Balfour Beatty Bundle
Who Really Controls Balfour Beatty?
Unraveling the mystery of Balfour Beatty SWOT Analysis is key to understanding its strategic moves and future potential. Knowing "Who owns Balfour Beatty" is more than just a matter of curiosity; it's a gateway to grasping its operational priorities and long-term vision. The company's ownership structure directly influences its ability to adapt and thrive in the ever-changing infrastructure landscape.

This exploration will dissect the Balfour Beatty ownership structure, from its roots with the founders to the current mix of Balfour Beatty shareholders and institutional Balfour Beatty investors. Understanding the Balfour Beatty parent company and the company's history of ownership provides crucial insights into its resilience and strategic positioning. We'll examine the key executives, the company's ownership transparency, and how these factors influence its financial performance, providing a comprehensive view of this infrastructure giant.
Who Founded Balfour Beatty?
The story of Balfour Beatty begins in 1909 with its founders, George Balfour and Andrew Beatty. Their partnership marked the start of a company that would grow into a significant player in the engineering and construction sectors. While specific details about the initial shareholding aren't readily available from the early 20th century, the company's foundation was built on the expertise of its founders.
George Balfour, a Scottish engineer, and Andrew Beatty, an Irish businessman, combined their skills to establish the firm. Their vision centered on electrical engineering and construction projects. This early focus set the stage for the company's future expansion and diversification. The initial ownership structure was straightforward, resting primarily with the founders themselves.
Early on, the company likely relied on internal capital and potentially investments from close associates. The absence of publicly available information regarding significant early backers, angel investors, or family members who held substantial stakes during Balfour Beatty's formative years is notable. Details on early agreements, such as vesting schedules or founder exits, are also not extensively documented. The founders' control and direction were crucial in shaping the company's path.
Understanding the early days of Balfour Beatty ownership involves looking at the founders and their initial roles. The company started as a partnership, with George Balfour and Andrew Beatty at the helm. Key aspects of the early ownership include:
- The founders, George Balfour and Andrew Beatty, were the primary owners.
- The company likely used internal capital and potentially small investments from close associates.
- There is limited public information about early investors or significant shareholders.
- The founders' vision and control were central to the company's initial direction.
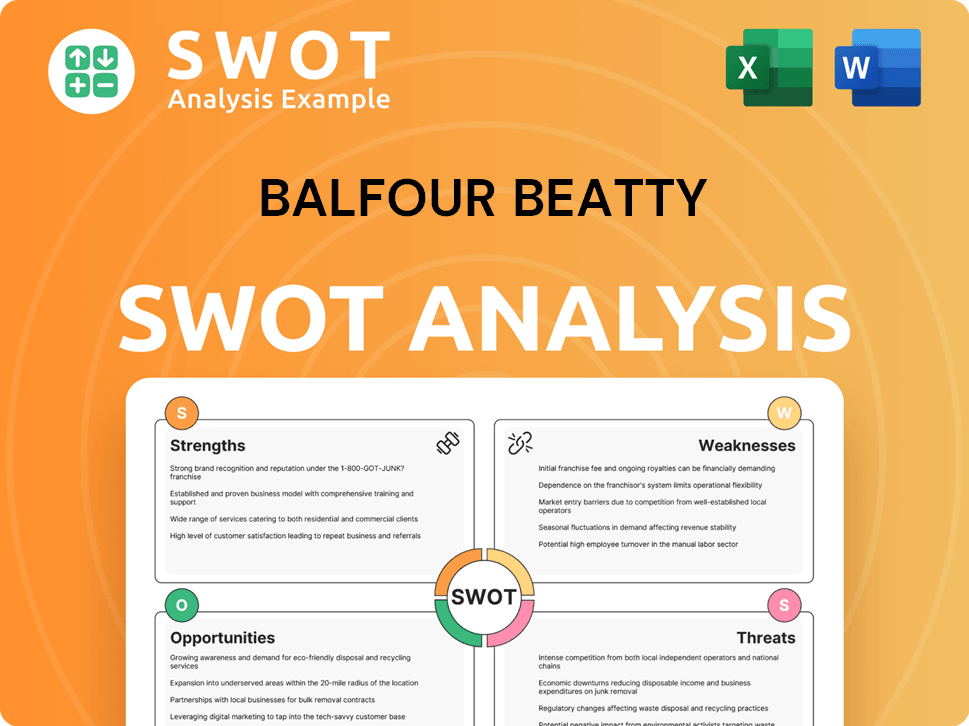
Balfour Beatty SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
How Has Balfour Beatty’s Ownership Changed Over Time?
