Pandora AS Bundle
Who Really Owns Pandora?
Ever wondered who pulls the strings behind the globally adored Pandora AS SWOT Analysis jewelry brand? Understanding the Pandora company owner is key to unlocking its strategic roadmap and future potential. From its humble beginnings to its current status as a global powerhouse, Pandora's ownership has undergone a fascinating transformation.

This exploration into Pandora AS ownership delves into the evolution of its ownership, from the founders' initial vision to the influence of major shareholders today. We'll uncover the key players shaping Pandora's destiny, examining the dynamics of its public shareholding and the impact of these ownership changes on its business strategies. Discover the forces that drive this iconic brand, from its product development and market positioning to its global expansion efforts.
Who Founded Pandora AS?
The story of Pandora A/S began in 1982, crafted by the vision of Per Enevoldsen and his wife, Winnie Enevoldsen. Initially, the business was a modest jewelry shop in Copenhagen, Denmark. Their focus was on importing jewelry from Thailand for retail.
The early years of Pandora A/S were marked by family ownership. Per and Winnie Enevoldsen held complete control of the company. This structure was typical of a small, privately-held business in its early stages, with the founders at the helm.
As the business evolved, the Enevoldsens transitioned from importing to designing and manufacturing their own jewelry. This strategic shift included hiring the first in-house designer in 1987 and establishing a manufacturing facility in Thailand in 1989. This move allowed for better control over production and costs. During this time, the ownership remained firmly with the founders.
The founders, Per and Winnie Enevoldsen, maintained full ownership during the initial years of Pandora A/S. There were no external investors or shareholders during this time. The company's growth was fueled by its own operational successes and the founders' vision.
- The Enevoldsens' background in the jewelry trade shaped their understanding of the market.
- Early agreements were internal family arrangements, not formal investment deals.
- The founders' control over the company directly reflected their vision of creating accessible, high-quality jewelry.
- The company's early focus was on importing jewelry, then transitioning to design and manufacturing.
For more information about the company's growth, consider reading the Growth Strategy of Pandora AS.
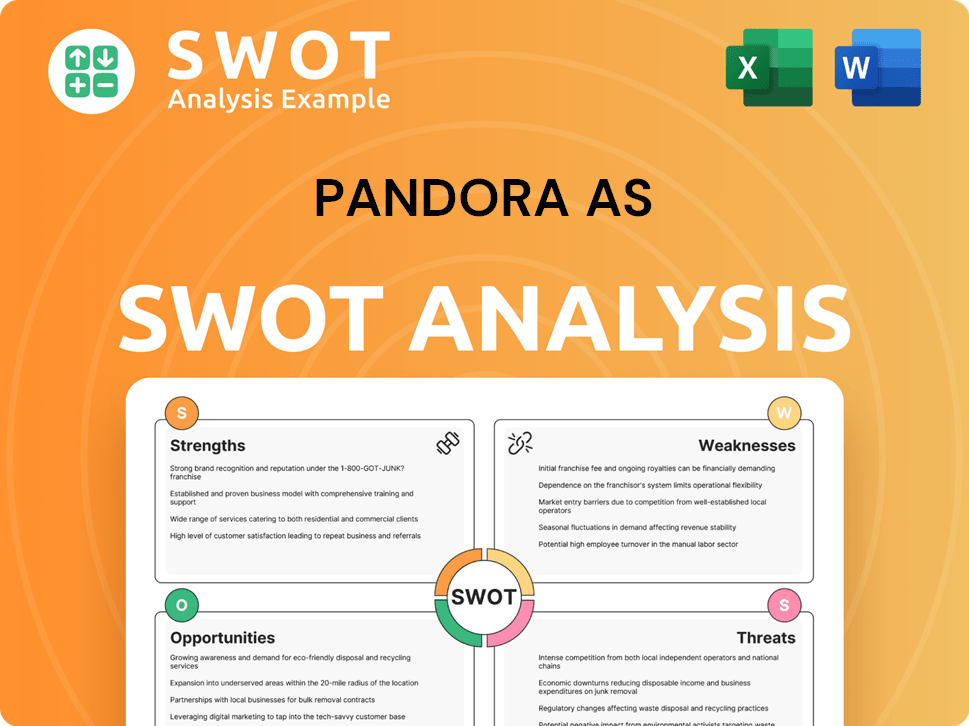
Pandora AS SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
How Has Pandora AS’s Ownership Changed Over Time?
