Xiaomi Bundle
How Did Xiaomi Rise to Tech Titan Status?
Founded in April 2010, the Xiaomi SWOT Analysis is a Chinese tech giant that has swiftly conquered the global market. From its humble beginnings, Xiaomi, driven by founder Lei Jun, aimed to deliver high-quality technology at accessible prices. This commitment to affordability and innovation quickly set Xiaomi apart in a competitive landscape.

This article delves into the brief history of Xiaomi, exploring the Xiaomi company origin story and the remarkable journey of Xiaomi smartphones. We'll examine Xiaomi's early years, its strategic growth, and its impact on the tech industry. Discover the key milestones, innovations, and challenges that have shaped Xiaomi's success story, and the current status of the company, including its future plans.
What is the Xiaomi Founding Story?
The story of the Xiaomi company begins on April 6, 2010, in Beijing, China. The company was founded by Lei Jun, a seasoned entrepreneur, along with six co-founders. Their goal was to offer high-quality tech products at prices that were accessible to everyone.
Lei Jun's vision was clear: to make advanced technology available without the premium price tag. The other co-founders brought in their expertise in software, hardware, and design. This mix of skills was vital for the company's early development.
The founders saw an opportunity to create better mobile phones, leading them to develop their own products. Xiaomi's journey started with software, specifically the MIUI, an Android-based firmware released on August 16, 2010. This customized Android ROM provided more features and a better user experience than standard Android.
Xiaomi's origin story is marked by a strong focus on community and user feedback, which was key to its initial success. The company's early funding came from a Series A round in 2010, raising $41 million.
- Xiaomi history begins in Beijing on April 6, 2010.
- Lei Jun and six co-founders launched the company.
- MIUI, an Android-based firmware, was launched on August 16, 2010.
- Initial funding included $41 million from investors.
The company's initial funding came from a Series A round in 2010, which raised $41 million. Investors included Temasek Holdings, IDG Capital, Qiming Venture Partners, and Qualcomm. Lei Jun's previous ventures also contributed to the start-up financing. Xiaomi initially sold its products online, which helped them keep prices low by avoiding expensive advertising. This strategy, along with social media engagement, allowed them to compete effectively.
Xiaomi's early success can be attributed to its innovative business model and focus on user feedback. The company quickly gained popularity in China and began its global expansion. Xiaomi's approach to product development and marketing set it apart from its competitors, leading to rapid growth. For a deeper dive into the competitive landscape, you can check out the Competitors Landscape of Xiaomi.
Today, Xiaomi is a major player in the global tech market, with a wide range of Xiaomi products, including Xiaomi smartphones. The company continues to innovate and expand its product offerings, maintaining its commitment to providing high-quality products at accessible prices. As of early 2024, Xiaomi's global market share in smartphones remains significant, reflecting its continued success and influence in the tech industry.
