Walt Disney Bundle
Who Really Owns the Magic? Unveiling Walt Disney Company Ownership
Ever wondered who truly steers the ship at the Walt Disney Company? This question is vital to understanding the strategic direction of a global entertainment giant. Founded in 1923, Disney has blossomed from a cartoon studio into a multifaceted empire, influencing everything from media to consumer products. Its ownership structure is a complex tapestry of institutional investors and public shareholders, reflecting its vast reach and market dominance.
Understanding Walt Disney SWOT Analysis can reveal how ownership impacts Disney's decisions, from acquisitions to streaming service expansions. Knowing who holds the power—through equity, board representation, or voting rights—offers insights into Disney's long-term vision and responsiveness to market trends. This exploration will delve into the evolution of Disney ownership, examining key investors, the influence of public shareholders, and how ownership changes have shaped the company's trajectory, providing a comprehensive view of who truly owns this entertainment powerhouse, including details on Disney shareholders and the Disney parent company.
Who Founded Walt Disney?
The Walt Disney Company, a global entertainment giant, traces its origins back to October 16, 1923. Founded by brothers Walt and Roy O. Disney, the company initially operated as the Disney Brothers Cartoon Studio. Their combined efforts laid the foundation for an empire that would redefine the entertainment industry.
While precise initial equity splits aren't widely documented for the early private venture, it's understood that Walt focused on creative endeavors, while Roy managed the business and finances. This division of labor was crucial in the company's early success. The brothers' complementary skills formed a strong partnership that drove the company forward.
Early financing came from various sources beyond the brothers' capital. Distribution agreements provided advances, acting like early investments. The company's growth was fueled by its success and reinvestment of profits, rather than significant stakes from outside investors. The founders' long-term involvement was key, and there's no readily available information about early vesting schedules or founder exits during the inception phase.
Walt Disney and Roy O. Disney founded the company in 1923. Walt focused on creative direction, while Roy managed the business and finances. Early financing included distribution agreements.
The company utilized distribution agreements for early financing. Profits were reinvested to fuel the growth of the company. There is no information about early vesting schedules or founder exits during the inception phase.
Walt's creative vision was central to the company's direction. Roy handled the practical business aspects. The partnership between the brothers was characterized by a complementary working relationship.
The company's success was driven by the brothers' combined efforts. Their complementary skills were key to the early success. There were no significant ownership disputes or buyouts among the founders.
The early years of the company are marked by the strong partnership between the founders. The focus was on building the business. The company's structure evolved significantly over time.
Walt Disney was the visionary creative leader. Roy O. Disney managed the business and finances. Both brothers were central to the company's operations for decades.
The early structure of the company, with Walt Disney and Roy O. Disney at the helm, set the stage for its future growth. The brothers' roles were clearly defined, with Walt leading the creative side and Roy managing the business operations. This division of labor helped the company navigate its initial challenges and lay the groundwork for the entertainment empire it would become. Understanding the Competitors Landscape of Walt Disney is crucial to understanding its position in the market.
The Walt Disney Company's early success was built on the partnership of Walt and Roy Disney.
- Walt Disney focused on creative direction.
- Roy O. Disney managed the business and finances.
- Early financing came from distribution agreements.
- The brothers' complementary skills drove the company forward.
