Chegg Bundle
Who Really Controls Chegg?
In the ever-evolving ed-tech arena, understanding Chegg SWOT Analysis is key to grasping its potential. Founded in 2005, Chegg transformed from a student classifieds site to a major online learning platform. This exploration will unravel the intricate web of Chegg ownership, revealing the key players steering this educational giant.
From its humble beginnings, Chegg company has seen its ownership structure evolve dramatically. Knowing who owns Chegg provides critical insights into its strategic direction, from the influence of Chegg investors to the decisions made by Chegg CEO and Chegg executives. This deep dive will analyze the company's history, its public status, and the impact of its major shareholders on Chegg's financial performance and future.
Who Founded Chegg?
The initial formation of the Chegg company involved a trio of co-founders: Aayush Phumbhra, Osman Rashid, and Josh Carlson. They launched the company in 2005, initially under the name Cheggpost, which served as a classifieds website designed for students. The early ownership structure, while not publicly detailed in terms of specific equity splits, likely saw the founders holding significant stakes, a common practice in startups.
Early financial backing for Chegg came from various sources, including angel investors and venture capital firms. These early investments were crucial for fueling the company's growth and expansion. The shift in business model in 2007, from classifieds to textbook rentals, marked a pivotal moment, reshaping its trajectory and attracting further investment.
One of the early investors was Gabriel Gordon, who provided initial funding. The evolution of Chegg's business model was a strategic move by the founding team to address the high cost of textbooks, which was instrumental in attracting more substantial venture capital. Early agreements would have included standard startup provisions such as vesting schedules to ensure founder commitment over time, and potentially buy-sell clauses to manage liquidity and ownership transfers among the early team.
Chegg was co-founded by Aayush Phumbhra, Osman Rashid, and Josh Carlson in 2005.
Initially, Chegg started as Cheggpost, a classifieds website for students.
Gabriel Gordon was a notable early investor.
The company shifted to textbook rentals in 2007.
Founders typically held significant initial stakes, which were diluted through funding rounds.
Key decisions were likely made by the founding team and early investors.
The early ownership structure of the Chegg company played a crucial role in shaping its direction. The founders, along with early investors, collectively determined the company's strategy and operational decisions. The initial focus on a classifieds platform evolved into a textbook rental service, which was a strategic move to capitalize on the needs of students. As of the end of 2023, Chegg's revenue was approximately $790 million. As of the end of 2024, Chegg's market capitalization was approximately $600 million, reflecting the company's value in the market. The evolution of Chegg ownership and its leadership has been instrumental in its ability to adapt and grow within the education technology sector. The current Chegg CEO is Nathan Schultz. Key Chegg executives and the Chegg board of directors continue to influence the company's strategic direction. The company's headquarters are located in Santa Clara, California.
