FirstEnergy Bundle
Who Really Controls FirstEnergy?
Uncover the intricate web of ownership that dictates the strategies and success of FirstEnergy, a leading FirstEnergy SWOT Analysis. Ever wondered who pulls the strings at this major energy provider? Understanding the ownership structure of a company like FirstEnergy is crucial for anyone looking to understand its future trajectory and financial performance. This exploration delves deep into the key players shaping the company's direction.

This analysis of FirstEnergy ownership will reveal the key individuals and institutional entities that hold significant stakes, providing critical insights into the company’s corporate governance and strategic direction. Learn about the history and background of this utility company, from its roots to its present-day operations. Explore the current FirstEnergy CEO, major shareholders, and the overall FirstEnergy corporate structure to gain a comprehensive understanding of this significant player in the energy sector. Discover the answers to questions like: Is FirstEnergy a publicly traded company? and Who owns FirstEnergy?
Who Founded FirstEnergy?
The formation of FirstEnergy, unlike a typical startup, didn't involve individual founders in the traditional sense. Instead, it emerged from the 1997 merger of Ohio Edison Company and Centerior Energy Corporation. This means the initial ownership structure wasn't about specific individuals but rather about consolidating the existing shareholders of the two merging utility companies.
Therefore, understanding FirstEnergy ownership involves looking at how the shareholders of Ohio Edison and Centerior Energy were integrated. The merger agreement dictated the initial distribution of ownership, with shareholders receiving shares in the newly formed FirstEnergy based on an exchange ratio. This approach differs significantly from the typical equity distribution seen in newly established private companies.
The merger's terms, including the share conversion and the integration of the two companies, were the primary focus of early agreements. There weren't any angel investors or early-stage investors acquiring stakes in the usual sense. The goal was to create a stronger, more efficient utility company, and control was directly tied to the proportional ownership derived from the merger agreement.
FirstEnergy was formed through the merger of Ohio Edison and Centerior Energy in 1997.
Early ownership was a consolidation of existing shareholders from the merging companies.
Share exchange ratios determined the initial distribution of ownership among pre-merger shareholders.
Unlike startups, FirstEnergy didn't have traditional individual founders.
Early agreements focused on the merger terms, not individual founder equity.
The combined entity aimed to create a stronger utility for a broader region.