The most significant shift in the Pandora AS ownership structure occurred with its Initial Public Offering (IPO) in October 2010. This transition moved the company from private to public, listing on the NASDAQ OMX Copenhagen stock exchange. Before the IPO, the private equity firm Axcel acquired a 60% stake in 2008 from the Enevoldsen family for DKK 1.1 billion, while the family retained a 40% share.
Following the IPO, the ownership of Pandora A/S diversified. The company's shift from a family-run business to a publicly traded corporation brought increased transparency and a focus on shareholder value. This evolution allowed Pandora to access capital markets for expansion and strategic initiatives. The transformation also led to stricter governance standards.
| Event | Date | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Axcel Acquisition | 2008 | Private equity firm acquired a majority stake, changing the ownership structure. |
| Initial Public Offering (IPO) | October 2010 | Transitioned from private to public ownership, increasing shareholder base. |
| Ongoing Ownership | Early 2025 | Institutional investors, pension funds, and investment companies hold significant shares. |
As of early 2025, the major shareholders of Pandora AS are primarily institutional investors, including large asset management firms like BlackRock, Inc. and The Vanguard Group. These firms typically hold significant stakes. No single entity, including the founding family, holds a controlling stake. The company's free float is substantial, indicating a wide distribution of shares among public investors. If you're interested in understanding more about the competitive environment, you can explore the Competitors Landscape of Pandora AS.
The ownership of Pandora has evolved significantly from its founding to its current state as a publicly traded company.
- The IPO in 2010 was a major turning point, shifting ownership to the public.
- Institutional investors now hold a significant portion of the shares.
- The company's governance and strategic focus have changed due to the shift in ownership.
- Understanding the ownership structure is crucial for investors and stakeholders.
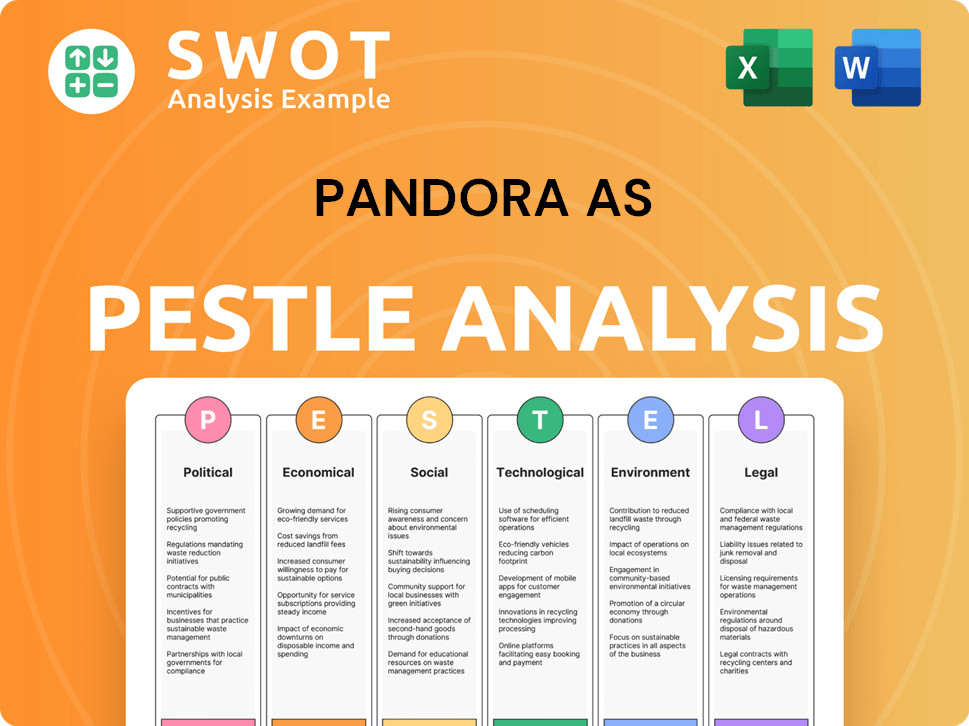
Pandora AS PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
Who Sits on Pandora AS’s Board?
As of early 2025, the Board of Directors of Pandora A/S is composed of independent members and individuals with substantial business or financial expertise. The board's structure aims to provide a balance of skills and perspectives essential for a global company. The Chairman of the Board is typically an independent figure, and other board members come from diverse backgrounds, including retail, finance, and international business. This structure helps ensure that the board can effectively oversee the company's strategic direction and operational performance. The focus is on maintaining a board that can navigate the complexities of the international jewelry market and respond to shareholder interests.
