National Grid Bundle
Who's Challenging National Grid in the Energy Arena?
The energy sector is undergoing a seismic shift, and National Grid, a key player in electricity and gas transmission, is at the heart of it. From its UK roots to its expansion across the Atlantic, National Grid faces a dynamic competitive landscape. Understanding its rivals and market positioning is crucial for anyone invested in the future of energy.

This exploration of the National Grid SWOT Analysis will dissect the company's competitive environment, identifying its main competitors and analyzing its market share in both the UK and the US. We'll delve into the energy industry analysis to understand how National Grid navigates the challenges and opportunities presented by its power grid rivals, and how it's responding to the changing market dynamics. This analysis will provide actionable insights into National Grid's strategic positioning and future outlook.
Where Does National Grid ’ Stand in the Current Market?
National Grid holds a significant market position within the energy sector, particularly in its core operating regions. In the UK, the company is the sole owner and operator of the high-voltage electricity transmission network in England and Wales, and the gas transmission network across Great Britain. This near-monopoly provides substantial stability and predictable revenue streams.
In the United States, National Grid delivers electricity and gas to approximately 20 million customers across Massachusetts, New York, and Rhode Island, making it one of the largest utility companies in the northeastern U.S. The company's primary product lines include electricity transmission, gas transmission, and electricity and gas distribution. This diversified portfolio strengthens its overall market position.
Recent financial data indicates that National Grid reported an underlying operating profit of £4.8 billion for the nine months ended December 31, 2024. This demonstrates robust financial health and underscores its strong market position.
National Grid's control over the UK's high-voltage electricity transmission and gas transmission networks gives it a significant advantage. This infrastructure ownership provides a stable foundation for the company. The company's position allows for consistent revenue generation due to the essential nature of its services.
In the United States, National Grid serves approximately 20 million customers. This large customer base provides a substantial revenue stream. The company's presence in key northeastern states strengthens its overall market share and diversification.
National Grid's financial health is demonstrated by its underlying operating profit of £4.8 billion for the nine months ended December 31, 2024. The company's strategic focus increasingly shifts towards renewable energy integration. The company plans a £42 billion investment over five years from 2024 to 2029.
National Grid is actively integrating renewable energy sources and smart grid technologies. This strategic shift aligns with broader industry trends and enhances its long-term competitiveness. Investments in grid modernization are crucial for maintaining its market position.
National Grid's strong market position is supported by its infrastructure ownership and significant investment plans. The company benefits from long-term contracts and essential service provision, ensuring stable revenue streams. Its focus on renewable energy and smart grid technologies positions it well for future growth. For a deeper understanding of the company's financial structure, consider reading about Revenue Streams & Business Model of National Grid .
- Near-monopoly in UK transmission networks.
- Large customer base in the northeastern U.S.
- Significant capital investment plans, including a projected £42 billion investment over five years from 2024 to 2029.
- Strong financial performance, with an underlying operating profit of £4.8 billion for the nine months ended December 31, 2024.
