Sears Holdings Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Sears Holdings Bundle
What is included in the product
Tailored exclusively for Sears Holdings, analyzing its position within its competitive landscape.
Clean, simplified layout—ready to copy into pitch decks or boardroom slides.
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Sears Holdings Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This is the complete analysis file. What you're previewing is what you get—professionally formatted and ready for your needs. The Sears Holdings Porter's Five Forces analysis examines industry rivalry, threat of new entrants, supplier power, buyer power, and threat of substitutes. The document details these forces, offering insights into Sears' competitive landscape. The analysis also covers the impact of these forces on the company’s performance. You'll receive this exact document.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Template
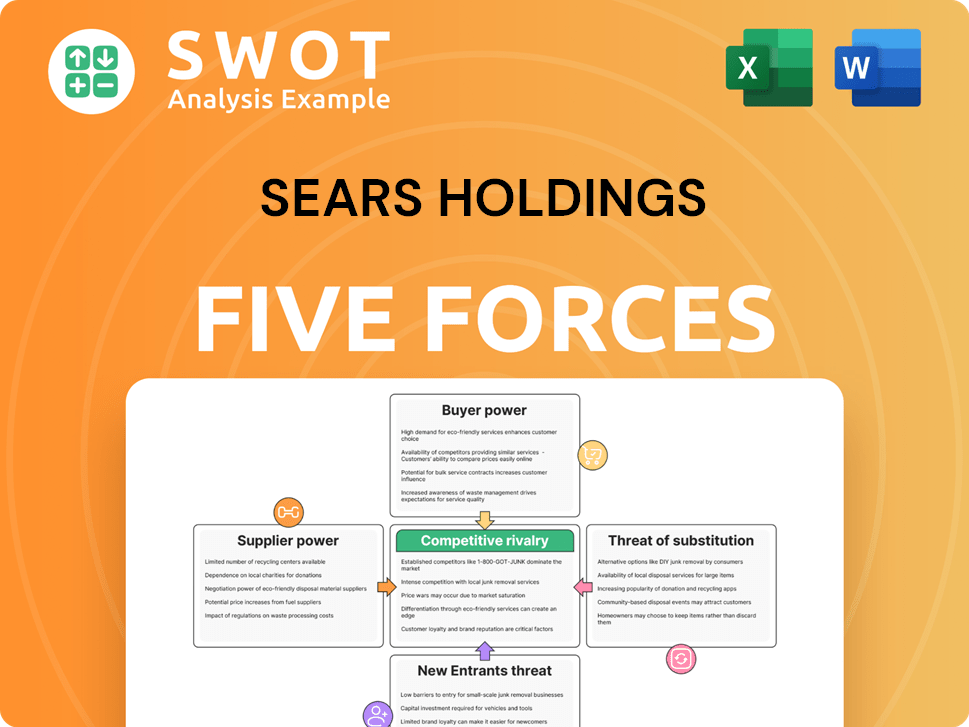
Sears Holdings faced intense competition, especially from well-established retailers. Its brand power waned, leaving it vulnerable to buyer influence. Suppliers held little sway due to the large number of readily available alternatives. The threat of new entrants was moderate. The rise of e-commerce and specialized retailers presented significant substitute threats.
Ready to move beyond the basics? Get a full strategic breakdown of Sears Holdings’s market position, competitive intensity, and external threats—all in one powerful analysis.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Sears and Kmart, major retailers, wielded substantial purchasing power, diminishing supplier dependence. Their massive order volumes enabled them to secure advantageous terms. For instance, in 2024, large retailers like Walmart and Target continued to leverage their size for favorable pricing. This buying power also meant Sears could easily switch suppliers, further increasing its leverage.
In the retail sector, Sears faced many suppliers for various products, enhancing its bargaining power. Sears could readily change suppliers if needed. This flexibility helped control supplier influence. However, for exclusive brands, supplier power could be slightly higher. In 2024, this dynamic remains relevant, with data showing competitive supplier landscapes in retail.
Sears and Kmart primarily sold standard products, reducing supplier bargaining power. These goods, easily sourced, limited suppliers' ability to dictate terms. This contrasts with specialized products, where suppliers might have more leverage. In 2024, the trend of readily available commodities continues, impacting retail dynamics. For example, the global market for generic consumer goods reached $2.5 trillion in 2023, underscoring this point.
