Costco Wholesale Bundle
How Does Costco Dominate the Retail Battlefield?
Costco Wholesale, a retail behemoth, has carved a unique niche in the competitive landscape. Its success hinges on a membership-based model offering unparalleled value, attracting a loyal customer base. This deep dive will dissect the Costco Wholesale SWOT Analysis, unraveling its core strengths and how it navigates the ever-evolving demands of the wholesale market.

Understanding Costco's competition is crucial for investors and business strategists alike. This analysis will explore Costco's main rivals, providing a comprehensive Costco market analysis and assessing its competitive advantages. We'll examine how Costco's pricing strategy and membership model impact its ability to compete within the retail industry, offering insights into the future of Costco's competitive landscape and how it deals with its competitors.
Where Does Costco Wholesale’ Stand in the Current Market?
Costco Wholesale Corporation's core operations center around a membership-based warehouse club model, offering a wide array of products at competitive prices. This approach, targeting both individual consumers and small businesses, is a key element of its market position. The company's value proposition emphasizes low prices, bulk quantities, and a curated selection of merchandise, including groceries, electronics, and apparel, which drives customer loyalty and repeat business.
The company's financial performance underscores its market strength. In fiscal year 2023, Costco reported net sales of $237.7 billion, demonstrating its substantial scale within the retail industry. Costco's business model analysis reveals a focus on high sales volume and efficient operations to maintain profitability while offering value to its members. The Owners & Shareholders of Costco Wholesale benefit from this strategy, which is reflected in strong financial metrics.
Costco's global presence, with warehouses across North America, Europe, Asia, and Australia, further solidifies its market position. This international footprint allows the company to diversify its revenue streams and adapt to various consumer preferences. The company's extensive geographic reach and diversified customer base contribute to its resilience in the competitive landscape.
Costco's competitive advantages include its membership model, which fosters customer loyalty and provides recurring revenue. The company's pricing strategy, offering products at low prices, attracts a large customer base. Costco's efficient supply chain and operational excellence contribute to its profitability and ability to compete effectively.
Costco's weaknesses include its reliance on a membership model, which can limit accessibility for some consumers. Its limited product selection compared to broader retailers is another potential challenge. The company's international expansion faces challenges related to adapting to local market conditions and competition.
Costco's market share compared to competitors is consistently strong within the wholesale market. While specific figures fluctuate, Costco typically ranks among the top retailers globally by revenue and sales volume. The company's high membership renewal rates, reaching 90.5% in the U.S. and Canada and 88.7% worldwide as of the end of fiscal year 2023, reflect its strong market position.
The impact of Amazon on Costco's competition is significant, particularly in e-commerce. Amazon's online retail presence and its own membership program, Amazon Prime, pose a challenge. Costco has responded by enhancing its e-commerce capabilities and offering services like same-day delivery to remain competitive.
The competitive landscape for Costco includes major players in the retail industry. Costco's main rivals include other warehouse clubs and large retailers. Costco's ability to maintain its value proposition and adapt to changing consumer behaviors is critical for its future.
- Sam's Club (a division of Walmart) is a direct competitor, operating under a similar membership-based model.
- Traditional retailers like Walmart and Target also compete, offering a broader range of products.
- Online retailers, particularly Amazon, pose a significant challenge through their e-commerce platforms and subscription services.
- Specialty retailers and other discount stores also contribute to the competitive pressure.