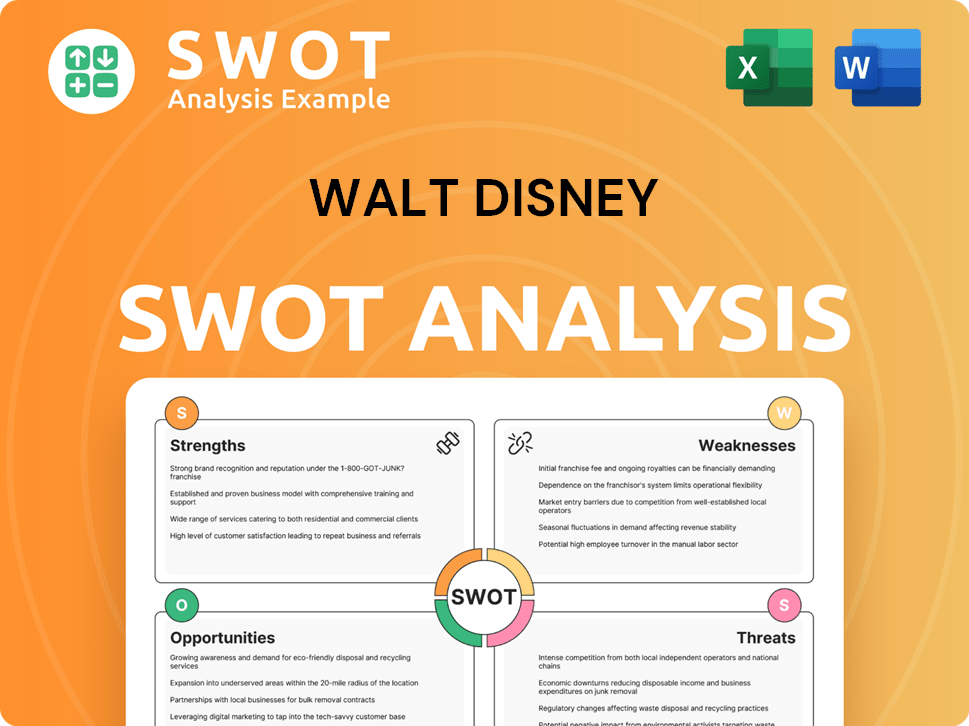
Walt Disney SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
How Has Walt Disney’s Ownership Changed Over Time?
The evolution of Walt Disney Company ownership has been marked by significant shifts since its inception. The company's initial public offering (IPO) on November 12, 1957, was a critical turning point. This transition from a privately held entity to a publicly traded corporation opened the door for a broader base of ownership, including both individual and institutional investors. This change fundamentally altered the company's structure and governance, setting the stage for its growth and expansion over the following decades. The shift to public ownership also introduced new dynamics in terms of shareholder expectations and corporate strategy.
The ownership structure of the Walt Disney Company is now heavily influenced by institutional investors. These entities, including asset management firms and mutual funds, hold a substantial portion of the company's shares. This dispersed ownership structure means no single entity has a controlling majority, impacting strategic decisions and governance practices.
| Institutional Investor | Shares Held (Approximate) | Value of Holdings (Approximate, as of March 31, 2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Vanguard Group Inc. | 114,831,489 | $20.9 billion |
| BlackRock Inc. | 96,876,432 | $17.6 billion |
| State Street Corp. | 48,272,357 | $8.8 billion |
The influence of major shareholders on the Walt Disney Company is considerable. These large institutional investors, while not directly involved in day-to-day operations, wield considerable power through their voting rights. Their influence extends to board elections, executive compensation, and major corporate actions. This heightened scrutiny has led to a greater emphasis on financial performance, shareholder returns, and robust corporate governance. The company's strategic decisions, such as investments in streaming services like Disney+ and acquisitions, are often carefully considered in light of their potential impact on these major institutional shareholders. To understand more about the company's strategic direction, you can read about the Growth Strategy of Walt Disney.
The Walt Disney Company is primarily owned by institutional investors, not a single individual or entity. The ownership structure has evolved significantly since the IPO in 1957. Major shareholders, such as Vanguard and BlackRock, exert considerable influence through their voting power.
- Institutional investors hold the majority of shares.
- The company's strategic decisions are influenced by shareholder expectations.
- No single entity holds a controlling stake.
- Disney is a publicly traded company.
