Perpetual Bundle
Who Really Owns Perpetual Company?
In the ever-shifting landscape of finance, understanding corporate ownership is key to informed decision-making. Perpetual Limited, a cornerstone of the Australian financial services sector since 1886, is undergoing a significant transformation. This pivotal shift, including the proposed sale of major business units, raises critical questions about its future direction and the stakeholders who shape it.
This exploration into Perpetual SWOT Analysis will uncover the intricacies of Perpetual Company ownership, from its historical roots to the present day. We'll examine the evolving company structure, the influence of major shareholders, and the implications for corporate governance. Understanding who owns Perpetual Company is essential for investors, analysts, and anyone seeking a comprehensive view of this financial powerhouse, including its legal structure and the role of its board of directors.
Who Founded Perpetual?
The origins of the company, now known as Perpetual, trace back to 1885, with its formal establishment as Perpetual Trustee Company Limited in 1886. This early phase involved a committee of business professionals, setting the stage for a company focused on wealth management and protection. The company's early structure and operations were designed to build trust and provide long-term fiduciary services.
Key figures in the company's founding included prominent individuals like Sir Edmund Barton, who would later become Australia's first Prime Minister, John Street from the Street family, and James Fairfax from the Fairfax family. These individuals played crucial roles in shaping the company's initial direction and establishing its commitment to responsible wealth management. The early focus was on building a reputable institution for managing and safeguarding assets.
The company's legal foundation was solidified in 1888 when the NSW Legislative Assembly granted Perpetual a special act. This act empowered the company to act as a corporate executor and trustee, attracting prominent citizens who appointed Perpetual to manage their estates, often for multiple generations. While specific details of the initial shareholdings are not readily available in public records, the involvement of these influential businessmen indicates a collective ownership model designed for long-term fiduciary responsibility.
Perpetual's origins began in 1885, evolving into Perpetual Trustee Company Limited in 1886. This early structure provided a foundation for its future operations. The initial focus was on establishing a trustworthy institution for wealth management.
Notable founders included Sir Edmund Barton, John Street, and James Fairfax. These individuals brought significant influence to the company. Their involvement was crucial in setting the company's ethical and operational standards.
The 1888 special act by the NSW Legislative Assembly was a pivotal moment. This act enabled the company to act as a corporate executor and trustee. This solidified its role in managing and protecting wealth.
Initial operations were based at 105 Pitt Street, Sydney. The first employee was an accountant named John Pewtress. The company's early focus was on building a reputable institution for managing and safeguarding assets.
The initial ownership model was a collective approach focused on fiduciary responsibility. While specific equity splits are not available, the founders' actions indicate a shared commitment. This model ensured long-term stability and trust.
The founding team's vision was to establish a trusted institution for wealth management. This core principle has endured throughout its history. The focus was on building a reputable institution for managing and safeguarding assets.
Understanding the early ownership of Perpetual provides insight into its long-term focus on fiduciary responsibility. The company's structure, established in 1886, was designed to ensure stability and trust. Key figures like Sir Edmund Barton and James Fairfax, along with the Street family, played crucial roles in shaping the company's initial direction. The special act of 1888 further solidified its role in wealth management. For further insights into the strategies employed by Perpetual, consider reading about the Marketing Strategy of Perpetual.
- The company's early structure was focused on collective ownership, emphasizing long-term fiduciary responsibility.
- The involvement of prominent figures like Sir Edmund Barton, John Street, and James Fairfax highlights the company's commitment to building trust.
- The 1888 act provided a strong legal foundation for its role as a corporate executor and trustee.
- The initial operations at 105 Pitt Street, Sydney, marked the beginning of its journey in wealth management.