The evolution of Balfour Beatty ownership has been significantly shaped by its transition to a publicly traded entity. This shift allowed for a wider distribution of shares, with the company's stock listed on the London Stock Exchange. The Balfour Beatty company structure reflects this, with a diverse base of shareholders.
Over the years, strategic moves like acquisitions and divestitures have played a crucial role in changing the company's asset portfolio. These actions have, in turn, influenced its market capitalization and the types of investors it attracts. For example, selling off certain assets or acquiring new businesses can lead to shifts in the company's market capitalization and investor interest. Detailed information about the Balfour Beatty shareholders, including institutional, individual, and insider holdings, is often found in its annual reports and regulatory filings.
| Event | Impact on Ownership | Year |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Public Offering (IPO) | Transition from private to public ownership, broadening shareholder base. | Early 20th century |
| Strategic Acquisitions | Expansion of asset base, potentially attracting new investors with different risk profiles. | Ongoing |
| Divestitures | Reduction of asset base, which can lead to shifts in market capitalization and investor focus. | Ongoing |
As of late 2024 and early 2025, the major shareholding in Balfour Beatty is largely dominated by institutional investors. These include large asset management firms, mutual funds, and pension funds. Firms like BlackRock, The Vanguard Group, and Norges Bank Investment Management (NBIM) are often among the top institutional holders. These firms typically hold significant portions of the company's shares, reflecting their investment strategies in the infrastructure sector. These major investors often engage with management on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) matters, and their voting power can significantly impact shareholder resolutions. To understand more about the company's strategic direction, you can read about the Growth Strategy of Balfour Beatty.
Balfour Beatty ownership is primarily held by institutional investors, reflecting its status as a publicly traded company.
- Institutional investors, such as BlackRock and The Vanguard Group, hold significant shares.
- Strategic acquisitions and divestitures have shaped the company's asset base and investor profile.
- Understanding the Balfour Beatty investors is crucial for assessing the company's financial health.
- The company's annual reports provide detailed breakdowns of shareholding.
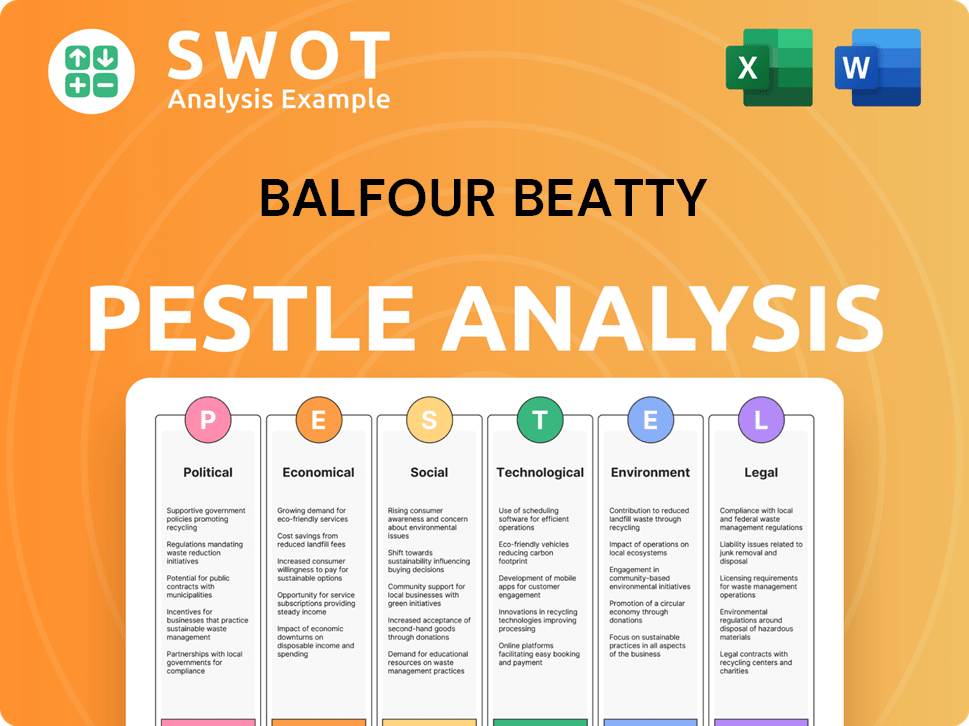
Balfour Beatty PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
Who Sits on Balfour Beatty’s Board?
