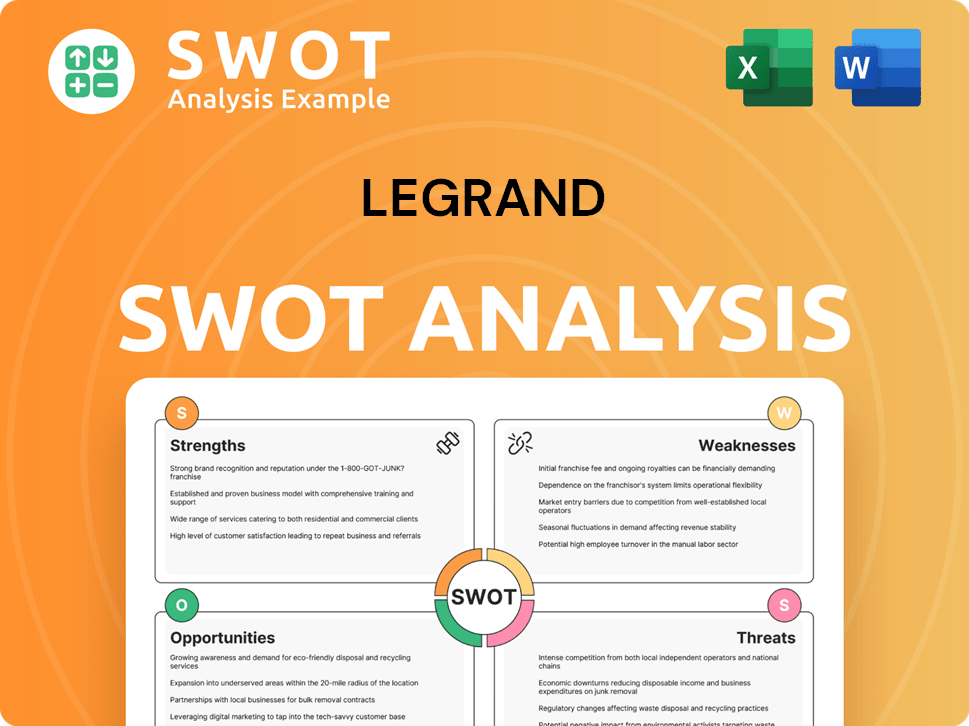
Legrand SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
What Drove the Early Growth of Legrand?
Following its shift towards electrical wiring devices in 1950, the Legrand company experienced significant growth. This expansion was fueled by the post-World War II reconstruction efforts in Europe, which spurred a boom in the building market. The company quickly broadened its product range to include protection products, cable management solutions, and emergency lighting, solidifying its position in the electrical equipment sector.
The initial growth of the
The
Throughout its early growth phase, the
By the 2000s, the
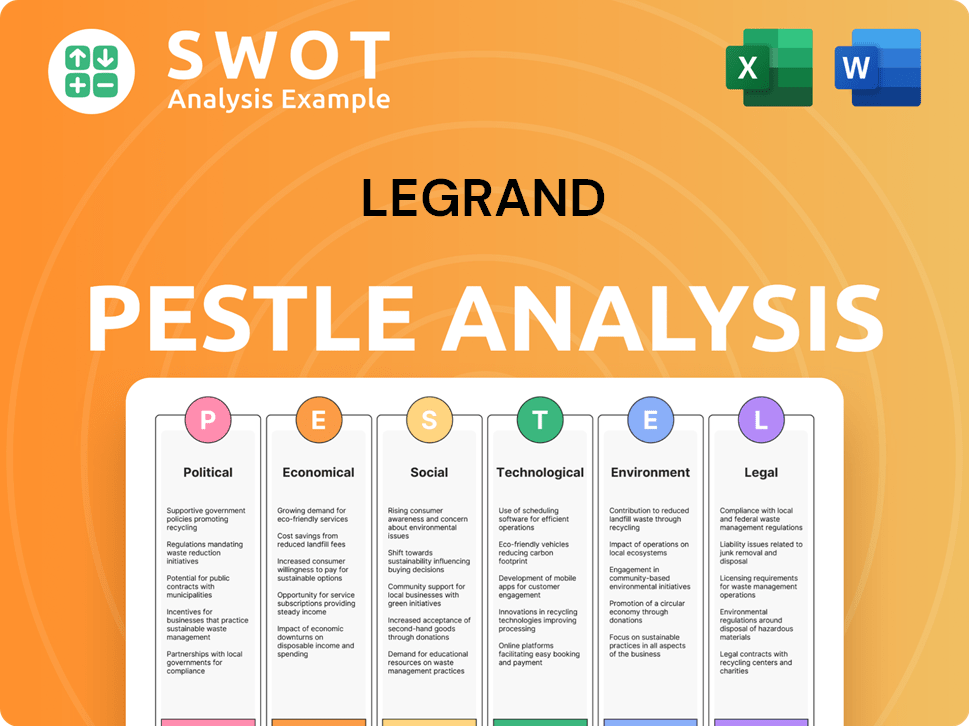
Legrand PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
What are the key Milestones in Legrand history?
