Rite Aid Bundle
What's the Story Behind Rite Aid's Rise and Challenges?
Rite Aid's journey is a compelling saga of growth and transformation within the American drugstore landscape. From its inception in 1962, this Rite Aid SWOT Analysis reveals a complex history marked by strategic pivots and significant industry influence. Discover how this Rite Aid company evolved to become a key player in the retail pharmacy sector.
This article delves into the Rite Aid history, exploring its Rite Aid timeline from its early years as Thrif D Discount Center to its current standing as a major drugstore chain. We'll examine its expansion strategy, including its impact on the pharmacy industry, store closures, and the challenges that have shaped its evolution as a prominent American company and pharmacy retailer.
What is the Rite Aid Founding Story?
The Rite Aid company, a prominent name in the American drugstore chain landscape, has a history rooted in the vision of its founder, Alex Grass. His entrepreneurial journey began in 1962, marking the start of what would become a significant player in the pharmacy retailer sector. The story of Rite Aid is one of adaptation, growth, and resilience in a competitive market.
Alex Grass launched the first store, initially named Thrif D Discount Center, in Scranton, Pennsylvania, on September 12, 1962. This marked the beginning of Rite Aid's journey. Grass, leveraging his experience in wholesale food distribution, saw an opportunity in the burgeoning discount retail market. The initial focus was on offering a range of health, beauty, and everyday products at competitive prices, catering to consumers seeking value.
The company's evolution from Thrif D to Rite Aid reflects its strategic shift and commitment to its core mission. The name change to Rite Aid, which occurred as the company expanded its offerings to include prescription medications, signifies its dedication to providing the 'right aid' to its customers. This transition was pivotal, transforming the business model and setting the stage for future growth. The early years were shaped by the economic and cultural context of the 1960s, with a growing consumer base and a shift towards discount shopping significantly influencing the company's initial success.
Rite Aid's founding story is a testament to entrepreneurial vision and adaptation within the pharmacy retail sector.
- Founding Date: September 12, 1962, marked the opening of the first store.
- Founder: Alex Grass, with a background in wholesale food distribution, identified a market opportunity.
- Initial Name: Thrif D Discount Center, later renamed Rite Aid.
- Business Model Shift: Transitioned from general discount merchandise to include prescription medications.
Rite Aid SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
What Drove the Early Growth of Rite Aid?
The early growth of the Rite Aid American company was marked by swift expansion through both new store openings and strategic acquisitions. Initially, the company established discount centers and quickly incorporated pharmacies, evolving into a full-fledged drugstore chain. This transformation was crucial in establishing its presence in the healthcare retail market. By the end of the 1960s, the Rite Aid company had significantly expanded its footprint, primarily across the Mid-Atlantic states.
A key milestone in the Rite Aid history was its public listing in 1968, which provided the capital needed for further expansion. This allowed the pharmacy retailer to accelerate its growth strategy.
Throughout the 1970s and 1980s, the Rite Aid company aggressively pursued acquisitions of smaller drugstore chains. This strategy helped the company enter new geographical markets and increase its store count significantly.
A significant acquisition during this period was the purchase of Gray Drug Fair in 1987, which added over 400 stores. These acquisitions, though sometimes leading to integration challenges, were crucial in making Rite Aid one of the largest drugstore chains in the U.S.
Leadership transitions, with Martin Grass taking over, guided the company through further expansions. The market generally responded positively, as consumers increasingly valued the convenience offered by drugstore chain.
Rite Aid PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
What are the key Milestones in Rite Aid history?
The Rite Aid company has a history marked by significant milestones, including periods of rapid expansion, strategic acquisitions, and major shifts in its business model. This American company's journey reflects the dynamic nature of the drugstore chain and pharmacy retailer industry.