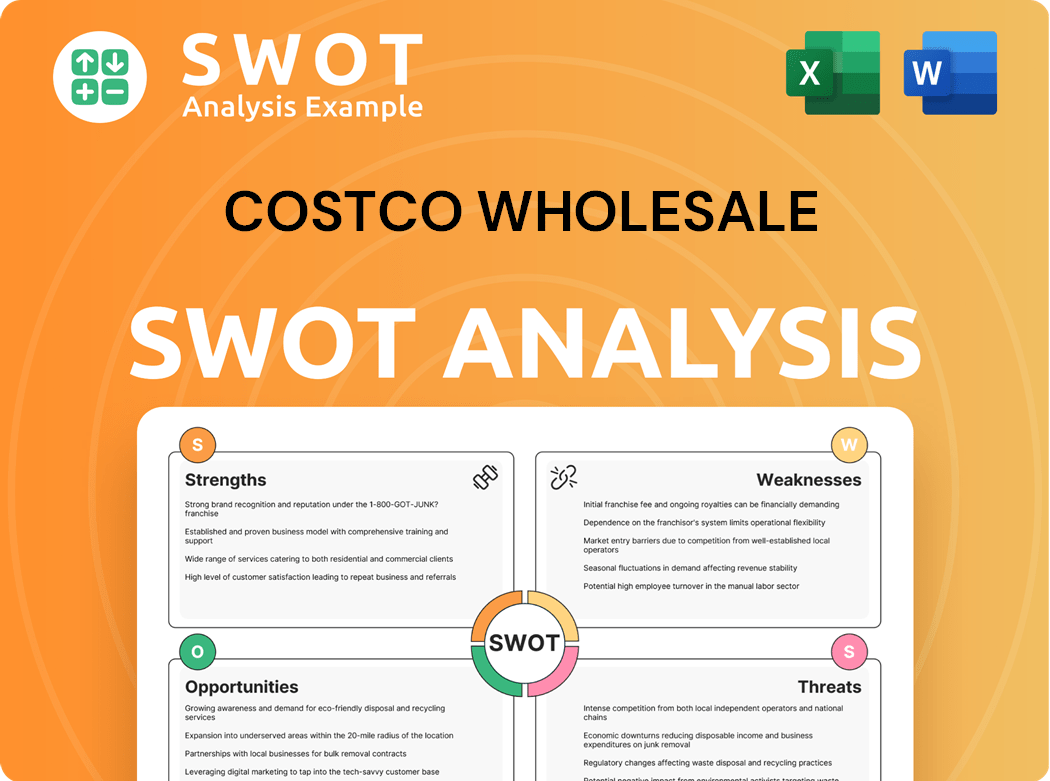
Costco Wholesale SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
Who Are the Main Competitors Challenging Costco Wholesale?
The competitive landscape for Costco Wholesale Corporation is multifaceted, encompassing direct and indirect rivals across various product categories and geographical markets. A thorough Marketing Strategy of Costco Wholesale analysis reveals that understanding these competitive dynamics is crucial for assessing its market position and future prospects. Costco's ability to maintain its competitive edge hinges on its strategic responses to these diverse challenges.
Direct competitors in the warehouse club segment, such as Sam's Club and BJ's Wholesale Club, pose significant challenges. These rivals compete intensely on membership fees, product pricing, and exclusive member benefits. Indirect competitors, including traditional retailers like Kroger, Albertsons, Target, and Walmart, as well as online giants like Amazon, further complicate the competitive environment. These companies challenge Costco through broader accessibility, diverse product ranges, and aggressive promotional activities.
Costco's main rivals, Sam's Club and BJ's Wholesale Club, directly compete in the warehouse club segment. Sam's Club leverages Walmart's vast supply chain and financial resources, focusing on price and product assortment to attract small businesses and budget-conscious consumers. BJ's Wholesale Club, primarily in the Eastern United States, offers a similar membership model, emphasizing convenience and a mix of national brands and private labels. In 2024, the wholesale market continues to evolve, with these competitors constantly vying for market share.
Sam's Club, owned by Walmart, is a major direct competitor, leveraging Walmart's extensive resources. BJ's Wholesale Club, with a strong presence in the Eastern US, offers a similar membership model. These competitors focus on price, product assortment, and member benefits.
Traditional brick-and-mortar retailers like Kroger, Albertsons, Target, and Walmart compete with Costco. These retailers offer broader accessibility and diverse product ranges. They often employ frequent promotional activities to attract customers.