Understanding the early ownership and the evolution of the business model provides valuable insights into Chegg's journey.
- Co-founded by Aayush Phumbhra, Osman Rashid, and Josh Carlson.
- Started as Cheggpost, a classifieds website.
- Pivoted to textbook rentals in 2007.
- Early investors played a crucial role in funding.
- The founders and early investors shaped key decisions.
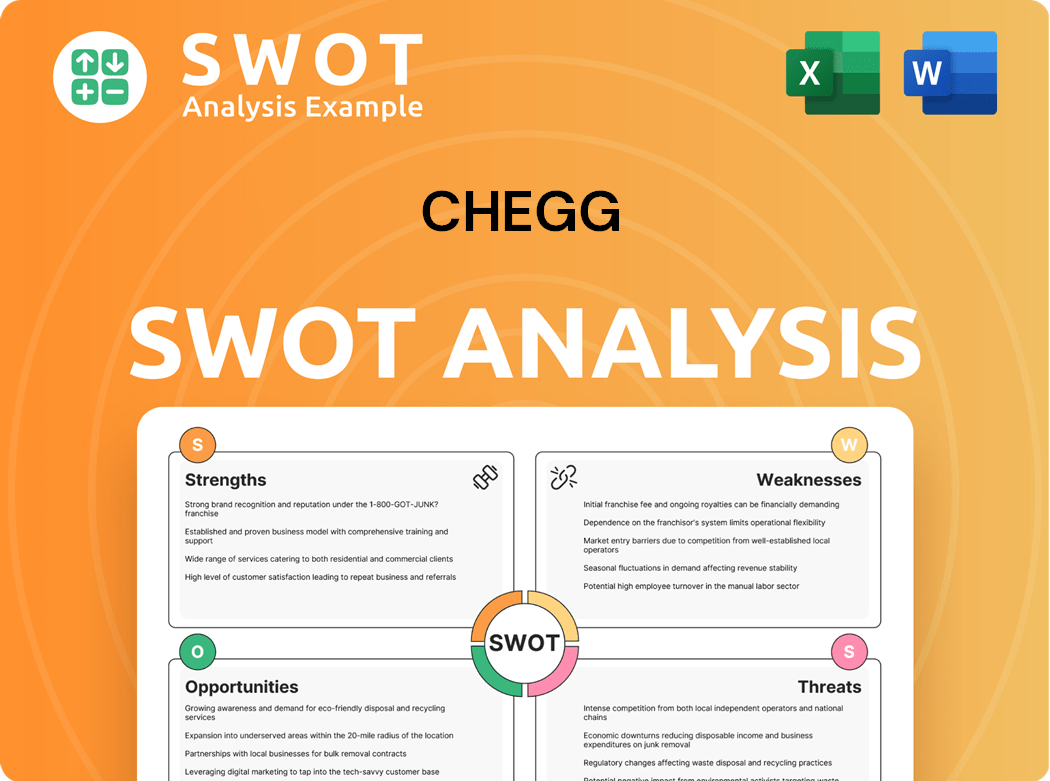
Chegg SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
How Has Chegg’s Ownership Changed Over Time?
The evolution of Chegg's ownership structure is marked by its transition from a privately held entity to a publicly traded company. The initial public offering (IPO) on November 13, 2013, was a pivotal moment. It introduced a diverse shareholder base, including institutional and individual investors. This shift significantly altered the company's financial and strategic landscape, aligning it with the expectations and demands of public market investors. This move opened up the company to a broader investor base, influencing its strategic direction and financial performance.
Post-IPO, the ownership dynamics of the Chegg company have been shaped by market cycles and strategic decisions. Founders' stakes typically dilute over time due to new share issuances and secondary offerings. The primary stakeholders now include institutional investors, whose significant holdings influence corporate governance and strategic decisions. These changes have directly impacted Chegg's strategy, pushing for continued growth in its subscription services and expansion into new areas of academic support, while also navigating competitive pressures and adapting to evolving student needs. The company's market capitalization reflects investor confidence in its business model.
| Event | Impact on Ownership | Date |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Public Offering (IPO) | Transition from private to public ownership, introduction of diverse shareholder base. | November 13, 2013 |
| Secondary Offerings | Dilution of existing shareholders' stakes, increased public float. | Ongoing |
| Institutional Investment | Increased influence of institutional investors on strategic decisions. | Ongoing |
As of March 30, 2024, major institutional holders of Chegg ownership include The Vanguard Group, BlackRock Inc., and Capital Research Global Investors. These firms collectively hold a significant percentage of the company's shares, influencing strategic decisions and governance. The shift in ownership has pushed for growth in subscription services and expansion into new areas of academic support. The company's market capitalization, which fluctuates with market conditions, reflects investor confidence in its business model. The current Chegg CEO is Dan Rosensweig, who has been instrumental in guiding the company through its growth phases. Understanding the dynamics of Chegg investors and their impact is crucial for assessing the company's future prospects.
The IPO in 2013 marked a significant shift in Chegg's ownership structure.
- Institutional investors now hold a substantial portion of the company's shares.
- The ownership structure continues to evolve, influenced by market cycles and strategic decisions.
- Understanding the major shareholders is crucial for assessing the company's future.
- The Chegg executives and board of directors play a crucial role in the company's direction.
