Xiaomi Bundle
Who Really Owns Xiaomi?
Ever wondered who pulls the strings at one of the world's leading tech giants? Xiaomi, a name synonymous with cutting-edge smartphones and smart home devices, has a fascinating ownership story. From its humble beginnings in Beijing to its global dominance, understanding Xiaomi's ownership structure is key to grasping its strategic direction and future potential.

The Xiaomi SWOT Analysis is a great tool for understanding the company's position. Unraveling the Xiaomi ownership structure reveals the influence of its founders, key investors, and the impact of going public. This exploration will examine the evolution of Xiaomi's ownership, including the roles of Xiaomi founder, Xiaomi executives, and Xiaomi shareholders, providing critical insights into the company's decision-making processes and its place in the competitive tech landscape. Understanding the Xiaomi parent company and the distribution of shares among Xiaomi investors is crucial for anyone looking to understand the company's trajectory.
Who Founded Xiaomi?
The story of Xiaomi begins on April 6, 2010, with eight co-founders coming together to create a company focused on high-quality, affordable technology. Understanding the Xiaomi ownership structure from its inception provides crucial insights into its evolution. The initial ownership and control were pivotal in shaping the company's strategic direction and operational dynamics.
Lei Jun, a well-known figure in the tech industry, played a central role in establishing Xiaomi. His experience with Kingsoft and Joyo.com set the stage for Xiaomi's innovative approach. While the exact initial equity split among the founders isn't fully detailed, Lei Jun held a significant stake, which positioned him as the Chairman and CEO from the start. This early structure was key to the company's vision.
Early support from angel investors and venture capital firms was crucial. Morningside Ventures was among the first to invest, demonstrating confidence in Xiaomi even before its official launch. Other early investors included Qiming Venture Partners and Shunwei Capital, a firm co-founded by Lei Jun. This early backing helped solidify Lei Jun's influence and the company's direction.
The eight co-founders of Xiaomi included Lei Jun, Lin Bin, Li Wanqiang, Zhou Guangping, Huang Jiangji, Liu De, Hong Feng, and Wang Chuan.
Lei Jun served as the Chairman and CEO, holding a significant stake and driving the company's vision.
Morningside Ventures, Qiming Venture Partners, and Shunwei Capital were among the early investors in Xiaomi.
The founders aimed to offer high-quality, affordable technology, which influenced the company's initial direction.
There were no major ownership disputes or buyouts reported among the core founding team during the initial phase.
The distribution of control likely reflected Lei Jun's leadership and strategic vision.
Understanding the early Xiaomi ownership structure is essential for grasping its growth trajectory. The initial backing from Lei Jun and early investors set the stage for the company's success. For more insights into the company's consumer base, check out this article about the Target Market of Xiaomi.
- Lei Jun's leadership was crucial in the initial phases.
- Early investors provided essential financial support.
- The founding team's cohesion contributed to early stability.
- The focus on affordable, high-quality tech defined the company's ethos.
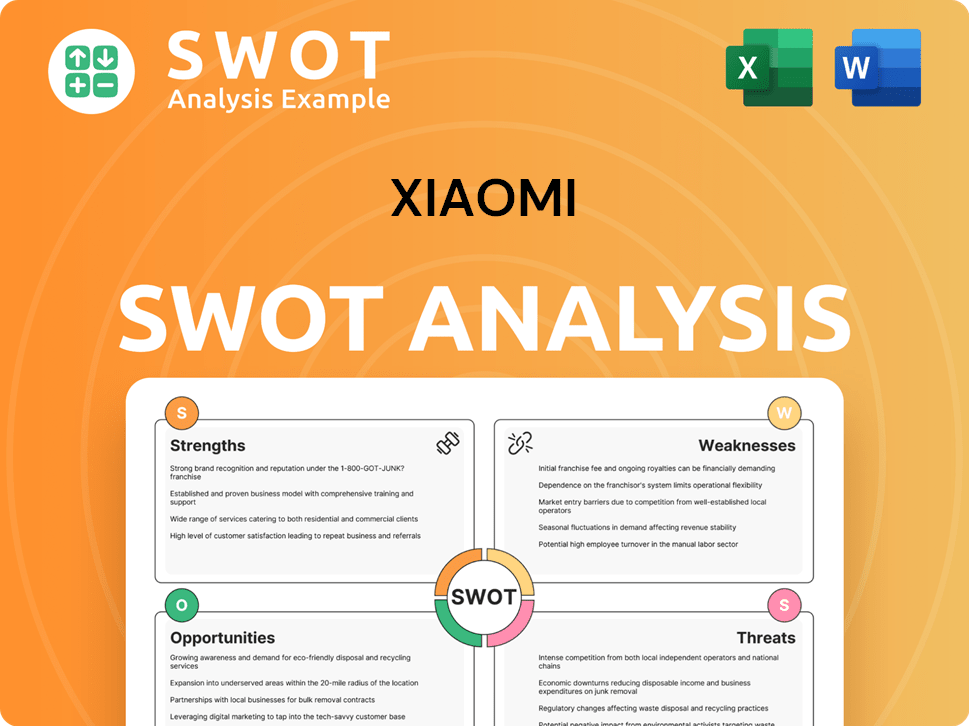
Xiaomi SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
How Has Xiaomi’s Ownership Changed Over Time?