National Grid SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
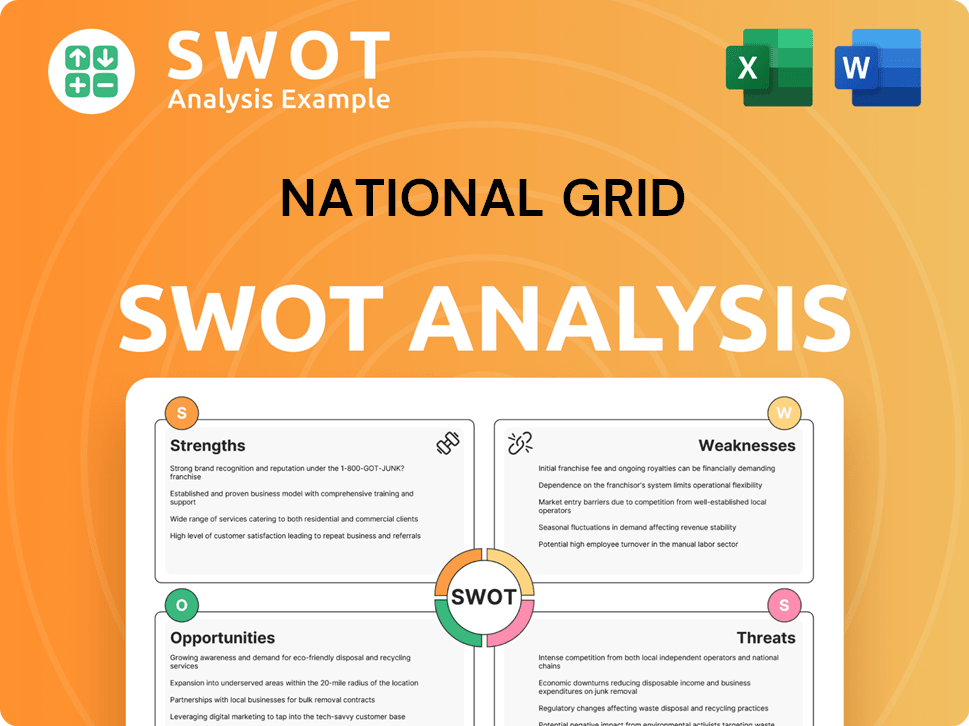
Who Are the Main Competitors Challenging National Grid ?
The competitive landscape for National Grid is multifaceted, primarily due to its role as a regulated energy infrastructure provider. Direct competition in its core transmission operations is limited, as it often operates in specific geographic regions or segments. However, the broader energy market introduces various forms of competition, both direct and indirect, which impacts its market position and strategic decisions.
Understanding the competitive dynamics is crucial for assessing National Grid's strategic positioning and future prospects. The company faces challenges from evolving energy technologies, regulatory changes, and the emergence of new market players. Analyzing the competitive environment allows for a comprehensive evaluation of its strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, which is vital for investors and stakeholders.
Indirect competition stems from the proliferation of distributed energy resources (DERs) like rooftop solar and battery storage, which can reduce reliance on centralized transmission. Energy service companies (ESCOs) and independent power producers (IPPs) also represent indirect competition as they offer alternative energy solutions or generate power that needs to be integrated into the grid. The push for localized energy generation and microgrids could further challenge the traditional utility model.
In the UK, while National Grid holds a significant position, other regulated network operators exist. These include companies like Scottish and Southern Electricity Networks (SSEN) and UK Power Networks, which operate regional networks. These companies indirectly compete for investment and regulatory attention within the energy sector.
In the US, National Grid faces competition from other large investor-owned utilities (IOUs). These IOUs serve distinct geographic areas. Examples include Consolidated Edison (Con Edison) in New York and Eversource Energy in New England. These companies compete for capital, talent, and influence in regulatory policy, influencing the Marketing Strategy of National Grid .
The rise of distributed energy resources (DERs), such as rooftop solar and battery storage, poses indirect competition. These technologies reduce reliance on centralized transmission. Independent power producers (IPPs) and energy service companies (ESCOs) also offer alternative energy solutions, creating competitive pressures.
New players focused on smart grid solutions, energy management, and electric vehicle charging infrastructure are emerging. These companies introduce new competitive dynamics, potentially challenging traditional utility models. Mergers and acquisitions within the utility sector can also alter the competitive landscape.
Assessing National Grid's market share requires analyzing its performance against competitors. In 2024, financial data reveals its position relative to other IOUs. Key metrics to consider include revenue, operating income, and capital expenditures. These figures provide insights into its competitive standing.
National Grid's strategic positioning involves grid modernization and investment in renewable energy infrastructure. The future outlook depends on its ability to adapt to market changes and technological advancements. Partnerships and collaborations with competitors can also shape its competitive position.
National Grid's competitive advantages include its established infrastructure and regulatory framework. However, it faces disadvantages from the slow pace of grid modernization and the challenges of integrating renewable energy sources. These factors influence its overall performance.
- Advantages: Extensive transmission network, regulatory protections, and long-term contracts.
- Disadvantages: High capital expenditure requirements, regulatory scrutiny, and the need for grid modernization.
- Opportunities: Investment in renewable energy projects, smart grid technologies, and expansion into new markets.
