Morgan Stanley Bundle
Who Really Controls Morgan Stanley?
Understanding the Morgan Stanley SWOT Analysis is crucial, but have you ever wondered who truly steers this financial giant? The ownership structure of Morgan Stanley is a complex web of institutional investors, public shareholders, and historical alliances. Unraveling this structure provides invaluable insights into its strategic direction and market influence. This exploration will delve into the key players and pivotal moments that have shaped Morgan Stanley's destiny.

The 2008 financial crisis dramatically altered Morgan Stanley's Morgan Stanley ownership, leading to a significant partnership with Mitsubishi UFJ Financial Group (MUFG). This strategic move, alongside the influence of major institutional investors, has shaped the company's trajectory. Examining the evolution of Morgan Stanley's ownership, including its Morgan Stanley shareholders and the roles of its Morgan Stanley executives, is key to understanding its current position and future prospects. This analysis will provide a comprehensive view of who owns Morgan Stanley and how that ownership impacts its operations.
Who Founded Morgan Stanley?
The firm, now known as Morgan Stanley, was established on September 16, 1935. The founders, Henry S. Morgan and Harold Stanley, were both formerly associated with J.P. Morgan & Co.
Their departure was a direct response to the Glass-Steagall Act of 1933, which required the separation of commercial and investment banking activities. J.P. Morgan & Co. chose to focus on commercial banking, leading Morgan and Stanley to create an investment banking firm.
In its first year, the new firm quickly made its mark in the financial world. It participated in public offerings and private placements totaling US$1.1 billion, capturing a 24% market share at the time. This early success highlighted the founders' vision for a focused investment bank.
Founded in 1935 by Henry S. Morgan and Harold Stanley.
Concentrated on investment banking following the Glass-Steagall Act.
Captured a 24% market share in its inaugural year.
Led underwriting for significant debentures and rail financing.
Started with a small team of just 13 employees, indicating concentrated ownership.
Underwent reorganization in 1941 to expand its securities business.
The early ownership of Morgan Stanley was primarily concentrated in the hands of its founders and key partners. While specific equity splits are not publicly detailed, the initial operation as a partnership with a small staff underscores the focused control. This structure allowed the founders to steer the firm's strategic direction and establish its core business practices. The firm's early success was marked by significant transactions, including leading the underwriting of US$100 million in debentures for United States Steel Corporation in 1938 and becoming the lead syndicate in U.S. rail financing in 1939. Perry Hall, the last founder to lead Morgan Stanley, served as head of the firm from 1951 to 1961. For more details on the business model, consider reading Revenue Streams & Business Model of Morgan Stanley.
- The founders, Henry S. Morgan and Harold Stanley, held significant initial control.
- Early operations were as a partnership, indicating concentrated ownership.
- Key early transactions included major underwriting deals.
- Perry Hall was the last founder to lead the firm.
