Waste Management Bundle
Can Waste Management Maintain Its Dominance in a Changing World?
The waste management industry is experiencing a dynamic shift, fueled by sustainability, technology, and regulations. Waste Management, Inc. has been a key player since 1968, evolving from simple disposal to comprehensive environmental services. Its leadership in North America is undeniable, but the competitive landscape is constantly reshaping. Understanding this landscape is vital for anyone interested in the future of this critical sector.

To truly grasp Waste Management's position, we must delve into the Waste Management SWOT Analysis and examine its rivals, market share, and strategic responses. This waste management industry analysis will uncover the competitive advantages of top waste management firms and explore the challenges facing waste management companies. Furthermore, we'll investigate the impact of regulations and market trends, providing insights into the future of the waste management competitive landscape and how to analyze waste management competition within the environmental services competition.
Where Does Waste Management’ Stand in the Current Market?
The subject company maintains a leading position in the North American waste management sector. Its extensive infrastructure and diverse service offerings are key differentiators. While specific market share figures for 2024-2025 are proprietary, it consistently ranks as the largest residential and commercial waste management company in the United States, significantly ahead of its competitors.
In 2023, the company reported revenues of approximately $20.4 billion, highlighting its scale and financial health compared to industry averages. Its primary services include collection, transfer, recycling, and disposal of solid waste, alongside a growing focus on renewable energy generation from landfill gas.
The company operates across all 50 U.S. states and Canada, serving a broad customer base. It has strategically shifted its focus to sustainability and resource recovery, investing heavily in recycling infrastructure and landfill gas-to-energy projects. This has allowed the company to capture new revenue streams and align with evolving environmental regulations and consumer preferences. The company holds a strong position in landfill ownership and operation, a critical asset in the waste disposal value chain.
The company's core operations encompass the collection, transportation, and disposal of waste materials. This includes residential, commercial, and industrial waste streams. It also provides recycling services to recover valuable materials and reduce landfill waste.
The company offers comprehensive waste management solutions, ensuring efficient and environmentally responsible waste handling. It emphasizes sustainability through recycling programs and renewable energy projects. Its extensive infrastructure and nationwide presence provide reliable services to a wide range of customers.
The company has a dominant market presence in North America, particularly in the United States. Its extensive network of landfills, transfer stations, and collection routes allows it to serve a large customer base. The company's market share in the waste management industry is significantly larger than its competitors.
The company's competitive advantages include its large scale, integrated operations, and strong brand recognition. Its focus on sustainability and investment in renewable energy projects further enhance its position. The company's extensive infrastructure and efficient logistics networks provide a cost advantage over smaller competitors.
The company's strengths include its extensive infrastructure, diverse service offerings, and strong financial performance. Its strategies focus on expanding recycling capabilities and investing in renewable energy projects. The company continues to adapt to evolving environmental regulations and consumer preferences.
- Extensive Landfill Network: Ownership and operation of numerous landfills provide a significant advantage in waste disposal.
- Integrated Operations: The company's integrated model, from collection to disposal, enhances efficiency and control.
- Sustainability Initiatives: Investments in recycling and renewable energy projects align with environmental goals and attract customers.
- Strategic Acquisitions: The company has a history of strategic acquisitions to expand its market presence and service offerings.
For a deeper understanding of the company's financial model and revenue streams, you can explore the Revenue Streams & Business Model of Waste Management.
