Teradata Bundle
How Did Teradata Revolutionize Data Analytics?
Born in 1979 in California, Teradata SWOT Analysis emerged as a visionary database company, aiming to conquer the burgeoning realm of big data. Their initial goal? To build a "database computer" capable of managing an unprecedented terabyte of information, a groundbreaking feat in the mainframe era. This bold ambition set the stage for Teradata's enduring legacy in the world of data warehousing and analytics.

From its origins, Teradata, a pivotal player in the Teradata corporation, has consistently adapted to the evolving landscape of data management. Its early innovations in parallel processing with microprocessors laid the groundwork for its current status as a leader in hybrid multi-cloud analytics. As we delve into the brief history of Teradata, we'll uncover the key milestones, strategic pivots, and technological advancements that have defined this influential data warehousing pioneer. With a strong financial performance in Q1 2025, Teradata's journey is a testament to the power of innovation and adaptability in the data-driven world.
What is the Teradata Founding Story?
The story of the Teradata company began with a vision to revolutionize data management. Incorporated on July 13, 1979, in Brentwood, California, the company emerged from a confluence of research and expertise. The founders aimed to create a database system capable of handling massive amounts of data, a concept that would define the company's future.
Teradata's founders identified a critical need for a system that could process data in parallel using multiple microprocessors. This innovative approach was designed specifically for decision support, setting the stage for the company's focus on data warehousing. The company's name itself, derived from the term 'terabytes,' reflected its ambitious goal to manage trillions of bytes of data.
The initial business model centered on developing and selling a specialized database computer. Their first product, the DBC/1012 database machine, was released in 1984. This product quickly gained recognition, marking a significant milestone in the company's early years. The company's early success was supported by initial funding rounds, which enabled the company to hire its research and development team.
Teradata's founding was marked by several key milestones that shaped its early trajectory.
- July 13, 1979: Teradata Corporation was incorporated in Brentwood, California.
- March 1980: A seed round of $150,000 was secured to facilitate design and patent work.
- July 1980: A venture capital round raised $2.5 million, enabling the hiring of a research and development team.
- 1984: The DBC/1012 database machine was released.
- 1986: Fortune magazine named the DBC/1012 'Product of the Year'.
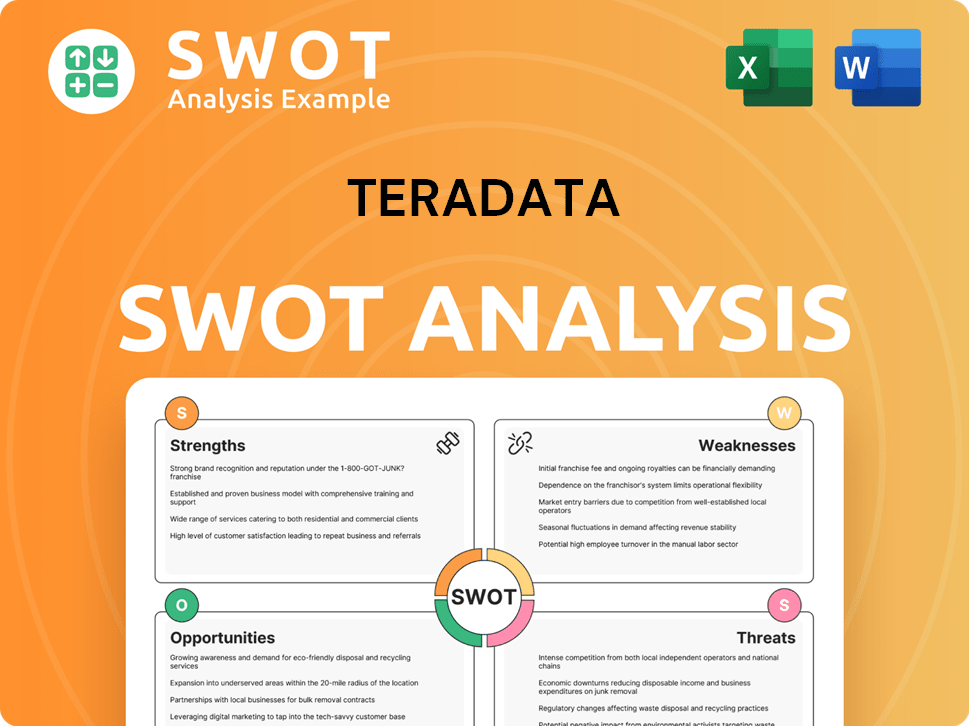
Teradata SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
What Drove the Early Growth of Teradata?
