Skanska Bundle
How Did Skanska Rise to Global Construction Dominance?
Skanska's story is a compelling narrative of innovation and expansion, transforming from a small Swedish concrete manufacturer into a global construction powerhouse. Founded in 1887, the company's commitment to building for the benefit of society has been a constant throughout its Skanska SWOT Analysis. This brief history of Skanska reveals how its early focus on Swedish infrastructure paved the way for its international success. Explore the key milestones that shaped Skanska's journey to becoming a leader in the construction industry.
From its humble beginnings, Skanska's evolution showcases its adaptability and foresight in the ever-changing construction landscape. Understanding the Skanska company background provides valuable insights into its strategic decisions and its ability to undertake complex Skanska projects. This overview of Skanska's history highlights its significant contributions to building development and its enduring impact on the global construction market, including its sustainability initiatives.
What is the Skanska Founding Story?
The Revenue Streams & Business Model of Skanska can be traced back to 1887, marking the inception of Aktiebolaget Skånska Cementgjuteriet in Malmö, Sweden. This marked the beginning of what would become a global construction and development giant. Engineer Rudolf Fredrik Berg was the visionary behind the company, initially focusing on concrete production.
The initial focus was on concrete products, capitalizing on the growing need for durable building materials. The company quickly expanded, evolving into a full-fledged construction firm within a decade. This early transformation set the stage for its future growth and diversification.
The early business model centered on producing and utilizing concrete for various construction needs, playing a pivotal role in developing Sweden's infrastructure. The name 'Skanska' became the official group name in 1984, even though it was already in general use. The company's early financial foundation likely came from bootstrapping and reinvesting early profits, which helped it grow quickly.
Skanska's history began in 1887 in Sweden, founded by Rudolf Fredrik Berg.
- The original focus was on concrete products.
- The company expanded into a comprehensive construction firm within a decade.
- The name 'Skanska' officially became the group's name in 1984.
- Early financial backing came from bootstrapping and reinvestment.
Skanska SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
What Drove the Early Growth of Skanska?
The early growth of the Skanska company was marked by rapid diversification and geographical expansion, setting the stage for its global presence. The company quickly moved beyond its Swedish roots, undertaking international projects and strategic acquisitions. This period saw the company build a strong foundation in both domestic and international markets, significantly impacting the construction industry.
In 1897, Skanska secured its first international order, supplying hollow concrete blocks to the UK. By 1902, the company had established a production facility in St. Petersburg, Russia, to fulfill a contract for concrete pipes. These early projects were key milestones in the Skanska timeline, showcasing its ability to operate internationally.
Domestically, Skanska played a crucial role in building Sweden's infrastructure, including constructing the country's first asphalt-paved road in 1927. These Skanska projects demonstrated the company's commitment to modernizing infrastructure. This work helped establish Skanska's reputation for quality and innovation in construction.
A significant strategic shift occurred in the mid-1950s as Skånska Cementgjuteriet focused on international markets. This expansion included ventures in South America, Africa, and Asia. This period of the Skanska company background highlights its evolving global presence.
In 1964, Skanska's sales surpassed SEK 1 billion, and in 1965, AB Skanska Cementgjuteriet was listed on the Stockholm Stock Exchange. By 2001, international expansion, including acquisitions in Finland, the UK, Norway, Poland, the Czech Republic, and Argentina, propelled Skanska's revenue to SEK 165 billion, with approximately 80,000 employees. This financial performance history reflects the company's growth.
Skanska PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
What are the key Milestones in Skanska history?
The Skanska history is marked by significant achievements and growth in the construction industry. From its early projects to its global presence today, the Skanska company has consistently demonstrated its ability to adapt and innovate within a dynamic market. This Skanska company background showcases the evolution of the firm through various Skanska projects and strategic initiatives.