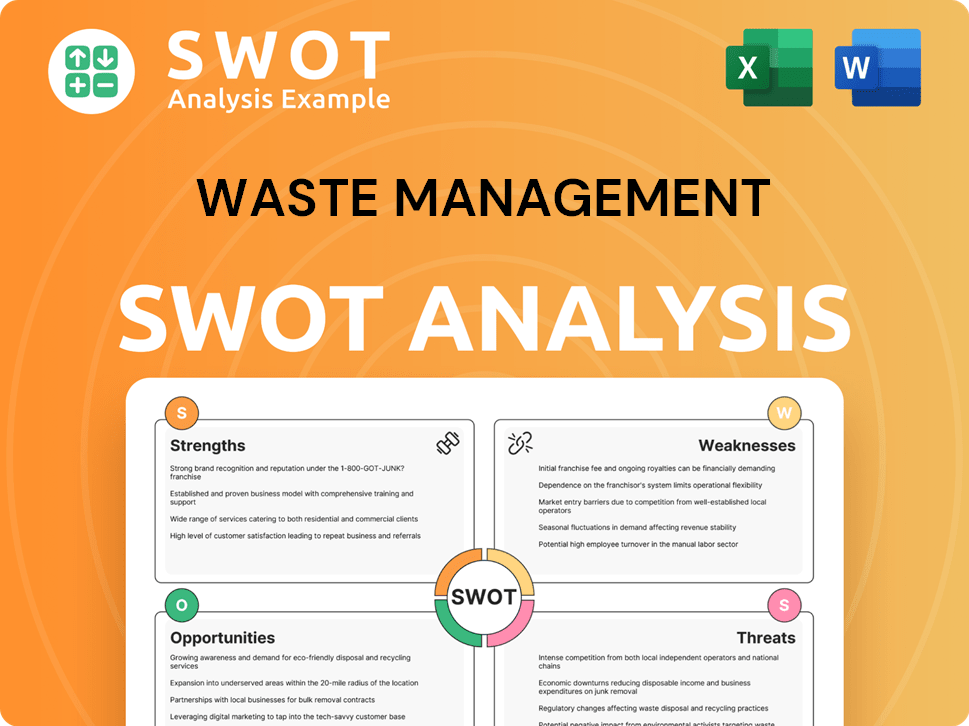
Waste Management SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
Who Are the Main Competitors Challenging Waste Management?
The waste management competitive landscape is a dynamic environment, shaped by a mix of large, integrated players and smaller, specialized firms. Understanding this landscape is crucial for anyone analyzing the waste management industry or seeking to make informed investment decisions. The competition is fierce, with companies constantly vying for market share through various strategies.
The competitive analysis waste sector reveals that companies compete on several fronts, including pricing, service offerings, technological innovation, and strategic acquisitions. This competition is further intensified by evolving regulations, environmental concerns, and the push for sustainable practices, all of which influence the strategies and performance of the key players.
The primary competitors in the waste management sector include large, integrated companies and smaller, regional players. These companies offer a range of services, from collection and disposal to recycling and waste-to-energy solutions. The competitive environment is also affected by emerging technologies and changing consumer preferences.
The most significant direct competitors include Republic Services, Inc. and GFL Environmental. These companies offer a similar range of services and compete directly for contracts and market share. They challenge through extensive networks and operational efficiency.
Indirect competitors include regional and local waste haulers, who often compete on price and personalized service. Emerging players in waste-to-energy and specialized recycling also pose indirect competition by offering alternative waste management solutions.
Companies employ various strategies, including competitive pricing, service innovation, and strategic acquisitions. Municipal contract bids are a common battleground. The focus on the circular economy principles fosters new business models, indirectly competing by reducing waste volumes.
The industry is influenced by factors like environmental regulations, technological advancements, and sustainability trends. These factors impact the competitive landscape by creating new opportunities and challenges for waste management companies. Mergers and acquisitions also play a significant role.
Key differentiators include operational efficiency, technological innovation, and customer service. Companies that can offer superior services at competitive prices, while also embracing sustainable practices, often gain a competitive edge. The ability to adapt to changing regulations is also crucial.
Future trends include increased adoption of waste-to-energy technologies, the growth of recycling programs, and the integration of digital solutions for waste management. The focus on the circular economy will also continue to shape the industry. These trends will likely intensify competition.
The waste management industry competitive environment is complex, with companies employing various strategies to gain market share. For instance, in 2024, Republic Services reported revenues of approximately $14.7 billion, demonstrating its strong position in the market. GFL Environmental has been aggressively expanding through acquisitions, particularly in North America, and reported revenues of approximately $7.2 billion in 2024. These figures highlight the scale and intensity of competition within the sector. To delve deeper into the financial aspects and strategic positioning of these companies, you can refer to a comprehensive analysis of the financial performance of Waste Management and its competitors.