The evolution of Xiaomi's ownership has been marked by pivotal events, starting with its founding. Initial funding rounds shaped the early ownership structure, primarily involving venture capital and private investors. The most significant shift occurred on July 9, 2018, when the company went public on the Hong Kong Stock Exchange (HKEX) under the stock code 1810.HK. This initial public offering (IPO) was a landmark event, valuing the company at approximately US$54 billion and transitioning its ownership from private investors to a mix of public shareholders.
Post-IPO, the ownership landscape of the company has continued to evolve. The inclusion of institutional investors, mutual funds, and individual insiders has diversified the shareholder base. Share buybacks have also played a role in adjusting ownership percentages. The transition to public ownership has increased scrutiny and broadened the stakeholder base, influencing strategic decisions related to profitability, global expansion, and shareholder returns. This dynamic environment is typical of large tech companies navigating global markets.
| Event | Impact on Ownership | Date |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Funding Rounds | Established early investor base, primarily venture capital. | Pre-IPO |
| IPO on HKEX | Shifted ownership to public shareholders, increased market capitalization. | July 9, 2018 |
| Share Buybacks | Influenced ownership percentages of remaining shareholders. | Ongoing |
As of early 2025, Lei Jun, the Xiaomi founder, remains the largest individual shareholder, though his exact percentage fluctuates. Major institutional investors, such as BlackRock, Vanguard, and Fidelity, hold significant stakes. These institutional investors, along with other Xiaomi shareholders, collectively hold a considerable portion of the publicly traded shares, influencing the company through their voting power. The company's market capitalization has fluctuated since its IPO, reflecting market performance and strategic decisions.
Lei Jun is the largest individual shareholder, maintaining a substantial stake. Institutional investors, like BlackRock and Vanguard, hold significant portions of the shares.
- The IPO in 2018 marked a major shift in ownership structure.
- Share buybacks have been used to influence ownership percentages.
- Public ownership brings increased scrutiny and a broader stakeholder base.
- The company's market capitalization reflects market performance.
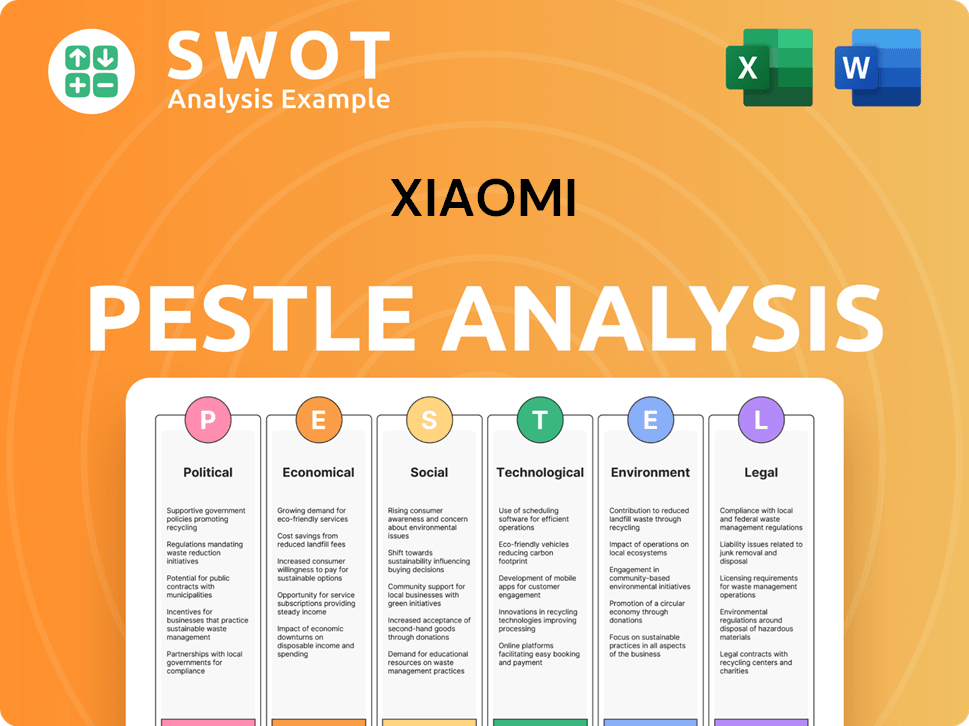
Xiaomi PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
Who Sits on Xiaomi’s Board?
