Simpson Thacher & Bartlett Bundle
Who Really Owns Simpson Thacher & Bartlett?
Unraveling the ownership structure of a legal giant like Simpson Thacher & Bartlett (STB law firm) is key to understanding its power and influence. This elite firm, founded in 1884, operates differently than publicly traded companies, making its ownership a fascinating subject. Discover the intricacies of the Simpson Thacher ownership model and how it shapes the firm's strategic direction.
Unlike corporations with shareholders, Simpson Thacher & Bartlett SWOT Analysis reveals a unique structure. This exploration goes beyond the basics, examining the roles of Simpson Thacher partners and the impact of their ownership on the firm's decisions. Learn who controls STB and how this influences its position in the competitive legal landscape. This analysis provides a comprehensive look at the key players and the firm's operational strategies.
Who Founded Simpson Thacher & Bartlett?
The foundation of Simpson Thacher & Bartlett, or STB law firm, was laid in 1884 by John W. Simpson, Thomas Thacher, and William B. Hornblower. Understanding the ownership structure from its inception is key to grasping how the firm has evolved. As a private partnership, the initial ownership was inherently vested in the founders.
In a private partnership like Simpson Thacher & Bartlett, the founders held the entire ownership stake. The allocation of equity among them would have reflected their contributions and agreements at the time of the firm's establishment. While specific percentages from 1884 are not publicly available, the structure typically involves distributing ownership and profits based on factors such as capital contributions, seniority, and performance.
Early agreements were crucial, outlining profit sharing, management responsibilities, and the process for admitting or withdrawing partners. These foundational documents shaped the firm's early operational and financial framework. The founders' vision directly influenced the distribution of control, fostering a meritocratic environment where partners shared in the firm's success and governance. The partnership agreement would have governed any initial ownership disputes or buyouts, ensuring smooth transitions.
Unlike corporations, law firm partnerships like Simpson Thacher & Bartlett do not have external investors acquiring stakes in the same way. Instead, capital is often contributed by the partners themselves or through internal firm financing. The structure emphasizes a collegial and meritocratic environment where partners share in the firm's success and governance. For more insights into the firm's financial aspects, you can explore Revenue Streams & Business Model of Simpson Thacher & Bartlett.
- The firm's ownership is primarily held by its partners.
- Early ownership was divided among the founding partners based on their contributions.
- Partnership agreements dictate the terms for joining, leaving, and retiring from the firm.
- The structure ensures a smooth transition of ownership and responsibilities.
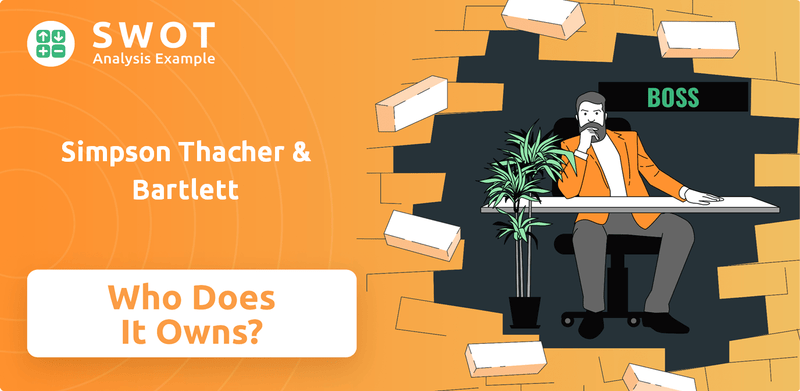
Simpson Thacher & Bartlett SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
How Has Simpson Thacher & Bartlett’s Ownership Changed Over Time?
As a private partnership, the ownership of Simpson Thacher & Bartlett (STB) differs significantly from that of publicly traded companies. The Simpson Thacher ownership structure is held by its partners, who are admitted based on merit and contribution. The firm does not have an IPO date or publicly traded shares. Major stakeholders include equity partners who share profits and have voting rights. While specific profit shares and the exact number of partners are not publicly disclosed, the firm had hundreds of partners globally as of 2024.
Key events affecting ownership in this STB law firm primarily involve the admission of new partners, retirements, departures, and changes in profit allocation. For instance, in 2024, Simpson Thacher announced the election of new partners, which inherently shifts the ownership landscape. These changes involve internal redistribution of ownership units based on firm performance and strategic needs. The firm's strong financial performance, with reported gross revenue of approximately $2.4 billion in 2023, directly benefits its partners through increased profit per equity partner (PPEP). This success reinforces the value of partnership and attracts top legal talent, further strengthening the partner-owned model.
| Aspect | Details | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Partner Admissions | New partners elected annually. | Expands the ownership base and brings in new perspectives. |
| Partner Departures | Retirements or departures of existing partners. | Changes the distribution of profit shares and voting rights. |
| Profit Allocation | Internal adjustments to how profits are distributed among partners. | Reflects the firm's performance and strategic priorities. |
The firm's strategy and governance are directly influenced by its partners, who collectively decide on major initiatives, expansions, and operational policies, ensuring alignment between ownership and strategic direction. The firm's structure ensures that the partners, who are the law firm owners, have direct control over the firm's future. This model contrasts with companies that have a CEO.