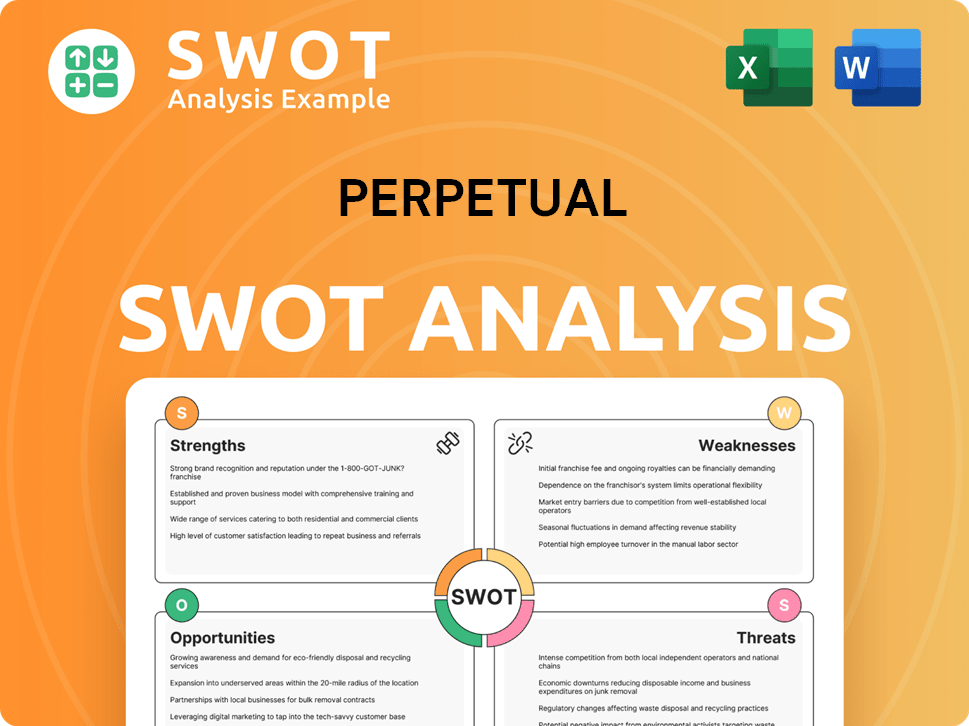
Perpetual SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
How Has Perpetual’s Ownership Changed Over Time?
The ownership structure of Perpetual Company, listed on the Australian Securities Exchange (ASX:PPT) since 1964, has seen significant changes. Initially, the company expanded organically. A key acquisition in 2013, The Trust Company, strengthened its position in the Australian trustee business. More recently, Perpetual has focused on building a global asset management presence through acquisitions, including Trillium Asset Management in 2020 and the Pendal Group in 2023, which included brands like J O Hambro, Regnan, and TSW.
A pivotal moment in Perpetual's history is the planned sale of its Corporate Trust and Wealth Management divisions to Kohlberg Kravis Roberts & Co. L.P. (KKR) for A$2.175 billion, announced in May 2024 and anticipated to finalize in February 2025. This strategic move will transform Perpetual into a pure-play global asset management firm. As of June 30, 2024, the streamlined entity managed over A$215 billion in assets under management (AUM). This shift is expected to reshape the company's strategy and governance, concentrating on its core asset management capabilities.
| Shareholder | Shares Held | Percentage Interest |
|---|---|---|
| Washington H. Soul Pattinson and Company Limited (as of December 2023) | 13,214,115 | 11.66% |
| State Street Corporation and Subsidiaries (as of March 2024) | 8,086,323 | 7.13% |
| BlackRock Group (as of June 2024) | 5,682,201 | 5.00% |
As of December 2023, Washington H. Soul Pattinson and Company Limited was the largest shareholder in Perpetual Company Ownership, holding 11.66% of the shares. Other significant institutional shareholders include State Street Corporation and its subsidiaries, which held 7.13% as of March 2024, and BlackRock Group, with 5.00% as of June 2024. These major stakeholders play a crucial role in the company's corporate governance and strategic direction.
Perpetual's ownership structure has evolved significantly since its listing, marked by strategic acquisitions and a shift towards global asset management.
- The sale of Corporate Trust and Wealth Management businesses to KKR is a major strategic move.
- Washington H. Soul Pattinson and Company Limited is the largest shareholder.
- Institutional investors like State Street and BlackRock hold significant stakes.
- The company's focus is now on its core asset management capabilities.
