Scania AB Bundle
How Did a Swedish Railway Car Maker Become a Global Trucking Powerhouse?
Embark on a journey through the Scania AB SWOT Analysis and discover the compelling story of Scania, a company that began in 1891 in Sweden with a vision far beyond its initial railway car production. This remarkable Scania AB history showcases its evolution from a humble start to a global leader in heavy-duty vehicles. Explore the pivotal moments and strategic decisions that have shaped this iconic Scania company.
From its early focus on robust engines to its current commitment to sustainable transport, the Scania trucks journey reflects over a century of engineering excellence and adaptation. Understanding the Scania timeline and Scania history facts reveals the key innovations and milestones that have propelled this Swedish truck manufacturer to the forefront of the automotive industry. Delve into the Scania AB company origins and uncover the secrets behind its enduring success.
What is the Scania AB Founding Story?
The story of Scania AB begins on December 11, 1891, with the founding of Vagnfabriks-Aktiebolaget i Södertelge (Vabis) in Södertälje, Sweden. This marked the inception of what would become a leading global manufacturer of trucks and buses. The company's origins were rooted in the burgeoning demand for railway rolling stock during a period of rapid industrialization in Sweden.
Vabis was established by local industrialists and businessmen. Their primary objective was to meet the growing needs of the expanding railway network. The name 'Vabis' itself, an acronym for 'Vagnfabriks-Aktiebolaget i Södertelge,' directly reflected its initial focus on manufacturing railway cars. This early venture was a response to the need for domestic production to support Sweden's infrastructure development.
The initial business model of Vabis centered on the production of railway cars, capitalizing on the significant growth potential in the railway sector. Early funding likely came from local investors and industrial capital, typical for a manufacturing venture of that scale in the late 19th century. The cultural and economic context of the time, characterized by rapid industrialization and the expansion of transportation networks, played a crucial role in the company's formation, creating a favorable environment for a railway car manufacturer.
Scania's roots are in the late 19th century, starting with railway cars. The company's early focus was on meeting the needs of Sweden's growing railway network.
- The company's initial name was Vabis.
- Vabis was founded in Södertälje, Sweden.
- The first products were railway wagons and carriages.
- The company's formation was influenced by industrialization.
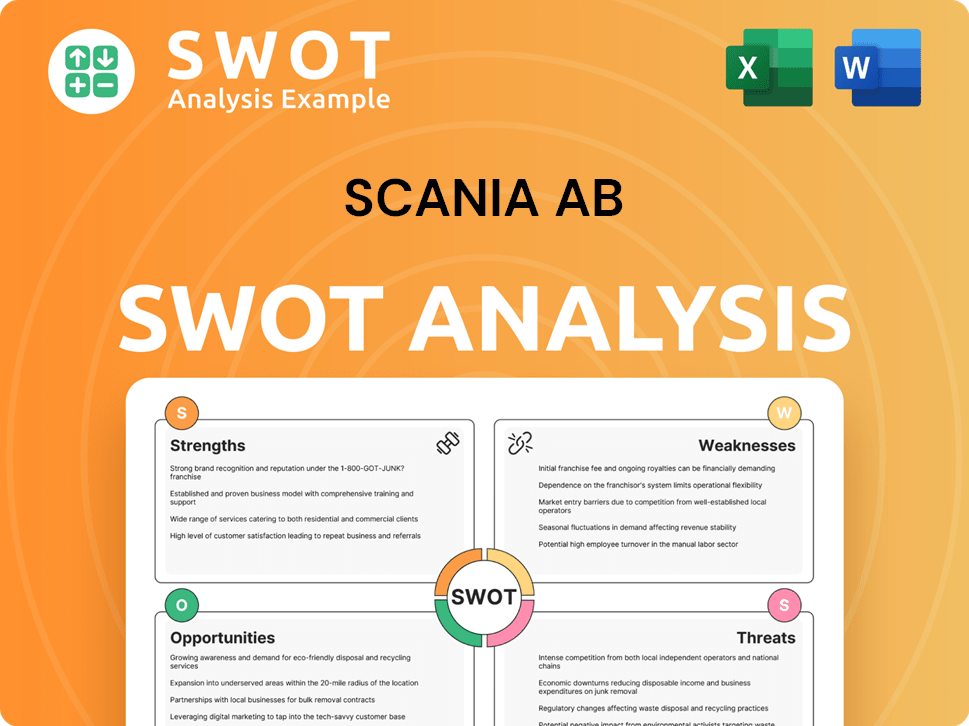
Scania AB SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
What Drove the Early Growth of Scania AB?