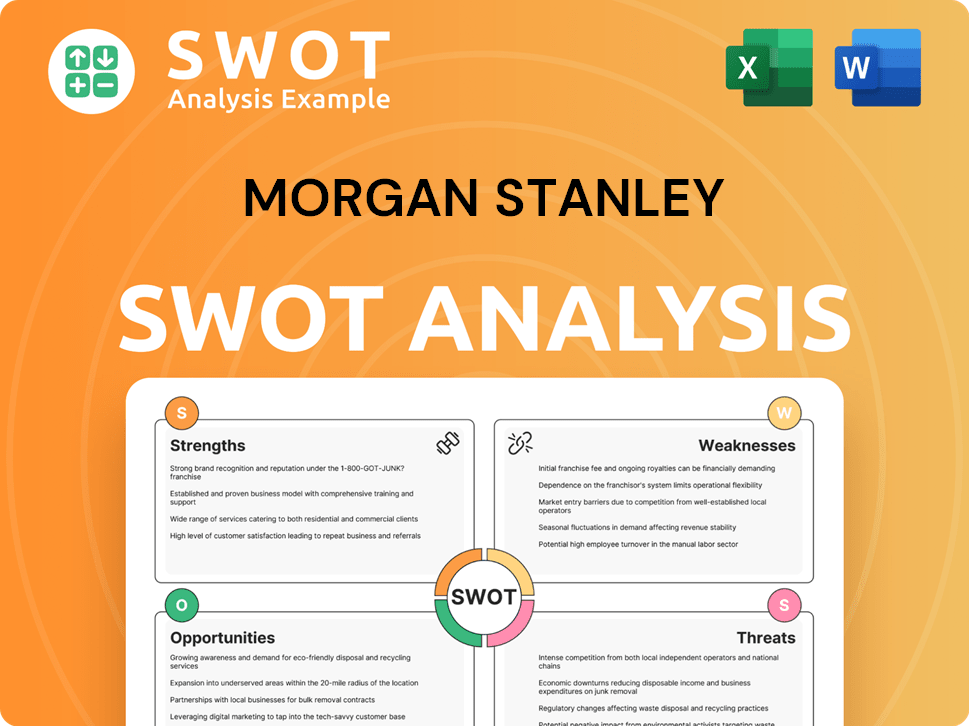
Morgan Stanley SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
How Has Morgan Stanley’s Ownership Changed Over Time?
The evolution of Morgan Stanley's ownership has been marked by significant transformations since its inception. Initially a private partnership, the firm went public in 1986, trading on the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) under the ticker symbol MS. This initial public offering (IPO) broadened its investor base. A pivotal moment arrived in 1997 with the merger with Dean Witter Discover & Co., creating the largest asset management and securities firm in America by equity capital at the time.
A major shift in the ownership structure occurred during the 2008 financial crisis. Mitsubishi UFJ Financial Group (MUFG) invested $9 billion, acquiring a 21% stake and forming a strategic alliance. This investment was crucial, and as of December 31, 2024, MUFG remains the largest shareholder, holding 23.38% of Morgan Stanley's shares. These changes have significantly influenced the company's strategic direction and global reach.
| Ownership Milestone | Date | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Public Offering (IPO) | 1986 | Morgan Stanley became a publicly traded company. |
| Merger with Dean Witter | 1997 | Created the largest asset management and securities firm in America by equity capital at the time. |
| MUFG Investment | 2008 | Mitsubishi UFJ Financial Group invested $9 billion, acquiring a 21% stake. |
As of April 2025, the majority of Morgan Stanley's shares are held by institutional investors, who collectively control 62%. The largest institutional shareholders include Mitsubishi UFJ Financial Group (23.38%), State Street Corporation (6.90%), The Vanguard Group (6.83%), BlackRock (5.90%), JP Morgan Chase (2.54%), Capital International Investors (1.86%), and Geode Capital Management (1.60%). Individual investors hold approximately 15%. Former CEO James Gorman was the largest individual shareholder as of April 2024, holding 886,445 shares, followed by current CEO Edward Pick with 802,668 shares. The executive officers and directors collectively own or have rights to acquire 3,868,694 shares.
Morgan Stanley's ownership structure is primarily influenced by institutional investors, with MUFG as the largest shareholder.
- The company's shift from a private partnership to a public entity in 1986 marked a significant change.
- The 2008 investment by MUFG was a pivotal moment, shaping its strategic alliances.
- Current ownership reflects a mix of institutional and individual investors, with executives holding considerable influence.
- Understanding the ownership structure is key to assessing the company's strategic direction.