Amazon represents a significant indirect competitor, offering vast selection, competitive pricing, and fast delivery. Amazon Prime membership provides convenience and a wide variety of goods. This poses a challenge to Costco's bulk purchase model.
Competitive pricing strategies are common, particularly during holiday seasons and for high-demand products. E-commerce and supply chain efficiency innovations by competitors like Amazon and Sam's Club pressure Costco. This necessitates enhancements in digital offerings and delivery capabilities.
Market share shifts are often incremental, reflecting the ongoing competition. New players in specialized e-commerce or discount retail could disrupt the landscape. Mergers and alliances, like Amazon's acquisition of Whole Foods, reshape competitive dynamics.
Costco's membership model is a key differentiator, influencing its competitive position. The annual membership fees contribute significantly to revenue. This model fosters customer loyalty and provides a stable revenue stream.
Costco's competitive advantages include its membership model, bulk purchasing options, and high-quality private label products. Challenges include competition from online retailers and the need to adapt to changing consumer preferences.
- Membership Model: Costco's membership model generates a recurring revenue stream and fosters customer loyalty.
- Bulk Purchasing: Offers significant savings for consumers and small businesses.
- Private Label Products: Kirkland Signature products provide high-quality alternatives.
- Online Competition: Amazon and other online retailers challenge Costco's market share.
- Changing Consumer Preferences: Adapting to evolving shopping habits and demands.
- Geographic Expansion: Expanding into new markets presents both opportunities and challenges.
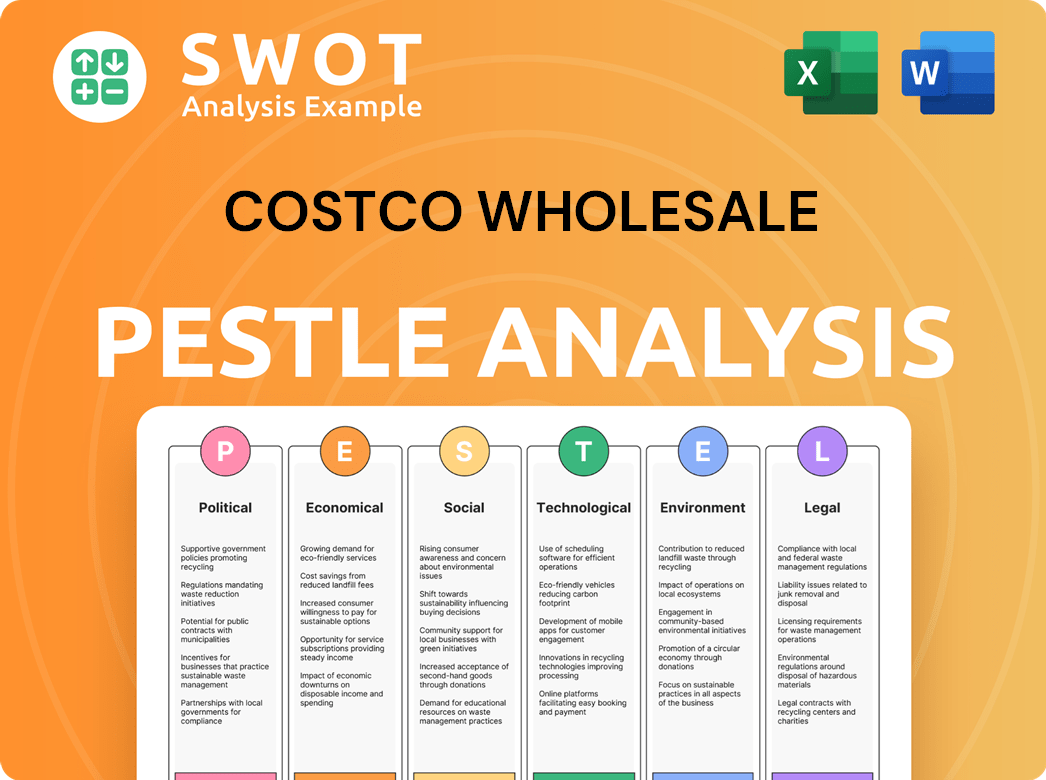
Costco Wholesale PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
What Gives Costco Wholesale a Competitive Edge Over Its Rivals?