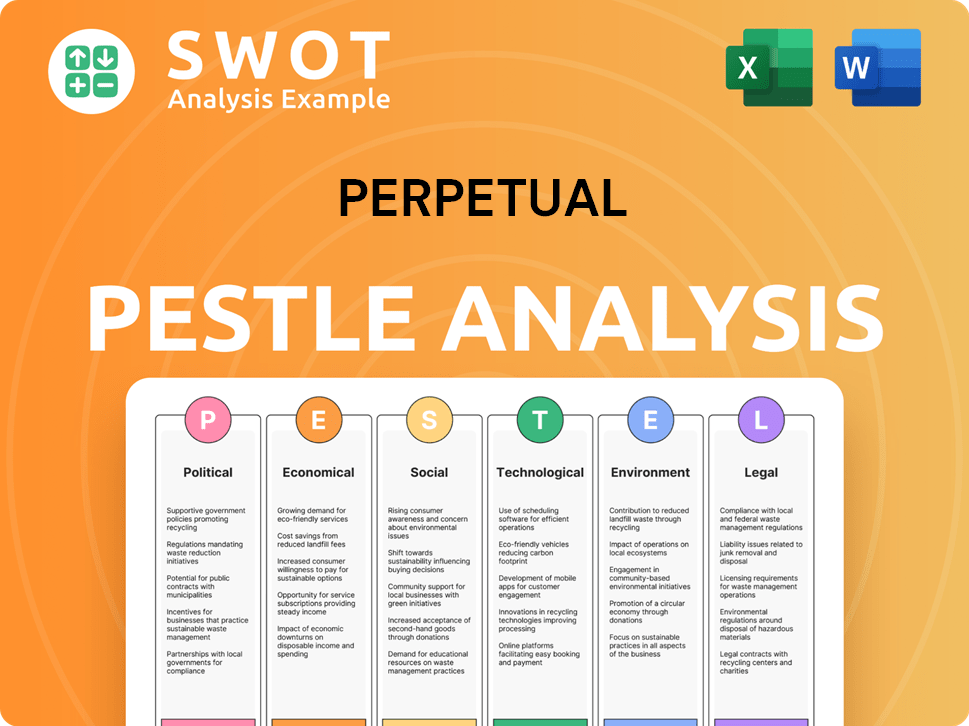
Perpetual PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
Who Sits on Perpetual’s Board?
The current Board of Directors of Perpetual Limited is pivotal in guiding the company, especially with its ongoing strategic shifts. As of February 2025, Gregory Cooper leads as Chairman, succeeding Tony D'Aloisio AM, who retired following the planned KKR transaction. Cooper, an Independent Non-executive Director since September 2019, brings extensive experience from the global investment industry. The Competitors Landscape of Perpetual highlights the importance of understanding its ownership and governance structure.
The Board has seen changes, including the retirements of Independent Non-Executive Directors Ian Hammond and Nancy Fox AM at the October 17, 2024, Annual General Meeting (AGM). Fiona Trafford-Walker now chairs the People & Remuneration Committee (PARC) after Ms. Fox's departure. Mona Aboelnaga Kanaan, an Independent Non-executive Director since June 2021, chairs the Technology and Cyber Security Committee. Sylvie Dimarco serves as Company Secretary, appointed in April 2020. These changes reflect the dynamic nature of the company's corporate governance.
| Director | Role | Appointment Date |
|---|---|---|
| Gregory Cooper | Chairman | September 2019 |
| Mona Aboelnaga Kanaan | Independent Non-executive Director | June 2021 |
| Fiona Trafford-Walker | Independent Non-executive Director | Not specified |
Perpetual operates with a one-share-one-vote structure, common in ASX-listed companies. While no single entity has outsized control through special voting rights, major shareholders like Washington H. Soul Pattinson and Company Limited, holding 11.66% as of December 2023, significantly influence the company. The Board's decisions, such as recommending the sale of Corporate Trust and Wealth Management businesses to KKR, underscore its strategic direction to streamline operations and concentrate on global asset management. This focus on the company's structure is crucial for understanding its future.
Perpetual Company's ownership structure is defined by its board of directors and major shareholders. The board's decisions, such as the sale of key business units, reflect its strategic direction. Understanding the corporate governance and business ownership provides insights into the company's operations.
- The Chairman and Board members play a crucial role in governance.
- Major shareholders, like Washington H. Soul Pattinson, have significant influence.
- The company's decisions are shaped by its strategic goals.
- The one-share-one-vote structure is standard for ASX-listed companies.
