Tata Steel Bundle
How did Tata Steel rise to become a global steel powerhouse?
From its inception in 1907, Tata Steel SWOT Analysis has been a story of ambition and transformation. Witness the remarkable journey of Tata Steel, a company that began in colonial India with a vision to industrialize the nation. Discover how this Indian steel pioneer evolved from a local enterprise into a multinational giant, leaving an indelible mark on the global steel industry.
The Tata Steel history showcases the Tata Group's commitment to nation-building, a principle that has driven its expansion and innovation. Founded by Jamsetji Nusserwanji Tata, the company's roots in Jamshedpur laid the groundwork for the Indian steel industry's growth. Today, Tata Steel stands as a testament to strategic vision and resilience, constantly adapting to the challenges and opportunities of the global market.
What is the Tata Steel Founding Story?
The story of Tata Steel, initially known as Tata Iron and Steel Company (TISCO), began on August 26, 1907. It was the brainchild of Jamsetji Nusserwanji Tata, a visionary who saw the potential for India's industrial growth. His goal was to establish a strong, self-sufficient steel industry within India, reducing the nation's reliance on imported steel.
Jamsetji, already a successful entrepreneur, understood the need for a domestic steel industry. His vision was to use India's natural resources to create a steel manufacturing base. This initiative was particularly important because, at the time, India depended heavily on foreign steel. This dependence slowed down infrastructure development and industrial progress.
The initial plan was to create a vertically integrated business. This meant that the company would handle everything from getting raw materials to producing finished steel products. The first products were pig iron and steel. The location of the plant was carefully chosen after extensive geological surveys. The site near the Subarnarekha and Kharkai rivers in present-day Jharkhand was selected because of its rich iron ore deposits, access to water, and proximity to coalfields. This location eventually developed into the city of Jamshedpur, named in honor of the founder.
The early days of Tata Steel were marked by a strong sense of Indian nationalism and a desire for economic independence. The company's creation was influenced by this growing nationalistic spirit.
- Funding came from Jamsetji Tata's personal wealth, Indian philanthropists, and public subscriptions.
- This made it a truly Indian enterprise from the start.
- Jamsetji's determination was crucial, even with skepticism from British authorities.
- The company faced many challenges in establishing such a large-scale industrial project in India.
The initial funding for TISCO came from a mix of sources. These included Jamsetji Tata's personal wealth, contributions from Indian philanthropists, and public subscriptions. This approach showed a unique blend of entrepreneurial spirit and nationalist fervor. The cultural and economic situation in India in the early 1900s, with its growing sense of nationalism and the wish for economic independence, greatly influenced the company's creation. Jamsetji's strong determination, even when facing doubts from British officials, was key to overcoming the many challenges of starting such a big industrial project in India. You can learn more about the company's business model and revenue streams by reading Revenue Streams & Business Model of Tata Steel.
Tata Steel SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
What Drove the Early Growth of Tata Steel?
Following its establishment, Tata Steel experienced considerable early growth and expansion. The first steel ingot rolled out in 1912, marking a key moment in India's industrial development. This initial success led to the launch of various steel products, catering to India's growing need for infrastructure. Early major clients included the Indian Railways, a significant consumer of steel for tracks and rolling stock, and various construction projects across the subcontinent.
The company's early growth emphasized increasing production capacity and diversifying its product portfolio. In the 1920s and 1930s, Tata Steel began producing a wider range of steel products, including rails, plates, and structural steel, strengthening its position in the Indian market. Early forays into new product categories were driven by market needs and technological advancements. The leadership remained within the Tata family or trusted associates, ensuring continuity of vision and strategic direction.
A significant milestone was the consistent reinvestment of profits to enhance and modernize facilities. This strategy enabled continuous technological upgrades and capacity expansion, crucial for maintaining a competitive edge. The market reception to Tata Steel's products was largely positive, driven by the quality of its steel and patriotic sentiment. The competitive landscape was less intense domestically, but the company faced indirect competition from imported steel.
Early major clients included the Indian Railways, which was a significant consumer of steel for tracks and rolling stock. The Jamshedpur facility became a hub of industrial activity. The company's initial team expanded steadily as operations scaled up, and the Jamshedpur facility became a hub of industrial activity. These early partnerships were crucial for establishing Tata Steel as a key player in the Indian steel market.
