CBOE Global Markets Bundle
How Has CBOE Global Markets Transformed the Financial Landscape?
Dive into the fascinating CBOE Global Markets SWOT Analysis to understand the company's strategic position. From its humble beginnings, CBOE Global Markets has revolutionized financial markets. Discover the pivotal moments that shaped this financial powerhouse and its enduring impact on global trading.

Founded in 1973 as the Chicago Board Options Exchange (CBOE), the company's CBOE history is a story of innovation. Its introduction of the Cboe Volatility Index (VIX) in 1993 marked a turning point, providing a crucial tool for risk management in financial markets. Today, CBOE Global Markets stands as a leading force in options trading and beyond, a testament to its strategic foresight and adaptive strategies in the stock exchange arena.
What is the CBOE Global Markets Founding Story?
The story of Cboe Global Markets, a prominent player in today's financial landscape, begins with the vision to revolutionize options trading. This vision materialized on April 26, 1973, with the founding of the Chicago Board Options Exchange (CBOE) by the Chicago Board of Trade (CBOT). This marked a pivotal moment, introducing a centralized and regulated marketplace for standardized options contracts, a significant departure from the existing over-the-counter model.
The inception of CBOE was driven by the need for more efficient and transparent financial instruments, a critical demand in the early 1970s. Edmund 'Eddie' O'Connor, then vice chairman of the Chicago Board of Trade, conceived the idea in 1969. His goal was to create a system that would simplify and standardize options trading, making it more accessible and less complex than the existing unregulated market.
The establishment of CBOE was not without its challenges. Initial resistance from the New York brokerage community and regulatory hurdles had to be overcome. However, with the approval from the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) in October 1971, the path was cleared for CBOE to become an independent entity. The exchange officially began trading in the former smoking lounge of the CBOT building, immediately capturing the interest of traders. The Target Market of CBOE Global Markets has expanded significantly since its inception.
The CBOE's founding was a response to the inefficiencies of the over-the-counter options market.
- The initial concept came from Edmund O'Connor, aiming to standardize and bring transparency to options trading.
- Joseph Sullivan, the first president of CBOE, played a crucial role in navigating regulatory approvals.
- Trading commenced on April 26, 1973, with the exchange trading 34,599 contracts in its first month.
- The establishment of CBOE marked a significant shift towards a centralized, regulated marketplace for options.
CBOE Global Markets SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format

What Drove the Early Growth of CBOE Global Markets?
The early years of CBOE Global Markets were marked by swift expansion and innovation in the financial markets. Founded in 1973, the company quickly gained traction, establishing itself as a key player in options trading. This period saw the introduction of crucial technologies and the expansion of product offerings, laying the groundwork for future growth.
Following its inception, CBOE experienced significant growth. By 1976, monthly trading volume had surged to 1.5 million contracts, demonstrating strong market interest in options trading. This rapid increase highlighted the growing acceptance and utility of options within the financial markets.
CBOE embraced technological advancements early on, introducing computerized price reporting in 1975. The company expanded its product offerings by adding 'put' options in 1977. These initiatives enhanced efficiency and broadened the appeal of options trading.
A pivotal moment came in 1983 with the creation of options on broad-based indices, including the S&P 100 (OEX) and S&P 500 (SPX). These became highly active U.S. index options. In 1984, CBOE relocated its headquarters to 400 S. LaSalle Street in Chicago, reflecting its growing stature in the financial world.
CBOE continued its expansion through strategic initiatives, such as establishing The Options Institute in 1985 to educate investors. Key product launches in the 1990s included LEAPS in 1990, FLEX options in 1993, and options on the Nasdaq-100 Index in 1994, further diversifying its offerings.
