National Grid Bundle
How Did National Grid Power Up the World?
Ever wondered about the backbone of the energy that lights our homes and fuels our businesses? National Grid, a global leader in electricity and gas, has a fascinating story. From its roots in the UK's pioneering electricity transmission to its current international presence, the company's evolution is a testament to innovation and strategic growth. Understanding the National Grid SWOT Analysis is key to grasping its market position.

This journey, from the early days of electricity in the UK to its modern infrastructure, is a vital piece of the puzzle for anyone interested in the history of electricity transmission and the future of gas distribution. Exploring the National Grid company's timeline reveals key milestones that shaped its role in the energy sector, impacting not only the UK economy but also global energy security. Learn about National Grid's early years, its infrastructure development, and its plans for the future.
What is the National Grid Founding Story?
The formal establishment of the National Grid Company plc, now simply known as National Grid, occurred in London in 1990. This pivotal moment marked a significant shift in the UK's energy sector, stemming from the privatization of the Central Electricity Generating Board (CEGB).
The creation of National Grid was a direct response to the need for a more efficient and market-driven approach to electricity transmission. The company's initial focus was on owning and operating the high-voltage electricity transmission network, a critical infrastructure for the UK.
The Mission, Vision & Core Values of National Grid reflects the company's commitment to energy delivery.
- The National Grid Company plc was established in 1990.
- It emerged from the privatization of the Central Electricity Generating Board (CEGB).
- The initial business model focused on electricity transmission.
- The company was initially owned by regional electricity companies (RECs).
The roots of National Grid's infrastructure can be traced back to the early 20th century. As early as 1925, Lord Weir recommended a 'national gridiron' to standardize electricity supply. This led to the creation of the Central Electricity Board in 1926, laying the foundation for the modern grid. The National Grid Group plc was first listed on the London Stock Exchange in December 1995, marking a significant move towards private ownership.
In 2024, National Grid's transmission network in the UK transported approximately 350 TWh of electricity. The company's investment in the UK's electricity transmission infrastructure reached approximately £1.7 billion in the fiscal year 2024. National Grid's role has evolved to include significant investments in renewable energy integration, aiming to support the UK's transition to a low-carbon economy. The company is also heavily involved in gas distribution, with a focus on safety and efficiency.
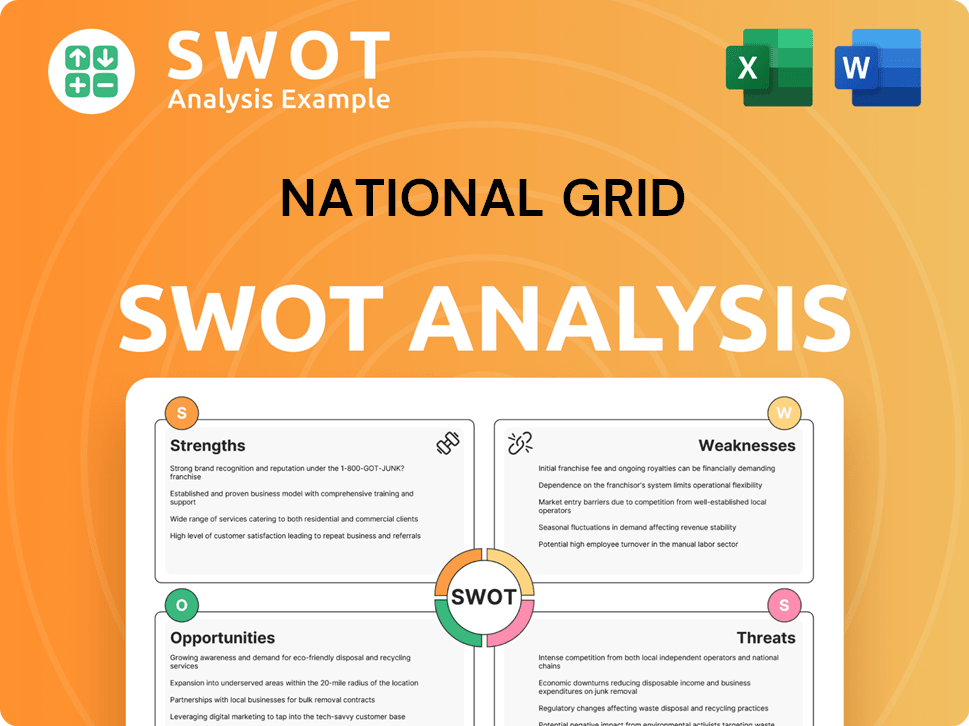
National Grid SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
What Drove the Early Growth of National Grid ?