As of early 2025, the board of directors at Xiaomi includes a mix of executive, non-executive, and independent non-executive directors. Lei Jun, the Xiaomi founder, serves as Executive Director, Chairman, and CEO. Other executive directors typically include key management personnel. Non-executive directors often represent major shareholders or strategic partners, while independent non-executive directors provide oversight and contribute to corporate governance. Understanding the composition of the board is crucial for anyone examining Xiaomi ownership and the direction of the company.
The structure ensures a balance of perspectives, with independent directors providing unbiased oversight. This structure is designed to ensure the long-term vision and stability of the company under its founders' leadership. The board's composition reflects the company's commitment to both strategic direction and corporate governance, which is key for Xiaomi investors.
| Director Type | Role | Responsibilities |
|---|---|---|
| Executive Directors | Lei Jun (Chairman & CEO) | Overseeing daily operations, strategic planning |
| Non-Executive Directors | Represents major shareholders | Providing oversight, contributing to strategic decisions |
| Independent Non-Executive Directors | Provides oversight | Ensuring corporate governance and compliance |
Xiaomi utilizes a weighted voting rights (WVR) structure, also known as a dual-class share structure. This arrangement allows Lei Jun and other founding shareholders to retain significant control disproportionate to their economic interest. Class A shares, held by the founders, have more voting rights than the Class B shares held by public investors. This structure, a key feature since the IPO, gives the founding team outsized control over major corporate decisions, including board appointments and strategic initiatives. This structure is a crucial aspect of understanding the Xiaomi ownership structure.
The board includes executive, non-executive, and independent directors, with Lei Jun at the helm. The WVR structure gives founders significant control. This structure affects how Xiaomi shareholders influence the company.
- Lei Jun maintains a strong leadership role.
- Non-executive directors represent key stakeholders.
- WVR structure ensures founder control.
- This structure is a key aspect of the company's governance.
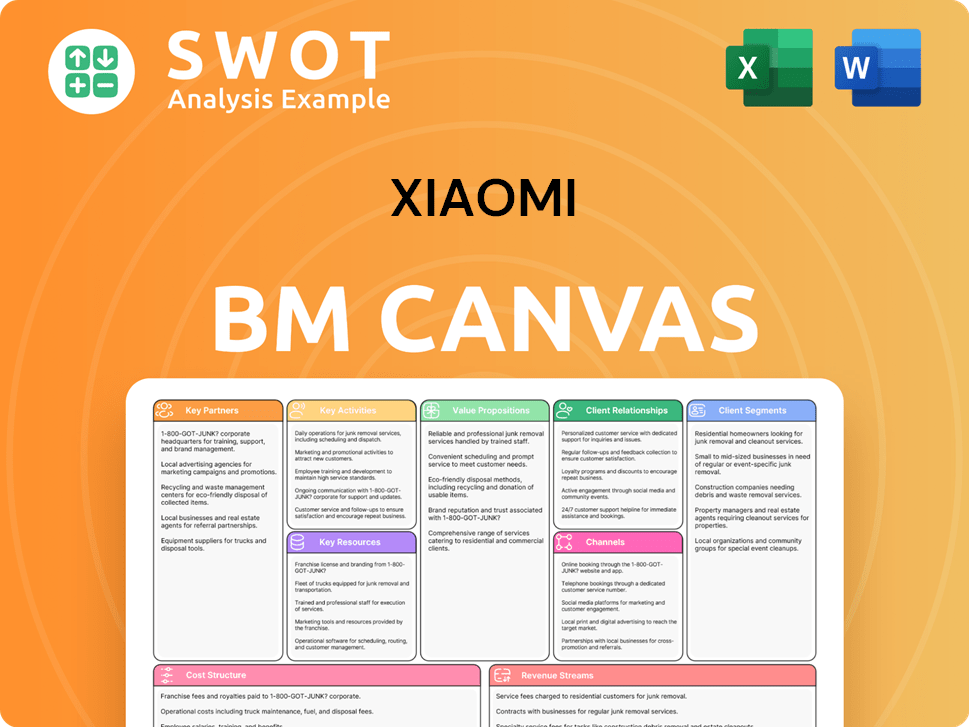
Xiaomi Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What Recent Changes Have Shaped Xiaomi’s Ownership Landscape?