Backward Integration Potential was limited
Sears Holdings' backward integration wasn't a major move. They could've bought suppliers, but didn't go all-in. Manufacturing is complex and expensive, so they stayed focused on retail. Their strategy prioritized retail and distribution. The threat of Sears becoming a supplier was small.
- Limited Backward Integration: Sears didn't aggressively pursue owning its suppliers.
- Focus on Retail: Their main focus was on running stores and managing the supply chain.
- Capital Intensive: Manufacturing requires significant investment, which Sears avoided.
- Minimal Supplier Threat: Sears wasn't likely to become a major supplier itself.
Supplier Concentration was a factor
Supplier concentration played a role in Sears's business, particularly where a few major companies dominated. These suppliers, especially in categories like appliances and certain apparel brands, had more leverage. This meant they could influence pricing and terms to their advantage. Sears, though large, faced these pressures, impacting profitability.
- Whirlpool's revenue in 2023 was approximately $19.4 billion.
- Apparel brands like Levi Strauss & Co., with 2023 revenue of $6.2 billion, also held supplier power.
- Sears Holdings' overall performance faced challenges, with declining sales impacting its ability to negotiate effectively.
Sears often had considerable bargaining power with suppliers due to its large order volumes and ability to switch vendors. This power was enhanced by a competitive supplier landscape, particularly for standard products readily available in the market. However, supplier concentration, especially among major appliance and apparel brands like Whirlpool (2023 revenue: $19.4B) and Levi Strauss ($6.2B), slightly increased supplier influence.
| Factor | Impact on Supplier Power | 2024 Context |
|---|---|---|
| Sears' Purchasing Power | High, due to order size and alternatives. | Retailers continue leveraging size for favorable terms. |
| Supplier Landscape | Competitive for standard goods, reducing leverage. | Commodity markets remain accessible, affecting retail. |
| Supplier Concentration | Increased influence from key brands. | Whirlpool's and Levi's financial performance. |
Customers Bargaining Power
Sears faced intense price sensitivity from customers. Competition from Walmart, Target, and Amazon meant even small price differences drove customers away. In 2024, retail margins remained tight; Sears' need to match competitors limited profit potential. Frequent promotions were necessary to attract and retain customers, reflecting the high price sensitivity.
Sears faced strong customer bargaining power due to numerous retail options. Consumers could easily switch to competitors, both physical and online. This availability of substitutes pressured prices. In 2024, online retail sales continue to grow, intensifying competition.
Switching costs for Sears customers were notably low. Consumers could easily shift to competitors like Walmart or Target. This lack of friction significantly increased buyer power. Online retailers amplified this, making it even simpler to compare prices and switch. In 2024, e-commerce sales continued to grow, further reducing switching costs.
Product Differentiation was limited
Sears Holdings struggled with limited product differentiation. Many items sold at Sears and Kmart were also available at competitors, reducing uniqueness. This lack of distinctiveness boosted buyer power, as customers could easily switch retailers. Private-label brands were introduced to differentiate, but often didn't fully succeed.
- In 2024, the retail industry saw increased competition, with consumers having numerous choices.
- Sears Holdings' inability to offer unique products made it vulnerable.
- Competitors like Amazon and Walmart offered similar products, intensifying the issue.
- Private labels aimed to set Sears apart, but faced challenges in a crowded market.
Information Availability was high
Customers wielded considerable power due to information availability. The internet and comparison websites provided easy access to product details, prices, and retailer data. This transparency enabled customers to find the best deals and make informed choices, increasing their bargaining power. Online reviews further influenced purchasing decisions.
- In 2024, e-commerce sales reached $1.1 trillion in the U.S., showcasing the impact of online information on consumer behavior.
- Websites like Amazon and Walmart offer price comparisons, empowering customers.
- Consumer Reports and other review sites provide product ratings.
- Over 80% of consumers research products online before buying.