- Threats: Competition from DERs, changes in regulatory policies, and economic downturns.
National Grid PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
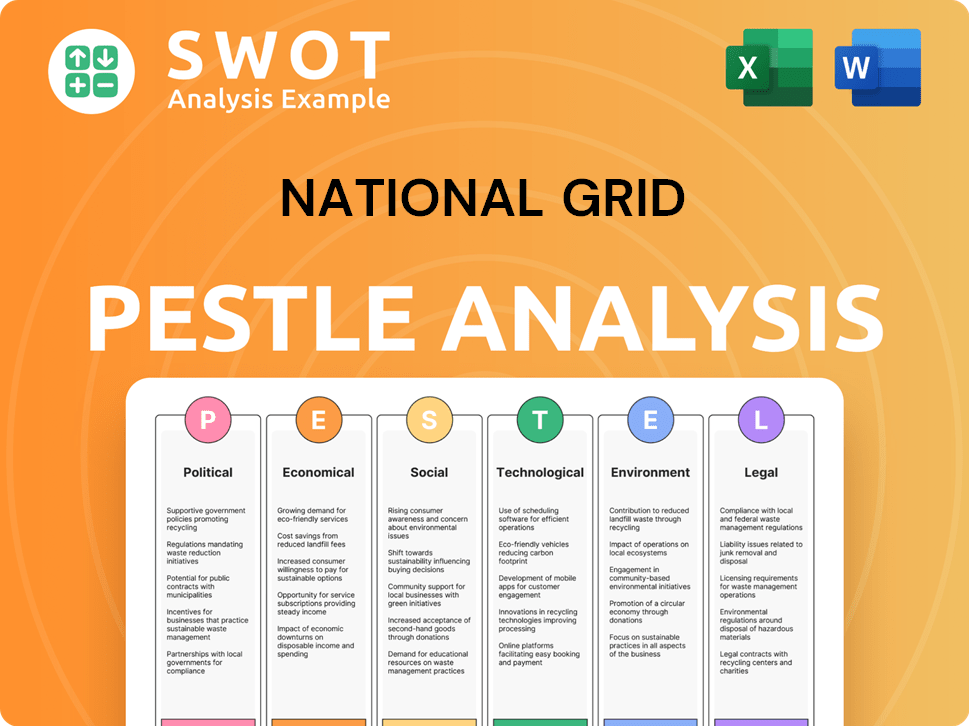
What Gives National Grid a Competitive Edge Over Its Rivals?
Analyzing the competitive landscape for utility companies reveals that National Grid, a key player, holds several strategic advantages. These advantages are crucial in understanding its market position and how it navigates the energy industry. The company's strengths are rooted in its infrastructure, regulatory relationships, and financial capacity, enabling it to maintain a strong competitive edge.
Understanding the dynamics of National Grid competition requires a look at its core strengths. The company's focus on innovation and strategic investments, such as the planned £42 billion investment over five years, further solidifies its position. This investment underscores its commitment to enhancing infrastructure and technological capabilities. These factors collectively contribute to National Grid's sustained success in a competitive market.
National Grid's competitive advantages are significant in the context of energy industry analysis. The company's ability to secure approvals and manage complex energy networks is critical. Its brand equity and customer trust also play a vital role. These elements contribute to National Grid's ability to compete effectively and maintain its market share.
National Grid's ownership of critical infrastructure, including high-voltage electricity transmission networks in England and Wales and gas transmission networks in Great Britain, creates a substantial barrier to entry for potential rivals. This foundational asset base provides a stable revenue stream. This strategic advantage allows the company to maintain a strong market position.
Strong relationships with regulatory bodies in both the UK and the US are a key advantage. These relationships enable National Grid to navigate complex regulatory environments. This advantage is essential for securing approvals for investments and operations.
Extensive experience in managing complex energy networks ensures high reliability and efficiency. This expertise is crucial in the utility sector. This operational excellence supports its competitive position.
Substantial financial resources and access to capital markets enable significant investment in network upgrades and modernization. This financial strength supports its long-term growth. This allows the company to enhance its infrastructure and technological capabilities.
