J.Jill Bundle
Who Really Owns J.Jill?
Ever wondered who pulls the strings at J.Jill, the women's apparel retailer? Understanding J.Jill SWOT Analysis is key to grasping its strategic moves. From its humble beginnings to its current market position, J.Jill's ownership structure has undergone a fascinating transformation.

The J.Jill company's ownership structure is a critical factor influencing its performance, and understanding who owns J.Jill is vital for anyone invested in the J.Jill business. This analysis will delve into the J.Jill ownership, revealing the key players behind the brand and how their influence shapes the company's future, including J.Jill stock.
Who Founded J.Jill?
The story of J.Jill began in 1959, founded by Jill Roberts. The company started as a catalog business, which was a common direct-to-consumer model at the time. The initial ownership was most likely held by the founder and possibly a small group of early investors or family members who provided the initial capital.
Jill Roberts' vision was to offer women comfortable and stylish clothing, a niche that the brand has maintained over the years. This initial focus on a specific market segment helped define the company's early identity and direction.
Early funding for J.Jill likely came from traditional sources like bank loans or small private investments to support its growth and catalog distribution. Publicly available information doesn't detail specific early backers, angel investors, or family members who acquired stakes during this phase.
Early funding for J.Jill likely came from traditional sources like bank loans or small private investments to support its growth and catalog distribution.
Jill Roberts' vision was to offer women comfortable and stylish clothing, a niche that the brand has maintained over the years.
The initial ownership was most likely held by the founder and possibly a small group of early investors or family members who provided the initial capital.
The company started as a catalog business, which was a common direct-to-consumer model at the time.
The founding team's vision for a distinct women's apparel brand was primarily reflected in the curated product offerings and direct marketing approach that defined its early operations.
Details regarding early agreements like vesting schedules, buy-sell clauses, or founder exits from the very nascent stages are not publicly disclosed.
Details about early agreements, such as vesting schedules or founder exits, from the initial stages are not publicly accessible. The focus of the founding team on creating a distinct women's apparel brand was reflected in its curated product offerings and direct marketing methods, which defined its early operations. To understand more about the J.Jill company, you can also explore the company's profile.
The early days of J.Jill involved a catalog-based business model, with ownership primarily held by the founder and potentially a small group of early investors.
- The brand's focus on comfortable and stylish clothing for women has been a consistent element since its inception.
- Early funding likely came from bank loans and private investments, with details on specific early backers not publicly available.
- The company's early operations were defined by its curated product offerings and direct marketing approach.
- Information on early agreements and founder exits from the initial stages is not publicly disclosed.
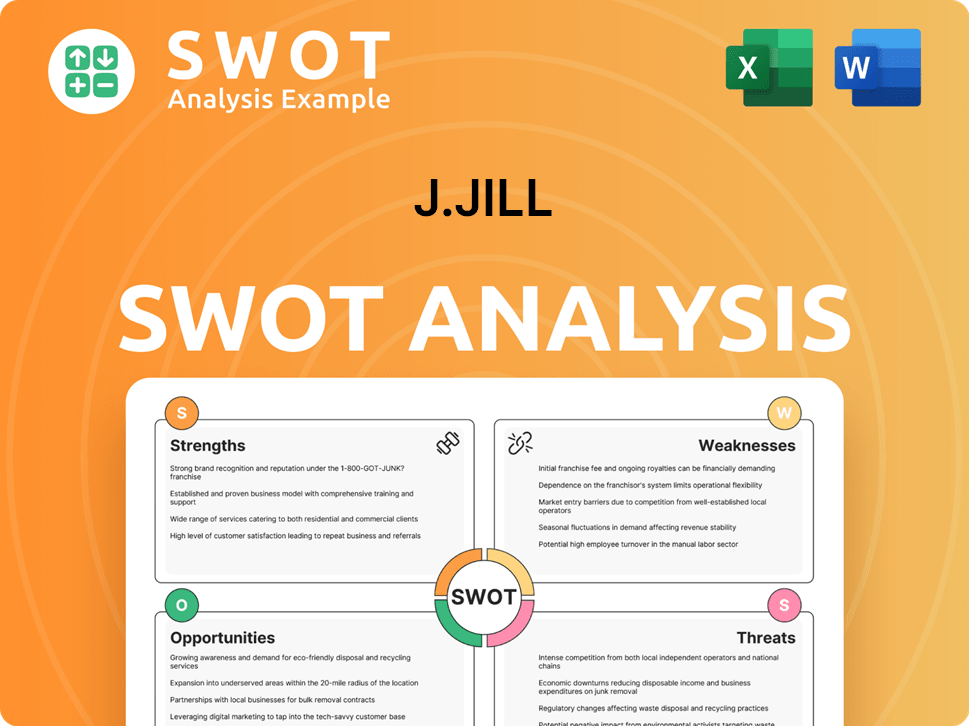
J.Jill SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
How Has J.Jill’s Ownership Changed Over Time?