Sears faced strong customer bargaining power. Consumers had many retail choices. Online options and low switching costs amplified this. Product similarity and readily available information intensified it.
| Aspect | Impact | 2024 Data |
|---|---|---|
| Retail Options | Many choices, high switching | E-commerce sales reached $1.1T in the U.S. |
| Product Similarity | Low differentiation, price focus | Amazon and Walmart offered similar goods. |
| Information Availability | Empowered buyers | Over 80% research online before buying. |
Rivalry Among Competitors
The retail industry witnessed intense competition, with giants like Walmart, Target, and Amazon battling for dominance. This fierce rivalry squeezed prices and profit margins. In 2024, Amazon's net sales surged, highlighting the pressure on traditional retailers. Sears, lacking a strong differentiation strategy, found it hard to keep up. The company's market share steadily declined against these powerful competitors.
The retail industry saw slow growth, intensifying competition for existing customers. The struggle for market share became more intense as new customer acquisition slowed. E-commerce's rise also altered spending patterns, boosting rivalry. In 2024, retail sales increased by only 3.6%, reflecting sluggish growth.
Sears Holdings faced high exit barriers, including long-term lease obligations and the challenge of selling extensive real estate holdings. These barriers made it difficult for Sears to downsize or exit underperforming locations. Consequently, the company struggled to adapt to changing market conditions. This situation intensified competitive pressure, contributing to its financial distress.
Low Differentiation existed
Sears Holdings faced intense competition due to low differentiation. The company struggled to distinguish its offerings, resulting in price wars and reduced profits. Many products were similar to those of competitors, making it hard to attract customers. Sears' brand image declined with store closures and financial troubles. In 2024, the retail industry saw razor-thin margins, reflecting this competitive pressure.
- Price wars eroded profitability.
- Lack of unique offerings.
- Brand image suffered.
- Intense competition.
Numerous Competitors existed
Sears Holdings faced intense competition due to many rivals. These included national chains like Walmart and Target, regional players, and online retailers such as Amazon. The wide range of competitors, all seeking consumer spending, created a very competitive market environment. This pressure affected Sears' profitability and market share. In 2024, e-commerce sales continue to grow, intensifying rivalry.
- Walmart's 2024 revenue is projected to be over $650 billion, highlighting the scale of its competition.
- Amazon's retail sales in 2024 are estimated to exceed $300 billion, showing the power of online competitors.
- Target's 2024 revenue is forecasted to surpass $100 billion, indicating another major player in the market.
Sears faced fierce competition, especially from Walmart and Amazon. These rivals engaged in price wars, squeezing profit margins, and making it hard to compete. In 2024, Amazon's retail sales surged, underlining this pressure.
| Competitive Element | Impact on Sears | 2024 Data Highlight |
|---|---|---|
| Price Wars | Reduced profitability | Retail margins remain tight |
| Lack of Differentiation | Customer loss to rivals | Amazon's retail sales ~$300B |
| Numerous Competitors | Market share decline | Walmart's revenue over $650B |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The emergence of online retailers like Amazon posed a substantial threat to Sears. Amazon's convenience, competitive pricing, and vast product selection drew customers away. This shift in consumer preference negatively affected Sears' sales and market share. In 2024, Amazon's net sales reached approximately $575 billion, highlighting the scale of this competitive pressure.
Discount retailers like Walmart and Target presented viable alternatives to Sears, especially for budget-conscious shoppers. These competitors offered similar merchandise at significantly lower prices, a critical factor in attracting customers. Walmart's revenue in 2023 was over $600 billion, highlighting its market dominance.
These retailers also broadened their product lines and enhanced their shopping environments, increasing their appeal to a wider demographic. Sears, conversely, faced challenges competing on both price and the overall shopping experience. Target's comparable sales grew by 0.7% in 2023, showcasing its ability to adapt.
Specialty retailers, concentrating on areas like home improvement or electronics, offered a more focused experience. These retailers often provided superior customer service and a wider array of specialized products. This shift drew customers away from department stores; in 2024, home improvement stores like Home Depot saw revenue increase by 3.5%, reflecting this trend. The enhanced customer experience and product knowledge of specialty stores played a significant role. This impacted department stores, which struggled to compete effectively.
Rental and Used Goods markets grew
The rise of rental services and the used goods market presented viable alternatives for consumers, affecting Sears Holdings. Renting offered short-term access, while used goods provided affordability compared to new items. This shift influenced sales, especially in durable goods categories.
- The global rental market was valued at $60.4 billion in 2023.