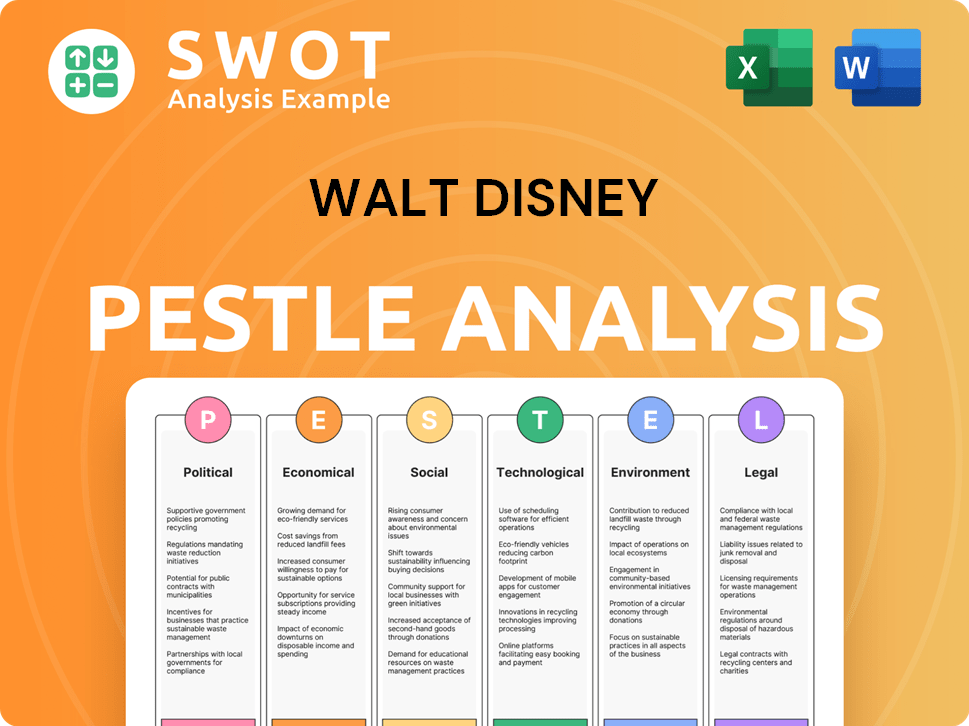
Walt Disney PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
Who Sits on Walt Disney’s Board?
As of early 2025, the Board of Directors of The Walt Disney Company includes a mix of experienced individuals. Key figures include Robert A. Iger, the Chief Executive Officer, and Mary T. Barra, the Lead Independent Director. Other board members are Safra A. Catz, Amy L. Chang, D. Jeremy Darroch, Carolyn Everson, Michael B.G. Froman, James P. Gorman, Calvin R. McDonald, and Mark G. Parker. The board's composition reflects a commitment to diverse expertise and shareholder representation, ensuring a balance of perspectives to oversee the company's strategic direction.
The board's structure emphasizes independent oversight, with a majority of independent directors. The company operates under a one-share-one-vote structure for its common stock. This means that voting power is directly proportional to the number of shares held, ensuring that all shareholders have a voice in the company's decisions. This structure is crucial for maintaining transparency and accountability in how the company is managed. For more insights, you can explore the Growth Strategy of Walt Disney.
| Board Member | Title | Key Role |
|---|---|---|
| Robert A. Iger | Chief Executive Officer | Oversees the company's overall strategy and operations. |
| Mary T. Barra | Lead Independent Director | Provides independent oversight and leadership to the board. |
| Safra A. Catz | Director | Brings expertise in technology and finance. |
Recent events, such as the 2024 proxy battle involving Nelson Peltz's Trian Fund Management, highlight the dynamics of Disney shareholders and the board's role. In April 2024, shareholders re-elected all 12 of the company's nominated directors, rejecting bids from activist investors. This outcome underscored the existing board's mandate and the support from a significant portion of the shareholder base. These events emphasize the importance of shareholder engagement and the board's role in navigating challenges while focusing on long-term value creation. The market capitalization of Disney is a significant indicator of its value, reflecting investor confidence and the company's overall financial health.
The Walt Disney Company is a publicly traded company, meaning ownership is distributed among many shareholders, including institutional investors and individuals.
- The board of directors is responsible for overseeing the company's strategy and management.
- Shareholders vote on key decisions, including the election of directors.
- Activist investors can influence company direction through proxy battles.
- The one-share-one-vote structure ensures fair voting rights for all shareholders.
