Aurora Bundle
Who Really Owns Aurora Company?
Unraveling the ownership structure of a company is like peering behind the curtain of its future. Aurora Cannabis Inc., a Canadian cannabis giant, has undergone a fascinating transformation, making its ownership a complex and evolving story. Understanding who controls Aurora, from its inception to its current market position, is crucial for anyone seeking to grasp its strategic direction and potential.
From its roots in 2006, Aurora has grown significantly, becoming a major player in the global cannabis market. This deep dive into Aurora SWOT Analysis will explore the shifts in major stakeholders, including institutional investors and public shareholders, and examine how these changes have influenced the company's strategic trajectory and governance. We'll uncover details about the Aurora company ownership, including the board of directors, recent ownership trends, and the key sources of information used in this analysis, providing actionable insights for investors and stakeholders alike, including information about Aurora Innovation and its shareholders.
Who Founded Aurora?
The company, initially a private entity, was co-founded in 2006 by Terry Booth, Steve Dobler, and Dale Lesack. The founders played crucial roles in establishing the company's early operations and setting its strategic direction. While specific equity splits at the company's inception are not publicly detailed, the founders' influence was significant in the company's initial development.
Terry Booth, who served as CEO for many years, was a key figure in the company's early growth. He guided its expansion through the early stages of the Canadian medical cannabis market. Steve Dobler also held important leadership positions, contributing to the company's operational build-out. Their combined efforts were instrumental in shaping the company's initial trajectory.
Early financial backing for the company likely came from angel investors, friends, and family, as is typical for startups in emerging industries. These initial investments were vital for funding the establishment of cultivation facilities and securing the necessary licenses to operate within Canada's regulated cannabis framework. The founders' vision focused on rapid expansion and market penetration, which influenced how control and ownership were initially structured.
The early ownership structure of the company was primarily shaped by the founders and initial investors. These early investors provided the capital needed to launch and grow the business. The company's founders, Terry Booth, Steve Dobler, and Dale Lesack, held significant influence in the early stages.
- Initial funding rounds typically involved angel investors and early-stage venture capital.
- The founders' equity stakes were crucial in aligning their incentives with the company's long-term success.
- Details on specific ownership percentages from the initial years are not publicly available.
- The company's growth strategy focused on expanding production capacity and market share.
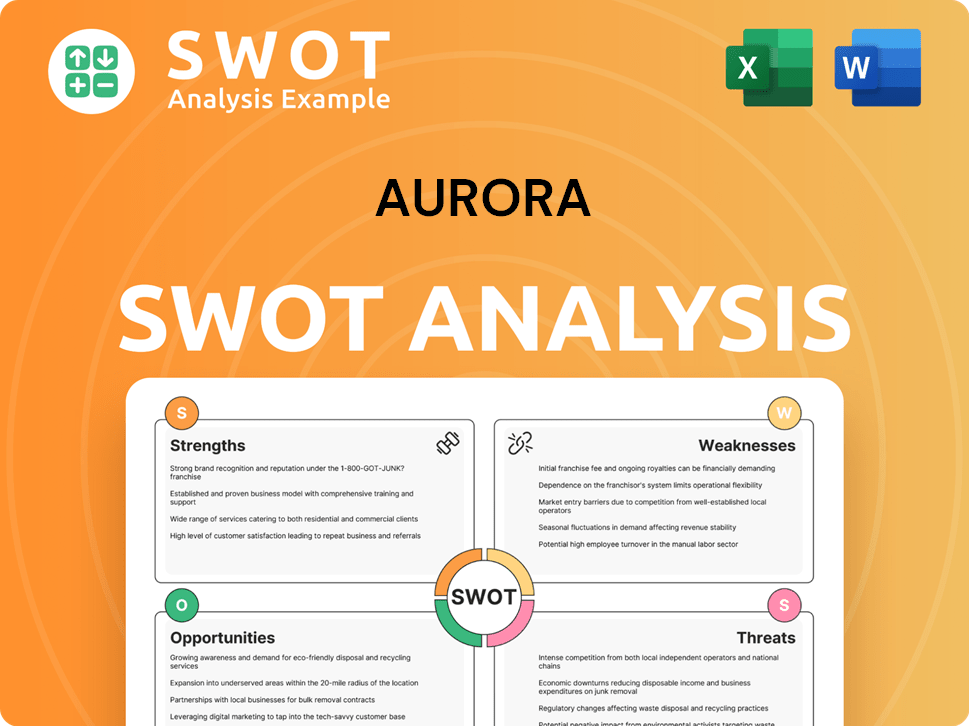
Aurora SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
How Has Aurora’s Ownership Changed Over Time?