The challenges facing waste management companies include rising operational costs, environmental regulations, and public scrutiny. However, there are also significant opportunities, such as the growing demand for sustainable solutions and the increasing focus on recycling and waste-to-energy technologies. These trends are creating new avenues for growth and innovation within the industry.
- Compliance with environmental regulations.
- Managing operational costs, including fuel and labor.
- Investing in new technologies, such as waste-to-energy plants.
- Adapting to changing consumer preferences and demands.
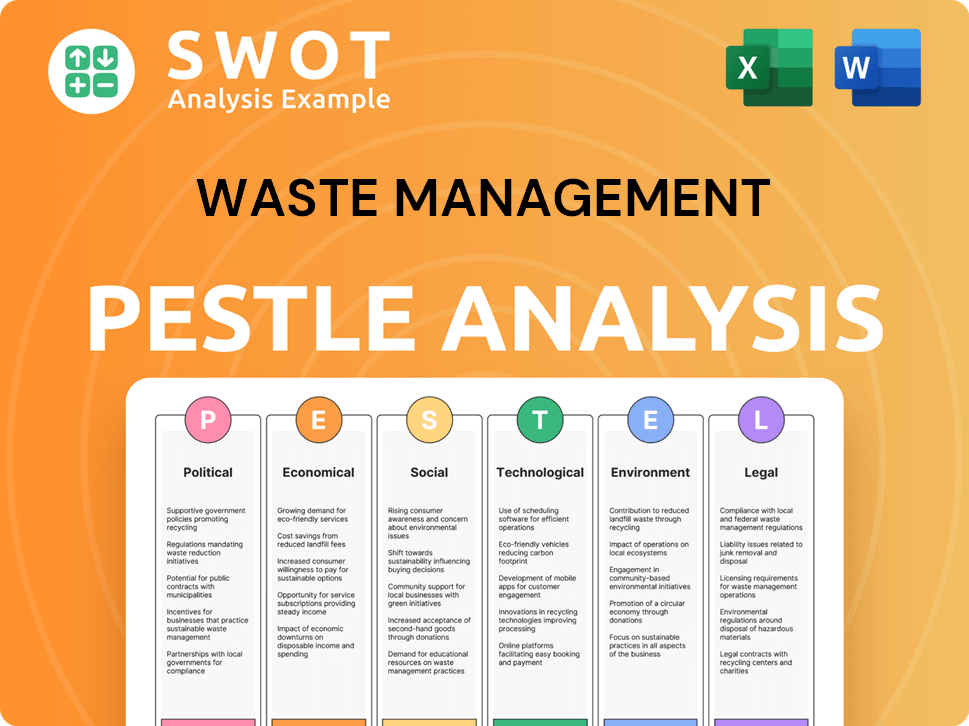
Waste Management PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
What Gives Waste Management a Competitive Edge Over Its Rivals?
The competitive landscape of the waste management industry is shaped by a few key players, with a focus on operational efficiency, technological innovation, and sustainable practices. Understanding the competitive dynamics involves analyzing market share, service offerings, and strategic initiatives. This analysis is crucial for investors, businesses, and policymakers to make informed decisions in this essential sector. A deep dive into the Marketing Strategy of Waste Management offers further insights into their market positioning.
The waste management industry is undergoing significant transformation, driven by evolving environmental regulations, technological advancements, and increasing public awareness of sustainability. This evolution influences the competitive dynamics, creating both challenges and opportunities for companies. Key players are constantly adapting their strategies to meet these changing demands, focusing on innovation and efficiency.
Analyzing the competitive landscape requires examining the strengths and weaknesses of major companies. This includes their infrastructure, service portfolios, financial performance, and strategic partnerships. It also involves assessing their responses to market trends, such as the growing demand for recycling and waste-to-energy solutions. The competitive analysis helps in understanding the industry's future trajectory.
Waste Management's vast network of collection routes, transfer stations, recycling facilities, and landfills is a core competitive advantage. This extensive infrastructure provides a significant operational footprint across North America. The strategic locations of these facilities allow for efficient waste handling and processing.
The company's large-scale operations result in significant economies of scale, enabling cost-effective waste management solutions. This advantage allows for competitive pricing and improved profitability compared to smaller competitors. Economies of scale are crucial in an industry with high fixed costs.