The board's composition is regularly reviewed and adjusted to align with best practices in corporate governance and support the company's strategic objectives. Decisions made by the board, such as major investments, strategic partnerships, or executive appointments, are influenced by the collective interests of its diverse shareholder base. This approach helps ensure that the company remains responsive to shareholder concerns and market trends. The board's role is crucial in overseeing the company's performance and ensuring its long-term success in a competitive market. The Marketing Strategy of Pandora AS is also influenced by the board's decisions.
| Board Member | Role | Background |
|---|---|---|
| Anders Godtfredsen | Chairman | Extensive experience in retail and finance |
| Helena Helmersson | Board Member | CEO of H&M |
| Casper Mejer Rasmussen | Board Member | CFO of Pandora |
The voting structure of Pandora A/S generally follows a one-share-one-vote principle, common for publicly traded companies. This ensures that voting power is directly proportional to the number of shares held. There are no known special voting rights or founder shares that grant outsized control to any individual or entity. This structure promotes fairness and transparency in the company's governance. The company's commitment to corporate governance is evident in its board composition and voting structure, which are designed to protect shareholder interests and support long-term value creation. The company's focus on strong corporate governance reflects its commitment to maintaining investor confidence and ensuring sustainable growth.
Understanding the board of directors and voting power is crucial for anyone interested in Pandora jewelry and Pandora AS ownership.
- The board is composed of independent members and experts.
- Voting rights are based on a one-share-one-vote principle.
- The company focuses on strong corporate governance.
- The board's decisions influence the company's strategic direction.
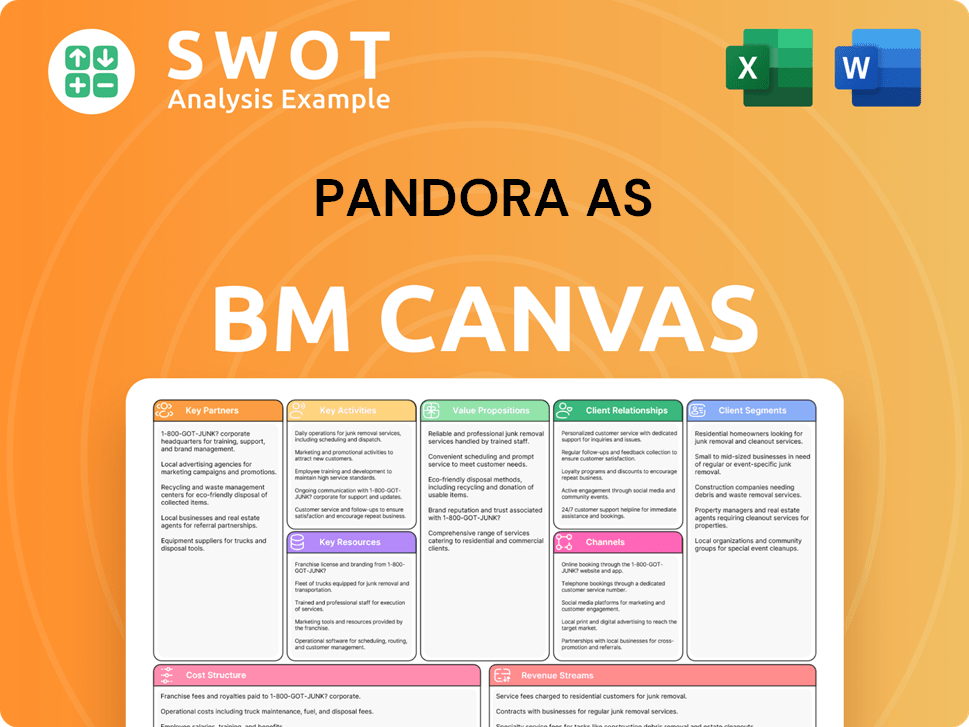
Pandora AS Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What Recent Changes Have Shaped Pandora AS’s Ownership Landscape?
Over the past few years, the ownership of Pandora A/S has seen continued evolution, primarily characterized by the sustained presence of institutional investors. This reflects a broader market trend where institutional ownership, both passive and active, is increasing in well-established companies. While there haven't been major shifts in controlling stakes, Pandora has been involved in share repurchase programs as part of its capital allocation strategy. For example, in 2024, Pandora announced a new share buyback program of up to DKK 3.0 billion, which demonstrates its commitment to returning value to shareholders and potentially influencing ownership percentages over time.