The journey of Aurora's ownership has been marked by significant shifts since its inception. Initially a private entity, the company transitioned to the public market, listing on the Toronto Stock Exchange (TSX) under the symbol 'ACB' and the Nasdaq Global Select Market (NASDAQ), also under 'ACB'. This move broadened the ownership base, moving beyond the original founders and early investors to include a diverse group of institutional and individual shareholders. This transition was a pivotal moment in the evolution of the company's ownership structure, paving the way for future growth and investment.
The company's ownership structure has been shaped by various capital raises, including equity offerings to fund expansion, acquisitions, and operational growth. These financial maneuvers have led to a gradual dilution of the founders' initial stakes, a common trend in the lifecycle of publicly traded companies. Strategic partnerships and acquisitions have also played a role, potentially introducing new significant shareholders and altering the equity allocation. These changes in ownership directly impact the company's strategy and governance, as major shareholders often influence decisions through their voting power and engagement with management and the board of directors. Understanding the Aurora Company Ownership is crucial for investors and stakeholders alike.
| Event | Impact on Ownership | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Public Offering (IPO) | Diversification of Ownership | Transitioned from private to public, opening up shares to a broader investor base. |
| Equity Offerings | Dilution of Existing Stakes | Raised capital for expansion, acquisitions, and operations, leading to a decrease in the percentage held by existing shareholders. |
| Strategic Partnerships/Acquisitions | Potential for New Shareholders | Partnerships or acquisitions could introduce new significant shareholders, altering the ownership structure. |
As of early 2025, the major shareholders in Aurora Company include a mix of institutional investors, mutual funds, and index funds, alongside individual insiders, including some of the original founders and current executives. Large asset management firms and exchange-traded funds (ETFs) are often among the largest institutional holders. The exact percentages held by specific institutional investors fluctuate based on market activity, but firms like Vanguard Group Inc. and BlackRock Inc. frequently appear in the top shareholder lists. This highlights the significant role of institutional investors in the company's ownership and the influence they wield. Understanding Who owns Aurora is key for anyone interested in the company.
Aurora's ownership has evolved significantly since its inception, transitioning from private to public ownership.
- Institutional investors, mutual funds, and index funds are major shareholders.
- Equity offerings and acquisitions have impacted the ownership structure.
- Understanding the Aurora company ownership structure is essential for investors.
- The company's stock symbol is ACB.