Empower with Milestones Table| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 1962 | The first store opened in Scranton, Pennsylvania, marking the Rite Aid founding date. |
| 1968 | The company went public, beginning its journey as a publicly traded entity. |
| 1990s | Aggressive expansion led to increased store count, competing with larger rivals. |
| 1999-2000 | Accounting scandals emerged, leading to leadership changes and financial restructuring. |
| 2015 | Proposed merger with Walgreens was announced, but it was blocked by regulators. |
| 2018 | A significant number of stores were sold to Walgreens, reducing the company's footprint. |
| 2023 | The company filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy, signaling major financial challenges. |
Rite Aid's innovations included the introduction of pharmacy benefit management (PBM) services, which evolved into Elixir, aimed at controlling prescription costs and offering integrated healthcare solutions. The company also invested in computerized pharmacy systems to improve efficiency and customer service, reflecting its focus on technology to streamline operations.
The development of PBM services, now known as Elixir, was a key innovation. This allowed the company to manage prescription costs and offer integrated healthcare solutions. This strategic move aimed to control prescription costs and provide integrated healthcare solutions.
Investing in computerized pharmacy systems improved efficiency. This technological advancement enhanced customer service and streamlined operations. These systems helped manage prescriptions and improve overall pharmacy operations.
Aggressive expansion in the 1990s was a key strategy. This growth aimed to increase market share and compete with larger rivals. The company aimed to establish a wider presence across the United States.
Attempting mergers and acquisitions to adapt to market changes. These partnerships aimed to strengthen the company's position in the competitive landscape. The goal was to enhance market presence and service offerings.
The Rite Aid company faced significant challenges, including accounting scandals in the late 1990s and early 2000s, which led to a crisis of confidence and financial instability. Intense competition from larger chains like CVS and Walgreens, as well as big-box retailers with pharmacy departments, also put pressure on the company's market position. For more details, you can explore the Revenue Streams & Business Model of Rite Aid.
The accounting scandals led to a major crisis of confidence. This resulted in significant leadership changes and a decline in the stock price. The company had to undergo substantial restructuring to regain financial stability.
Competition from larger chains like CVS and Walgreens was a constant challenge. New entrants, including big-box retailers with pharmacy departments, also increased the pressure. This competitive environment impacted Rite Aid's market share and profitability.
Ongoing financial struggles led to bankruptcy filings in 2023. The company continues to restructure operations and divest non-core assets. These actions are aimed at adapting to a changing healthcare landscape.
The failed merger with Walgreens in 2015 highlighted regulatory hurdles. These challenges impacted the company's strategic plans and expansion efforts. The inability to gain regulatory approval significantly altered Rite Aid's trajectory.
Rite Aid Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What is the Timeline of Key Events for Rite Aid?
The Rite Aid history began in 1962 when Alex Grass opened the first Thrif D Discount Center in Scranton, Pennsylvania. The company's journey includes significant milestones, such as going public in 1968 and major acquisitions like Gray Drug Fair in 1987 and Perry Drug Stores in 1994. Rite Aid faced an accounting scandal in 1999, leading to financial difficulties, and expanded further by acquiring Brooks Eckerd in 2007, which made it the third-largest drugstore chain in the U.S. at the time. Attempts to merge with Walgreens in 2015 were unsuccessful, and the company filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy in 2023 to restructure.
| Year | Key Event |
|---|---|
| 1962 | Alex Grass opened the first Thrif D Discount Center in Scranton, Pennsylvania, marking the beginning of the Rite Aid company. |
| 1968 | The company went public as Rite Aid Corporation, signaling its expansion and growth potential. |
| 1987 | Rite Aid acquired Gray Drug Fair, expanding its presence and market reach as a pharmacy retailer. |
| 1994 | Rite Aid acquired Perry Drug Stores, further consolidating its position in the drugstore chain market. |
| 1999 | An accounting scandal led to significant financial difficulties and leadership changes, impacting the company's performance. |
| 2007 | Rite Aid acquired Brooks Eckerd, becoming the third-largest drugstore chain in the U.S. at the time, enhancing its market share. |
| 2015 | A proposed merger with Walgreens was terminated due to regulatory concerns, altering the company's expansion plans. |
| 2018 | A portion of Rite Aid stores were sold to Walgreens, changing the company's operational structure. |
| 2020 | Rite Aid rebrands its PBM business as Elixir, focusing on pharmacy benefit management. |
| 2023 | Rite Aid filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy protection to restructure its debt and operations, impacting its future strategy. |
| 2024-2025 | Rite Aid continues restructuring efforts, including store closures and asset sales, aiming to emerge as a leaner, more focused healthcare services company. |
Rite Aid's future is heavily influenced by its ongoing restructuring under Chapter 11 bankruptcy. As of early 2025, the company is focused on reducing its retail footprint and streamlining operations. Store closures are a key part of this strategy, with the goal of improving financial stability.