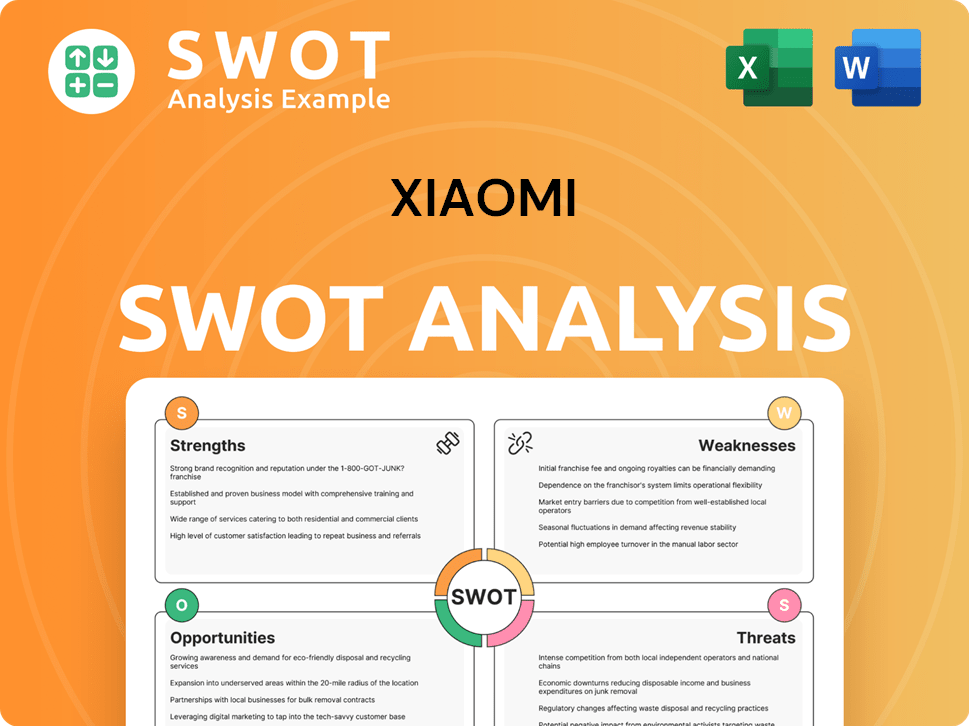
Xiaomi SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
What Drove the Early Growth of Xiaomi?
The early growth of the Xiaomi company was marked by rapid product development and a unique approach to sales and user engagement. Following the launch of its MIUI firmware in August 2010, the company released its first smartphone, the Xiaomi Mi 1, in August 2011. This marked its transition into hardware, quickly gaining consumer attention.
The Xiaomi Mi 1, pre-installed with MIUI, was an instant success. It sold out in just 34 seconds, demonstrating strong initial consumer interest. The aggressive pricing of the Mi 1, offering high-end specifications at a competitive price, quickly attracted customers. This early success set the stage for the company's future growth in the smartphone market.
In December 2011, Xiaomi secured a Series B funding round of $90 million, followed by a Series C round in June 2012, raising $216 million at a $4 billion valuation. These funding rounds provided the capital needed to expand operations, develop new products, and compete in the rapidly growing smartphone market. The high valuation reflected investor confidence in the company's potential.
By 2014, the company had become the largest smartphone vendor in China, surpassing Samsung. Its market share in Q2 2014 was approximately 14.6%. This achievement was fueled by 'hunger marketing' tactics, creating high demand and reducing inventory costs. This strategy helped the company quickly gain a significant share of the Chinese market.
International expansion began in February 2014 with an international headquarters in Singapore, followed by entry into markets like India and Indonesia. India became a cornerstone of the company's global growth, becoming the largest smartphone brand there in Q3 2017. The company diversified into smart home devices and IoT products in March 2015, laying the groundwork for its ecosystem. To understand more about their business model, you can read about the Revenue Streams & Business Model of Xiaomi.
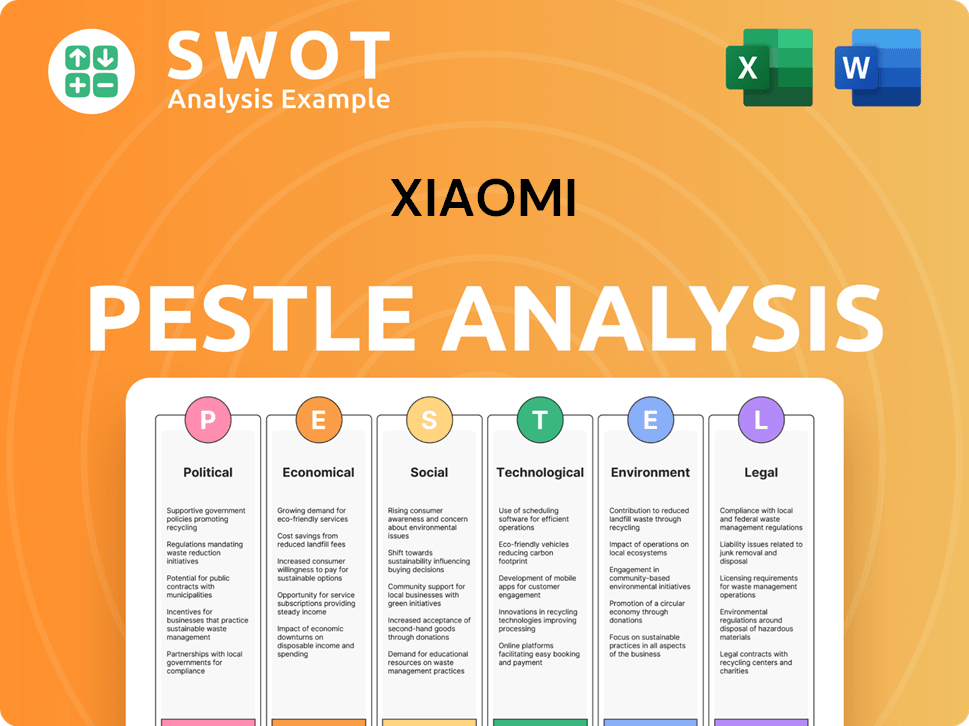
Xiaomi PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
What are the key Milestones in Xiaomi history?