- The used goods market in the U.S. saw a significant growth of 15% in 2024.
- Sears' appliance sales declined by 8% in 2024 due to these market dynamics.
Changing Consumer preferences mattered
Shifting consumer preferences significantly threatened Sears. Consumers increasingly favored experiences, impacting demand for physical goods sold by department stores. This shift diverted spending to travel and entertainment, reducing purchases at Sears. The company's reliance on traditional retail suffered from these evolving tastes.
- In 2024, spending on experiences is projected to continue growing, outpacing goods.
- Department store sales have steadily declined.
- Sears struggled to adapt to this trend, losing market share.
- Consumers prioritized services and experiences over products.
Threat of substitutes significantly impacted Sears Holdings. Consumers shifted to online retailers, discount stores, specialty shops, and rental services. These alternatives provided convenience, lower prices, and specialized experiences, drawing customers away. Sears struggled to compete.
| Substitute | Impact | 2024 Data |
|---|---|---|
| Online Retailers | Convenience, Price | Amazon Net Sales: ~$575B |
| Discount Retailers | Lower Prices | Walmart Revenue (2023): ~$600B |
| Specialty Stores | Focused Experience | Home Depot Revenue Increase (2024): 3.5% |
Entrants Threaten
Establishing a large-scale brick-and-mortar retail operation demands substantial capital. Leasing property, inventory, and staffing costs are high. In 2024, real estate costs were up 6%, impacting retailers. These high upfront costs limited new competitors. Sears faced this, hindering its ability to adapt.
Establishing a strong brand in retail is hard, requiring substantial marketing investments. Consumer loyalty to familiar brands hinders new competitors. Sears, despite its struggles, still had brand recognition, making it tough for entrants. In 2024, brand-building costs in retail averaged $500,000-$2 million annually.
Large retailers thrive on economies of scale, securing better supplier prices and efficient operations. New entrants face challenges in matching these cost efficiencies, creating a competitive disadvantage. In 2024, Walmart's revenue reached approximately $648 billion, showcasing significant scale advantages. Sears, despite its decline, retained some scale benefits.
Established Supply Chains were crucial
Developing a reliable and efficient supply chain is essential for success in the retail industry, especially for large-scale operations. Established retailers, like Sears, benefit from well-developed supply chains and logistics networks, providing a significant competitive advantage. New entrants struggle to replicate these complex, often decades-long, setups, facing substantial barriers to entry. Sears, despite its decline, possessed existing infrastructure, potentially offering some advantages over startups.
- Walmart's supply chain efficiency in 2024 allowed it to offer lower prices, a key competitive advantage.
- Amazon's investment in logistics, with over $100 billion spent on fulfillment in 2023, highlights the cost of building a supply chain.
- Sears' bankruptcy in 2019 underscored the importance of adapting supply chains to changing consumer demands.
- In 2024, supply chain disruptions still impacted retail, emphasizing the need for resilient networks.
Regulatory Barriers were moderate
Regulatory barriers for retail businesses, like Sears Holdings, were moderate in 2024. New entrants faced zoning laws and safety regulations, but these were not major deterrents. The shift to online retail further lessened the impact of physical regulatory hurdles. Sears Holdings filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy in 2018 [1]. This shows that regulatory hurdles weren't the primary cause of its struggles.
- Zoning laws and safety regulations were in place.
- Online retail's growth reduced the impact of physical barriers.
- Sears Holdings' bankruptcy wasn't primarily due to regulations.
New entrants faced significant hurdles due to high initial capital requirements, like substantial real estate and inventory costs; in 2024, real estate costs rose, affecting retailers.
Building brand recognition required considerable marketing investments to challenge established brands like Sears, with average brand-building costs in retail between $500,000 and $2 million annually.
Economies of scale favored large retailers, creating cost advantages that new competitors struggled to match; Walmart's 2024 revenue of $648 billion highlights this advantage.
| Barrier | Description | Impact on Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Needs | High startup costs | Limits new competitors |
| Brand Identity | Brand-building costs | Tough for new entrants |
| Economies of Scale | Large-scale efficiencies | Creates cost disadvantages |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
The analysis uses Sears Holdings' SEC filings, market research reports, and industry publications. These provide key insights for each force assessment.