The Legrand company has a rich history marked by significant milestones that have shaped its growth and global presence. From its early days as a porcelain manufacturer to its evolution into a leading provider of electrical and digital building infrastructures, the company's journey reflects strategic decisions and adaptability in a dynamic market. The Legrand history is a testament to its resilience and forward-thinking approach.
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 1919 | Introduction of electrical switches using porcelain, a pioneering use of the material for insulation. |
| 1949 | Strategic shift to electrical equipment after a factory fire, capitalizing on the post-war building boom. |
| 1966 | Establishment of the first subsidiary outside France, in Belgium, marking the beginning of international expansion. |
| 1977 | First non-European subsidiary established in Brazil, further extending its global reach. |
| 1989 | Acquisition of BTicino in Italy, solidifying its position in the European market. |
| 2005 | Acquisition of ICM Group (Cablofil brand), enhancing its presence in wire mesh cable trays. |
| 2006 | Acquisition of the electrical wiring devices division of TCL China, strengthening its foothold in key markets. |
| 2015 | Launch of the Eliot program to accelerate Internet of Things (IoT) offerings, focusing on connected building solutions. |
Legrand has consistently demonstrated a commitment to innovation, particularly in the realm of electrical equipment and smart building solutions. The company's focus on research and development has led to the creation of cutting-edge products and services that meet the evolving needs of its customers. These innovations have not only enhanced its product offerings but also strengthened its market position.
In 1919, Legrand pioneered the use of porcelain for electrical switches, a groundbreaking innovation that improved insulation and safety. This early innovation set the stage for the company's future advancements in electrical solutions.
Following a factory fire in 1949, Legrand strategically shifted its focus to electrical equipment, capitalizing on the post-war building boom. This decision proved pivotal in establishing its presence in the market.
Legrand's expansion strategy included key acquisitions, such as BTicino in 1989, and ICM Group in 2005, which broadened its product portfolio and geographic reach. These moves were crucial for solidifying its market presence.
The launch of the Eliot program in 2015 marked a significant step into the Internet of Things (IoT) for connected building solutions. This initiative demonstrated Legrand's commitment to smart home technology.
In 2020, Legrand introduced new energy-efficient home automation products at the Consumer Electronics Show, showcasing its dedication to sustainability and innovation in the smart home sector. This was a move to meet the growing demand for sustainable solutions.
Legrand has deployed new GenAI products, Gaia and Elia, to optimize product information for employees and customers. Elia is designed to provide enhanced product information and content generation.
Despite its successes, Legrand has faced various challenges, including market downturns and regulatory issues. The company has demonstrated resilience by adapting to changing market conditions and implementing strategic measures to mitigate risks. In 2024, Legrand achieved sales growth despite a generally depressed building market, showcasing its ability to navigate difficult economic environments.
Legrand has faced challenges from market downturns, particularly in the building sector, requiring strategic adjustments. In 2024, Legrand achieved sales growth despite a generally depressed building market, demonstrating its resilience.
The company has had to manage the impact of customs policies, especially in the United States, by implementing price adjustments and supply chain modifications. These measures were essential to maintain competitiveness.