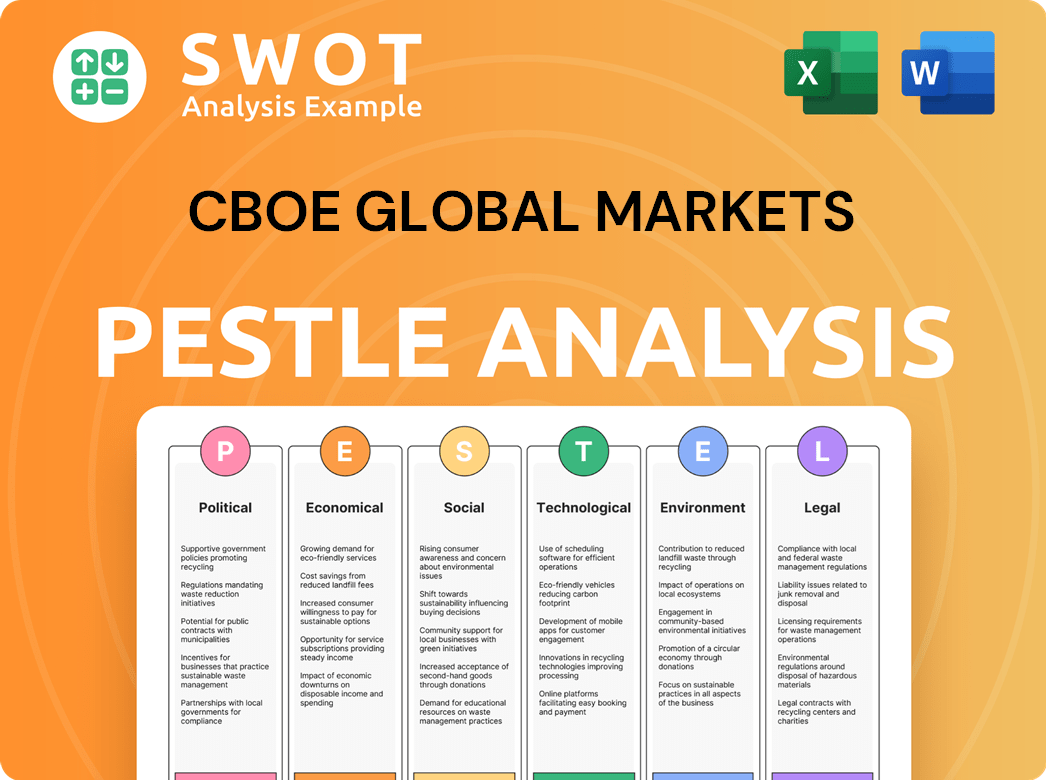
CBOE Global Markets PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
What are the key Milestones in CBOE Global Markets history?
The history of CBOE Global Markets, a prominent player in the financial markets, is marked by significant milestones and strategic developments. From its inception, CBOE company has consistently evolved, adapting to market dynamics and technological advancements while expanding its global footprint. This evolution has solidified its position as a key stock exchange.
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 1973 | CBOE, the first listed options trading exchange, begins trading. |
| 1993 | CBOE introduces the CBOE Volatility Index (VIX), a benchmark for market volatility. |
| 2004 | CBOE launches VIX futures, expanding its derivatives offerings. |
| 2005 | CBOE introduces Weeklys options, enhancing trading flexibility. |
| 2011 | CBOE launches the electronic S&P options contract (SPXpm). |
| 2020 | CBOE acquires Trade Alert, expanding its market data capabilities. |
| 2021 | CBOE acquires Chi-X Asia Pacific, increasing its presence in the Asia-Pacific region. |
| 2022 | CBOE acquires ErisX, entering the digital asset market. |
| 2024 | CBOE announces plans to wind down its digital asset spot market operations. |
CBOE Global Markets has consistently been at the forefront of innovation in the financial sector. The introduction of the VIX in 1993 was a groundbreaking move, establishing a key benchmark for market volatility. Further innovation includes the launch of VIX-based products and the introduction of Weeklys options, enhancing trading flexibility.
The CBOE Volatility Index (VIX) is a key innovation. The VIX offers a real-time market estimate of expected volatility.
CBOE launched VIX futures, providing traders with more tools. These futures contracts allow for hedging and speculation on market volatility.
CBOE introduced Weeklys options to increase trading flexibility. These options have shorter lifespans, giving traders more opportunities.
CBOE has invested heavily in electronic trading platforms. This has increased speed and efficiency in trading.
CBOE has expanded globally through acquisitions. This includes a strong presence in Europe and Asia Pacific.
