Western Digital Bundle
How did Western Digital become a data storage giant?
From its humble beginnings as a semiconductor manufacturer in 1970, Western Digital has transformed into a global leader in data storage. This journey, marked by innovation and strategic adaptation, showcases a remarkable evolution. What began as a vision for integrated circuits has blossomed into a dominant force in the digital world, offering crucial infrastructure for our data-driven society.
Initially focused on semiconductors, the Western Digital SWOT Analysis reveals how the company strategically shifted its focus. The company's early vision, spearheaded by founder Alvin B. Phillips, laid the groundwork for its future dominance as a hard drive manufacturer. Today, Western Digital's market capitalization of approximately $25 billion reflects its significant impact and influence on the tech industry, making its WD history a compelling story of growth and resilience.
What is the Western Digital Founding Story?
The story of Western Digital (WD) begins on April 23, 1970. It was founded by Alvin B. Phillips, a former General Electric employee. Phillips, with his expertise in semiconductor technology, saw an opportunity in the growing market for integrated circuits, especially for calculator chips.
The company's initial focus was on manufacturing these specialized semiconductors. Western Digital aimed to become a major supplier of calculator chips, a rapidly expanding market at the time. The early funding came from venture capital firms and private investors, reflecting confidence in Phillips' vision and the potential of the semiconductor industry. The company's first products were integrated circuits, essential components for early electronic devices.
The late 1960s and early 1970s were a time of rapid advancements in electronics and increasing demand for computing power, which significantly influenced Western Digital's creation and initial direction. This period saw the rise of many semiconductor companies, all trying to capitalize on the technological revolution. Understanding the WD history is key to appreciating its evolution.
Western Digital's founding was driven by the burgeoning semiconductor market.
- Founded on April 23, 1970, by Alvin B. Phillips.
- Initially focused on manufacturing integrated circuits for calculators.
- Funded by venture capital and private investors.
- Operated during a period of rapid technological advancement in electronics.
Western Digital SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
What Drove the Early Growth of Western Digital?
The early growth of Western Digital, or WD, saw a shift from semiconductors to storage solutions. Initially, the company produced chips, but the mid-1970s marked a pivotal change towards data storage, driven by the rise of personal computers. This transition established WD's presence in the storage market, setting the stage for future expansion.
WD started by manufacturing semiconductors, including chips for calculators. This early focus provided a foundation for understanding electronic components. The company's initial products, though not storage-related, were crucial for establishing its manufacturing capabilities and technical expertise. These early ventures set the stage for the company's later innovations in storage technology.
The mid-1970s saw a strategic pivot towards storage products. The introduction of the FD1771 floppy disk controller in 1976 was a key moment. This product firmly established WD in the storage market, moving away from its initial focus on general-purpose semiconductors. This move was vital in shaping WD's future as a leading hard drive manufacturer.
Throughout the late 1970s and 1980s, WD expanded its product line to include hard disk drive controllers and complete hard disk drives. The acquisition of Tandon Corporation's hard drive manufacturing operations in 1988 was a significant step. This acquisition significantly boosted WD's manufacturing capabilities and market share, allowing WD to become a vertically integrated manufacturer.
WD expanded its global presence, establishing manufacturing facilities and sales offices worldwide. Leadership transitions played a role in guiding the company through rapid expansion and technological changes. The company navigated a competitive landscape, focusing on high-performance and reliable storage solutions. For more insights, see the Growth Strategy of Western Digital.
Western Digital PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
What are the key Milestones in Western Digital history?
The history of Western Digital (WD) is marked by significant milestones that have shaped the data storage industry. From its early days as a manufacturer of integrated circuits to its current status as a leading provider of storage solutions, WD has consistently adapted and innovated. The company's journey includes pivotal moments that have defined its trajectory and solidified its position in the market. To understand the evolution of Western Digital, exploring its key milestones is essential.