Tata Steel's commitment to quality and its strategic location provided it with a distinct advantage. By the mid-20th century, Tata Steel had firmly established itself as India's premier steel producer, laying the groundwork for its eventual global expansion. The company's growth efforts during this period were instrumental in shaping its trajectory, demonstrating a consistent focus on self-reliance and industrial leadership within India.
Tata Steel PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
What are the key Milestones in Tata Steel history?
The Tata Steel story is marked by significant milestones, reflecting its growth and impact on the steel industry. From its beginnings in India to its global expansion, the company has consistently adapted to changing market dynamics. The Tata Group's commitment to innovation and social responsibility has been a constant throughout its history, shaping its identity and influence.
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 1907 | Tata Steel was founded by Jamsetji N. Tata, establishing India's first integrated steel plant in Jamshedpur. |
| 1912 | Production of steel commenced at the Jamshedpur plant, marking a significant step for the Indian steel industry. |
| 1945 | Tata Steel became a public company, opening its ownership to a wider base of investors. |
| 1950s-1960s | The company expanded its production capacity to meet the growing demand in post-independence India. |
| 2007 | Tata Steel acquired the Corus Group for approximately $12.04 billion, significantly expanding its global footprint. |
| 2018 | Tata Steel announced a major restructuring plan to streamline its European operations, reflecting changing market conditions. |
| 2021 | Tata Steel announced a commitment to reduce its carbon emissions by 30% by 2030. |
Tata Steel has consistently focused on technological advancements in steel manufacturing. This includes developing new grades of steel and improving production processes to enhance efficiency and product quality. The company's research and development efforts have led to innovations that have benefited various industries.
Tata Steel was among the first to adopt advanced steelmaking technologies, enhancing its production capabilities. This early embrace of technology helped improve efficiency and product quality.
The company has consistently invested in research to develop specialized steel grades. These innovations have been tailored to meet the specific needs of various industries, including automotive and construction.
Tata Steel has focused on optimizing its manufacturing processes. This has led to increased efficiency and reduced production costs, enhancing its competitiveness.
Tata Steel is investing in digital technologies to improve its operations. This includes the use of data analytics and automation to improve decision-making and streamline processes.
Tata Steel is implementing sustainable practices to reduce its environmental impact. This includes investing in cleaner production methods and exploring alternative energy sources.
Tata Steel has collaborated with technology providers to enhance its capabilities. These partnerships have helped the company adopt cutting-edge technologies.
Tata Steel has faced numerous challenges, including economic downturns and intense competition. The company has addressed these issues through strategic restructuring and operational improvements. The acquisition of Corus Group, while a major achievement, also presented integration hurdles and market volatility.
Fluctuations in global steel prices and demand have significantly impacted Tata Steel's profitability. The company has had to adapt to changing market conditions to remain competitive.
The steel industry is highly competitive, with both domestic and international players vying for market share. Tata Steel has responded by focusing on innovation and cost optimization.
The acquisition of Corus Group brought integration challenges, including aligning different operational cultures and managing a larger, more diverse business. These challenges required significant restructuring efforts.
Global economic recessions and periods of low steel demand have affected Tata Steel's financial performance. The company has had to implement cost-cutting measures and adapt its strategies.
Tata Steel has focused on improving operational efficiency to reduce costs and enhance productivity. This includes streamlining processes and investing in new technologies.
Tata Steel has faced labor disputes at various times, which have disrupted operations and impacted production. The company has worked to maintain positive labor relations.
Tata Steel Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What is the Timeline of Key Events for Tata Steel?