The early years of the Teradata company were crucial in establishing its foothold in the data management sector. Following the introduction of its DBC/1012 database machine in 1984, the Teradata corporation went public in 1987. A significant milestone was achieved in 1992 when Teradata built the first system exceeding one terabyte for Wal-Mart, showcasing its ability to handle massive datasets.
Teradata's initial public offering in 1987 marked a pivotal moment in its journey. The company's focus on data warehousing and database solutions quickly gained traction. This early success set the stage for future expansion and technological advancements within the database company landscape.
In September 1991, AT&T Corporation acquired NCR Corporation, which then acquired Teradata for approximately $250 million in December 1991. This acquisition led to Teradata's integration into NCR in January 1992, becoming a division of AT&T GIS. This strategic move significantly influenced Teradata's growth.
As part of NCR, Teradata expanded its market reach, becoming a world leader in scalable data warehouse solutions by 1997. This period saw significant advancements in data warehousing technology, solidifying Teradata's position in the market. This expansion was key to establishing Teradata's reputation.
The acquisition of Strategic Technologies & Systems in 1999 and Ceres Integrated Solutions in 2000 further broadened Teradata's offerings. In January 2007, NCR announced Teradata would become an independent public company, with Michael F. Koehler as CEO. This transition marked a new chapter for the Teradata company. To learn more about the company's values, read Mission, Vision & Core Values of Teradata.
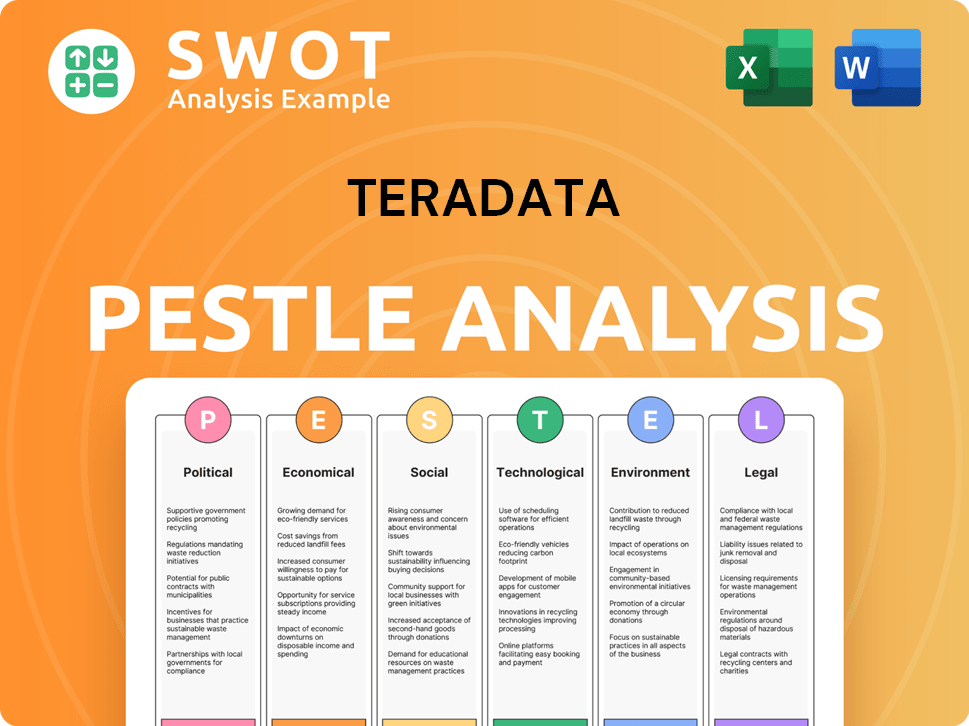
Teradata PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
What are the key Milestones in Teradata history?
The Teradata history is marked by significant milestones in the data warehousing and database company landscape. From its early innovations to its strategic expansions and adaptations, Teradata has consistently evolved to meet the changing demands of the market.
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 1984 | Released the DBC/1012 database machine. |
| 1986 | The DBC/1012 was recognized as 'Product of the Year' by Fortune magazine. |
| 1992 | Built the first system over 1 terabyte for Wal-Mart. |
| 1997 | Recognized as the world leader in scalable data warehouse solutions. |
| 2002 | Released Teradata version V2R5. |
| 2006 | Introduced the Teradata Master Data Management solution. |
| 2007 | Spun off from NCR. |
| 2008-2012 | Made several acquisitions, including Claraview, Kickfire, Aprimo, Aster Data Systems, and eCircle. |
| 2016 | Launched IntelliFlex, a new hardware product line. |
| 2024 | Launched VantageCloud Lake on Google Cloud in June. |
| 2025 | Introduced the Enterprise Vector Store in March. |
Teradata's innovation journey is highlighted by its pioneering work in data warehousing, with the release of the DBC/1012 machine being a pivotal moment. The company has consistently expanded its offerings, integrating AI capabilities and cloud solutions, such as the Enterprise Vector Store and VantageCloud Lake, to stay ahead in the industry.