The competitive landscape for retailers is constantly evolving, and understanding the strategies of key players like Costco is crucial. A deep dive into the Costco competition reveals a robust business model designed to maintain its market position. This analysis considers Costco's competitive advantages, its approach to the wholesale market, and how it navigates the retail industry.
Costco's success is built on a foundation of strategic choices that set it apart. Its membership model, operational efficiency, and focus on value have allowed it to thrive. Examining the competitive landscape helps to understand the dynamics at play and how Costco maintains its edge.
To understand Costco's position, it's important to look at its strengths and how it competes with rivals. The company's ability to offer low prices and high-quality products has cultivated a loyal customer base. For more insights, you can refer to a brief history of Costco Wholesale.
Costco's membership model is a core competitive advantage. It generates a steady revenue stream through annual fees, which reached $4.6 billion in fiscal year 2023. This allows the company to operate with thin margins on merchandise sales, offering low prices to its members.
As a major player in the wholesale market, Costco leverages its size to negotiate favorable terms with suppliers. This purchasing power allows it to secure lower costs, which are then passed on to members. Efficient inventory management also plays a key role.
The Kirkland Signature brand offers high-quality products at competitive prices, fostering customer loyalty. In fiscal year 2023, Kirkland Signature sales accounted for approximately $60 billion, representing about 26% of total net sales. This contributes significantly to Costco's value proposition.
Costco's efficient supply chain and distribution network contribute to its cost leadership. Its unique 'treasure hunt' shopping experience encourages frequent visits and impulse purchases. This focus on efficiency and value has helped it deal with its competitors.
Costco's competitive advantages are multifaceted, including its membership model, economies of scale, and the Kirkland Signature brand, which are key factors in its success. These advantages allow Costco to offer exceptional value, driving high membership renewal rates, which were at 90.5% in the U.S. and Canada at the end of fiscal year 2023.
- Membership Fees: Provide a stable revenue stream.
- Low Prices: Attract and retain customers.
- Efficient Operations: Reduce costs and maximize efficiency.