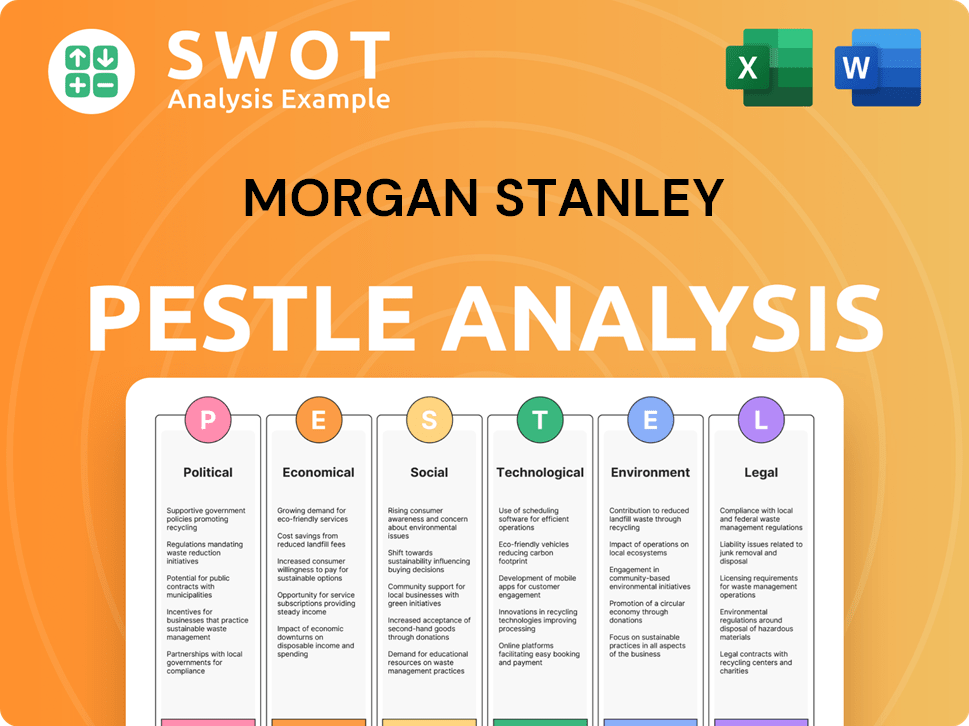
Morgan Stanley PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
Who Sits on Morgan Stanley’s Board?
As of January 2025, the leadership of Morgan Stanley includes Ted Pick as Chairman and CEO. The Board of Directors plays a crucial role in overseeing the company's strategic direction and governance. The board was set to decrease from 15 to 13 directors as of January 1, 2025, following resignations and retirements.
The board members as of May 2024 were: Ted Pick, Megan Butler, Thomas H. Glocer, Robert H. Herz, Erika H. James, Hironori Kamezawa, Shelley B. Leibowitz, Jami Miscik, Masato Miyachi, Dennis M. Nally, Douglas L. Peterson, Mary L. Schapiro, and Perry M. Traquina. Masato Miyachi and Hironori Kamezawa represent Mitsubishi UFJ Financial Group (MUFG), the largest shareholder. These directors, while representing a major shareholder, may not have direct ownership positions beyond their roles.
| Board Member | Position | Affiliation |
|---|---|---|
| Ted Pick | Chairman and CEO | Morgan Stanley |
| Megan Butler | Director | Independent |
| Thomas H. Glocer | Director | Independent |
| Robert H. Herz | Director | Independent |
| Erika H. James | Director | Independent |
| Hironori Kamezawa | Director | Mitsubishi UFJ Financial Group (MUFG) |
| Shelley B. Leibowitz | Director | Independent |
| Jami Miscik | Director | Independent |
| Masato Miyachi | Director | Mitsubishi UFJ Financial Group (MUFG) |
| Dennis M. Nally | Director | Independent |
| Douglas L. Peterson | Director | Independent |
| Mary L. Schapiro | Director | Independent |
| Perry M. Traquina | Director | Independent |
Morgan Stanley's voting structure is based on one-share-one-vote. The collective ownership of executives and directors, including CEO Ted Pick, shows a vested interest in the company's performance. As of April 2024, CEO Edward Pick held 802,668 shares. Former CEO James Gorman held approximately 886,445 shares as of April 2024. Recent developments include the transition of leadership from James Gorman to Ted Pick. Consistent dividend payments for 32 consecutive years reflect strong corporate governance.