Simpson Thacher & Bartlett is structured as a private partnership, with ownership held by its partners. The firm's partners are the key stakeholders, influencing strategic decisions and benefiting from the firm's financial performance.
- Ownership is held by equity partners.
- Decisions are made collectively by the partners.
- Financial success directly benefits the partners.
- The firm does not have an external CEO.
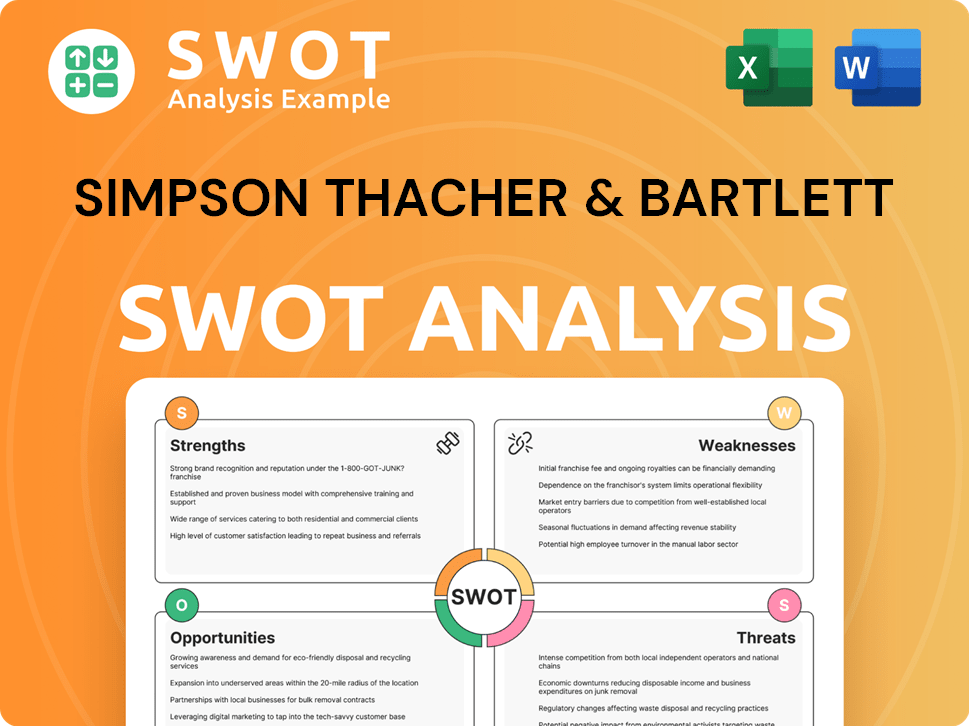
Simpson Thacher & Bartlett PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
Who Sits on Simpson Thacher & Bartlett’s Board?
As a private partnership, the structure of Simpson Thacher & Bartlett (STB) does not include a traditional 'Board of Directors' like public corporations. Instead, the firm's governance is managed by a management or executive committee. This committee is composed of senior partners who are elected by the partnership. The committee is responsible for overseeing the firm's strategic direction, financial management, and operational decisions. The exact composition of this committee is not publicly available, but it consists of highly influential equity partners who represent the collective interests of the partnership. The firm's structure is designed to foster consensus among its partners, reflecting a shared ownership model.
The governance of Simpson Thacher ownership is primarily handled internally. Key decisions are made by the management committee, which includes senior partners. These partners have significant influence over the firm's direction. The firm's structure avoids the complexities of public company governance, such as proxy battles or activist investor campaigns, as there are no public shareholders. Instead, any internal disagreements are resolved through the firm's partnership agreement and adherence to professional ethics. Understanding the internal dynamics of STB law firm is crucial for anyone interested in its operations and strategic direction.
| Governance Aspect | Details | Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Management Committee | Composed of senior partners; oversees strategic direction, financial management, and operations. | Key decision-making body; ensures alignment with partner interests. |
| Voting Structure | Generally 'one-partner, one-vote' for significant matters. | Promotes equitable influence among partners. |
| Public Company Elements | No public shareholders, proxy battles, or activist investor campaigns. | Simplifies governance compared to public corporations. |
The voting structure within Simpson Thacher partners is generally based on a 'one-partner, one-vote' principle for significant matters, although profit allocations and capital contributions can vary among partners. Seniority and contribution often play a role in influence, if not direct voting power. The firm's structure is designed to foster consensus among its partners, reflecting the shared ownership model. For a deeper dive into how they approach their business, consider reading about the Marketing Strategy of Simpson Thacher & Bartlett.
The firm's governance is managed by a management committee consisting of senior partners.
