Fortum Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Fortum Bundle
What is included in the product
Tailored exclusively for Fortum, analyzing its position within its competitive landscape.
Swap in your own data, labels, and notes to reflect current business conditions.
Preview Before You Purchase
Fortum Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This is the complete Fortum Porter's Five Forces analysis. The document you're previewing is the exact one you'll receive instantly after purchase.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Template
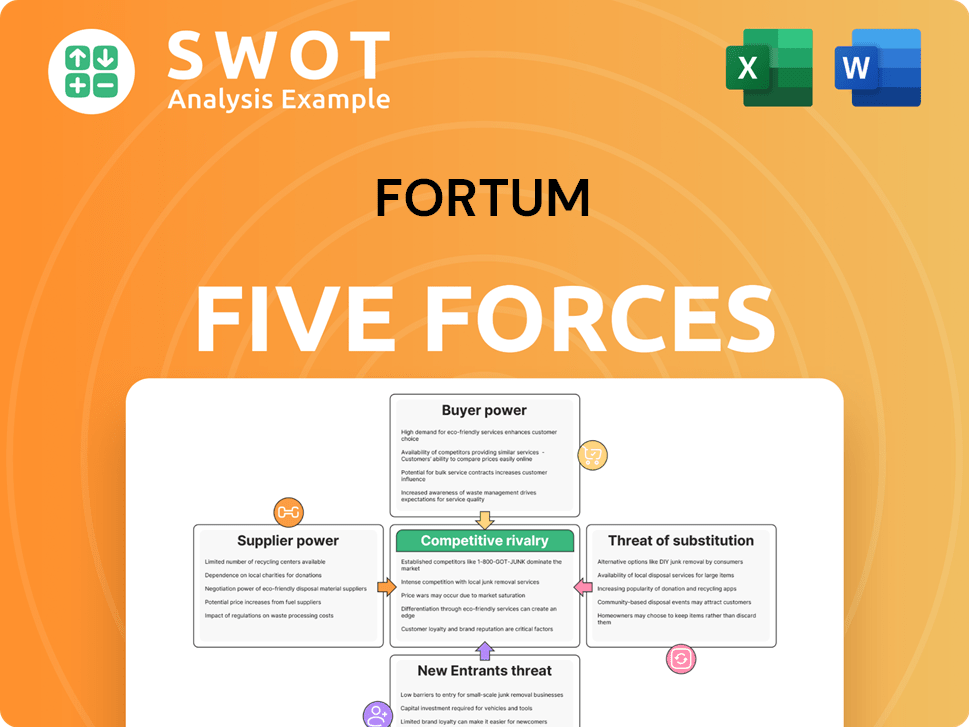
Fortum's competitive landscape is shaped by the interplay of five key forces. Buyer power, supplier power, and the threat of substitutes, new entrants, and competitive rivalry all influence its profitability. Analyzing these forces offers insights into Fortum's market position and vulnerabilities. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for strategic planning and investment decisions. This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Fortum’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Fortum faces supplier concentration challenges due to its reliance on specialized equipment and fuel. In 2024, the energy sector saw significant price fluctuations for essential components. The fewer suppliers, the stronger their ability to dictate terms. This can impact Fortum's operational costs and profitability. For example, the price of uranium, a key input for nuclear energy, has increased by 10% in 2024, impacting companies like Fortum.
Switching costs for Fortum can be high. Power generation has unique technical needs. Changing suppliers is costly, especially for nuclear or hydro. This limits Fortum's ability to negotiate. Fortum's 2024 annual report shows these costs.
Supplier forward integration is a significant threat. If suppliers, like those of nuclear fuel, decide to generate power themselves, they could become direct competitors. This shift could enable them to control supply and potentially raise prices, impacting Fortum's profitability. For instance, in 2024, the cost of key components for renewable energy projects increased by about 15%. This underscores the potential impact of supplier integration.
Impact of Geopolitical Factors
Geopolitical instability significantly impacts supplier power. Disruptions to supply chains, like those seen in Eastern Europe, can limit resource availability and drive up costs. This gives suppliers greater control over companies. For example, the price of natural gas, a key resource for Fortum, has been highly volatile due to political events.