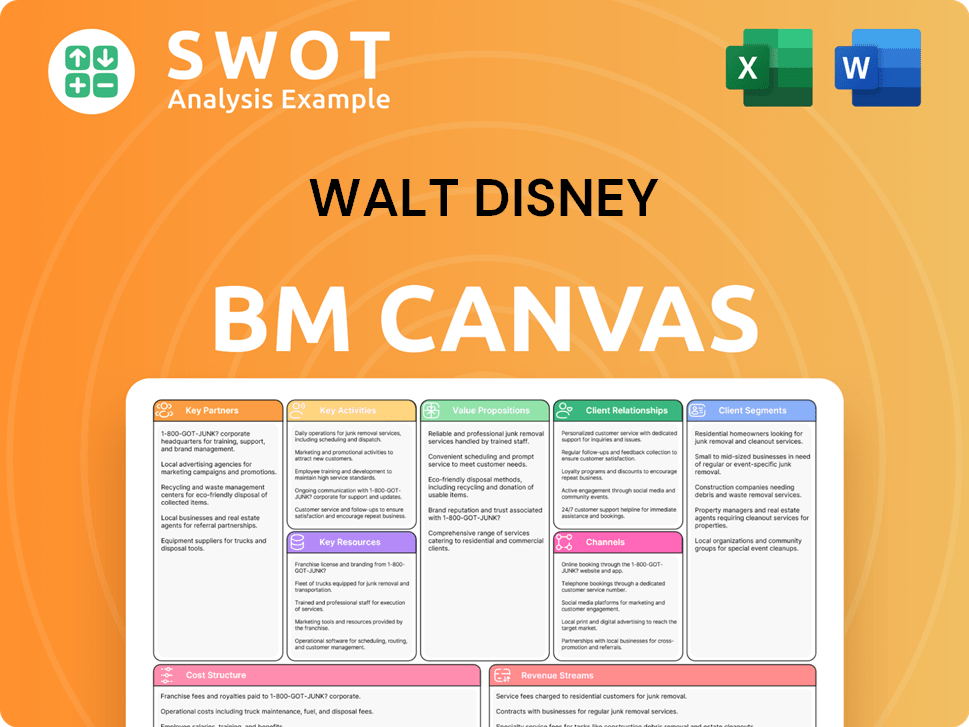
Walt Disney Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What Recent Changes Have Shaped Walt Disney’s Ownership Landscape?
Over the past few years, the ownership structure of The Walt Disney Company has seen significant developments, primarily characterized by the continued dominance of institutional investors. Firms like Vanguard, BlackRock, and State Street hold substantial stakes, reflecting a broader trend of passive investing. This concentration of ownership has intensified the focus on corporate governance and shareholder returns. The return of Robert A. Iger as CEO in November 2022, replacing Bob Chapek, was a pivotal event, influencing investor confidence and stock performance.
Disney's strategic moves, particularly in its direct-to-consumer streaming services, have been closely watched by shareholders. While there haven't been major shifts in the overall ownership percentages, the capital allocation towards these ventures has been substantial. These investments directly impact the company's financial health and its attractiveness to investors. The proxy battle with Trian Fund Management in early 2024 highlighted the heightened scrutiny from large shareholders regarding profitability and corporate strategy. For more details, check out the Brief History of Walt Disney.
| Shareholder | Approximate % Ownership (as of late 2024) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| The Vanguard Group, Inc. | ~7.8% | One of the largest institutional holders. |
| BlackRock, Inc. | ~6.3% | Another significant institutional investor. |
| State Street Corporation | ~4.0% | A major player in institutional ownership. |
The ownership of Disney remains largely institutional, influencing the company's strategic decisions and financial performance. The focus on streaming services and the scrutiny from major shareholders, like those involved in the 2024 proxy battle, shape the company's direction.
Robert A. Iger's return as CEO in November 2022. This leadership change significantly impacted investor confidence and stock performance. The move aimed to revitalize the company's creative output and address challenges in the streaming business.
Dominance of institutional investors like Vanguard and BlackRock. This trend reflects a broader market shift towards passive investing. It increases the focus on corporate governance and shareholder returns.
Heavy investment in direct-to-consumer streaming services. This strategic shift is closely watched by shareholders. The profitability of these ventures directly impacts the company's financial health.
Heightened scrutiny from large shareholders. The proxy battle with Trian Fund Management in early 2024 highlighted this. Focus is on profitability, succession planning, and overall corporate strategy.
Walt Disney Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of Walt Disney Company?
- What is Competitive Landscape of Walt Disney Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Walt Disney Company?
- How Does Walt Disney Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Walt Disney Company?
- What is Brief History of Walt Disney Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Walt Disney Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.