A significant part of Rite Aid's future strategy involves its Elixir PBM business. The company aims to leverage Elixir to provide integrated pharmacy solutions and manage healthcare costs. This shift towards PBM services is a key element of their strategic focus.
Industry trends, such as the increasing demand for telehealth and cost-effective prescription solutions, will influence Rite Aid's trajectory. The company faces challenges in a competitive market, including the need to adapt to evolving consumer preferences and healthcare dynamics. The American company must navigate the changing healthcare landscape.
Rite Aid is expected to emerge from bankruptcy with a smaller retail presence, focusing on profitable stores and enhancing its digital capabilities. The company is committed to serving communities and providing accessible healthcare services. This involves strategic store closures and optimizing its operational model.
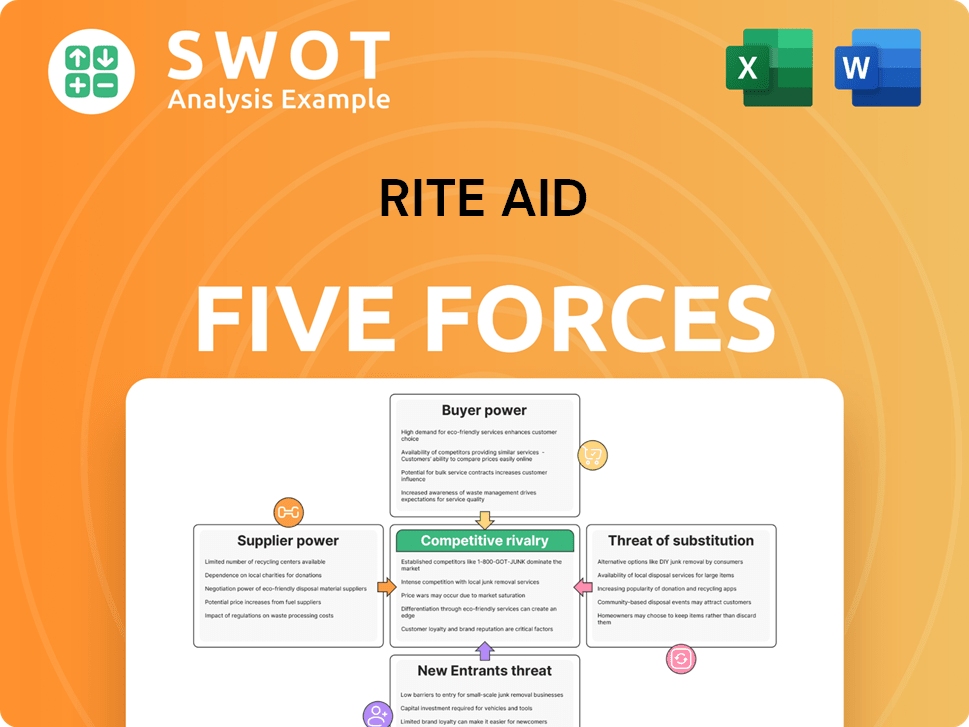
Rite Aid Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What is Competitive Landscape of Rite Aid Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Rite Aid Company?
- How Does Rite Aid Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Rite Aid Company?
- What is Brief History of Rite Aid Company?
- Who Owns Rite Aid Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Rite Aid Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.