- Energy prices surged in 2024 due to geopolitical tensions.
- Fortum's reliance on certain suppliers increased due to these disruptions.
- Supply chain diversification became a priority for risk management.
- Geopolitical risks continue to shape supplier relationships.
Renewable Technology Supply
The bargaining power of suppliers in renewable technology, like solar panels and wind turbines, is influenced by global market forces. Increased demand coupled with potential supply constraints could elevate suppliers' leverage. This dynamic can impact Fortum's renewable energy investments and operational expenses. For example, in 2024, the price of polysilicon, a key component for solar panels, fluctuated significantly due to supply chain issues.
- Global demand for renewable energy components is rising, potentially increasing supplier power.
- Supply chain disruptions can further empower suppliers by limiting availability.
- Fortum must manage supplier relationships and costs to maintain project profitability.
- Fluctuations in raw material prices (e.g., polysilicon) directly affect operational costs.
Fortum's supplier power is amplified by limited options and high switching costs. Geopolitical events and supply chain disruptions in 2024 further concentrated supplier control. Fluctuating raw material prices and supplier integration pose ongoing risks.
| Factor | Impact | 2024 Data |
|---|---|---|
| Concentration | Limited options | Uranium price up 10% |
| Switching Costs | High costs | Nuclear/hydro constraints |
| Integration | Supplier competition | Renewable component up 15% |
Customers Bargaining Power
Fortum's customer base includes industrial and residential clients, with a notable concentration of large industrial customers. These major consumers have significant bargaining power. In 2024, industrial clients accounted for a substantial portion of Fortum's energy sales. They can negotiate favorable rates, potentially impacting Fortum's revenue and profit margins. For example, a 5% discount to major industrial clients could affect profitability.
Customer switching costs significantly impact Fortum's bargaining power. Switching energy providers is easy for many, boosting their power. Residential and smaller commercial customers can switch with minimal hassle. Fortum must maintain competitive pricing and top-notch service. In 2024, energy prices fluctuated, emphasizing consumer choice and provider competition.
Customers' bargaining power increases with more energy choices. Distributed generation, like solar, is growing. For example, in 2024, solar capacity increased by 30% in some regions, giving customers alternatives. This reduces reliance on traditional utilities.
Price Sensitivity of Customers
Fortum faces customer price sensitivity in both industrial and residential sectors, influencing their willingness to pay for energy. High energy prices prompt customers to seek cheaper alternatives or reduce consumption, directly affecting Fortum's sales. This dynamic is crucial for the company's revenue projections and strategic decisions. In 2024, residential electricity prices in Finland averaged around 10-12 cents per kWh, showing the price's impact on customer behavior.
- Industrial customers can shift demand, impacting profitability.
- Residential consumers can adopt energy-saving practices.
- Price fluctuations directly influence Fortum's revenue.
- Customer price sensitivity is a key market factor.
Regulatory Influence on Pricing
Government regulations significantly shape energy prices, impacting customer choices. Policies promoting renewables or setting price caps directly influence Fortum's pricing and customer interactions. For example, Finland's energy policies, where Fortum operates, emphasize sustainability. Regulatory changes can shift buyer power, affecting profitability. In 2024, renewable energy's share in Finland's electricity consumption was approximately 50%.
- Policy Impact: Regulations like feed-in tariffs or carbon pricing directly affect customer costs.
- Price Controls: Price caps limit Fortum's ability to adjust prices, affecting revenue.
- Renewable Mandates: Requirements for renewable energy sources influence customer demand.
- Customer Choice: Subsidies for renewables increase customer adoption.