The Board of Directors at Balfour Beatty plays a critical role in the company's governance and its relationship to ownership. As of early 2025, the board typically includes executive directors, who are also part of the company's management, and non-executive directors, many of whom are independent. The composition of the board is designed to provide oversight and ensure the interests of all shareholders are considered. The company's structure aims to balance internal management with external, independent oversight.
While specific names and their affiliations can change, major shareholders often do not have direct representatives on the Board in the same way a private equity firm might in a portfolio company. Instead, independent non-executive directors are appointed to provide oversight and ensure the interests of all shareholders are considered. This structure is common in publicly listed companies and aims to balance the interests of various stakeholders.
| Board Role | Description | Key Responsibilities |
|---|---|---|
| Executive Directors | Members of the company's management team | Day-to-day operations, strategic execution |
| Non-Executive Directors | Independent members providing oversight | Monitoring performance, ensuring accountability |
| Independent Directors | Non-executive directors without ties to management | Representing shareholder interests, providing objective viewpoints |
The voting structure for Balfour Beatty shares is generally one-share-one-vote, which is common for publicly listed companies on the London Stock Exchange. This means that each ordinary share carries equal voting rights. There is no public information suggesting the existence of dual-class shares or other mechanisms that would grant outsized control to any specific individual or entity. Recent proxy battles or activist investor campaigns are not prominently reported for Balfour Beatty in early 2025, suggesting a relatively stable governance environment. For more details on the company's financial workings, you can explore the Revenue Streams & Business Model of Balfour Beatty.
Understanding the board's composition and voting structure is crucial for assessing Balfour Beatty's ownership and control. The one-share-one-vote system ensures equitable voting rights among shareholders.
- The Board of Directors oversees company strategy and performance.
- Non-executive directors provide independent oversight.
- Shareholders have equal voting rights.
- The company's governance structure is designed to protect shareholder interests.
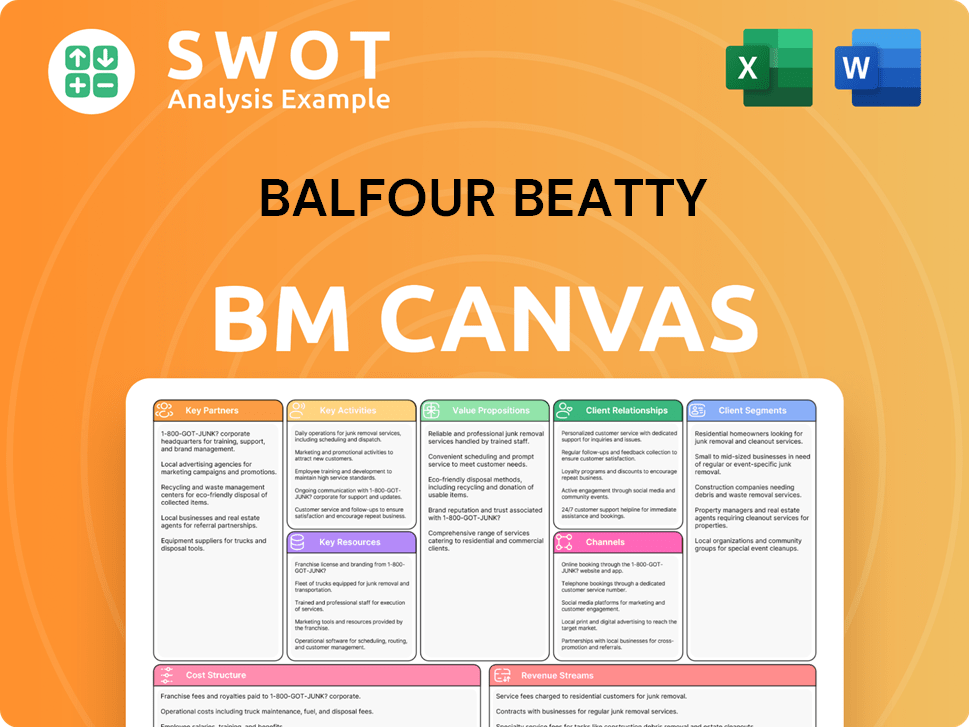
Balfour Beatty Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What Recent Changes Have Shaped Balfour Beatty’s Ownership Landscape?
In the past few years (2022-2025), the Balfour Beatty ownership structure has seen ongoing trends typical of large, publicly traded companies. There have been no major shifts like a privatization. Instead, the company has engaged in standard financial activities. These include share buyback programs, which impact the proportion of ownership held by existing Balfour Beatty shareholders, and potential secondary offerings, which could dilute ownership.