The early growth of the National Grid company, after its formation in 1990, saw a significant transition and expansion. The company's initial years were marked by strategic moves, including becoming a publicly traded entity. This period set the stage for its evolution into a major player in the UK energy market and beyond. This is a brief history of National Grid.
In December 1995, National Grid was listed on the London Stock Exchange, a pivotal moment that allowed private investors to participate alongside the regional electricity and gas companies. This move provided the company with access to capital for future growth and expansion. The UK energy sector began to evolve as the company gained a broader shareholder base.
The new millennium saw National Grid expanding internationally, with a strong focus on the United States. In March 2000, the company acquired New England Electric System and Eastern Utilities Associates. Further acquisitions in the US, such as Niagara Mohawk Power Corporation in January 2002, solidified its presence in the American market.
A significant development was the merger with Lattice Group, which owned the Transco gas distribution business, in October 2002. This merger unified the UK gas and high-voltage electricity transmission businesses. The company was renamed National Grid Transco plc as a result.
In February 2006, National Grid announced the acquisition of KeySpan Corporation for $7.3 billion. This acquisition, along with New England Gas Company, doubled the size of its American subsidiary. By July 2005, the company was renamed National Grid plc, streamlining its identity. Owners & Shareholders of National Grid played a crucial role during this period.
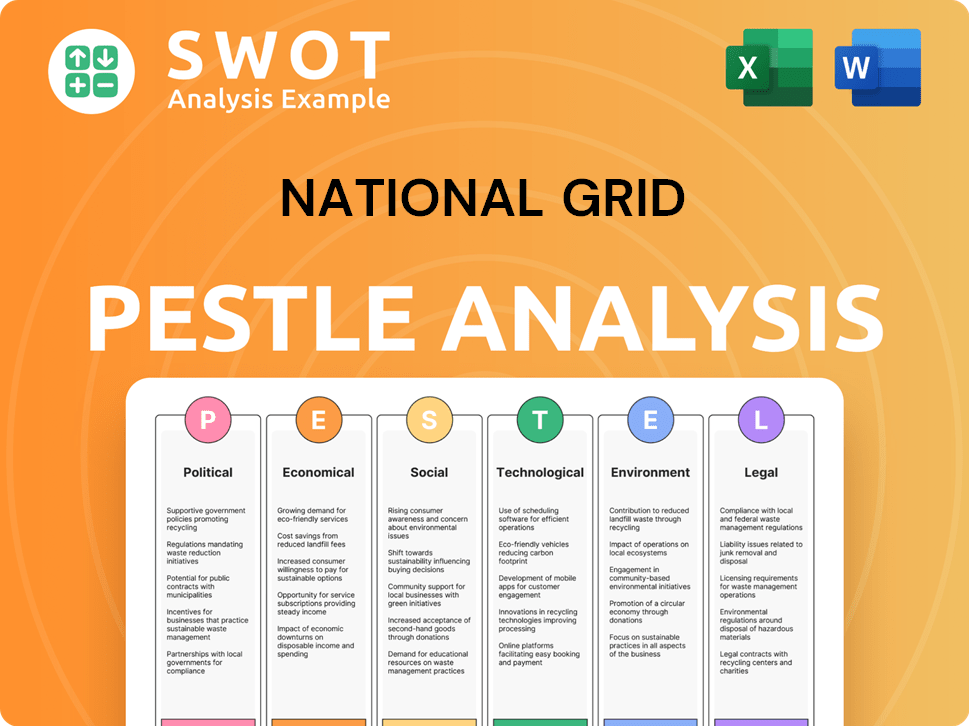
National Grid PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
What are the key Milestones in National Grid history?
The National Grid company has a rich history marked by significant milestones and strategic shifts in the UK energy sector. These achievements reflect its evolution and adaptation to the changing energy landscape.
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 2021 | Acquired Western Power Distribution (WPD) for £7.8 billion, becoming the largest electricity distribution network operator in the UK. |
| 2019 | National Grid's Electricity System Operator (ESO) announced its intent to join the Powering Past Coal Alliance, targeting a zero-carbon electricity system by 2025. |
| 2024 | Announced a £60 billion investment program between 2024 and 2029, with a significant portion allocated to upgrading and expanding UK electricity transmission and distribution. |
Innovation is central to National Grid's strategy, particularly in advancing the UK energy infrastructure. The company is actively investing in new infrastructure to meet growing electricity demand and facilitate the rollout of renewables and clean technologies.