The early growth of the company, now known as Scania AB, showcases its adaptability and strategic foresight within the transportation sector. Initially involved in railway cars, the company quickly recognized the potential of motorized vehicles, producing its first motor car in 1902. This early move into automotive manufacturing marked a significant shift, laying the foundation for its future as a leading Swedish truck manufacturer.
Vabis, the precursor to the modern Scania, started with a focus on railway cars. The company's early recognition of the potential in motorized vehicles led to the production of its first motor car in 1902. This strategic move diversified its business model and set the stage for future growth in the automotive industry.
In 1911, the merger of Vabis and Maskinfabriks-Aktiebolaget Scania created Scania-Vabis. Maskinfabriks-Aktiebolaget Scania, founded in 1900, brought truck and engine expertise. This merger combined railway car and early automobile experience with truck and engine knowledge, strengthening the company's position.
Scania-Vabis expanded its product range to include trucks, buses, and marine engines. Early facilities were established in Södertälje and Malmö, Sweden. The company's focus on producing reliable vehicles helped build its reputation in the heavy vehicle market.
The merger of Vabis and Scania enabled the company to compete more effectively in the growing automotive market. This strategic consolidation set the trajectory for Scania to become a major industrial player. By focusing on durability and reliability, the company established a strong foundation for its future success in the Scania trucks market.
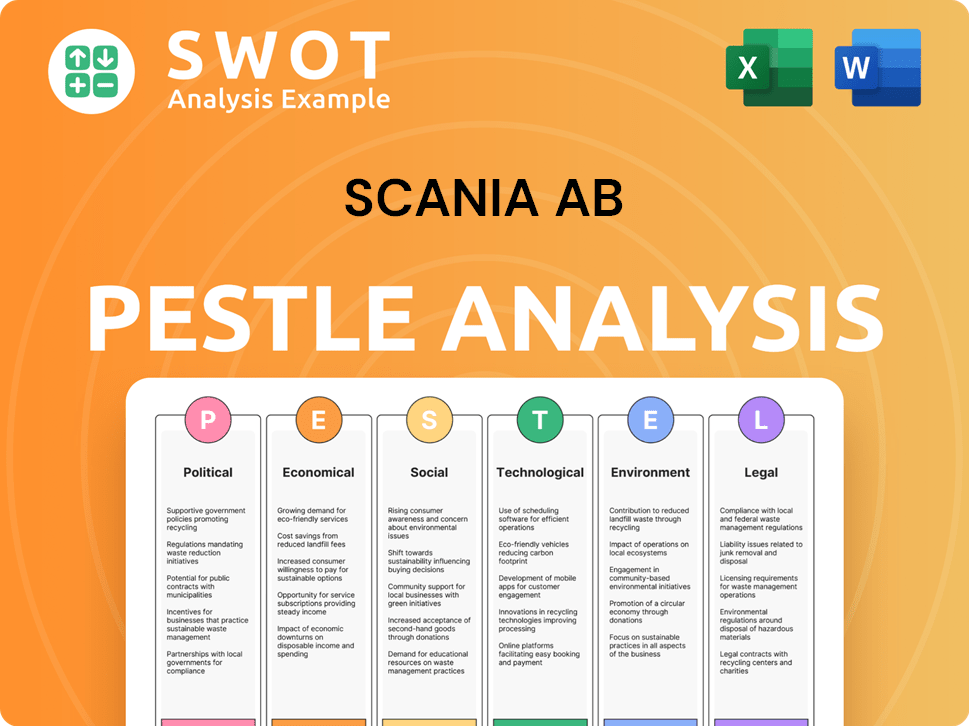
Scania AB PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
What are the key Milestones in Scania AB history?