The Xiaomi company has a rich Xiaomi history, marked by significant achievements that have shaped its trajectory in the tech industry. From its inception, the company has consistently pushed boundaries, achieving remarkable milestones that have solidified its position in the global market. Understanding the Xiaomi timeline is crucial to appreciating its journey.
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 2010 | Launched MIUI, a customized Android operating system, establishing a strong software foundation. |
| 2011 | Released the Xiaomi Mi 1, marking its entry into the smartphone market with high-spec hardware at competitive prices. |
| 2014 | Became the top smartphone brand in China, showcasing its aggressive pricing and online sales strategy. |
| 2017 | Implemented 'New Retail' strategies, integrating online and offline channels to improve sales and distribution. |
| 2019 | Appeared on the Fortune Global 500 list for the first time, reflecting its global expansion and financial success. |
Xiaomi's success is fueled by its innovative spirit, constantly introducing new Xiaomi products and technologies. The company's focus on user experience and community engagement has also driven its innovation.
MIUI, launched in August 2010, was a key innovation, offering extensive customization and functionalities, setting the stage for a dedicated user base. This software-first approach helped build brand loyalty even before their first smartphone.
Xiaomi disrupted the market with its aggressive pricing strategy, making high-quality technology accessible to a broader audience. This strategy helped them gain significant market share, especially in the early years.
Xiaomi expanded beyond Xiaomi smartphones to create a diverse ecosystem of IoT products, including smart home devices and wearables. This diversification broadened its market reach and revenue streams.
Initially, Xiaomi focused on online sales, which helped reduce costs and reach a wider audience. This strategy was crucial in the early stages of its growth, allowing it to compete effectively.
In response to market challenges, Xiaomi adopted a 'New Retail' strategy, integrating online and offline channels. This approach helped improve distribution and customer experience, leading to better sales.
Xiaomi built a strong community around its brand, fostering loyalty and gathering valuable feedback. This engagement helped the company understand and meet customer needs, driving product development.
Despite its successes, Xiaomi has faced several challenges throughout its journey. These challenges have tested the company's resilience and adaptability.
In 2016, Xiaomi experienced a sales decline, dropping from the top position in China. This downturn was attributed to distribution issues and over-reliance on online sales.
Xiaomi faced fierce competition from other Chinese brands, such as Huawei, Oppo, and Vivo, which also adopted aggressive pricing strategies. This competition put pressure on market share and profitability.
During its international expansion, Xiaomi encountered patent lawsuits, which posed challenges to its global growth. These legal issues required the company to invest in intellectual property protection.
Xiaomi faced challenges related to its distribution chain, particularly in the early years. These issues affected its ability to reach customers efficiently and manage inventory effectively.
Initially, Xiaomi's heavy reliance on online sales created vulnerabilities, as it limited its reach and customer experience. This prompted the company to diversify its sales channels.