The evolution of J.Jill ownership reflects a journey through various corporate structures, from private equity ownership to its current status as a publicly traded company. The J.Jill company has seen several shifts in its ownership, each influencing its strategic direction and operational focus. Understanding the J.Jill owner and the changes in its ownership structure provides insights into the company's financial health and strategic decisions over time.
In 2000, Golden Gate Capital acquired J.Jill from its founders, setting the stage for subsequent ownership transitions. The company was later acquired by Talbots Inc. in 2006 for roughly $517 million, which integrated J.Jill into a larger retail portfolio. In 2015, Arcapita acquired J.Jill for $120 million, a move that led to a strategic repositioning of the brand. The most significant change occurred in March 2017, when J.Jill went public with an IPO, trading under the ticker symbol 'JILL' on the New York Stock Exchange.
| Year | Event | Impact on Ownership |
|---|---|---|
| 2000 | Acquisition by Golden Gate Capital | Transition to private equity ownership |
| 2006 | Acquisition by Talbots Inc. | Integration into a larger retail portfolio |
| 2015 | Acquisition by Arcapita | Strategic repositioning and investment in direct-to-consumer channels |
| 2017 | Initial Public Offering (IPO) | Diversification of ownership with public shareholders |
The IPO in 2017 marked a significant turning point, allowing institutional investors and the public to acquire shares of J.Jill stock. As of March 31, 2024, major institutional holders included The Vanguard Group, Inc. and BlackRock, Inc., reflecting a substantial portion of the company's outstanding shares. These institutional investors play a crucial role in shaping the company's strategy and governance. For more information on how the company targets its customers, you can read about the Target Market of J.Jill.
J.Jill's ownership has evolved significantly. From private equity ownership to being a publicly traded company, the shifts have influenced its strategic direction. Institutional investors now hold a significant portion of the company's shares.
- Golden Gate Capital acquired J.Jill in 2000.
- Talbots Inc. acquired J.Jill in 2006.
- Arcapita acquired J.Jill in 2015.
- The IPO occurred in March 2017.
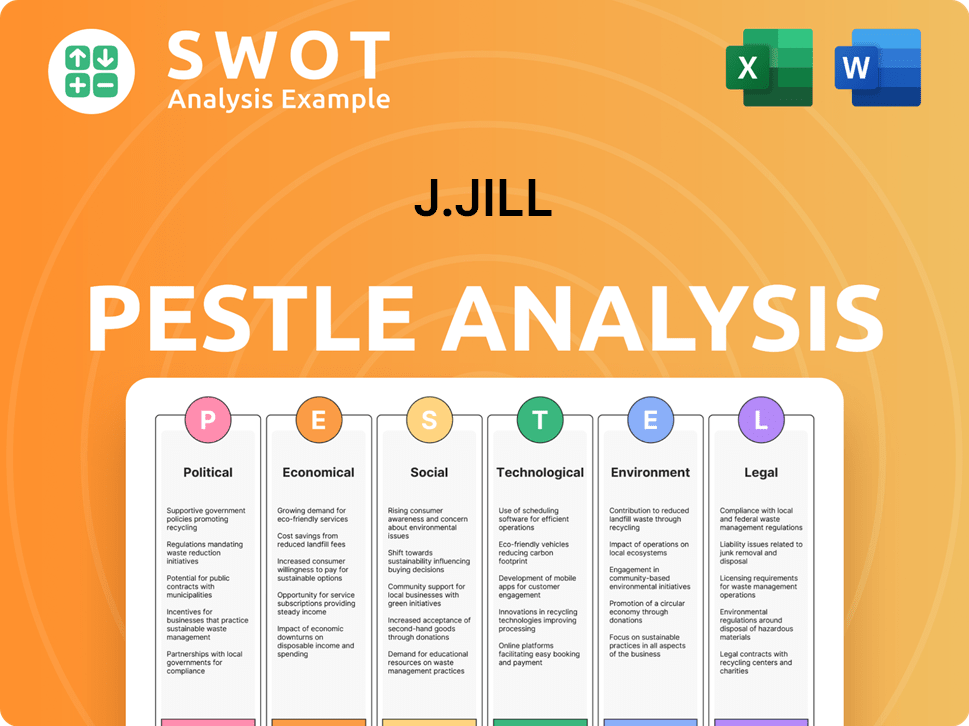
J.Jill PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
Who Sits on J.Jill’s Board?