- Kirkland Signature: Offers value and builds brand loyalty.
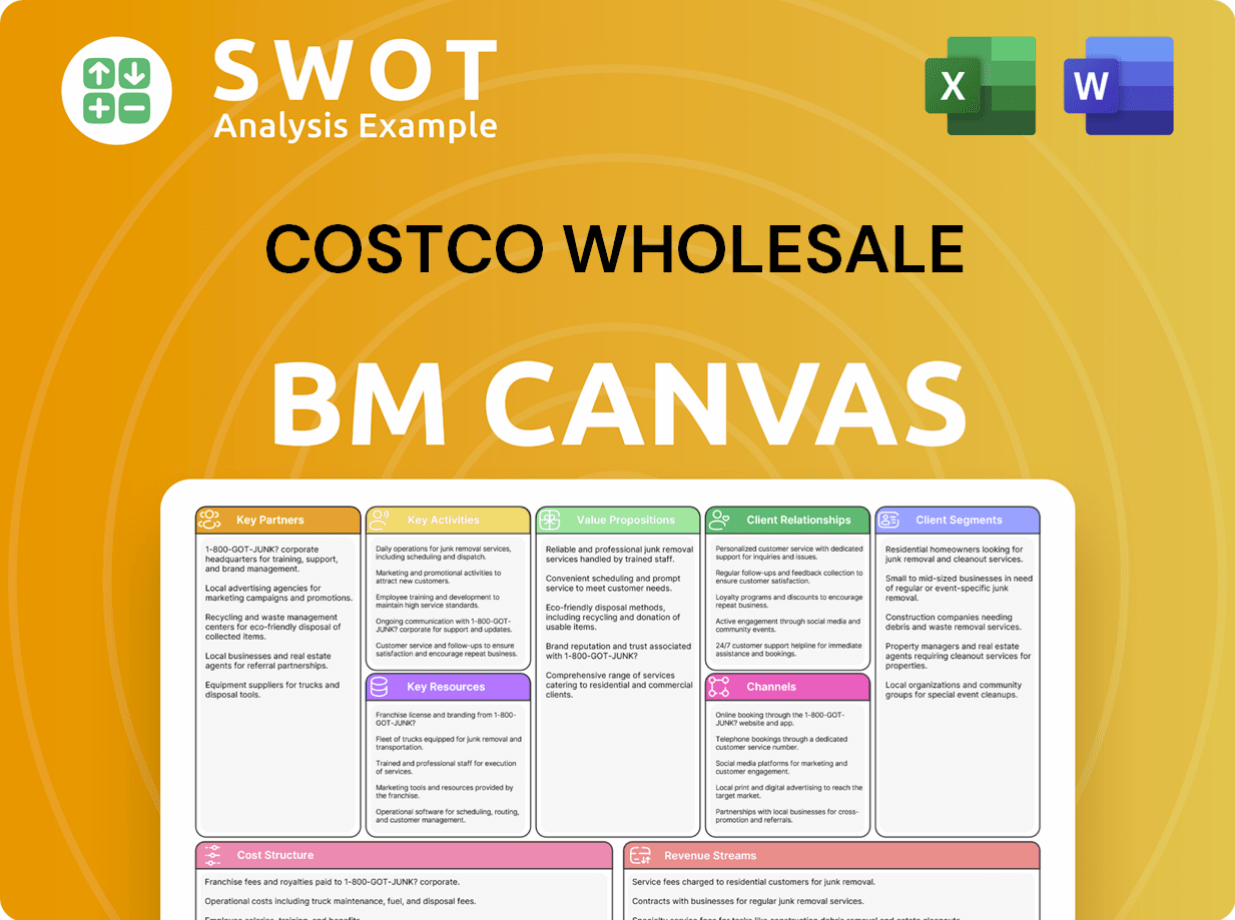
Costco Wholesale Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What Industry Trends Are Reshaping Costco Wholesale’s Competitive Landscape?
Understanding the retail landscape is crucial for evaluating the competitive positioning of Costco Wholesale. The company operates within the wholesale market, a segment of the broader retail industry, facing competition from various players. A comprehensive Costco market analysis reveals both strengths and vulnerabilities that shape its future outlook. The competitive landscape is dynamic, influenced by technological advancements, changing consumer preferences, and economic factors.
The primary risks involve adapting to evolving consumer behaviors, managing operational costs amidst regulatory changes, and effectively competing with both traditional and online retailers. However, opportunities exist in international expansion, product innovation, and leveraging brand loyalty. The future outlook for Costco is positive, contingent on its ability to adapt and capitalize on emerging trends within the wholesale market. For a deeper dive into their operational strategies, consider reading about the Revenue Streams & Business Model of Costco Wholesale.
The retail industry is experiencing significant shifts driven by e-commerce growth and supply chain advancements. Consumer preferences are evolving towards sustainability and personalized shopping experiences. Regulatory changes regarding data privacy and minimum wages are also impacting operational costs and consumer behavior. The wholesale market is seeing increased demand for online shopping and convenience.
Costco faces challenges from new market entrants using direct-to-consumer models and specialized e-commerce platforms. Intensified competition from online giants like Amazon, and traditional retailers investing in omnichannel strategies pose a threat. Declining demand for bulk purchases among certain demographics and increased regulation on large format stores could also pose challenges. The company must compete effectively with its main rivals.
Expansion into emerging international markets offers significant growth potential for new membership and sales. Product innovation, particularly in private label offerings, can differentiate Costco's offerings. Strategic partnerships with technology companies for enhanced logistics and personalized marketing could boost its competitive edge. Leveraging brand loyalty to expand service offerings unlocks new revenue streams.