National Grid's competitive advantages are multifaceted, encompassing infrastructure ownership, regulatory relationships, operational expertise, and financial strength. These elements collectively contribute to its robust market position. This strategic positioning allows the company to maintain its competitive edge in the energy sector.
- Infrastructure Ownership: Owning critical national infrastructure creates a significant barrier to entry.
- Regulatory Relationships: Strong relationships with regulatory bodies facilitate operational approvals.
- Operational Expertise: Extensive experience ensures high reliability and efficiency in energy management.
- Financial Resources: Substantial financial capacity supports significant investment in network upgrades.
National Grid Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
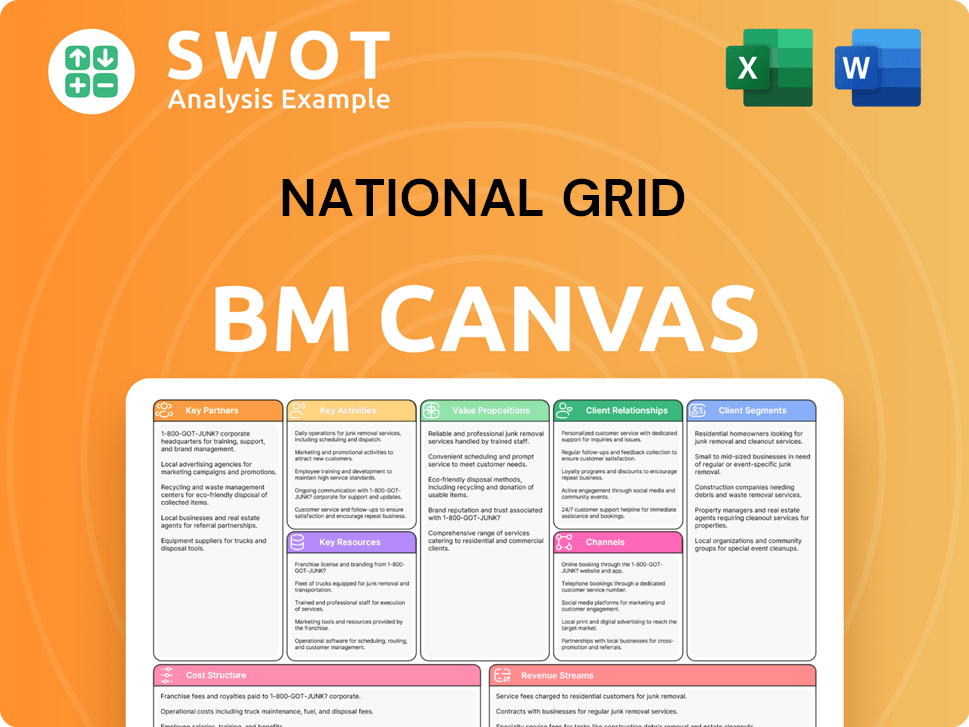
What Industry Trends Are Reshaping National Grid ’s Competitive Landscape?
The energy industry is experiencing a significant transformation, with a strong push towards decarbonization and the integration of renewable energy sources. This shift presents both challenges and opportunities for companies like National Grid. The company faces the task of modernizing its infrastructure to accommodate the growing complexity of a decentralized energy system while ensuring grid stability and addressing environmental concerns.
The competitive landscape for National Grid is evolving, influenced by regulatory changes, technological advancements, and increasing public scrutiny. The company must navigate these factors to maintain its market position and capitalize on opportunities in areas like grid modernization, electric vehicle charging infrastructure, and hydrogen development. The future outlook for National Grid depends on its ability to adapt to these changes and remain a key player in the energy transition.
The energy sector is witnessing a strong trend towards decarbonization, driving the integration of renewables like wind and solar. This shift requires significant investment in grid modernization and energy storage. Regulatory changes and incentives for clean energy also play a crucial role in shaping the strategies of utility companies like National Grid.
Future challenges include managing the increasing complexity of a decentralized energy system and ensuring grid stability amidst growing demand. Cyberattacks on critical infrastructure and public scrutiny regarding energy affordability and environmental impact are also significant concerns. Addressing these challenges is crucial for National Grid's long-term success.