The infrastructure and construction sectors are seeing an increase in institutional ownership. Large asset managers continue to build their positions. Founder dilution is a natural part of the process for established public companies. This happens as the original founders' stakes decrease. Consolidation through mergers and acquisitions could indirectly affect Balfour Beatty's ownership if the company were involved in a major transaction. While not a dominant theme recently, activist investors remain a potential influence on any publicly traded company, pushing for changes in governance or financial performance. The company's public statements and analyst reports in 2024 and 2025 focus on operational performance and financial outlook.
| Metric | Details | Source/Date |
|---|---|---|
| Market Capitalization | Approximately £1.8 billion | LSE, May 2024 |
| Institutional Ownership | Over 60% | Company Filings, Q1 2024 |
| Share Buyback Programs | Ongoing, details vary annually | Annual Reports, 2022-2024 |
The ownership structure of Balfour Beatty reflects the company's position as a significant player in the infrastructure and construction industries. Understanding the dynamics of Balfour Beatty investors and the broader market trends is crucial for anyone interested in the company's performance. For a deeper dive into how the company approaches its market presence, consider exploring the Marketing Strategy of Balfour Beatty.
Who owns Balfour Beatty? Primarily institutional investors hold a significant portion of the shares. The Balfour Beatty parent company is the publicly listed entity itself. The company's ownership is spread among various institutional investors and individual shareholders.
Institutional ownership is increasing, and share buybacks are common. Founder dilution has occurred over time. Mergers and acquisitions could indirectly affect ownership. The focus remains on operational performance and financial outlook.
Ownership structure influences strategic decisions and financial performance. Institutional investors often drive a focus on profitability and shareholder value. The company's ability to attract and retain investors depends on its financial results.
Continued focus on operational efficiency and strategic investments is expected. The company may pursue further share buybacks or consider secondary offerings. The infrastructure sector's growth will likely influence Balfour Beatty's company structure.
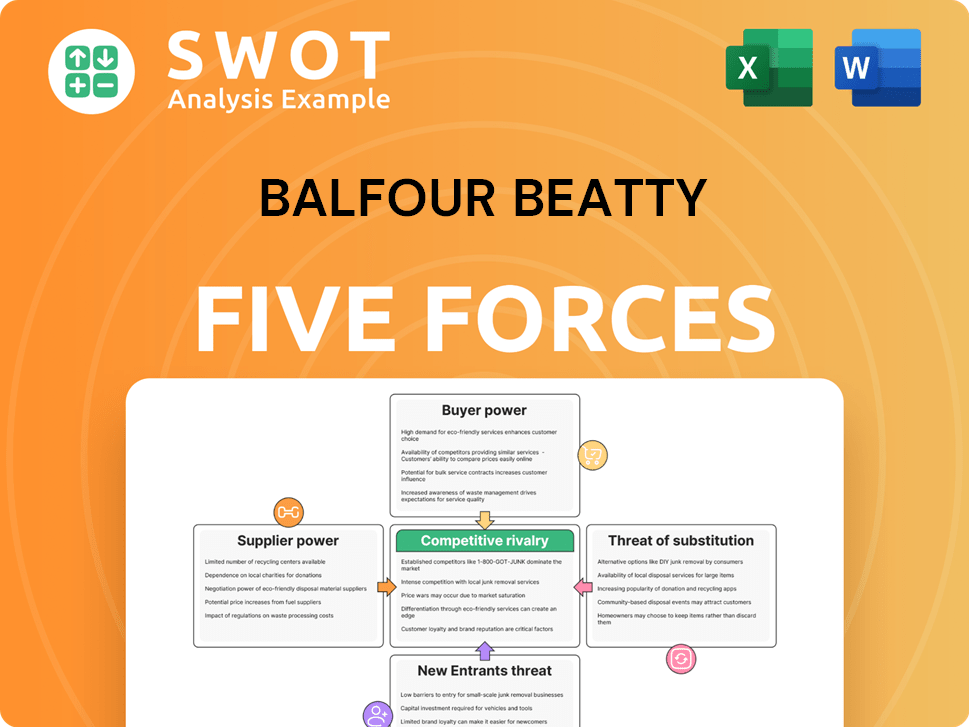
Balfour Beatty Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of Balfour Beatty Company?
- What is Competitive Landscape of Balfour Beatty Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Balfour Beatty Company?
- How Does Balfour Beatty Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Balfour Beatty Company?
- What is Brief History of Balfour Beatty Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Balfour Beatty Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.