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 1952 | Introduction of the Allbetong method of prefabricated construction, enhancing efficiency. |
| 1965 | Notable role in the relocation of the Abu Simbel temple in Egypt, showcasing engineering capabilities. |
| 2000 | Became the first global construction company to be environmentally certified to ISO 14000, highlighting sustainability. |
| 2009 | New York headquarters became the first LEED Platinum certified office in the Empire State Building, showing commitment to green building. |
| 2011 | Recognized as the greenest company in the UK, reinforcing environmental leadership. |
| 2024 | Honored with Procore's Groundbreaker Award for Excellence in Innovation, for AI-powered tools. |
Skanska has consistently embraced innovation throughout its history. The company's commitment to sustainability is a key aspect, with early adoption of environmental certifications and later recognition for green practices. More recently, Skanska has integrated advanced technologies, such as AI-powered tools, to improve project management and decision-making.
Introduced in 1952, this prefabricated construction method significantly improved construction efficiency. This innovation allowed for faster project completion and reduced costs, setting a new standard in the industry.
Skanska was the first global construction company to be environmentally certified to ISO 14000 in 2000. This early adoption of environmental standards demonstrated a commitment to sustainable practices, influencing the construction industry.
In 2009, Skanska's New York headquarters achieved LEED Platinum certification. This highlighted the company's dedication to sustainable building practices and environmental responsibility.
In 2024, Skanska was recognized for its innovative use of AI tools like Operational Risk Sidekick and Safety Sidekick. These tools leverage advanced AI models to enhance project insights and decision-making.
Skanska is piloting zero-emissions electric compaction rollers in Los Angeles, showing a commitment to sustainable construction. This initiative marks a step towards reducing the environmental impact of construction equipment.
In 2022, Skanska underwent a rebranding to align with market changes and customer expectations. This included a new logo and the slogan 'Shaping the way we live,' reflecting a focus on the future.
Despite its successes, Skanska has faced challenges, including environmental incidents and the need for strategic restructuring. These experiences led to improved environmental processes and a refined business focus. The company's Skanska timeline demonstrates its ability to overcome obstacles and adapt to changing market conditions.
The environmental incident at Hallandsås in 1997, although a setback, prompted a stronger environmental adaptation process. Skanska used this experience to improve its environmental management practices across all operations.
The early 2000s saw restructuring to increase profitability, including divesting operations in certain regions. This strategic shift allowed Skanska to focus on its core construction services and strengthen its global presence.
Skanska strategically divested non-core operations, such as its shareholding in Piren AB. This move helped the company concentrate on its primary role as a full-scale international construction services provider.
The construction industry faces cyclical market conditions and economic fluctuations. Skanska has had to navigate periods of economic downturns and changing customer demands.
The rapid advancement of technology presents both opportunities and challenges. Skanska must continually invest in new technologies to stay competitive.
Increasing environmental regulations and customer demands for sustainable practices pose challenges. Skanska must continue to innovate and adapt to meet these evolving expectations.
Skanska Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What is the Timeline of Key Events for Skanska?
The Skanska company boasts a rich history, marked by significant milestones that have shaped its global presence and impact on the construction industry. From its humble beginnings in Sweden to its current status as a leading construction and development firm, Skanska's journey is a testament to its adaptability and commitment to innovation. The following table highlights key events in the Skanska history.
| Year | Key Event |
|---|---|
| 1887 | Aktiebolaget Skånska Cementgjuteriet was founded in Malmö, Sweden. |
| 1897 | Skanska secured its first international contract for concrete blocks in the UK. |
| 1954 | The company made its first investment in commercial property development with the Spinneriet district in Malmö. |
| 1965 | Skanska was listed on the Stockholm Stock Exchange A-list. |
| 1971 | Entry into the United States market began with subway projects in New York and Washington D.C. |
| 1984 | The company officially changed its name to Skanska. |
| 1995 | Skanska won the contract for the Oresund Bridge, a major Nordic infrastructure project. |
| 2000 | The construction division of Kvaerner was acquired, significantly expanding Skanska's global presence, and it became the first global construction company to be environmentally certified to ISO 14000. |
| 2007 | Integration and rebranding of acquired U.S. entities began under the Skanska USA banners. |
| 2009 | Skanska’s New York headquarters became the first LEED Platinum certified office in the Empire State Building. |
| 2010 | Skanska completed MetLife Stadium in the U.S. |
| 2011 | The company was ranked the greenest company in the UK by The Sunday Times. |
| 2022 | Skanska underwent a significant brand renewal, introducing a new visual identity and the slogan 'Shaping the way we live.' |
| 2024 | Skanska was recognized as a 'Climate Leader in Europe' by the Financial Times for the third consecutive year. |
| 2025 | Expected completion of a $75 million healthcare facility in the Northwestern United States. |
The U.S. market is expected to remain Skanska's primary growth engine, driven by infrastructure and data center projects. The company is actively developing two data centers, one in Virginia and another in Georgia, with expected completion early in 2025, and a project in Arizona scheduled for 2026. This strategic focus highlights the company's commitment to high-growth sectors.