The DBC/1012 was a groundbreaking innovation that set the stage for Teradata's future in data warehousing.
Building the first system over 1 terabyte for Wal-Mart demonstrated Teradata's ability to handle massive datasets.
This solution enhanced Teradata's capabilities for managing and deploying large data warehouse applications.
The launch of IntelliFlex marked a significant hardware advancement for the company.
The launch of VantageCloud Lake on Google Cloud in June 2024, expanded cloud offerings.
Introduced in March 2025, it enhances AI capabilities by unifying structured and unstructured data.
Teradata has faced challenges in navigating market downturns and competitive pressures, requiring strategic pivots. The company's transformation to a cloud-first model has been a significant undertaking, reflected in its financial performance.
Teradata has had to navigate economic challenges that impacted its market position.
The company has faced competition from other database company and data warehousing providers.
This strategic shift involved significant investments and adjustments to the business model.
In Q1 2025, despite a 10% year-over-year decline in total revenue to $418 million, non-GAAP diluted EPS increased by 16% to $0.66.
Public cloud ARR increased by 16% year-over-year in constant currency to $606 million in Q1 2025, indicating strong growth in this area.
Teradata was recognized as a 'Visionary' in the 2024 Gartner Magic Quadrant and a 'Leader' in The Forrester Wave™: Data Management for Analytics Platforms, Q2 2025.
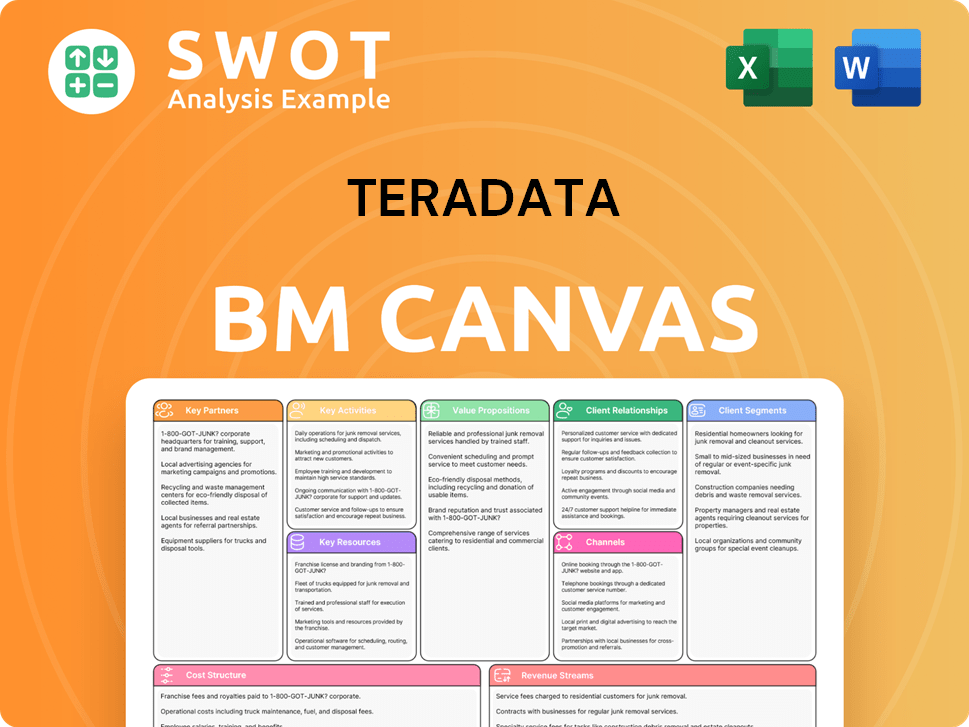
Teradata Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What is the Timeline of Key Events for Teradata?