Costco's competitive position is evolving towards a more integrated omnichannel approach. The company's strategy involves international expansion, technology investments to optimize supply chains and member experience, and a focus on delivering value. The company's business model analysis reveals that its success depends on adapting to market changes. Understanding how Costco deals with its competitors is key to its future success.
Costco's competitive advantages include its membership model, value pricing, and private label offerings. The company's market share compared to competitors, such as Walmart and Sam's Club, is significant. The impact of Amazon on Costco's competition is a critical factor. Costco's pricing strategy and competition are essential for maintaining a strong market position. The future of Costco's competitive landscape hinges on its ability to adapt to these factors.
- International Expansion: Focus on entering new markets, particularly in Asia, where there is significant growth potential.
- Digital Transformation: Enhance e-commerce capabilities and integrate online and in-store experiences.
- Product Innovation: Develop new private label products that cater to evolving consumer preferences.
- Strategic Partnerships: Collaborate with technology firms to improve logistics, marketing, and in-store technology.
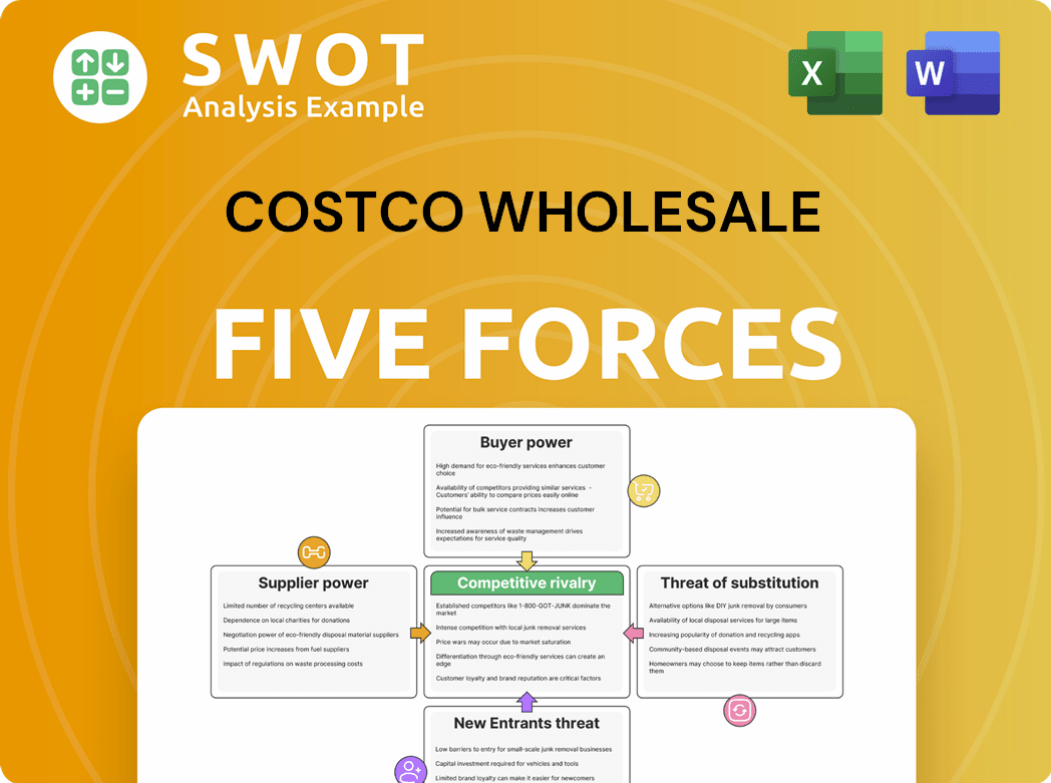
Costco Wholesale Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of Costco Wholesale Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Costco Wholesale Company?
- How Does Costco Wholesale Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Costco Wholesale Company?
- What is Brief History of Costco Wholesale Company?
- Who Owns Costco Wholesale Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Costco Wholesale Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.