The transition to a clean energy economy creates vast opportunities for grid infrastructure upgrades and electric vehicle charging infrastructure. Strategic partnerships and acquisitions in renewable energy projects can further solidify its market position. Expanding into new services like energy storage presents growth avenues for National Grid.
National Grid's strategy focuses on significant capital investment in its networks to support renewable integration and enhance resilience. The company aims to become a key enabler of a net-zero future. This involves a proactive approach to grid modernization and strategic partnerships to remain a resilient player in the evolving energy landscape.
National Grid's competitive landscape is shaped by its ability to adapt to industry trends and address future challenges. Its strategic positioning involves significant capital investment in infrastructure, particularly in the UK and US. The company's focus on renewable integration and resilience is crucial for maintaining its market share.
- Renewable Energy Integration: The company is investing heavily in projects that support the integration of renewable energy sources into its grid, such as offshore wind projects.
- Grid Modernization: National Grid is actively modernizing its infrastructure to improve efficiency, reliability, and capacity, including the deployment of smart grid technologies.
- Strategic Partnerships: The company is forming partnerships and collaborations to enhance its capabilities in areas like energy storage and electric vehicle charging infrastructure.
- Regulatory Compliance: National Grid must navigate complex regulatory environments, including emissions targets and incentives for clean energy.
- Financial Performance: The company's financial performance is crucial for its ability to invest in future projects and maintain its competitive edge. In 2024, National Grid reported significant investments in grid infrastructure.
The Brief History of National Grid reveals the company's evolution and its adaptation to the changing energy landscape, which is essential for understanding its current competitive position. The company's ability to adapt to these trends and challenges will determine its long-term success in the evolving energy market.
National Grid Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
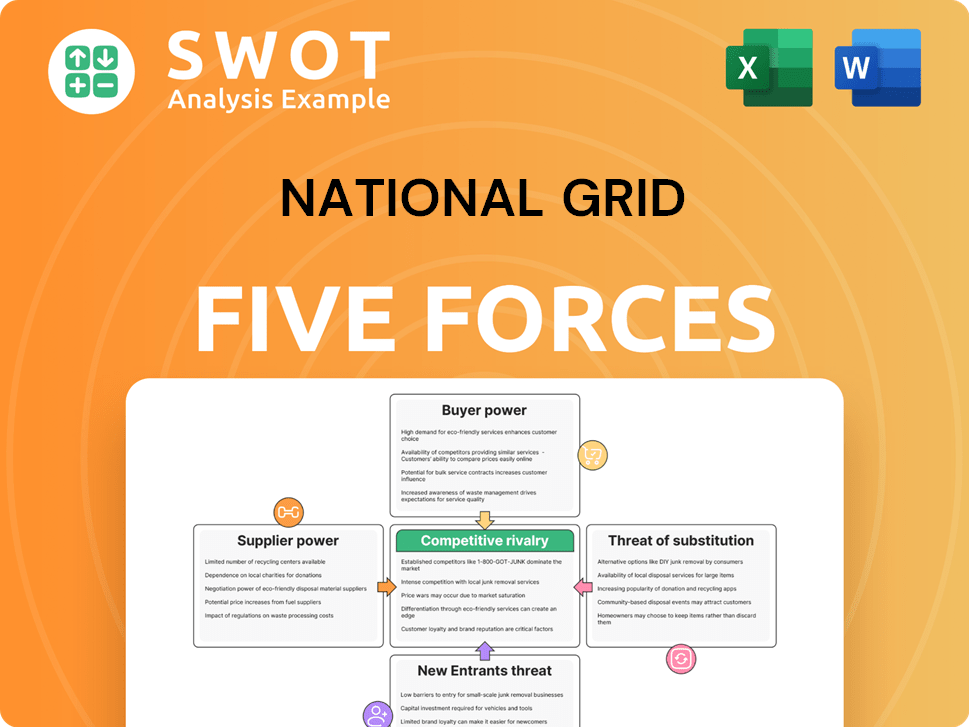
Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of National Grid Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of National Grid Company?
- How Does National Grid Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of National Grid Company?
- What is Brief History of National Grid Company?
- Who Owns National Grid Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of National Grid Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.