The Teradata company, a prominent database company, has a rich history marked by technological innovation and strategic shifts. Founded in 1979 in Brentwood, California, the company quickly established itself in the data warehousing space. Over the years, it has evolved from a pioneer in database machines to a leader in hybrid AI solutions, adapting to the changing demands of the data-driven world.
| Year | Key Event |
|---|---|
| 1979 | Teradata corporation was incorporated in Brentwood, California. |
| 1984 | Released its first product, the DBC/1012 database machine. |
| 1986 | Fortune magazine named DBC/1012 'Product of the Year.' |
| 1987 | Teradata went public with its first stock offering. |
| 1991 | Acquired by NCR Corporation, which was subsequently acquired by AT&T. |
| 1992 | Built the first system over 1 terabyte for Wal-Mart. |
| 1997 | Became the world leader in scalable data warehouse solutions as part of NCR. |
| 2007 | Spun off from NCR to become an independent public company. |
| 2010 | Acquired Aprimo for approximately $550 million. |
| 2011 | Acquired Aster Data Systems for about $263 million. |
| 2016 | Announced the IntelliFlex hardware product line. |
| 2024 (June) | Launched VantageCloud Lake on Google Cloud. |
| 2025 (March) | Introduced the Enterprise Vector Store. |
| 2025 (May) | Reported Q1 2025 public cloud ARR of $606 million, a 16% year-on-year increase. |
The company is prioritizing a cloud-first strategy, focusing on profitable growth in the cloud computing market. This involves expanding its cloud offerings and enhancing its capabilities to meet the growing demand for cloud-based data solutions. The company's Q1 2025 public cloud ARR reached $606 million, demonstrating significant growth.
Teradata is positioning itself as a leader in hybrid AI solutions, integrating AI capabilities into its data platform to provide advanced analytics and insights. This approach aims to help customers leverage generative AI and other AI technologies. Upcoming innovations in 2025 are designed to extend hybrid AI environments.
The company expects continued growth in 2025. Public cloud ARR is projected to grow between 14% and 18% year-over-year. Total ARR growth is expected to range from flat to 2%. Non-GAAP diluted earnings per share are projected to be between $2.15 and $2.25 for the year.
Teradata's long-term vision centers around an 'Integrated Data Plane,' which aims to provide a seamless experience for users by abstracting away infrastructure complexity. This approach aligns with the company's founding vision of enabling confident decision-making and innovation through effective data management and analysis.
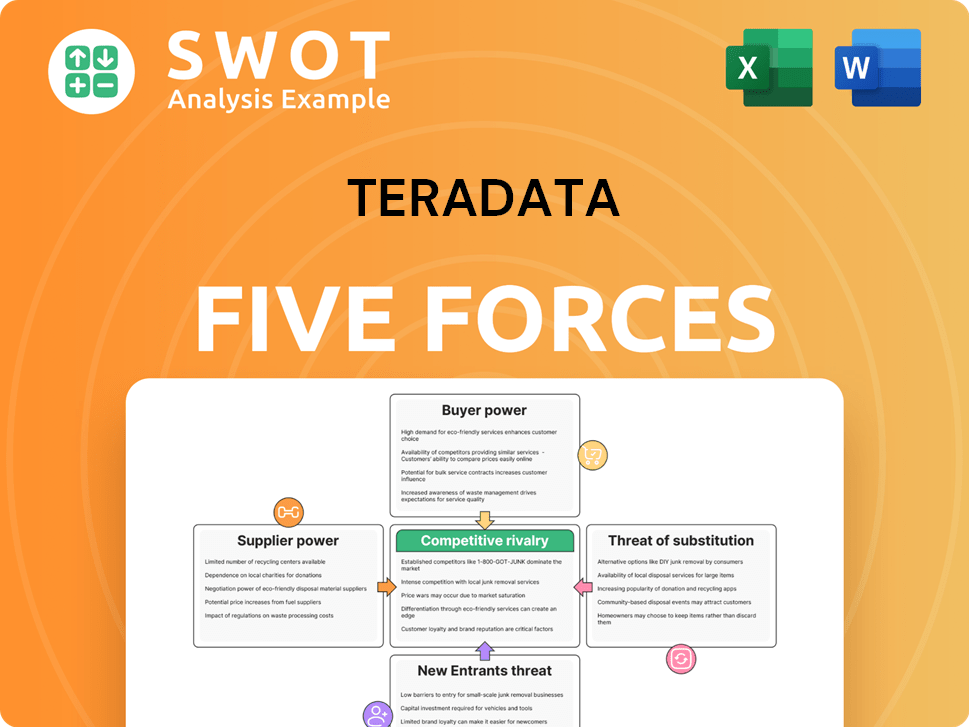
Teradata Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What is Competitive Landscape of Teradata Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Teradata Company?
- How Does Teradata Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Teradata Company?
- What is Brief History of Teradata Company?
- Who Owns Teradata Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Teradata Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.