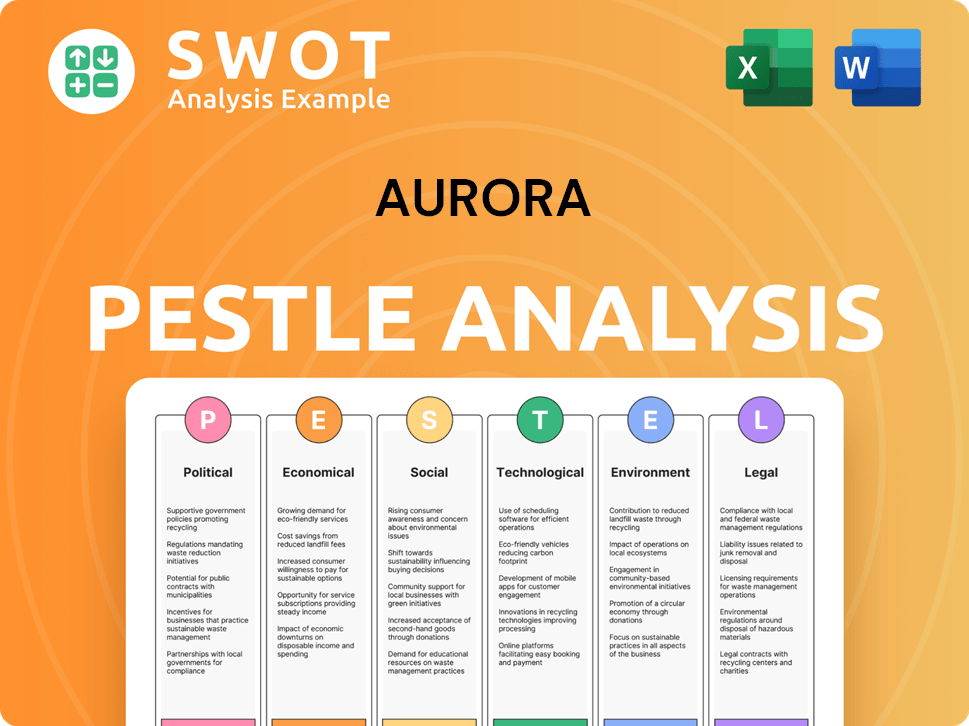
Aurora PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
Who Sits on Aurora’s Board?
The current Board of Directors of the Aurora Company plays a crucial role in the company's governance and strategic oversight. As of early 2025, the board includes a mix of independent directors and individuals affiliated with major shareholders or the company's executive management. The specific composition of the board, including names and affiliations, is detailed in the company's proxy statements and annual information forms filed with regulatory bodies. Independent directors are appointed to provide unbiased oversight and ensure adherence to corporate governance best practices. Understanding the Aurora Company Ownership structure is key to assessing the board's influence.
The board's responsibilities include overseeing financial performance, approving strategic initiatives, managing risk, and ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements. The presence of significant institutional investors can influence board decisions through their engagement with management and voting on shareholder proposals. The board's decisions are critical for the future of Aurora Innovation and its Aurora autonomous vehicles projects. The board's actions directly impact Aurora shareholders.
| Director | Affiliation | Role |
|---|---|---|
| (Data will be available in early 2025 proxy statements) | (Data will be available in early 2025 proxy statements) | (Data will be available in early 2025 proxy statements) |
| (Data will be available in early 2025 proxy statements) | (Data will be available in early 2025 proxy statements) | (Data will be available in early 2025 proxy statements) |
| (Data will be available in early 2025 proxy statements) | (Data will be available in early 2025 proxy statements) | (Data will be available in early 2025 proxy statements) |
Aurora Cannabis operates under a one-share-one-vote structure for its common shares, meaning each share generally carries one vote in shareholder matters. This structure promotes a more equitable distribution of voting power among shareholders. While there have been no widely reported recent proxy battles or activist investor campaigns that have significantly altered the company's decision-making framework, the board remains accountable to its shareholders. For more information about the company's structure, you can read this article about the company's ownership.
The Board of Directors oversees strategic direction and governance.
- The board includes independent directors and those with ties to major shareholders.
- Shareholders have equal voting rights (one-share-one-vote).
- Board decisions are influenced by institutional investors.
- Information on the board is updated in proxy statements.