Industrial clients wield strong bargaining power, influencing Fortum's revenue and profits. Customer switching is easy, increasing their power to negotiate better terms. Price sensitivity, amplified by energy choices and government policies, shapes customer behavior. In 2024, renewable energy adoption influenced this.
| Aspect | Impact | 2024 Data |
|---|---|---|
| Industrial Clients | Negotiate rates | 5% discount impact |
| Switching Costs | Easy switching | Price fluctuations |
| Price Sensitivity | Demand reduction | Finland: 10-12 cents/kWh |
Rivalry Among Competitors
The Nordic energy market is competitive. Fortum faces intense rivalry. In 2024, Fortum's market share was around 20%. Competition includes Statkraft, and Vattenfall. This leads to tight margins and strategic battles.
The energy sector's growth rate significantly impacts competitive rivalry. Slow growth can lead to fierce competition, as seen in 2024 with companies vying for a smaller customer base. Conversely, higher growth can ease rivalry. For instance, the renewable energy segment saw robust expansion in 2024, potentially reducing direct competition intensity.
Energy products are largely commodities, intensifying price competition. Fortum faces challenges in differentiating its core energy offerings. However, Fortum attempts to stand out by providing sustainable energy solutions. For instance, in 2024, Fortum increased its investment in renewable energy by 15%. Basic energy services remain undifferentiated, fueling rivalry.
Exit Barriers
High exit barriers in the energy industry, such as Fortum's, intensify competition. Substantial infrastructure investments and long-term contracts make exiting the market challenging. This leads to persistent competition, even amid low profitability. For example, in 2024, Fortum's investments in renewable energy projects totaled €1.5 billion. This illustrates the financial commitment.
- Significant capital expenditures in power plants and grids.
- Long-term power purchase agreements.
- Regulatory hurdles and environmental liabilities.
Strategic Moves by Competitors
Fortum faces intense competition, especially with strategic moves from rivals. Vattenfall and Ørsted's actions, including mergers and tech advancements, reshape the market. These moves force Fortum to adapt and innovate to stay competitive. Adapting to these changes is vital for Fortum's market position.
- Vattenfall's 2024 investments in offshore wind projects, totaling billions, directly challenge Fortum.
- Ørsted's strategic partnerships in green hydrogen projects also intensify competition in renewable energy.
- The European Commission's 2024 directives on renewable energy capacity expansion add pressure.
- These factors require Fortum to enhance efficiency and strategic agility.
Competitive rivalry significantly impacts Fortum's operations. Intense competition in 2024, with players like Statkraft, kept margins tight. The renewable energy segment showed growth, but undifferentiated energy products fueled price wars. High exit barriers and strategic moves by rivals like Vattenfall increased the pressure.
| Factor | Impact | 2024 Data |
|---|---|---|
| Market Share | High competition | Fortum ~20% |
| Renewable Investments | Strategic response | Fortum €1.5B |
| Rival Actions | Market shifts | Vattenfall offshore wind investments |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Energy efficiency measures pose a threat to Fortum. These measures, which lower overall energy use, directly substitute energy generation. For instance, the International Energy Agency (IEA) reported that in 2024, energy efficiency improvements avoided 15% of global energy demand. Government incentives and tech advancements further decrease demand for Fortum's energy products.
The threat of substitutes for Fortum includes alternative energy sources like solar and wind. These renewables are direct substitutes for traditional power generation. In 2024, renewable energy sources accounted for over 40% of global electricity capacity. Increased adoption of these alternatives reduces reliance on conventional sources. The International Energy Agency (IEA) projects renewables to supply over 50% of global electricity by 2030.
Customers increasingly turn to on-site generation, like solar panels, reducing reliance on traditional grids. Distributed generation technologies directly challenge Fortum's business model. The global solar PV capacity additions reached approximately 350 GW in 2023, signaling significant growth. This shift presents a major threat as it substitutes grid electricity. Fortum must adapt to this changing landscape.
Fuel Switching
The threat of substitutes for Fortum involves customers potentially switching from electricity to alternative fuel sources. This shift, like adopting natural gas or biofuels, directly impacts electricity demand. The cost and availability of these alternatives significantly influence customers' decisions to move away from Fortum's electricity. In 2024, the price of natural gas, a key substitute, saw fluctuations, affecting consumer choices. The rise in renewable energy options, such as solar and wind, also presents a substitute threat.