The initial ownership of FirstEnergy, a major energy provider, was distributed among the former shareholders of Ohio Edison and Centerior Energy. The merger agreement determined the share distribution. As of 2024, FirstEnergy Corporation is a publicly traded company, and its stock ownership is diverse, with institutional investors holding a significant portion of the shares. Understanding the
- The merger of Ohio Edison and Centerior Energy in 1997 formed FirstEnergy.
- Shareholders of the merging companies received shares in the new entity.
- The distribution of control was based on proportional ownership from the merger.
- FirstEnergy is a publicly traded company, and its ownership is diverse.
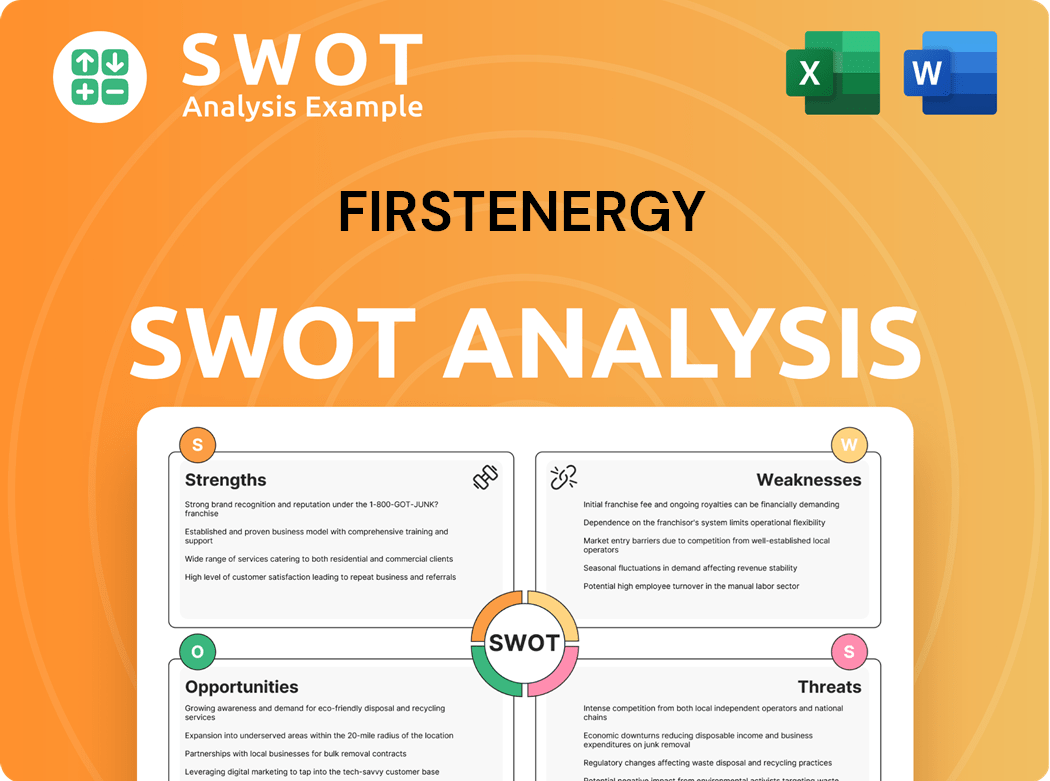
FirstEnergy SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
How Has FirstEnergy’s Ownership Changed Over Time?
The ownership structure of FirstEnergy Corporation (FE) has evolved since its inception in 1997, primarily influenced by its status as a publicly traded entity. The initial public offering (IPO) effectively occurred with its formation, inheriting the public investor base of its predecessor companies. Major shifts in shareholding are largely driven by institutional investors, mutual funds, and index funds. Understanding the dynamics of FirstEnergy ownership is crucial for investors and stakeholders alike.
As a publicly traded utility company, changes in FirstEnergy's ownership are primarily reflected in the holdings of institutional investors. These shifts can be influenced by market performance, strategic decisions, and broader economic trends. The company's history and background include significant events that have shaped its current ownership structure, reflecting the ongoing evolution of the energy provider in response to market demands and regulatory changes.
| Event | Impact | Date |
|---|---|---|
| Formation of FirstEnergy | Initial public offering (IPO) and establishment of public ownership. | 1997 |
| Acquisitions and Mergers | Consolidated ownership and expanded the investor base. | Ongoing |
| Institutional Investment Trends | Increased influence of large institutional investors. | Ongoing |
As of March 30, 2025, institutional investors held approximately 83.21% of FirstEnergy's outstanding shares. This concentration of ownership among large institutional investors means their collective decisions significantly influence shareholder votes and corporate direction. The Vanguard Group Inc. held 14.34% of FirstEnergy as of December 31, 2024, making it the largest institutional shareholder. BlackRock Inc. held 11.75%, and State Street Corp held 7.44%. For more insights into their strategic direction, consider exploring the Growth Strategy of FirstEnergy.
Institutional investors hold a significant majority of FirstEnergy's shares, influencing corporate strategy and governance.
- The Vanguard Group, BlackRock, and State Street are among the top institutional shareholders.
- Major stakeholders impact decisions on capital expenditures and executive compensation.
- Understanding the ownership structure is crucial for investors and stakeholders.
- FirstEnergy's ownership has evolved since its formation in 1997.