In the past few years, specifically from 2022 to 2025, the ownership structure of Xiaomi has been subject to various changes. The company has actively engaged in share buybacks, particularly in 2024. These actions can consolidate ownership among existing shareholders and potentially boost earnings per share. For instance, significant share repurchase programs were announced in 2024, which reflects the company's confidence in its valuation.
Industry trends indicate a rise in institutional ownership within the technology sector, and Xiaomi is no exception. Large asset managers and index funds continue to be significant Xiaomi shareholders. Despite founder dilution being a natural consequence of funding rounds and public offerings, Lei Jun has maintained a strong controlling stake due to the weighted voting rights structure. Xiaomi's ongoing investment in research and development and its expansion into new product categories also suggest a continued need for capital, which could lead to further equity adjustments. The company's global expansion, especially in the EV market with the launch of its SU7 electric vehicle in 2024, may attract new strategic investors or partnerships, influencing future ownership dynamics.
| Ownership Category | Approximate Percentage (2024) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Lei Jun | ~10-15% | Through weighted voting rights. |
| Institutional Investors | ~40-50% | Including large asset managers and index funds. |
| Public Shareholders | ~35-45% | Remaining shares available in the market. |
Understanding the ownership dynamics is crucial for investors. The share buyback programs, as well as the strategic moves, are all part of the company's strategy. To further understand the company's trajectory, you can explore the Growth Strategy of Xiaomi.
Major institutional investors include prominent global asset management firms. These firms hold a significant percentage of Xiaomi's shares. They are key players in the company's shareholder base.
Lei Jun, the Xiaomi founder, maintains a significant influence through his shareholding and the weighted voting rights structure. His continued involvement is critical for the company's strategic direction. His decisions have a significant impact on the company.
Share buybacks in 2024 have reduced the number of outstanding shares. This action increases the percentage ownership of existing shareholders. This also boosts the earnings per share.
The company's focus on global expansion and new product categories suggests a need for capital. This could lead to further equity adjustments. The company's future is looking bright.
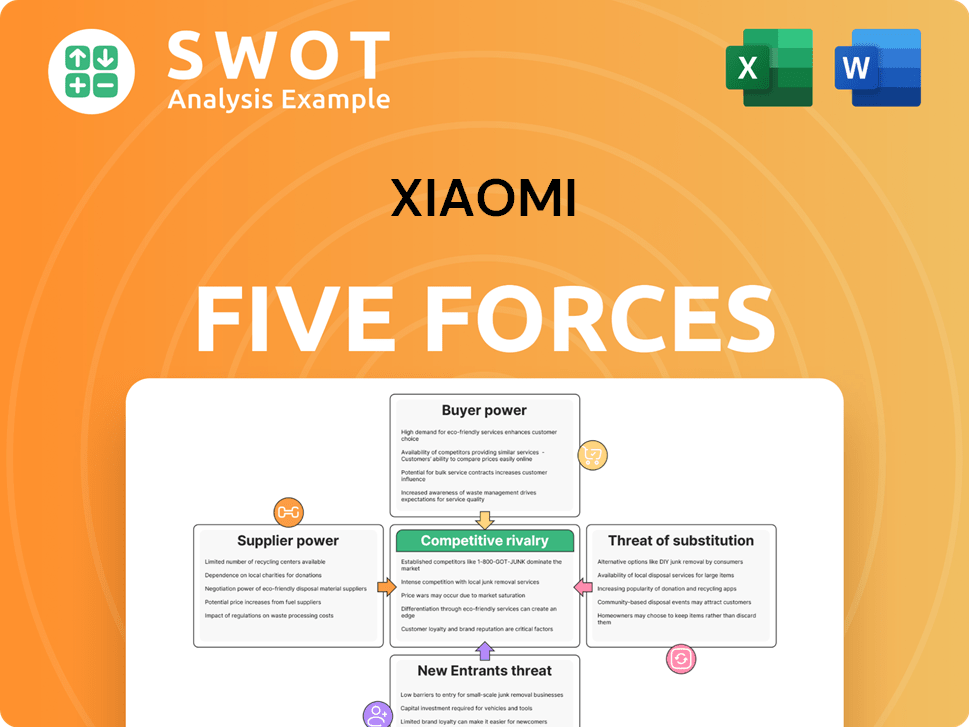
Xiaomi Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of Xiaomi Company?
- What is Competitive Landscape of Xiaomi Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Xiaomi Company?
- How Does Xiaomi Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Xiaomi Company?
- What is Brief History of Xiaomi Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Xiaomi Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.