The Tata Steel history is a story of pioneering spirit and industrial growth, beginning in the early 20th century and evolving into a global steel giant. The company's journey reflects the development of the Indian steel industry and its significant contributions to the national economy. From its inception in Jamshedpur to its global expansions, Tata Steel has consistently adapted and innovated, making it a key player in the worldwide steel market.
| Year | Key Event |
|---|---|
| 1907 | Tata Steel, originally known as Tata Iron and Steel Company (TISCO), was founded by Jamsetji Tata in Jamshedpur. |
| 1912 | The first steel ingot was produced, marking the beginning of steel production in India. |
| 1945 | TISCO became a public company, expanding its ownership and reach. |
| 1950s-1960s | Tata Steel expanded its production capacity and modernized its facilities to meet the growing demand for steel in India. |
| 1990s | The company began its global expansion, acquiring assets and establishing a presence in international markets. |
| 2007 | Tata Steel acquired Corus Group, a major European steel producer, significantly increasing its global footprint. |
| 2016 | Tata Steel sold its Long Products Europe business to Greybull Capital LLP. |
| 2020 | Tata Steel announced a restructuring plan to streamline its European operations. |
Tata Steel continues to be a significant player in the global steel market. The company is focusing on expanding its presence in high-growth markets. Recent investments and acquisitions are aimed at increasing its production capacity and improving its product portfolio. The company is also investing in sustainable steel production methods.
Tata Steel is investing heavily in technological advancements to improve efficiency and reduce environmental impact. This includes the implementation of smart manufacturing processes and the adoption of digital technologies. The company is also exploring new methods of steel production, such as hydrogen-based steelmaking, to reduce carbon emissions. These advancements are crucial for maintaining competitiveness.
Sustainability is a major focus for Tata Steel, with initiatives aimed at reducing its carbon footprint and promoting environmental responsibility. The company is committed to reducing its greenhouse gas emissions by investing in renewable energy sources. It is also focused on circular economy principles and waste reduction. These efforts are aligned with global sustainability goals.
Tata Steel's financial performance in recent years has been influenced by market conditions and strategic decisions. The company's revenue in fiscal year 2024 was approximately $30 billion. The company is expected to maintain a stable financial outlook, with a focus on cost optimization and strategic investments. The company anticipates a positive outlook for the steel industry in the long term.
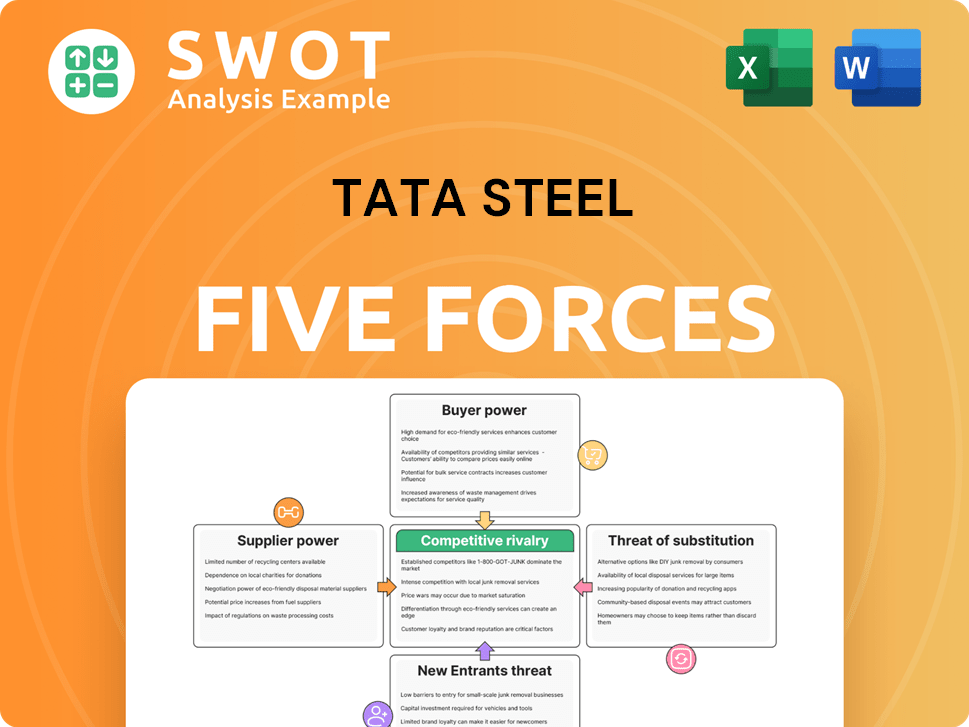
Tata Steel Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What is Competitive Landscape of Tata Steel Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Tata Steel Company?
- How Does Tata Steel Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Tata Steel Company?
- What is Brief History of Tata Steel Company?
- Who Owns Tata Steel Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Tata Steel Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.