National Grid is investing £60 billion between 2024 and 2029, with £23 billion dedicated to upgrading and expanding UK electricity transmission. This investment is crucial for enabling the accelerated adoption of low-carbon domestic technologies.
The Electricity System Operator (ESO) aims to achieve a zero-carbon electricity system by 2025, demonstrating a commitment to renewable energy sources. This initiative showcases the company's dedication to sustainability.
The company is focused on enabling the integration of renewable energy sources into the grid. This includes investments in infrastructure and technologies to support the transition to cleaner energy.
Challenges have been a constant factor in the National Grid company's history. These include market downturns and the inherent complexities of managing vast energy networks.
The £7 billion capital raise in 2024, as part of the £60 billion investment plan, represents a substantial financial commitment. This underscores the scale of the company's modernization and decarbonization efforts.
National Grid operates within a dynamic market environment, facing challenges such as fluctuating energy prices and regulatory changes. Adapting to these conditions requires strategic agility and resilience.
Managing and maintaining vast energy networks presents significant operational challenges. This includes ensuring the reliability and security of electricity transmission and gas distribution systems.
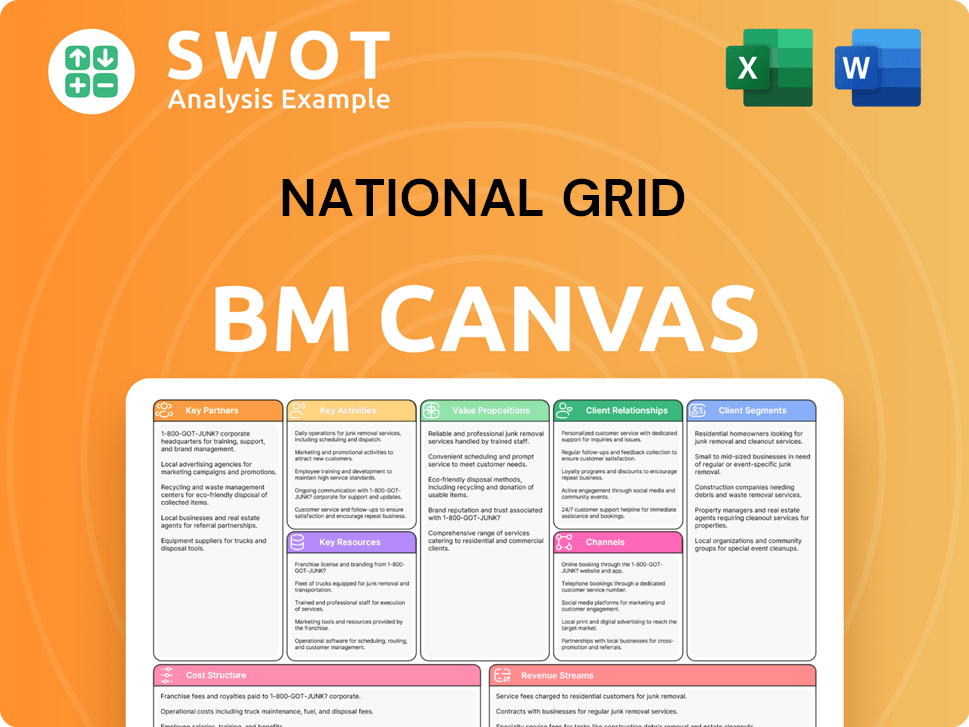
National Grid Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What is the Timeline of Key Events for National Grid ?
The Brief History of National Grid showcases a journey of transformation and expansion within the UK energy sector. From its inception as a transmission entity to its current focus on grid modernization and the energy transition, the company has consistently adapted to meet evolving energy demands. Key milestones include significant acquisitions in the US, strategic divestitures, and a major shift towards renewable energy and infrastructure upgrades, reflecting its commitment to a sustainable future.