Leadership changes and industry trends have also played a role. While leadership changes don't directly alter ownership, they can indirectly influence investor confidence. Pandora has maintained a stable leadership team focused on its 'Phoenix' strategy. Furthermore, industry trends such as ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) investing are also influencing Pandora. Large institutional investors are increasingly incorporating ESG criteria into their investment decisions, which impacts their allocation to companies like Pandora. This encourages companies to demonstrate strong ESG performance, potentially attracting or retaining certain types of institutional investors. The company is now firmly in the realm of widely held public ownership.
| Aspect | Details | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Institutional Investors | Significant presence in the shareholder base. | Reflects market trends and influences stock performance. |
| Share Buyback Programs | Pandora's commitment to returning value to shareholders. | Increases earnings per share and consolidates ownership. |
| ESG Investing | Growing importance of ESG criteria for institutional investors. | Encourages strong ESG performance, potentially attracting investors. |
The evolution of Pandora AS's ownership structure is primarily driven by market dynamics and investor sentiment. Future changes will likely be influenced by the company's financial performance, rather than significant shifts in controlling stakes or planned privatization. Currently, the company is a publicly traded entity, with no single entity holding a controlling stake. This structure reflects the company's mature phase and its integration into the global financial market. The share buyback programs are a key aspect of the company's financial strategy to enhance shareholder value.
The ownership of Pandora A/S has seen a continued strong presence of institutional investors, reflecting a broader market trend. Share repurchase programs are part of its capital allocation strategy.
Pandora announced a new share buyback program of up to DKK 3.0 billion. This demonstrates a commitment to returning value to shareholders and potentially impacting ownership percentages over time.
Large institutional investors are increasingly incorporating ESG criteria into their investment decisions, which can impact their allocation to companies like Pandora.
Future ownership changes are likely to be driven by market dynamics, investor sentiment, and Pandora's ongoing financial performance.
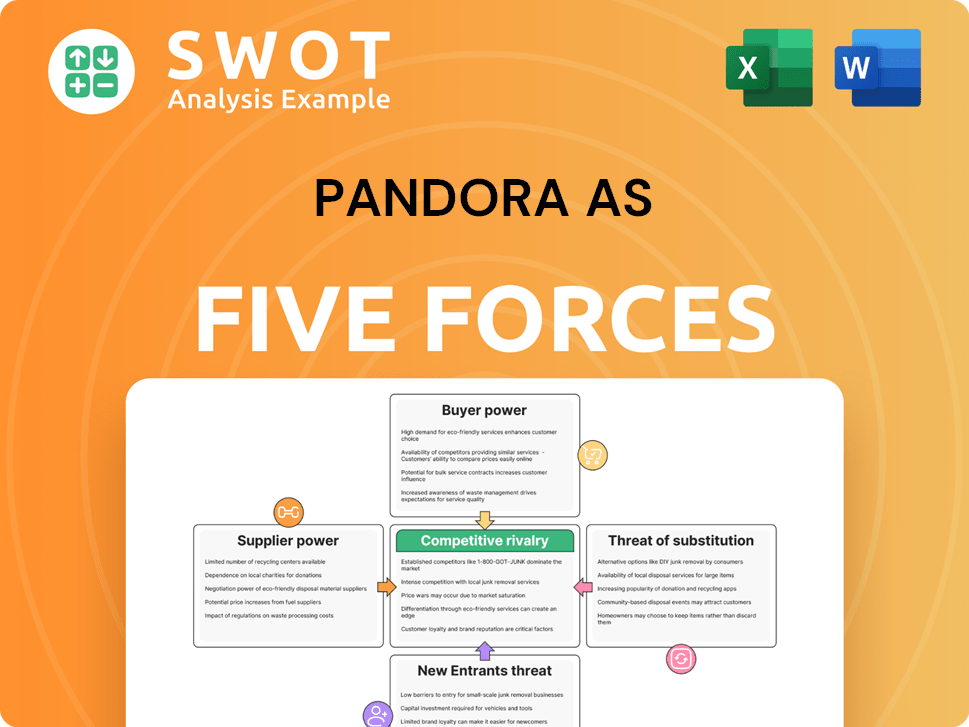
Pandora AS Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of Pandora AS Company?
- What is Competitive Landscape of Pandora AS Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Pandora AS Company?
- How Does Pandora AS Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Pandora AS Company?
- What is Brief History of Pandora AS Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Pandora AS Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.