Continuous innovation and adaptation are crucial for Xiaomi to maintain its market relevance. The company must stay ahead of technological advancements and changing consumer preferences.
For further insights into Xiaomi's market positioning, consider exploring the Target Market of Xiaomi.
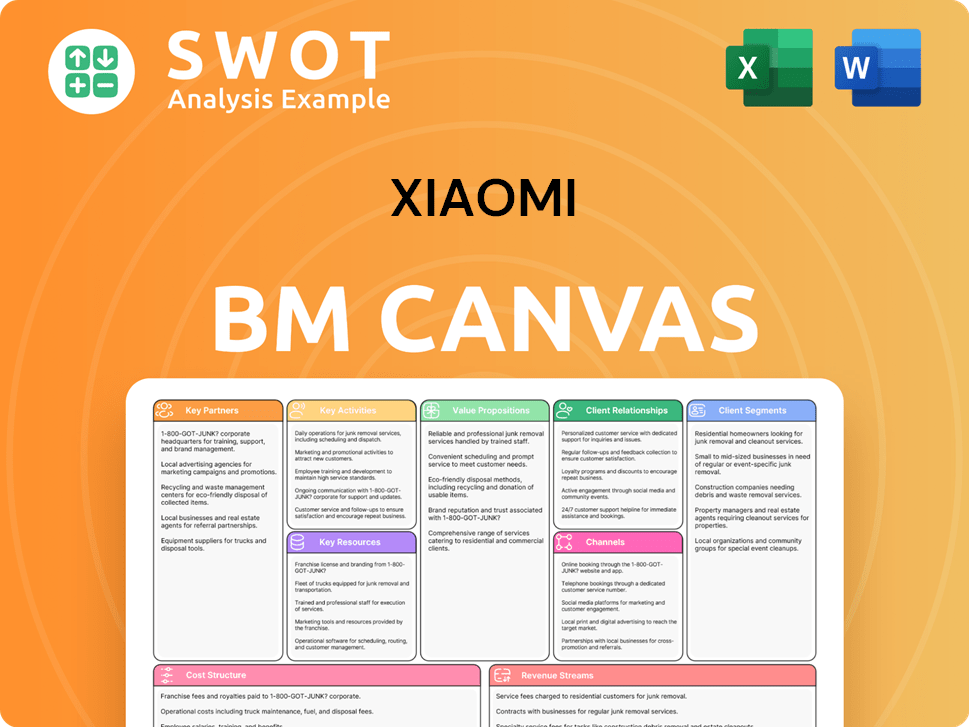
Xiaomi Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What is the Timeline of Key Events for Xiaomi?
The Xiaomi company has a rich history marked by rapid growth and innovation. Founded on April 6, 2010, by Lei Jun and six associates, the company quickly made a name for itself in the tech industry. From its early days with the MIUI firmware to its expansion into smartphones and smart home devices, Xiaomi has consistently pushed boundaries. The company's IPO in July 2018, and its entry into the Fortune Global 500 list, further solidified its global presence. With a focus on R&D and expansion into the EV market, Xiaomi continues to evolve and adapt to the changing market landscape.
| Year | Key Event |
|---|---|
| April 6, 2010 | Xiaomi Corporation was co-founded by Lei Jun and six associates in Beijing, China. |
| August 16, 2010 | Xiaomi launched its first Android-based firmware, MIUI. |
| August 2011 | Xiaomi released its first smartphone, the Xiaomi Mi 1, which sold out in 34 seconds. |
| December 2014 | Xiaomi raised US$1.1 billion at a valuation of over US$45 billion, making it one of the most valuable private technology companies globally. |
| 2014 | Xiaomi became the largest smartphone vendor in China. |
| March 2015 | Xiaomi expanded its product line into smart home devices. |
| July 2018 | Xiaomi went public on the Hong Kong Stock Exchange, raising $4.72 billion in its IPO. |
| 2019 | Xiaomi appeared on the Fortune Global 500 list for the first time. |
| 2021 | Xiaomi announced a US$10 billion investment into electric vehicles (EVs). |
| Late 2023 | Xiaomi Auto unveiled its first production vehicle, the Xiaomi SU7. |
| March 28, 2024 | Xiaomi officially launched the SU7 sedan in Beijing. |
| Q1 2025 | Xiaomi recorded a revenue of RMB 111.3 billion, a 47.4% increase year-over-year, and an adjusted net profit of RMB 10.7 billion, up 64.5% year-on-year. |
| May 2025 | Xiaomi unveiled its first self-developed smartphone SoC chip, the Xring O1. |
Xiaomi aims to become the world's top smartphone retailer within three years. The company also targets a spot among the global top five carmakers within ten years. These goals showcase Xiaomi's aggressive expansion strategy and its commitment to market dominance.