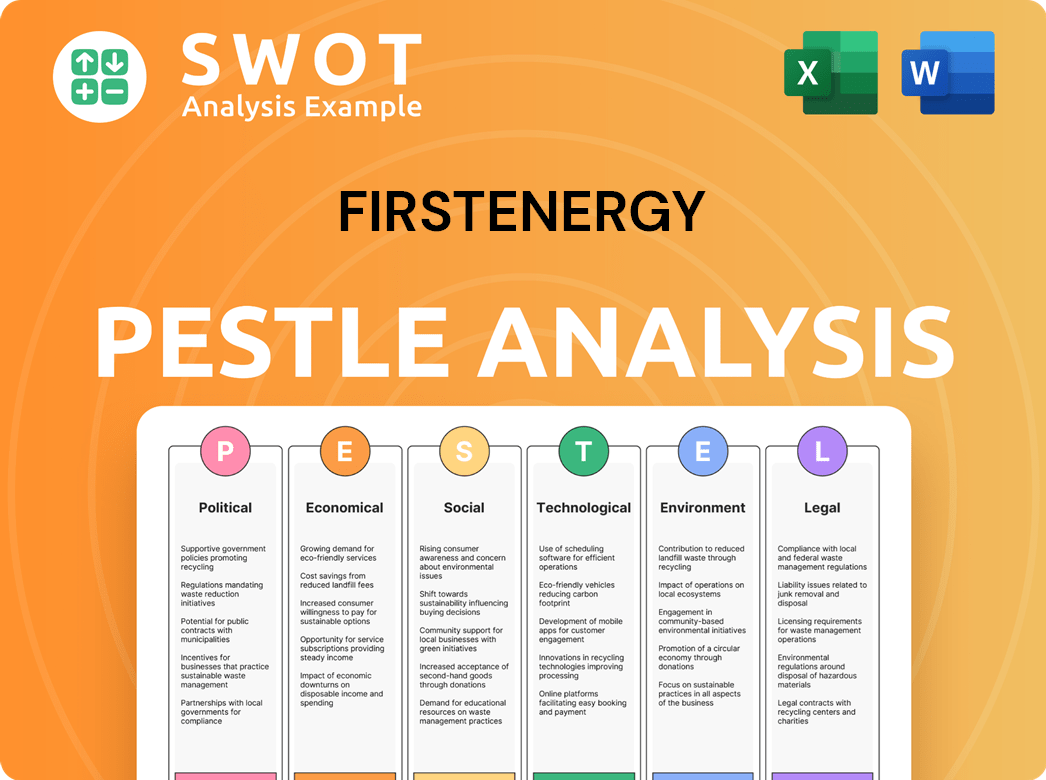
FirstEnergy PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
Who Sits on FirstEnergy’s Board?
As of early 2025, the board of directors at FirstEnergy Corporation, a prominent utility company, is composed of independent directors and individuals with extensive industry experience. This structure is designed to represent the interests of all shareholders, rather than being directly tied to specific major shareholders. Key figures on the board include John W. Somerhalder II (Chair of the Board), Brian X. Chin, and Lisa Winston Hicks, among others. The board's composition reflects a focus on independent oversight, particularly after the company faced governance challenges.
The governance structure of FirstEnergy is crucial for its operations. The board's role is to oversee the company's strategic direction and ensure accountability. The dispersed institutional FirstEnergy ownership structure means the board's decisions are pivotal in maintaining investor confidence and guiding the energy provider's future. The board's actions are especially important given the company's history and the need for strong governance.
| Board Member | Title | Key Role |
|---|---|---|
| John W. Somerhalder II | Chair of the Board | Oversees board meetings and strategic direction. |
| Brian X. Chin | Director | Contributes to board discussions and decision-making. |
| Lisa Winston Hicks | Director | Provides expertise and oversight. |
The voting structure for FirstEnergy common stock follows a one-share-one-vote system, which is standard for publicly traded companies. This means that each share of common stock grants its holder one vote on shareholder matters. There are no special voting rights or dual-class shares that would give disproportionate control to any single entity. However, large institutional investors, such as Vanguard and BlackRock, hold significant stakes, which gives them considerable voting power. Their proxy voting recommendations can significantly influence shareholder decisions, including director elections and proposals. Understanding the FirstEnergy stock ownership and voting dynamics is key to grasping the company's governance.
FirstEnergy's board of directors plays a crucial role in the company's governance and oversight. The voting structure is one-share-one-vote, which is typical for publicly traded companies. Institutional investors like Vanguard and BlackRock have significant voting power due to their large holdings.
- The board's composition includes independent directors and industry experts.
- The voting structure is one-share-one-vote.
- Institutional investors hold significant voting power.
- The governance structure aims to ensure accountability and transparency.