| Year | Key Event |
|---|---|
| 1990 | The National Grid Company plc was founded in London, taking over the transmission activities of the CEGB. |
| 1995 | National Grid Group plc was listed on the London Stock Exchange. |
| 2000 | National Grid Group acquired New England Electric System and Eastern Utilities Associates in the US. |
| 2002 | National Grid Group acquired Niagara Mohawk Power Corporation and merged with Lattice Group, forming National Grid Transco plc. |
| 2005 | National Grid Transco plc was renamed National Grid plc. |
| 2006-2007 | National Grid acquired KeySpan Corporation and New England Gas Company, expanding its US operations. |
| 2017 | National Grid sold a majority stake in its UK gas distribution business (Cadent Gas). |
| 2019 | National Grid disposed of its remaining 39% holding in Cadent Gas and announced its Electricity System Operator arm's intent to join the Powering Past Coal Alliance. |
| 2021 | National Grid acquired Western Power Distribution for £7.8 billion and announced plans to sell its Rhode Island gas and electricity network and a majority stake in its UK gas transmission business. |
| 2023 | National Grid was recognized as a 'Top Utility in Economic Development' by Site Selection Magazine. |
| 2024 | National Grid completed a major £7 billion equity raise and announced the sale of National Grid Renewables to Brookfield Asset Management for $1.7 billion, expected to complete in H1 FY2026. |
| 2025 | National Grid announced its full-year results for the period ending March 31, 2025, with record capital investment of almost £10 billion, a 20% increase from 2024, and underlying operating profit rising 12% to £5.36 billion. Zoë Yujnovich is announced as the next Chief Executive Officer, effective November 17, 2025. |
National Grid is heavily focused on the energy transition, with plans to invest approximately £60 billion over the five-year period from 2024/25 to 2028/29. This investment aims to significantly increase the proportion of its asset base that is electric, from 60% in 2021 to around 80% by 2028/29.
The 'Great Grid Upgrade' in the UK is a key strategic initiative. The company plans to build five times more new electric infrastructure in the next eight years than it has built over the last three decades to meet rapid electricity demand growth. This underscores the company's commitment to infrastructure development.
For FY2025, National Grid's financial results showed a strong performance, with underlying operating profit rising 12% to £5.36 billion. The company anticipates an underlying earnings per share (EPS) compound annual growth rate of 6-8% from a 2024/25 baseline of 73.3p, supported by its investment strategy.
National Grid is streamlining its business to focus on pure-play networks and divesting non-core assets. The company's forward-looking strategy remains tied to its founding vision of a robust and integrated energy system, with a clear emphasis on decarbonization and supporting economic growth. The appointment of Zoë Yujnovich as CEO signals a continued focus on these priorities.
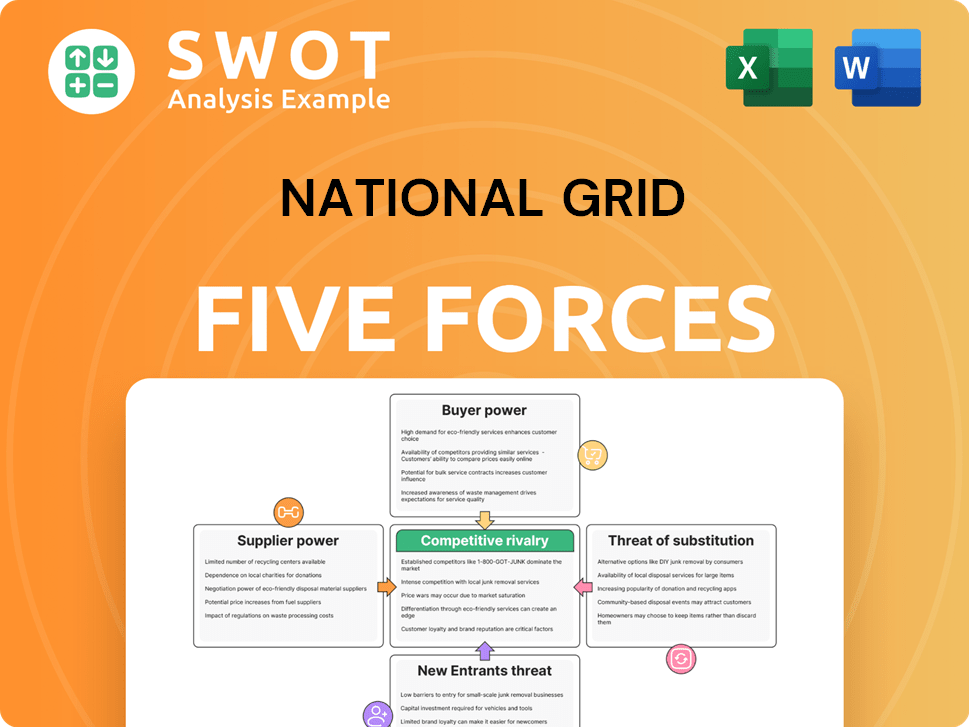
National Grid Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What is Competitive Landscape of National Grid Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of National Grid Company?
- How Does National Grid Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of National Grid Company?
- What is Brief History of National Grid Company?
- Who Owns National Grid Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of National Grid Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.