The Scania AB history is marked by significant milestones that have shaped the Swedish truck manufacturer into a global leader. From its early days to its current status, the company has consistently pushed boundaries.
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 1891 | Foundation of Vabis, one of the companies that would merge to form Scania-Vabis. |
| 1900 | Production of the first truck. |
| 1911 | Merger of Scania and Vabis to form Scania-Vabis. |
| 1969 | Scania-Vabis is renamed Scania. |
| 1980s | Introduction of the modular system, a groundbreaking innovation in design and manufacturing. |
| 2015 | Became a wholly-owned subsidiary of Volkswagen AG. |
| 2024 | Announced a new generation of battery electric trucks for regional long-haul transport. |
Scania's innovations have been pivotal in the evolution of the trucking industry. The modular system, introduced in the 1980s, allowed for greater customization and improved serviceability. This approach became a hallmark of Scania's engineering prowess, enhancing efficiency and adaptability.
The modular system revolutionized truck design and manufacturing, enabling greater customization and reduced production costs. This innovation improved serviceability and became a key differentiator for Scania.
Scania pioneered sustainable transport solutions with its early adoption of ethanol-fueled engines in the 1980s. This initiative demonstrated the company's commitment to reducing emissions and promoting alternative fuels.
Scania continues to develop alternative fuel technologies and electrification initiatives in the 21st century. The company is investing heavily in research and development to create sustainable transport solutions.
In 2024, Scania announced a new generation of battery electric trucks for regional long-haul transport. This move underscores Scania's commitment to electrification and reducing carbon emissions.
The Scania company has faced numerous challenges throughout its history. Economic downturns and fluctuating fuel prices have necessitated continuous adaptation. The company has also navigated various ownership changes, requiring strategic adjustments.
Economic fluctuations have required Scania to adapt its strategies to maintain profitability and market share. These challenges demand agility and strategic planning.
Fluctuating fuel prices impact operational costs and customer demand, necessitating efficient fuel management and the development of alternative fuel solutions. This has been a persistent challenge.
Transitions in ownership, such as the move to Volkswagen AG, required strategic adjustments in governance and operational alignment. These changes can be complex.
The pressure to decarbonize transport has led to significant investments in renewable fuels and electric vehicles. This has driven innovation.
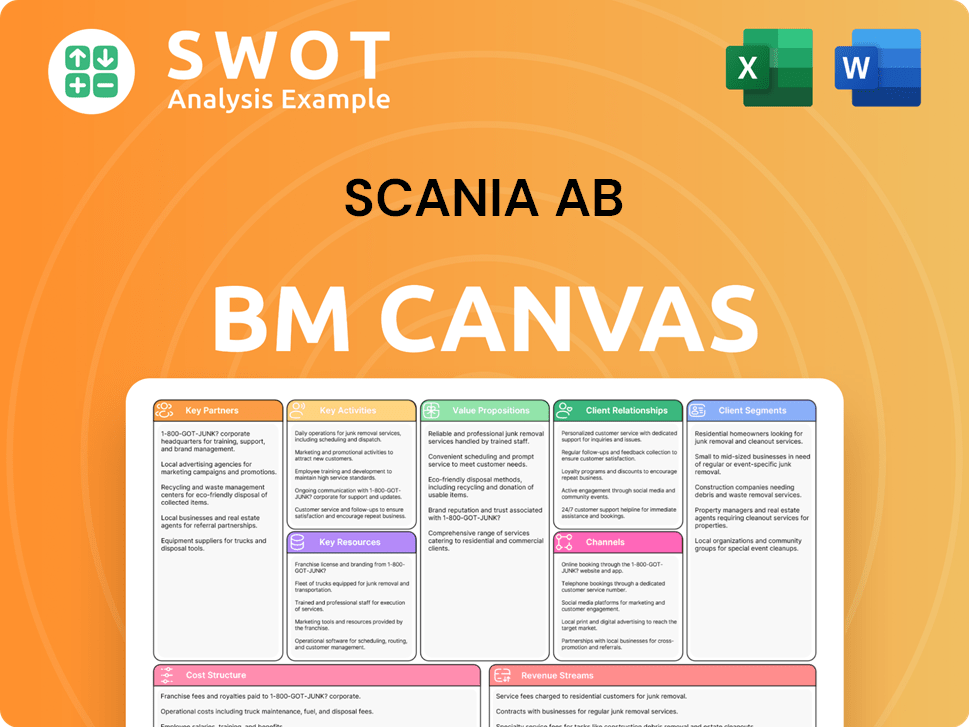
Scania AB Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What is the Timeline of Key Events for Scania AB?