The current board of directors of the J.Jill company plays a crucial role in its governance and strategic direction. As of early 2025, the board typically includes a mix of independent directors and representatives of major shareholders. These individuals bring expertise in areas like retail, finance, and e-commerce, ensuring a diverse skill set to guide the company. The presence of independent directors is important for objective decision-making and strong corporate governance.
The board's composition often reflects the interests of significant shareholders, with directors potentially having backgrounds tied to investment firms. The board's decisions, including executive compensation and strategic initiatives, are subject to shareholder approval and influence. This structure helps ensure accountability to a broad base of equity holders. The board aims to maintain a majority of independent directors to ensure objective decision-making and strong corporate governance.
| Board Member | Title | Relevant Experience |
|---|---|---|
| James S. MacPhee | Chairman of the Board | Extensive experience in retail and financial management |
| Claire Spofford | Director | Expertise in e-commerce and digital strategy |
| Michael J. Henry | Director | Background in finance and investment |
J.Jill operates with a standard one-share-one-vote voting structure, meaning each share of common stock generally entitles its holder to one vote on matters submitted to shareholders. This structure ensures that voting power is directly proportional to equity ownership. The board and management remain accountable to a broad base of equity holders. For more insights, you can explore the Marketing Strategy of J.Jill.
The voting structure at J.Jill ensures that voting power aligns directly with share ownership. Large institutional investors can significantly influence the company's direction through their collective voting power.
- One-share-one-vote structure.
- No dual-class shares.
- Shareholder influence on executive compensation.
- Board decisions subject to shareholder approval.
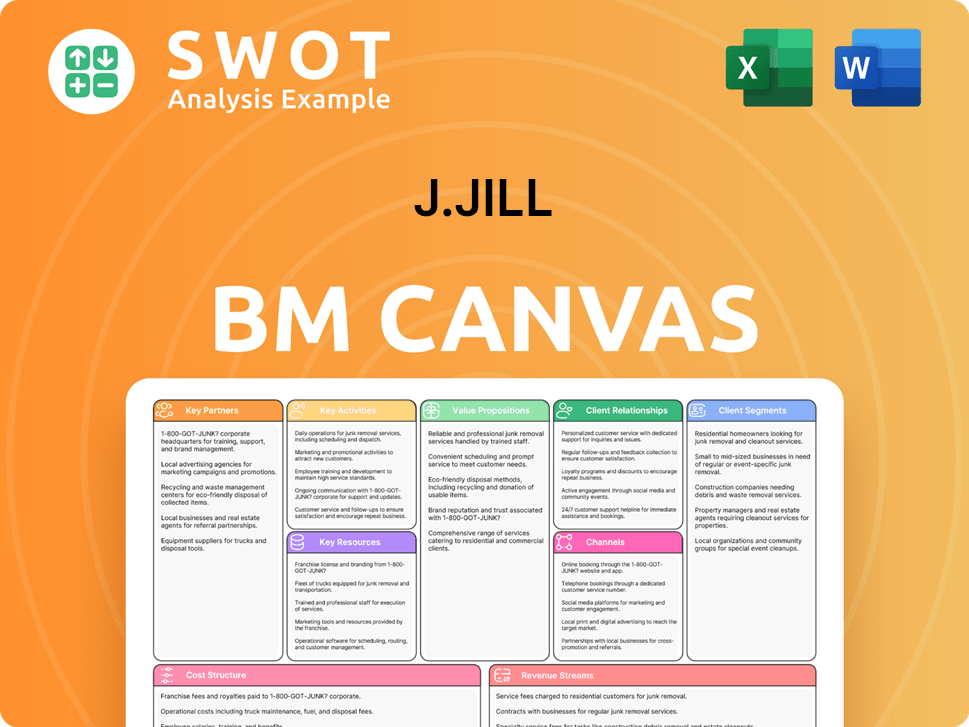
J.Jill Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What Recent Changes Have Shaped J.Jill’s Ownership Landscape?