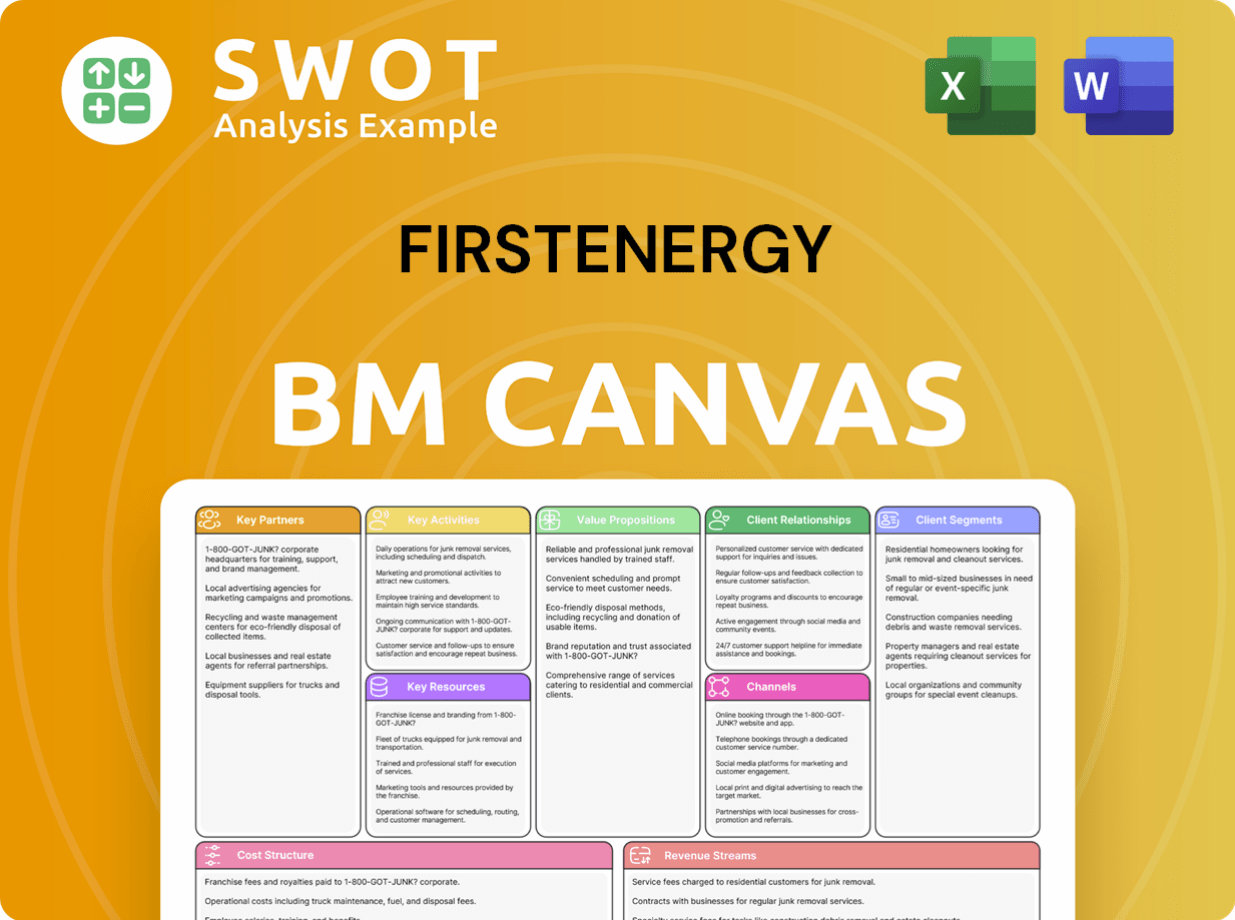
FirstEnergy Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What Recent Changes Have Shaped FirstEnergy’s Ownership Landscape?
Over the past few years, the ownership structure of FirstEnergy has shown a continued shift, reflecting broader trends in the utility sector. A key trend is the gradual increase in institutional ownership. This is consistent with the market trend where passive investment vehicles, managed by firms like Vanguard and BlackRock, continue to accumulate shares across various sectors, including utilities, due to their stable returns and dividend payouts. The company has not seen major share buybacks or secondary offerings that drastically alter the ownership structure recently.