CBOE focuses on data and analytics through its Cboe Data Vantage business. This positions CBOE for future growth.
Despite its successes, CBOE has faced various challenges, including market downturns and competitive pressures. Strategic pivots, such as global expansion and acquisitions, have been crucial for maintaining growth. For example, in April 2024, CBOE decided to wind down its digital asset spot market operations, demonstrating the need to adapt to evolving market conditions.
CBOE must navigate volatile market environments. This requires robust infrastructure and risk management.
CBOE faces competition from other exchanges and trading platforms. Innovation and strategic partnerships are essential.
Changes in market regulations can affect CBOE's operations. CBOE must adapt to these changes to maintain compliance.
Keeping up with technological advancements is crucial. CBOE must continue to invest in its technology platform.
Expanding globally involves various risks, including economic and political uncertainties. Strategic planning is important.
The decision to wind down the digital asset spot market shows the challenges. Regulatory clarity is important for this market.
CBOE Global Markets Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout

What is the Timeline of Key Events for CBOE Global Markets?
The history of CBOE Global Markets, a key player in the financial markets, is marked by innovation and strategic expansion. Founded as the Chicago Board Options Exchange (CBOE) in 1973, it revolutionized options trading. Over the years, Cboe has introduced numerous financial products, expanded its global footprint, and embraced technological advancements. This journey reflects its commitment to shaping financial markets and providing diverse trading opportunities.
| Year | Key Event |
|---|---|
| 1973 | Founded as the Chicago Board Options Exchange (CBOE), marking the first exchange to list standardized options. |
| 1977 | Added 'put' options to its offerings, expanding trading opportunities. |
| 1983 | Launched options on the S&P 100 (OEX) and S&P 500 (SPX) indices, broadening its product range. |
| 1993 | Launched the Cboe Volatility Index (VIX), a key measure of market volatility, and introduced Flexible Exchange (FLEX) options. |
| 2004 | Began trading VIX futures, further diversifying its offerings. |
| 2010 | CBOE Holdings, Inc. went public with an IPO on NASDAQ. |
| 2017 | Acquired BATS Global Markets for approximately $3.2 billion and rebranded to Cboe Global Markets. |
| 2020 | Acquired Hanweck, FT Options, Trade Alert, and EuroCCP, expanding its services. |
| 2021 | Completed acquisition of Chi-X Asia Pacific, expanding into Japan and Australia. |
| 2022 | Acquired Eris Digital Holdings (ErisX) and opened a new open-outcry trading floor in Chicago. |
| 2024 | Announced plans to wind down Cboe Digital Spot Market operations and integrate digital asset derivatives into existing businesses. |
| 2025 | Anticipates final technology migration in Canada, with Cboe Canada transitioning to Cboe's proprietary technology platform; Craig Donohue assumes CEO role in May 2025. |
Cboe Global Markets anticipates continued growth in 2025 and beyond, fueled by strategic initiatives. The company projects organic total net revenue growth in the mid to high single digits for fiscal year 2025. This indicates a positive outlook for the company's financial performance and market position.
Analysts expect Cboe's EPS to rise by 6.7% year-over-year to $9.86 in fiscal 2026, demonstrating strong earnings potential. Cboe's focus on key areas such as options trading and data business expansion is expected to drive long-term growth and profitability.
Cboe plans to further penetrate retail channels and import international demand to U.S. markets for its derivatives franchise. Expansion of its data business globally through cloud distribution and replicating its success in Europe in APAC and Canada are also key initiatives. These strategies aim to increase market share and revenue streams.
The company plans to transition its cash-settled bitcoin and ether futures contracts to the Cboe Futures Exchange (CFE) in the first half of 2025, consolidating U.S. futures products. Cboe's investment in artificial intelligence (AI) and its AI Center of Excellence are expected to lead to more new initiatives in 2025.
CBOE Global Markets Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked

Related Blogs
- What is Competitive Landscape of CBOE Global Markets Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of CBOE Global Markets Company?
- How Does CBOE Global Markets Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of CBOE Global Markets Company?
- What is Brief History of CBOE Global Markets Company?
- Who Owns CBOE Global Markets Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of CBOE Global Markets Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.