In the last 3-5 years, the ownership structure of J.Jill has remained relatively stable, reflecting broader trends in the retail sector. The company has navigated the challenges of the post-COVID-19 environment by adjusting its operations and financial strategies. While there haven't been major shifts like large share buybacks, the ownership profile continues to evolve within the context of a dynamic market.
A key aspect of J.Jill's ownership is the significant role of institutional investors. As of March 31, 2024, institutional ownership accounted for approximately 75.32% of the company's stock. Major institutional holders include The Vanguard Group and BlackRock, Inc. This high level of institutional involvement is typical for publicly traded companies, indicating a reliance on professional money managers. The founder's direct ownership would have decreased after the IPO and any subsequent capital raises or acquisitions, which is a standard process for companies that go public.
| Ownership Type | Percentage (Approximate) | Key Holders |
|---|---|---|
| Institutional | ~75.32% (as of March 31, 2024) | The Vanguard Group, BlackRock, Inc. |
| Other | Remaining shares | Various individual and other institutional investors |
| Founder | Significantly diminished post-IPO | N/A |
The retail sector has seen consolidation and, occasionally, activist investor involvement, although there have been no significant activist campaigns targeting J.Jill recently. The company's strategic focus is on optimizing its multi-channel approach and serving its core customer base. Ownership trends support a stable, institutionally-backed public entity. For further insights into the financial aspects and business model, you can explore Revenue Streams & Business Model of J.Jill.
Institutional investors hold a significant majority of J.Jill's stock. The ownership structure reflects the company's stability as a publicly traded entity. Founder ownership has diminished over time, typical for public companies.
The Vanguard Group and BlackRock, Inc. are among the top institutional holders. These firms play a crucial role in investment decisions related to J.Jill. The company's stock is influenced by the strategies of these major shareholders.
Future changes in ownership may be driven by market conditions or strategic partnerships. The company's focus is on maintaining its multi-channel approach. Ownership dynamics reflect the broader retail industry trends.
Market conditions and strategic partnerships can influence ownership changes. Institutional investment adjustments will also play a role. The company's performance is closely tied to these factors.
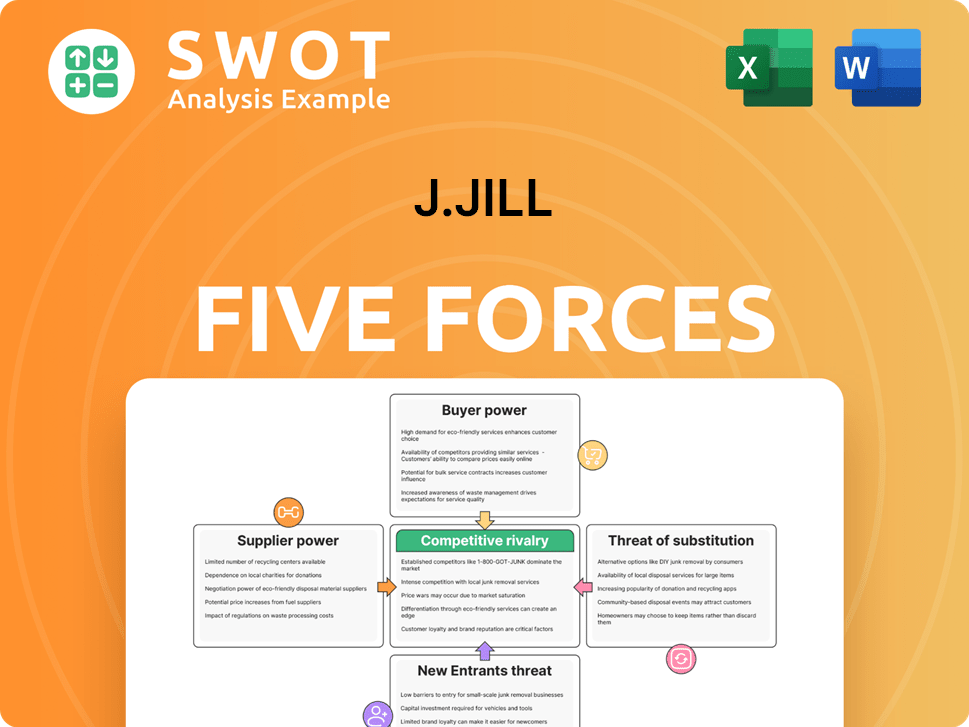
J.Jill Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of J.Jill Company?
- What is Competitive Landscape of J.Jill Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of J.Jill Company?
- How Does J.Jill Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of J.Jill Company?
- What is Brief History of J.Jill Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of J.Jill Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.