FirstEnergy Corporation has focused on strategic asset management, such as the sale of its unregulated generation assets, which indirectly affects its financial structure and attractiveness to different investor types. Leadership departures, especially following legal and regulatory challenges, have also influenced investor sentiment and board composition. Industry trends in the utility sector point towards continued institutional consolidation of ownership, as large funds seek stable, long-term investments. Public statements from FirstEnergy and analysts generally focus on operational performance, grid modernization, and regulatory outcomes, which indirectly influence investor interest and ownership stability. For more details, you can explore the Brief History of FirstEnergy.
| Ownership Type | Approximate Percentage | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Institutional Investors | Around 80% | Includes large asset managers and investment funds. |
| Retail Investors | Around 15% | Individual shareholders. |
| Other | Around 5% | Includes insiders and other entities. |
The rise of activist investors, while not prominently featured in FirstEnergy's recent history, remains a potential influence for any publicly traded energy provider. They can push for operational changes, financial restructuring, or changes in board composition. There have been no public announcements about potential privatization or significant planned changes in its public listing status.
Institutional ownership has gradually increased. Passive investment vehicles, like those managed by Vanguard and BlackRock, continue to accumulate shares. Strategic asset management and leadership changes have also played a role in the ownership structure.
Major shareholders of FirstEnergy include large institutional investors. These investors are attracted to the stable returns and dividend payouts that utility companies typically offer. This trend aligns with broader market dynamics.
Legal and regulatory challenges have influenced investor sentiment. Changes in executive leadership and board composition have also occurred. These factors can impact investor confidence and the company's financial performance.
The focus remains on operational performance and grid modernization. Regulatory outcomes and investor interest will continue to shape the ownership landscape. No privatization plans or significant changes in public listing status have been announced.
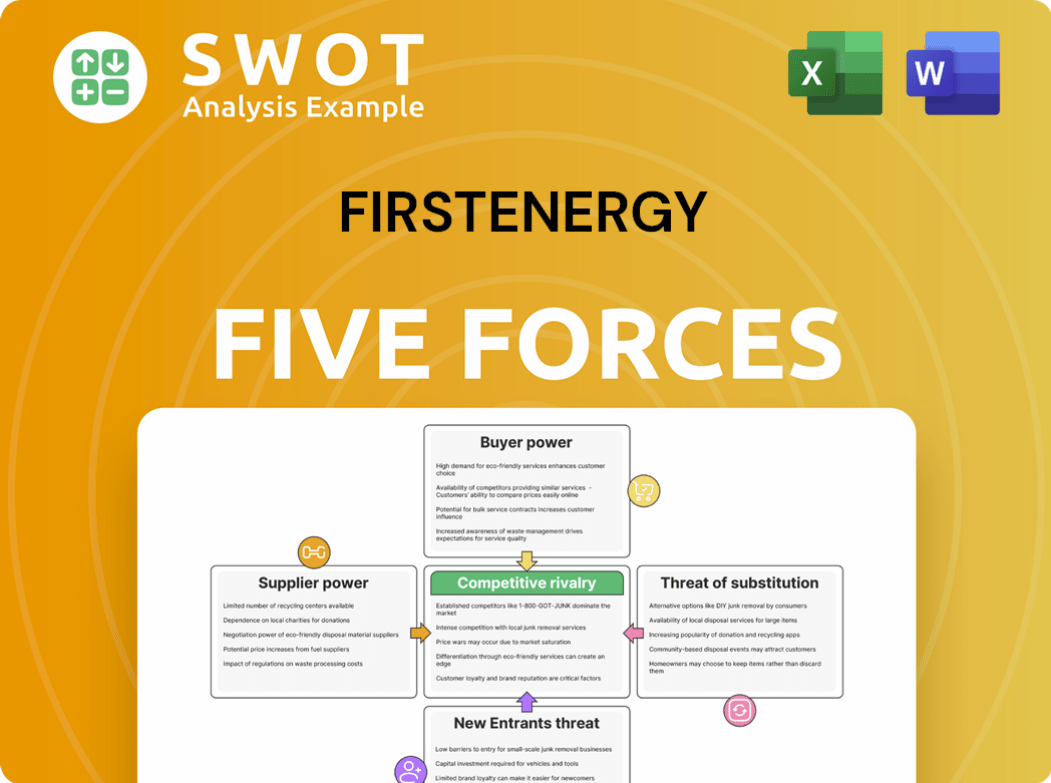
FirstEnergy Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of FirstEnergy Company?
- What is Competitive Landscape of FirstEnergy Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of FirstEnergy Company?
- How Does FirstEnergy Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of FirstEnergy Company?
- What is Brief History of FirstEnergy Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of FirstEnergy Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.