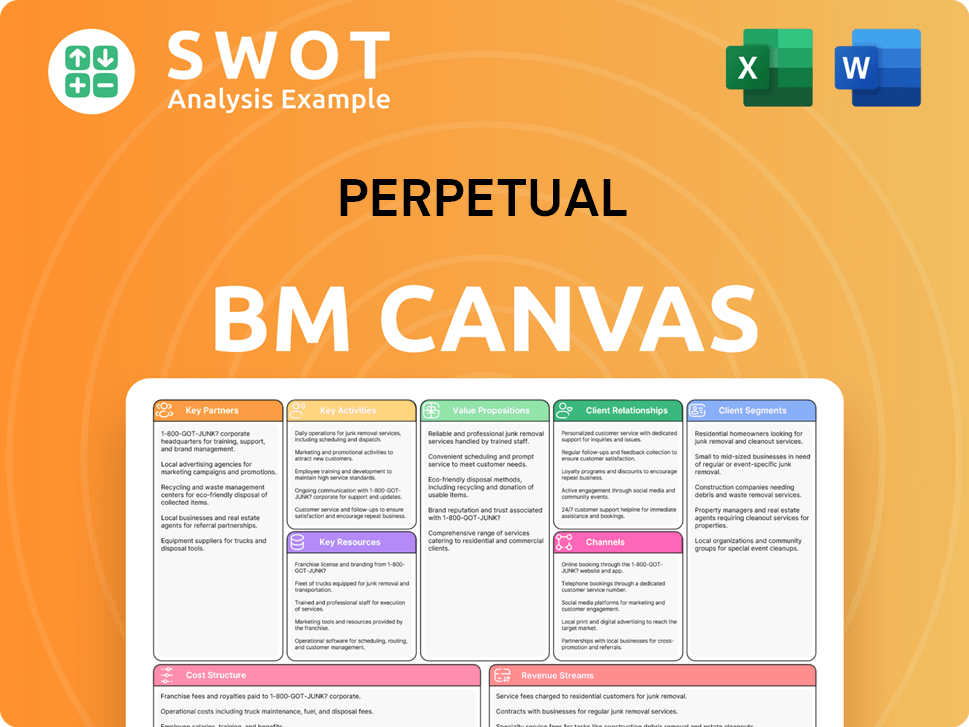
Perpetual Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What Recent Changes Have Shaped Perpetual’s Ownership Landscape?
Over the last few years, the ownership profile of Perpetual Company has seen significant shifts, particularly with its strategic focus on asset management. The company has been actively expanding its asset management capabilities through acquisitions, including Trillium Asset Management and a majority stake in Barrow Hanley Mewhinney & Strauss, LLC, in 2020. The acquisition of Pendal Group in 2023 further solidified its position in the global market. These moves have redefined the Company Structure and its strategic direction.
A major development in 2024 was the proposed sale of Perpetual Company's Corporate Trust and Wealth Management businesses to Kohlberg Kravis Roberts & Co. L.P. (KKR) for A$2.175 billion, announced in May 2024. This transaction was expected to transform Perpetual Company into a pure-play global asset management firm, with over A$215 billion in assets under management as of June 30, 2024. However, as of February 2025, the deal with KKR was terminated, and Perpetual Company now plans to separate its three businesses and pursue the sale of its Wealth Management arm. This has a direct impact on Business Ownership and the company's future.
The company's largest shareholder, as of December 2023, was Washington H. Soul Pattinson and Company Limited, holding 11.66% of the shares. Perpetual Company is also focusing on cost reduction, with a simplification program expected to deliver A$70 million to A$80 million in cost reductions by FY27. Furthermore, the company disclosed an 8.38% interest in Kenmare Resources Plc in June 2025, indicating direct investment in other publicly traded companies. For a deeper understanding of their target audience, you can read more about it in this article: Target Market of Perpetual.
| Key Development | Details | Date |
|---|---|---|
| Acquisition of Trillium Asset Management | Enhancement of global multi-boutique asset management capabilities | 2020 |
| Acquisition of Pendal Group | Solidified position as a global leader in multi-boutique asset management | 2023 |
| Proposed Sale of Corporate Trust and Wealth Management businesses to KKR | A$2.175 billion transaction, later terminated | Announced May 2024, Terminated February 2025 |
| Appointment of Bernard Reilly as CEO | Effective September 2, 2024 | September 2, 2024 |
Perpetual Company's ownership is primarily institutional. Major shareholders include Washington H. Soul Pattinson and Company Limited.
The company has made several acquisitions to expand its asset management capabilities, including Trillium Asset Management and Pendal Group.
The proposed sale of business units and leadership changes signal a shift towards a streamlined asset management focus.
Cost reduction programs and direct investments in other companies are part of the company's financial strategy.
Perpetual Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of Perpetual Company?
- What is Competitive Landscape of Perpetual Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Perpetual Company?
- How Does Perpetual Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Perpetual Company?
- What is Brief History of Perpetual Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Perpetual Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.