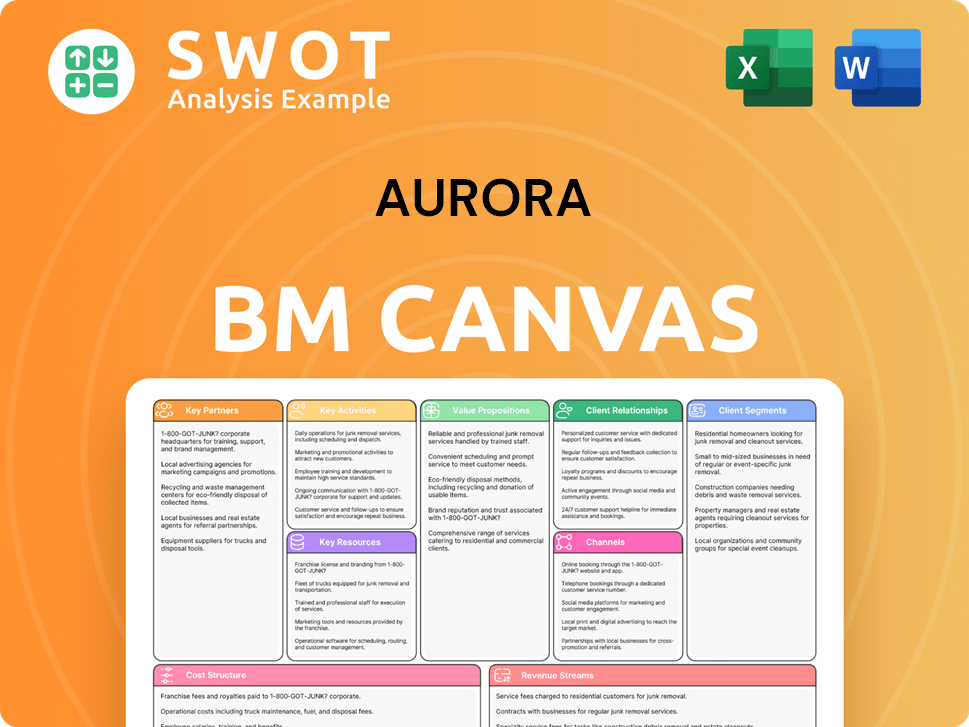
Aurora Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What Recent Changes Have Shaped Aurora’s Ownership Landscape?
Over the past three to five years (2022-2025), the ownership structure of Aurora Company has been influenced by strategic shifts aimed at enhancing financial performance and market positioning. The cannabis industry, including companies like Aurora, has been navigating a dynamic regulatory and economic environment. This has led to a focus on cost optimization, market consolidation, and strategic partnerships. These initiatives have the potential to impact the company's ownership profile through various means, including attracting new investors or altering the holdings of existing shareholders.
A notable trend impacting Aurora is the increasing institutional ownership as the cannabis sector matures. This can lead to greater stability in the shareholder base but also increased scrutiny from sophisticated investors. Founder dilution is another trend, as companies raise capital through equity offerings to fund growth, potentially reducing the percentage ownership of early investors. The evolving regulatory landscape for cannabis globally also plays a significant role in shaping investor interest and the overall ownership dynamics of companies like Aurora. Further insights can be found in the Marketing Strategy of Aurora.
| Metric | Data | Source/Year |
|---|---|---|
| Market Capitalization | Approximately $250 million (USD) | Yahoo Finance, May 2024 |
| Institutional Ownership | Around 15-20% | Financial Data Providers, Q1 2024 |
| Insider Ownership | Approximately 5-10% | Company Filings, 2024 |
Looking ahead, public statements from Aurora's management and analysts often touch upon future ownership changes, potential strategic alliances, or further market consolidation within the cannabis sector. The company's focus on profitability and sustainable growth may attract new strategic investors or lead to further adjustments in its ownership structure. The company's focus on Aurora Innovation and Aurora autonomous vehicles, and the overall market dynamics, will continue to shape the company's ownership.
Aurora's ownership structure is influenced by both institutional and insider holdings. Institutional investors hold a significant percentage of the shares, indicating a level of market acceptance. Insider ownership, including founders and key executives, represents a smaller but still important portion of the company.
Identifying the major investors in Aurora can provide insights into the company's strategic direction. These investors often include institutional funds and strategic partners. Understanding who these key investors are helps in assessing the company's financial stability and future prospects.
Market consolidation in the cannabis sector can significantly affect Aurora's ownership. Mergers and acquisitions can lead to changes in shareholder composition. Strategic partnerships can also alter the ownership dynamics.
Aurora's future ownership may be influenced by factors such as market performance and strategic decisions. Potential changes could include new investors, increased institutional holdings, or adjustments in insider ownership percentages. These factors will shape the company's path.
Aurora Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of Aurora Company?
- What is Competitive Landscape of Aurora Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Aurora Company?
- How Does Aurora Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Aurora Company?
- What is Brief History of Aurora Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Aurora Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.