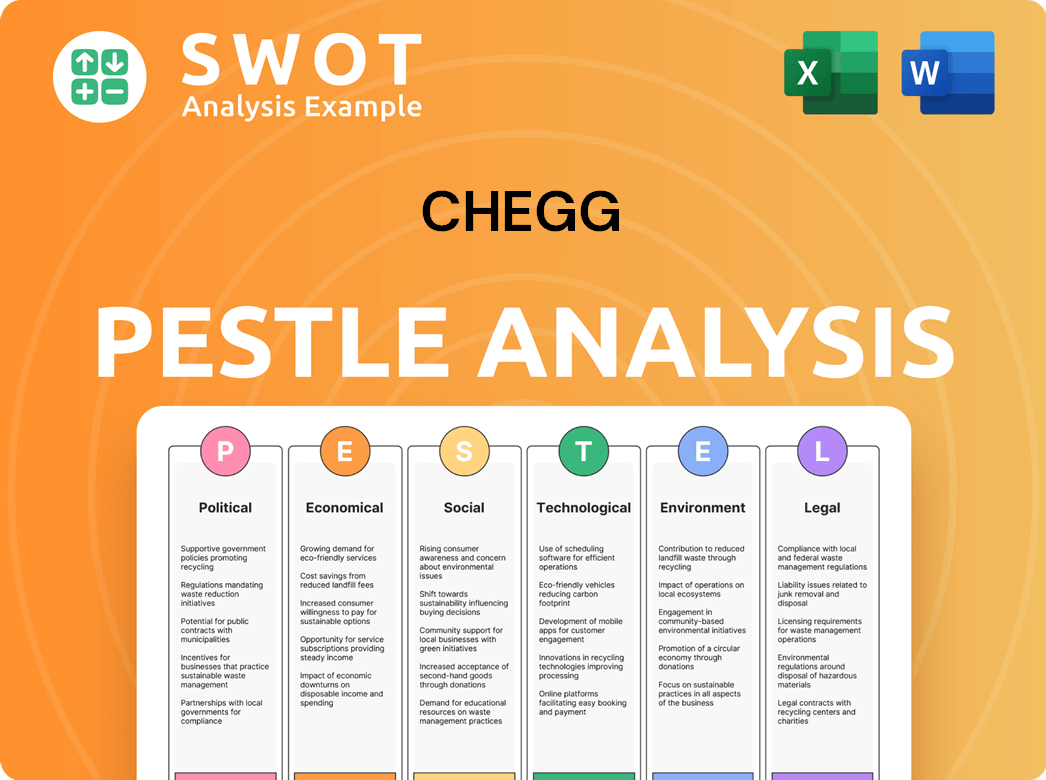
Chegg PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
Who Sits on Chegg’s Board?
As of early 2024, the board of directors for the Chegg company includes a mix of independent directors and those with ties to the company's history or significant shareholders. The board benefits from individuals with extensive experience in technology, education, and finance. Dan Rosensweig serves as the CEO and Co-Chairman of the Board. The presence of experienced individuals ensures that the company has the guidance necessary to navigate the complexities of the education technology market. Understanding Chegg ownership involves knowing the key figures steering the company.
The composition of the board aims to balance the interests of management, shareholders, and other stakeholders. The board's role is crucial in overseeing the company's strategic direction and ensuring accountability. The board's decisions significantly influence the company's performance and its ability to adapt to market changes. This structure helps maintain a balance between internal leadership and external oversight. Knowing who owns Chegg is essential for understanding the company's governance.
| Board Member | Title | Affiliation |
|---|---|---|
| Dan Rosensweig | CEO & Co-Chairman | Chegg |
| Other Board Members | Director | Various backgrounds in tech, finance, and education |
| Independent Directors | Director | Independent of the company |
Chegg operates under a one-share-one-vote voting structure. This means each common share generally entitles its holder to one vote on matters brought before shareholders. This structure ensures that voting power is directly proportional to the number of shares owned. The collective voting power of major institutional shareholders can be substantial. In recent years, Chegg has focused on strategic initiatives to enhance shareholder value. For more insights, explore the Competitors Landscape of Chegg to understand how Chegg positions itself in the market.
The board includes experienced leaders from various fields.
- Dan Rosensweig serves as CEO and Co-Chairman.
- The company uses a one-share-one-vote structure.
- Major institutional investors hold significant voting power.
- Independent directors play a crucial oversight role.