The Morgan Stanley ownership structure is primarily influenced by institutional investors and the holdings of company executives. Key figures like the CEO and other board members have a significant stake in the company's performance.
- The board of directors oversees the company's strategic direction.
- MUFG is the largest shareholder, represented by board members.
- The company operates on a one-share-one-vote basis.
- Consistent dividend payments reflect strong governance.
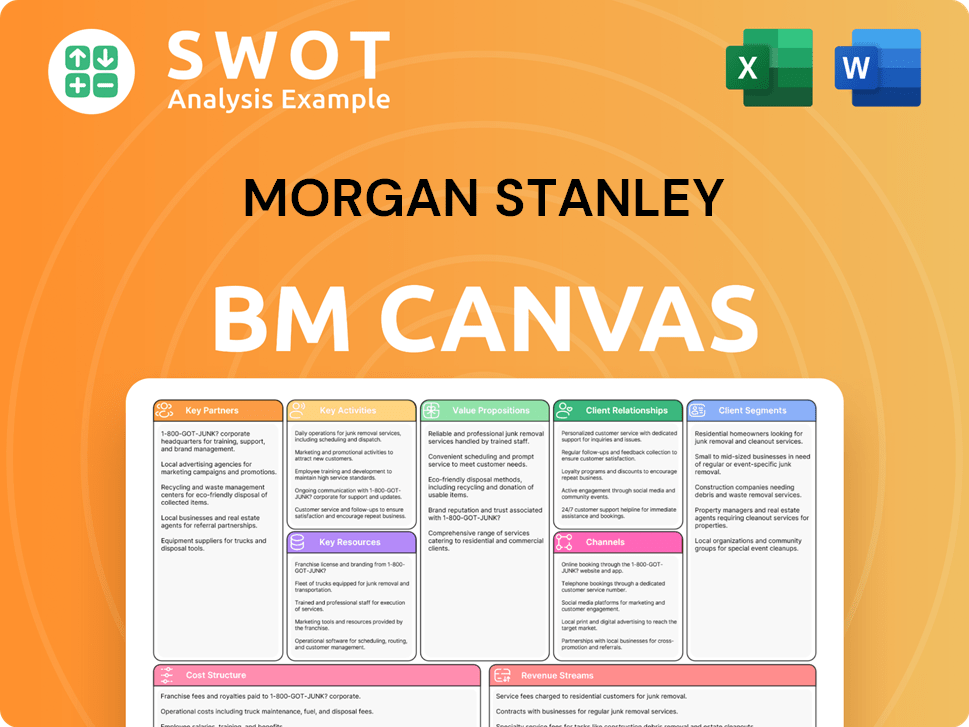
Morgan Stanley Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What Recent Changes Have Shaped Morgan Stanley’s Ownership Landscape?
Over the past few years, the ownership profile of Morgan Stanley has seen significant developments. A major shift occurred in leadership, with James Gorman stepping down as CEO in January 2024 and Ted Pick taking over, later becoming Chairman in January 2025. The firm has also been active in capital allocation, with a $20 billion share repurchase program authorized by the Board of Directors, beginning in the third quarter of 2024. Additionally, the quarterly common stock dividend increased to $0.925 per share from $0.85, also starting in the third quarter of 2024.