In Europe, civil projects are anticipated to remain stable, while residential and commercial building markets may experience a slow recovery. Skanska is adapting to these conditions, focusing on sustainable solutions and diversifying into life sciences and multi-family rental housing. Recent projects include OZMA (Washington, DC) and Heming (McLean, VA) and Kaye (Boston) under development.
Skanska is committed to sustainable and climate-resilient solutions, aiming for net-zero carbon emissions by 2045. This commitment is a core part of their strategy, reflecting the growing importance of environmental responsibility in the construction industry. The company's recognition as a Climate Leader in Europe underscores its dedication.
Digital transformation, including leveraging generative AI and machine learning, is critical for Skanska's future, improving decision-making and efficiency. This focus on technology allows the company to optimize its operations and maintain a competitive edge. Skanska is investing in innovative technologies to stay ahead.
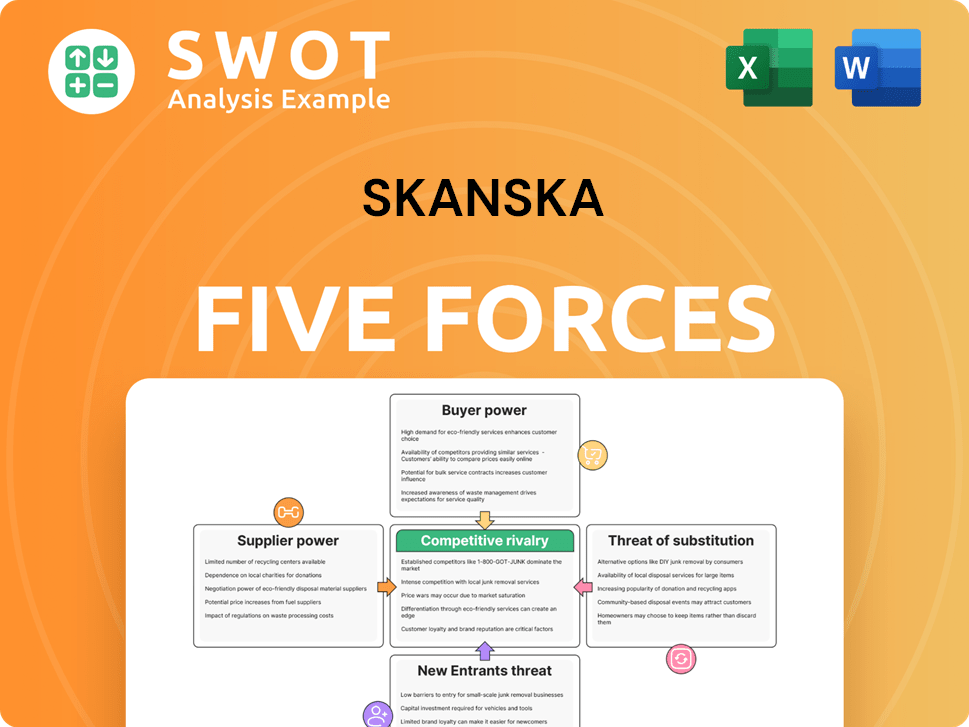
Skanska Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What is Competitive Landscape of Skanska Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Skanska Company?
- How Does Skanska Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Skanska Company?
- What is Brief History of Skanska Company?
- Who Owns Skanska Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Skanska Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.