- Natural gas prices in Europe saw volatility in 2024, impacting electricity demand.
- The increasing adoption of solar and wind power offers viable substitutes for traditional electricity sources.
- Biofuels continue to emerge as a substitute, though their market share is still developing.
Demand Response Programs
Demand response programs pose a threat to Fortum, as they encourage customers to cut energy use during peak times. These programs act as substitutes for new power generation, potentially impacting Fortum's revenue. The growing adoption of these programs could reduce the demand for Fortum's electricity. This shift could force Fortum to adjust its pricing strategies and energy production plans. In 2024, the global demand response market was valued at approximately $18 billion.
- Market growth: The demand response market is projected to reach $35 billion by 2030.
- Customer participation: Millions of customers participate in demand response programs globally.
- Impact on revenue: Reduced peak demand can lower electricity prices, affecting Fortum's earnings.
- Technological advancements: Smart grids and smart meters facilitate the effectiveness of demand response.
Fortum faces substitution threats from energy efficiency measures and alternative energy sources. Renewables accounted for over 40% of global electricity capacity in 2024. On-site generation, like solar, and demand response programs also challenge Fortum's traditional business model.
| Substitute Type | Impact on Fortum | 2024 Data |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency | Reduced demand | 15% of global energy demand avoided |
| Renewables | Direct competition | Over 40% of global electricity capacity |
| On-site Generation | Reduced grid reliance | Solar PV additions ≈ 350 GW in 2023 |
Entrants Threaten
The energy sector demands substantial capital, discouraging new competitors. Building power plants and grid infrastructure, plus regulatory compliance, is costly. For example, constructing a nuclear power plant can cost billions. In 2024, global energy investments were over $2.8 trillion.
Stringent regulations and licensing requirements pose significant barriers for new entrants in the energy sector. Environmental compliance, permit acquisition, and adherence to industry standards are costly and time-intensive. For instance, in 2024, the average time to secure environmental permits in the EU was 18-24 months, significantly delaying market entry. These hurdles protect incumbents like Fortum.
Existing energy companies like Fortum leverage economies of scale, which is a significant barrier for new entrants. Fortum's extensive infrastructure and large-scale operations provide a notable cost advantage. For instance, in 2024, Fortum's operational expenditure was over €1.5 billion, reflecting the scale of its activities. This cost efficiency makes it tough for smaller firms to compete on price.
Access to Distribution Channels
Accessing distribution channels poses a threat to Fortum. New entrants need to secure access to existing grid infrastructure, a significant hurdle. Building new distribution networks is costly and time-consuming, limiting market reach. This challenge impacts their ability to compete effectively. For example, in 2024, grid connection costs could range from €100,000 to over €1 million, depending on location and capacity.
- High capital investment for grid infrastructure.
- Long lead times for network establishment.
- Regulatory hurdles for grid access.
- Existing utilities have established customer relationships.
Brand Recognition and Customer Loyalty
Established energy companies like Fortum benefit from strong brand recognition and customer loyalty, posing a significant barrier to new entrants. Fortum's long-standing presence in the Nordic market, for example, gives it a competitive edge. New companies face challenges in attracting customers away from established brands. Building a comparable level of trust and recognition takes considerable time and resources. This makes it difficult for newcomers to gain market share effectively.
- Fortum has a strong brand reputation in the Nordic countries.
- New entrants struggle to compete with established customer loyalty.
- Building brand recognition needs time and money.
- Established companies have an advantage.
New entrants face high capital costs for infrastructure and significant regulatory hurdles. Building power plants and grids requires substantial investment and time, such as the $2.8 trillion in global energy investments in 2024. Economies of scale and established customer relationships further protect incumbents like Fortum.
| Barrier | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Costs | High investment needs for plants and grids. | Limits new entrants. |
| Regulations | Stringent licensing and environmental rules. | Delays market entry. |
| Scale | Existing companies have economies of scale. | Challenges price competition. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's analysis leverages annual reports, market research, financial statements, and industry publications. These sources inform assessment of competitive forces impacting Fortum.