- The voting structure is typically 'one-partner, one-vote'.
- Control is distributed among the equity partners, avoiding dual-class shares.
- Internal disagreements are handled through partnership mechanisms.
- No public shareholders, thus no proxy battles or activist campaigns.
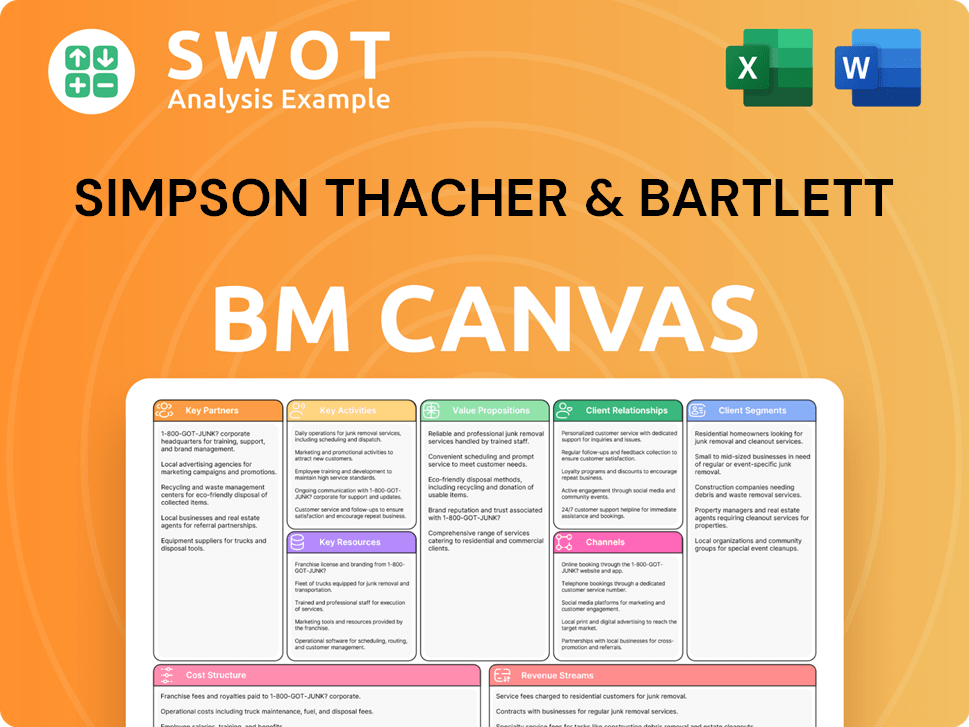
Simpson Thacher & Bartlett Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What Recent Changes Have Shaped Simpson Thacher & Bartlett’s Ownership Landscape?
Over the past few years (2022-2025), Simpson Thacher & Bartlett (STB) has maintained its position as a leading global law firm. A key aspect of this has been the strategic growth in its primary practice areas. In 2024, the firm announced the election of 20 new partners, showcasing its commitment to developing internal talent and expanding its ownership base. This internal promotion is the main way the firm's ownership structure evolves. The firm's involvement in high-profile mergers, acquisitions, capital markets, and private equity transactions contributes significantly to its financial success and partner profits.
Industry trends in the legal sector, including increased competition for top talent, have led firms to enhance partner compensation and benefits. While there's no 'founder dilution' in the traditional corporate sense, the admission of new partners gradually expands the ownership structure. The firm focuses on maintaining its elite status, attracting top legal talent, and serving its high-profile client base. The private partnership model remains central to the firm's identity and operational philosophy, with no public statements about future ownership changes like privatization or public listing.
| Metric | Details | Year |
|---|---|---|
| Number of New Partners Elected | 20 | 2024 |
| Key Practice Areas | Mergers & Acquisitions, Capital Markets, Private Equity | 2023-2024 |
| Ownership Structure | Private Partnership | Ongoing |
The firm's focus remains on attracting and retaining top legal talent, which is crucial in the competitive legal market. The firm's consistent involvement in major deals reinforces its market leadership and financial performance, which directly impacts the compensation and benefits for Simpson Thacher partners. The firm continues to be involved in significant transactions. This strategic approach is key to maintaining its elite status and serving its high-profile client base.
Internal promotions are the primary mechanism for ownership changes at Simpson Thacher. New partners are admitted regularly, expanding the ownership base. The firm's private partnership model remains unchanged.
The firm concentrates on its elite status, attracting top talent, and serving its high-profile clients. This focus is supported by involvement in significant deals. Maintaining financial success is a priority.
Simpson Thacher & Bartlett Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of Simpson Thacher & Bartlett Company?
- What is Competitive Landscape of Simpson Thacher & Bartlett Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Simpson Thacher & Bartlett Company?
- How Does Simpson Thacher & Bartlett Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Simpson Thacher & Bartlett Company?
- What is Brief History of Simpson Thacher & Bartlett Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Simpson Thacher & Bartlett Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.