The company's involvement in mergers and acquisitions remains substantial, particularly in advisory roles. For instance, it topped the M&A financial advisor rankings by value in the construction sector with $41 billion in deals during 2024, and in the financial services sector with $96 billion in deals. Furthermore, Morgan Stanley launched a Private Market Transactions Desk in March 2024 to cater to the growing private markets. The Investment Management division saw its assets under management increase to $1.7 trillion by the end of 2024, with long-term net inflows of $18 billion for the year. These changes reflect a dynamic landscape for the company, influencing its ownership and strategic direction.
| Metric | Details | Year |
|---|---|---|
| Institutional Ownership | Approximately 85.45% of shares | May 2025 |
| Assets Under Management (Investment Management) | $1.7 trillion | Year-end 2024 |
| M&A Deals (Financial Services Sector) | $96 billion | 2024 |
The ownership of Morgan Stanley is primarily influenced by institutional investors, who held approximately 85.45% of the shares as of May 2025. This indicates a strong presence of large financial institutions in the company's ownership structure. The leadership transition and capital allocation strategies, such as share repurchases and dividend increases, reflect a commitment to shareholder value. For a deeper understanding of how the company is growing, you can read about the Growth Strategy of Morgan Stanley.
Institutional investors hold a significant portion of Morgan Stanley's shares. The company's leadership changes and capital allocation strategies impact the shareholder value.
The firm has seen leadership transitions and strategic capital deployment. The company is also active in mergers and acquisitions, expanding its offerings.
The Investment Management division has seen growth in assets under management. The firm has increased dividends and repurchased shares to return capital.
Morgan Stanley's focus remains on supporting clients and driving earnings. The company's strong capital position supports its strategic initiatives.
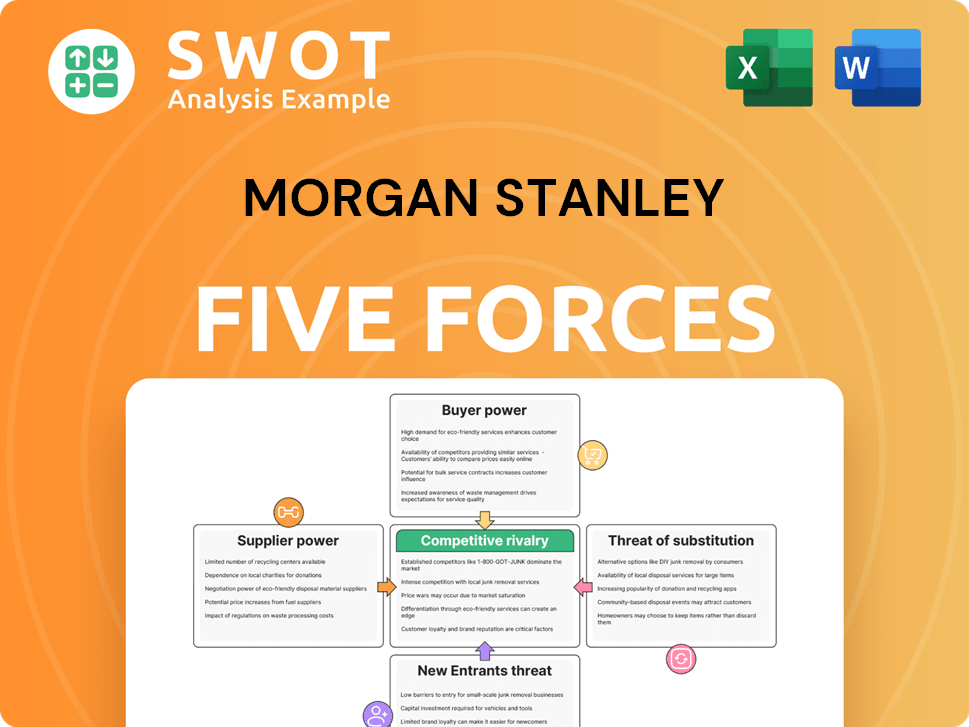
Morgan Stanley Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of Morgan Stanley Company?
- What is Competitive Landscape of Morgan Stanley Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Morgan Stanley Company?
- How Does Morgan Stanley Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Morgan Stanley Company?
- What is Brief History of Morgan Stanley Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Morgan Stanley Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.