Investments in proprietary technologies, such as landfill gas-to-energy conversion and advanced recycling processes, differentiate Waste Management. Automation and data analytics optimize collection routes and processing efficiency. These technologies enhance operational capabilities and reduce environmental impact.
The company's strong brand equity, built over decades of reliable service, fosters high customer loyalty. This brand recognition provides a competitive edge in attracting and retaining customers. High customer loyalty translates into stable revenue streams.
Waste Management's competitive advantages include its extensive infrastructure, economies of scale, technological innovation, and strong brand recognition. The company's integrated service offerings and commitment to sustainability further enhance its market position. These advantages have allowed the company to maintain a significant market share.
- Extensive Infrastructure: A vast network of collection routes, transfer stations, and landfills across North America.
- Economies of Scale: Large-scale operations leading to cost-effective waste management solutions.
- Technological Investments: Proprietary technologies in landfill gas-to-energy and advanced recycling.
- Brand Recognition: Strong brand equity built over decades, fostering high customer loyalty.
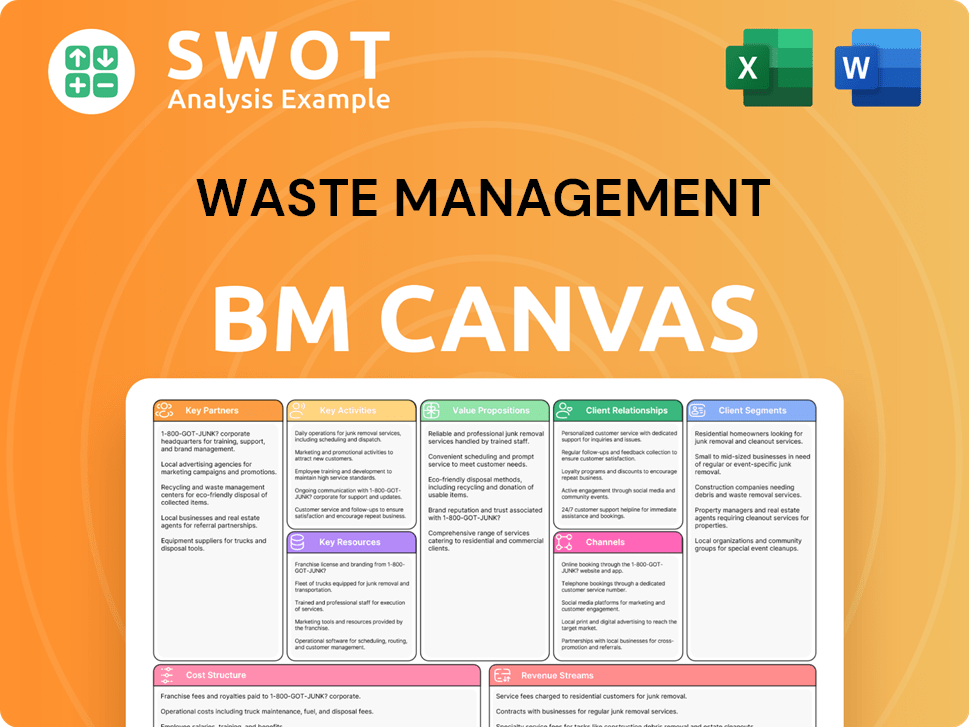
Waste Management Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What Industry Trends Are Reshaping Waste Management’s Competitive Landscape?
The waste management industry is experiencing significant shifts driven by sustainability demands, technological advancements, and evolving regulations. This dynamic environment presents both opportunities and challenges for companies. A thorough waste management competitive landscape analysis is crucial for understanding the sector's current state and future trajectory.
The industry is seeing increased emphasis on circular economy principles and technological integration. Companies need to adapt to stricter environmental standards and changing waste generation patterns. Understanding the waste management industry analysis is key to navigating these complexities and making informed strategic decisions.
The waste management sector is increasingly focused on sustainability, resource recovery, and technological innovation. Consumer preferences and corporate sustainability goals are driving demand for recycling and resource recovery. Advancements like AI-powered sorting and waste-to-energy technologies are transforming operations.