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 1970 | Founded as General Digital, later renamed Western Digital. |
| Early 1980s | Entered the hard drive market, marking a significant shift in focus. |
| Early 1990s | Introduced the Caviar series of hard drives, which gained popularity for personal computers. |
| 2000s | Expanded into the enterprise storage market, offering high-capacity drives for data centers. |
| 2016 | Acquired SanDisk for approximately $19 billion, strengthening its position in the NAND flash memory market. |
| 2020 | Announced strategic partnerships and investments to advance data storage technologies. |
Throughout its history, Western Digital has been at the forefront of storage technology, consistently pushing the boundaries of what's possible. The company's commitment to innovation has led to numerous advancements in hard drive technology, solid-state drives (SSDs), and overall storage solutions. This dedication to innovation has not only improved its products but also significantly influenced the broader computing landscape.
The Caviar series of hard drives revolutionized personal computing by offering reliable and high-performance storage solutions. These drives became a staple in PCs, significantly boosting Western Digital's market presence.
WD has secured numerous patents for advancements in magnetic recording technology, increasing storage density and data access speeds. These innovations have been critical to the evolution of hard drives and overall storage capabilities.
The company's strategic move into the enterprise storage market provided high-capacity and high-performance drives for data centers. This expansion allowed WD to capitalize on the growing demand for robust storage solutions in business environments.
WD's acquisition of SanDisk in 2016 provided a strong foothold in the NAND flash memory market, crucial for SSD production. This strategic move enabled WD to diversify its product offerings and meet the increasing demand for faster storage solutions.
WD has consistently innovated in data storage architectures, improving data management and access efficiency. These advancements have helped optimize storage performance and reliability across various product lines.
WD has expanded its offerings to include cloud storage solutions, catering to the growing need for accessible and scalable data storage. This expansion reflects the company's adaptation to the evolving storage landscape.
Despite its successes, Western Digital has faced several challenges that have tested its resilience and strategic agility. These challenges have included economic downturns, supply chain disruptions, and the rapid evolution of storage technologies. The ability to overcome these obstacles has been crucial to WD's long-term success and market position. For more information about the people who have shaped the company, you can read about Owners & Shareholders of Western Digital.
The devastating floods in Thailand in 2011 severely impacted WD's manufacturing operations, leading to supply chain disruptions and financial setbacks. Despite the challenges, WD quickly recovered and rebuilt its production capabilities.
The ongoing shift from traditional HDDs to Solid State Drives (SSDs) has presented a significant challenge. WD addressed this by acquiring SanDisk, which provided a strong foothold in the NAND flash memory market.
WD has consistently faced intense competition from other major players in the storage industry. To maintain its market share, WD has focused on innovation, strategic acquisitions, and cost-effective production.
Economic downturns have impacted the demand for storage solutions, affecting WD's financial performance. WD has adapted by diversifying its product offerings and managing its operational costs to mitigate the effects of economic fluctuations.
Rapid technological advancements have required WD to continuously innovate and adapt. WD has invested heavily in research and development to stay at the forefront of data storage innovation and maintain its competitive edge.
Global supply chain issues, including those exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic, have impacted WD's production and distribution capabilities. WD has worked to diversify its supply chain and improve its resilience to external shocks.
Western Digital Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What is the Timeline of Key Events for Western Digital?
The journey of the Western Digital company, or WD, is marked by several key milestones, from its origins in semiconductor manufacturing to its current position as a leading storage solutions provider. The company's evolution includes strategic acquisitions, technological innovations, and adaptations to market changes. This WD history reflects its growth and impact on the computing industry.