Legrand faced an enforceable decision by the French Competition Authority regarding pricing practices between 2012 and 2015, resulting in a €43 million payment in 2025, which Legrand has appealed. This highlights the importance of regulatory compliance.
Legrand has had to make supply chain adjustments to mitigate the effects of customs policies, ensuring the continuity of operations. These adjustments were crucial for maintaining market presence.
To address customs policies, Legrand implemented price adjustments, which were part of a broader strategy to maintain profitability. These adjustments were vital for adapting to changing market conditions.
Legrand implemented savings plans to manage costs and maintain competitiveness in the face of various challenges. These plans were essential for ensuring financial stability.
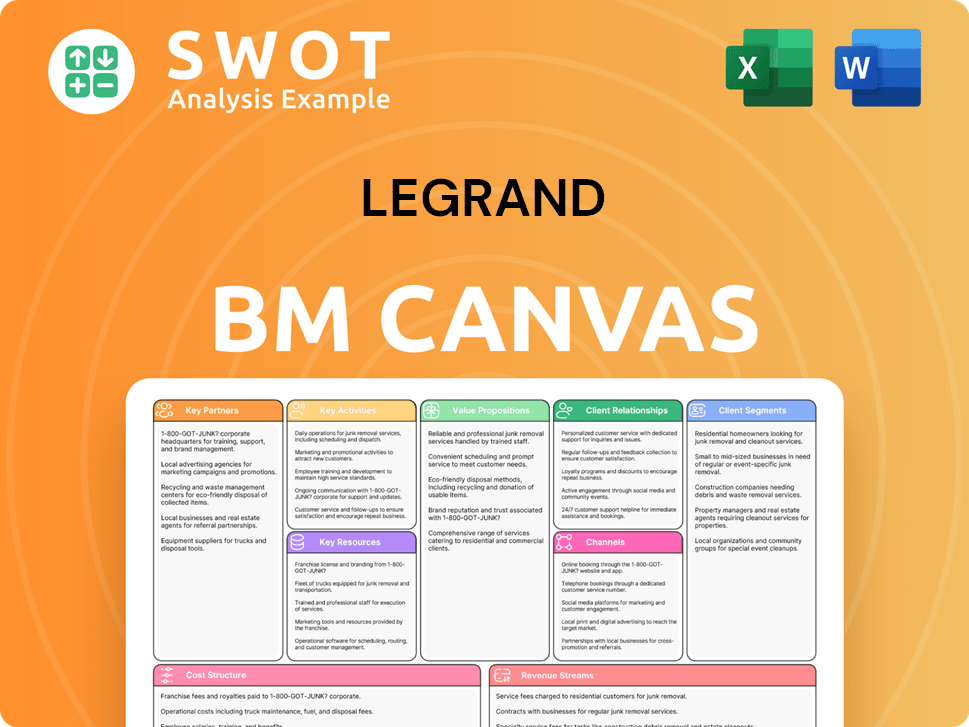
Legrand Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What is the Timeline of Key Events for Legrand?
The Legrand history is a testament to strategic adaptation and growth, evolving from a porcelain workshop to a global leader in electrical equipment. The French company's journey is marked by pivotal acquisitions, technological advancements, and a strong commitment to sustainability. This Legrand company timeline of events highlights key moments that have shaped its trajectory.
| Year | Key Event |
|---|---|
| 1865 | Founding of a porcelain tableware workshop in Limoges, France. |
| 1904 | Frédéric Legrand takes over the business, and the name 'Legrand' is established. |
| 1919 | Entry into the electrical equipment market with the manufacturing of switches using porcelain. |
| 1949 | A factory fire leads to a strategic shift to focus solely on electrical wiring devices. |
| 1950 | Legrand abandons the porcelain business to concentrate on electrical fittings. |
| 1966 | First subsidiary established outside France, in Belgium. |
| 1977 | First subsidiary outside Europe, in Brazil. |
| 1989 | Acquisition of BTicino, Italy's largest electrical equipment manufacturer. |
| 2000 | Acquisition of The Wiremold Company in North America. |
| 2003 | Investment funds KKR and Wendel Investissement acquire the entire share capital, taking Legrand private. |
| 2005 | Acquisition of ICM Group (Cablofil brand), a world leader in wire mesh cable trays. |
| 2015 | Launch of the Eliot program to accelerate deployment of Internet of Things (IoT) offerings. |
| 2018 | Acquisition of Netatmo, a French startup specializing in IoT. |
| 2024 | Legrand reports sales of €8.6 billion and achieves a 113% CSR roadmap achievement rate; the datacenter business represents 20% of sales. |
| 2025 | Legrand launches its 6th CSR roadmap for 2025-2027, focusing on diversity, climate change, circular economy, customer service, and responsible business practices. |
Legrand aims for revenue between €12 billion and €15 billion by 2030, a significant increase from the €8.6 billion reported in 2024. For 2025, the company anticipates sales growth between +6% and +10%, driven by organic growth and acquisitions. The company is focused on expanding its product range and geographical reach.