The Scania AB history reflects a journey of innovation and adaptation within the global automotive industry. From its humble beginnings in Sweden, the Scania company has evolved into a leading manufacturer of trucks and buses, known for its engineering excellence and commitment to sustainability. The company's strategic decisions and technological advancements have shaped its trajectory, allowing it to navigate market challenges and capitalize on emerging opportunities. Key moments in the Scania timeline highlight its ability to innovate and adapt to changing market dynamics.
| Year | Key Event |
|---|---|
| 1891 | Vagnfabriks-Aktiebolaget i Södertelge (Vabis) is founded in Södertälje, Sweden. |
| 1902 | Vabis produces its first motor car. |
| 1911 | Vabis merges with Maskinfabriks-Aktiebolaget Scania to form Scania-Vabis. |
| 1923 | Scania-Vabis introduces its first bus chassis. |
| 1936 | The company develops its first diesel engine. |
| 1969 | Scania-Vabis merges with Saab AB, forming Saab-Scania, later becoming simply Scania. |
| 1980s | Scania introduces its revolutionary modular system for trucks and buses. |
| 1995 | Scania is demerged from Saab-Scania and becomes an independent company, Scania AB. |
| 2000s | Increased focus on sustainable transport solutions, including alternative fuels. |
| 2015 | Volkswagen AG acquires full ownership of Scania, making it a wholly-owned subsidiary. |
| 2024 | Scania introduces new battery electric trucks for regional long-haul transport. |
| 2025 | Scania continues to invest significantly in electrification and autonomous driving technologies. |
Scania is heavily investing in the electrification of its vehicle fleet. The company aims for 50% of its sales volume in Europe to be battery electric by 2030. This involves continuous investments in battery technology, charging infrastructure, and the development of a comprehensive electric vehicle ecosystem. Scania's commitment to electric trucks is a key part of its strategy to reduce emissions and promote sustainable transport solutions.
Autonomous driving technologies are a major focus for Scania. The company is actively involved in the development of autonomous transport systems to improve efficiency and safety in logistics. This includes testing and implementing self-driving trucks for various applications. The advancements in AI and automation are pivotal for Scania's long-term growth, and the company is actively integrating these technologies into its products.
Scania is expanding its service offerings and leveraging connectivity for predictive maintenance. This includes providing tailored solutions to optimize fleet management for its customers. By utilizing data and connectivity, Scania aims to enhance the operational efficiency and reduce downtime for its clients. The focus on services is crucial for maintaining customer loyalty and driving revenue growth.
Industry trends such as the increasing demand for sustainable logistics and stricter emissions regulations are shaping Scania's future. The company is adapting to these changes by investing in electric vehicles, alternative fuels, and efficient transport solutions. The regulatory landscape, particularly in Europe, is pushing the adoption of cleaner transport, which aligns with Scania's strategic goals. The Swedish truck manufacturer is well-positioned to benefit from these market shifts.
Scania AB Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What is Competitive Landscape of Scania AB Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Scania AB Company?
- How Does Scania AB Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Scania AB Company?
- What is Brief History of Scania AB Company?
- Who Owns Scania AB Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Scania AB Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.