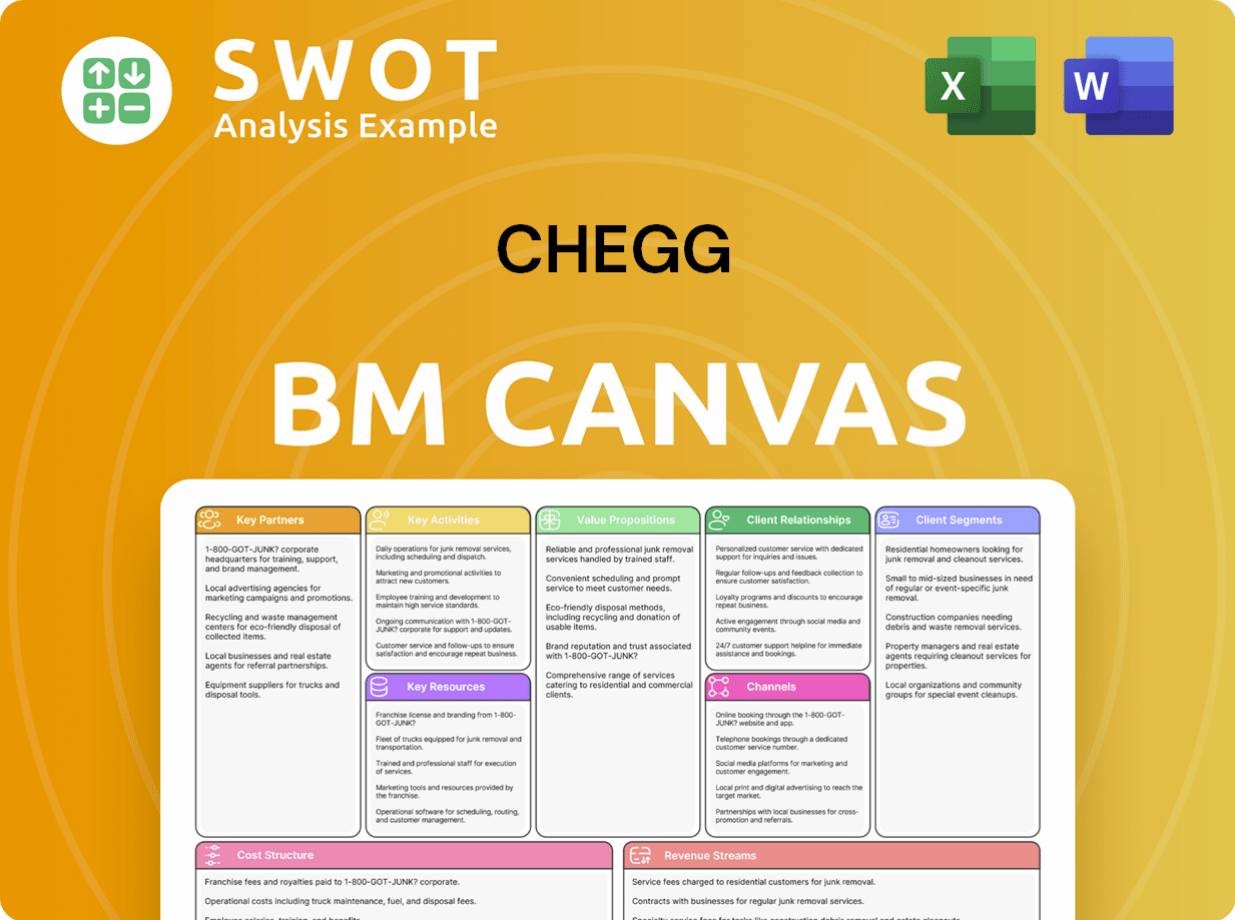
Chegg Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What Recent Changes Have Shaped Chegg’s Ownership Landscape?
In the past three to five years, the ownership structure of the Chegg company has seen shifts, largely mirroring broader trends in the education technology sector and the company's own performance. While specific details of significant share buybacks or secondary offerings in early 2024 aren't extensively available in public records, institutional ownership remains a key characteristic. Large asset managers continue to adjust their holdings based on Chegg's financial results, subscriber growth, and strategic initiatives, particularly those related to AI-powered learning tools and personalized support. The evolution of Chegg ownership is closely tied to its ability to adapt to the ever-changing educational landscape.
Industry trends indicate increasing institutional ownership across many sectors, and ed-tech is no exception. Founder dilution is a natural progression as companies mature and raise capital, and Chegg's ownership largely reflects this, with institutional investors holding the majority of shares. The company has been navigating a dynamic educational landscape, including the rapid integration of AI in learning, which impacts its product development and, by extension, investor sentiment. Strategic announcements regarding its AI capabilities and student success initiatives are closely watched by its investor base, influencing ownership trends and market valuation. The focus remains on sustainable growth and adapting its offerings to meet the evolving needs of students in a technologically advanced educational environment. For more insights into the company's strategic direction, consider reading about the Marketing Strategy of Chegg.
Institutional investors hold a significant majority of Chegg's shares. This trend reflects the maturity of the company and its position within the ed-tech market. Changes in institutional holdings often correlate with Chegg's financial performance and strategic moves.
The company's focus on AI and student success initiatives significantly influences investor sentiment. These initiatives are closely monitored, impacting ownership trends and market valuation. The integration of AI in learning is a key area of focus.
Chegg Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of Chegg Company?
- What is Competitive Landscape of Chegg Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Chegg Company?
- How Does Chegg Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Chegg Company?
- What is Brief History of Chegg Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Chegg Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.