Companies face challenges such as stricter environmental regulations, public perception issues, and fluctuating waste generation patterns. Rising labor and fuel costs also pose operational difficulties. Adapting to these challenges requires strategic planning and operational efficiency improvements.
Significant opportunities exist in emerging markets and the renewable energy sector. Expanding landfill gas-to-energy portfolios and exploring waste-to-energy technologies can drive growth. Strategic partnerships for waste reduction and innovative material recovery can create new revenue streams.
The competitive landscape is evolving towards integrated and technology-driven service models. Emphasis on resource recovery and sustainable practices is crucial for long-term resilience. Companies must continuously innovate to maintain a competitive edge.
The waste management competitive environment is impacted by various factors. Regulatory changes, such as those promoting extended producer responsibility, are reshaping the industry. The increasing demand for sustainable practices and the circular economy is also influencing competition. Companies must adapt to these changes to remain competitive. For more insights into the customer base, explore the Target Market of Waste Management.
The global waste management market is projected to reach $750 billion by 2028, growing at a CAGR of approximately 5.4% from 2021 to 2028. Recycling rates are increasing, with some regions targeting 70% recycling rates by 2030. Waste-to-energy projects are gaining traction, with the global capacity expected to increase by over 20% by 2027.
- The demand for waste management services is rising due to population growth and urbanization.
- Technological advancements, such as AI and automation, are optimizing operations and reducing costs.
- Sustainability and circular economy principles are driving the adoption of innovative waste management solutions.
- Mergers and acquisitions are reshaping the competitive landscape, leading to consolidation.
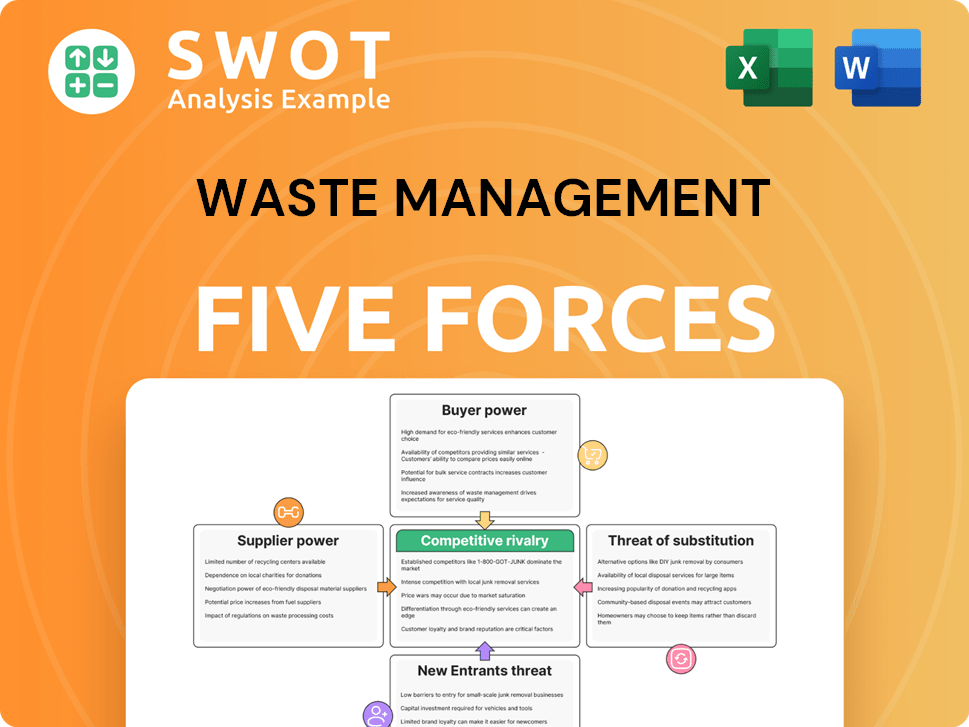
Waste Management Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of Waste Management Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Waste Management Company?
- How Does Waste Management Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Waste Management Company?
- What is Brief History of Waste Management Company?
- Who Owns Waste Management Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Waste Management Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.