The datacenter business is a key growth driver, already accounting for 20% of Group sales in 2024. This sector is experiencing accelerating organic growth, particularly in the first quarter of 2025. This focus highlights Legrand's adaptation to the evolving demands of digital infrastructure.
Legrand is committed to sustainability, aiming to reduce direct and indirect greenhouse gas emissions (Scopes 1 & 2) by 10% compared to 2024 levels by 2027. The company has set a goal to achieve Net Zero emissions by 2050, demonstrating its dedication to environmental responsibility. The company's sustainability initiatives are a core part of its strategy.
Legrand plans to allocate around €5 billion to acquisitions by 2030 to strengthen its market position. These acquisitions will focus on expanding its product offerings and geographical presence. This strategic approach supports the company's long-term growth objectives and market share.
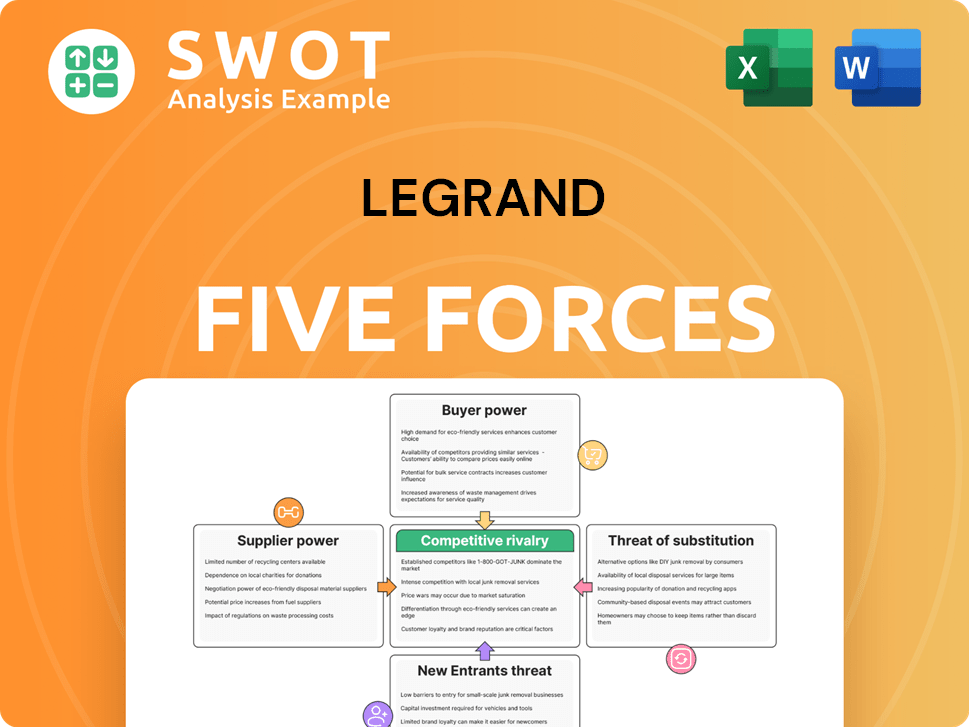
Legrand Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What is Competitive Landscape of Legrand Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Legrand Company?
- How Does Legrand Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Legrand Company?
- What is Brief History of Legrand Company?
- Who Owns Legrand Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Legrand Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.