| Year | Key Event |
|---|---|
| 1970 | Founded as Western Digital Corporation, initially focusing on semiconductor devices. |
| 1976 | Introduced the FD1771, the first single-chip floppy disk controller. |
| 1988 | Entered the hard drive manufacturer market by acquiring Tandon Corporation's hard drive manufacturing operations. |
| 1991 | Launched the Caviar series of hard drives, becoming a prominent player in the PC market. |
| 2001 | Shifted focus from desktop HDDs to enterprise and consumer electronics. |
| 2011 | Acquired Hitachi Global Storage Technologies (HGST) for approximately $4.8 billion, significantly expanding its HDD market share. |
| 2016 | Acquired SanDisk for approximately $19 billion, entering the NAND flash and SSD market. |
| 2020 | Celebrated its 50th anniversary, continuing to innovate in data storage. |
| 2023-2024 | Explored potential separation of its HDD and Flash businesses to unlock shareholder value. |
Western Digital is well-positioned to capitalize on the increasing demand for data storage, driven by AI, cloud computing, and the Internet of Things. The company's strategic initiatives include optimizing its product portfolio and enhancing its flash and HDD technologies. For example, in early 2024, WD was exploring a merger of its flash business with Kioxia, potentially reshaping the NAND flash market.
Analysts predict continued growth in the data storage market, with Western Digital expected to maintain its strong position through continuous innovation. The company's focus includes high-capacity HDDs and advanced SSD solutions. WD's leadership is committed to delivering differentiated products to meet the evolving needs of its diverse customer base. For more insights, check out the Marketing Strategy of Western Digital.
Western Digital continues to invest in research and development to improve its storage technologies. This includes advancements in both HDD and SSD technologies to meet the growing demands of data-intensive applications. The company's commitment to innovation is a key factor in its ability to remain competitive in the market.
The potential separation of its HDD and Flash businesses is a strategic move to unlock shareholder value. This restructuring could allow each business unit to focus on its specific market dynamics and growth opportunities. The company's financial performance in 2024 will likely reflect these strategic decisions and market conditions.
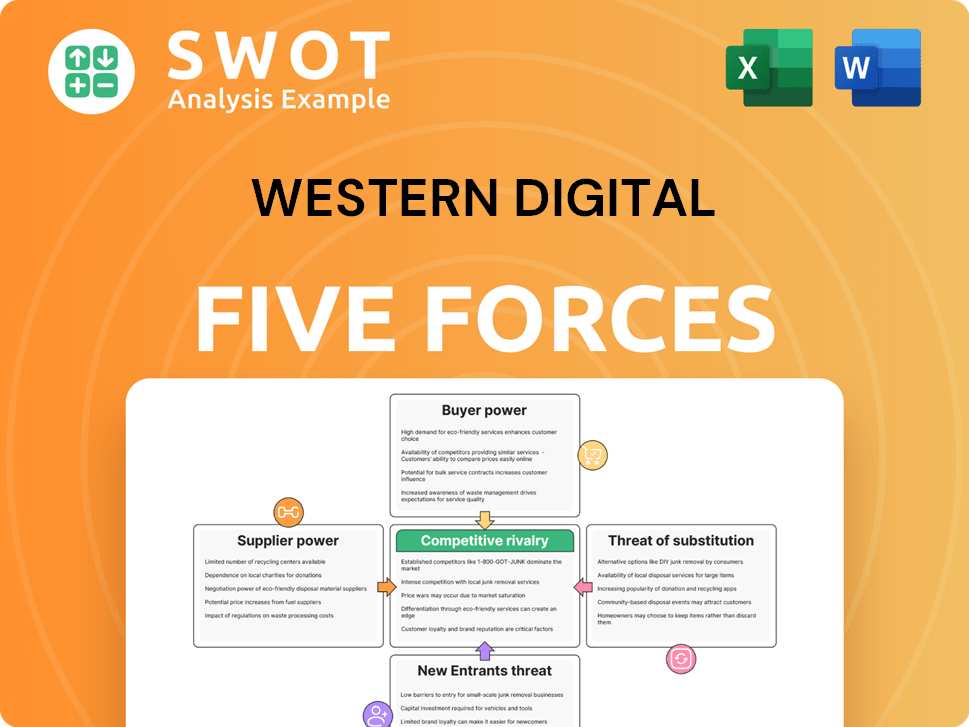
Western Digital Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What is Competitive Landscape of Western Digital Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Western Digital Company?
- How Does Western Digital Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Western Digital Company?
- What is Brief History of Western Digital Company?
- Who Owns Western Digital Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Western Digital Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.