Xiaomi is investing heavily in research and development, with a planned investment of 200 billion Chinese yuan over the next five years. This investment will focus on AI, operating systems, and chips. A significant portion, 50 billion yuan, will be allocated to its chip unit.
Xiaomi aims to deliver 300,000 SU7 series vehicles in 2025, expanding its production capacity and sales network. By January 2025, it plans to have 216 centers across 64 cities in China. This expansion highlights Xiaomi's commitment to the electric vehicle market.
Xiaomi's 'Human x Car x Home' smart ecosystem strategy, upgraded in October 2023, aims to seamlessly merge personal devices, smart home products, and cars. The company also plans to open more stores in Singapore by 2025, reaching 10 stores, and expand to 219 sales stores and 143 service centers by 2024.
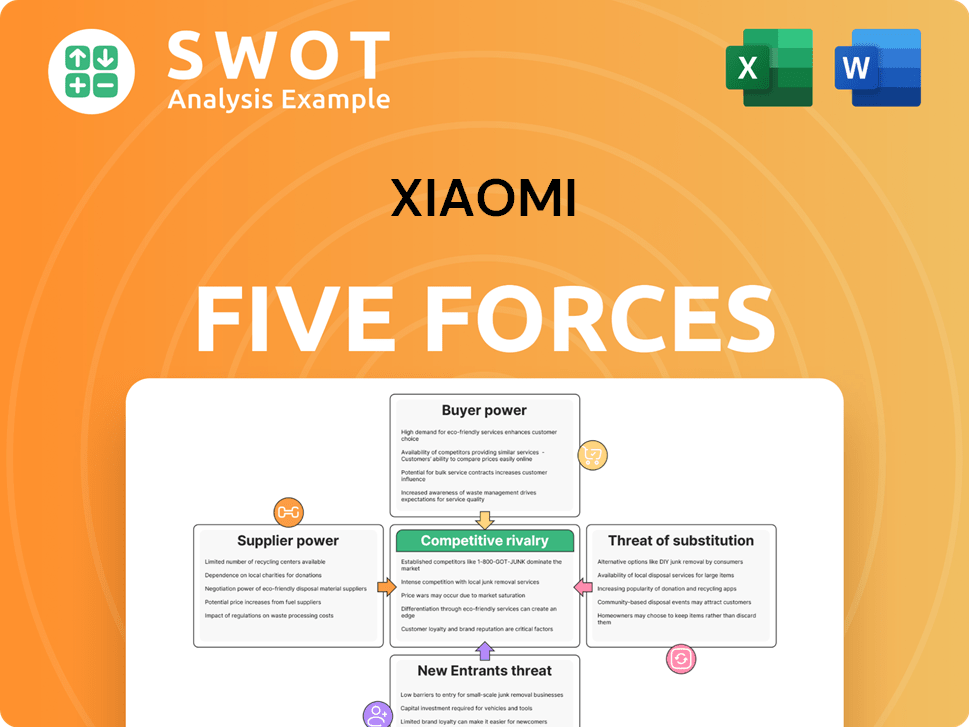
Xiaomi Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What is Competitive Landscape of Xiaomi Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Xiaomi Company?
- How Does Xiaomi Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Xiaomi Company?
- What is Brief History of Xiaomi Company?
- Who Owns Xiaomi Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Xiaomi Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.