Rite Aid Bundle
Can Rite Aid Navigate Its Transformation?
Rite Aid, a familiar name in the retail pharmacy sector, has been dispensing prescriptions and offering a wide array of products for over six decades. But how does this long-standing drugstore chain actually function, and what strategies does it employ to stay competitive? Understanding the Rite Aid SWOT Analysis is crucial to grasping the company's current position and future prospects.
Given its history, from its humble beginnings as Thrift D Discount Center to its current status as a major player in the healthcare landscape, understanding the Rite Aid business model is more critical than ever. This examination will explore the core operations of the Rite Aid company, its diverse revenue streams, and the strategic pivots it’s making to weather the storm. We'll delve into Rite Aid's financial performance, its evolving industry position, and the challenges it faces, providing a comprehensive understanding of how Rite Aid works in today's dynamic market, including Rite Aid pharmacy and Rite Aid stores.
What Are the Key Operations Driving Rite Aid’s Success?
The core operations of the Rite Aid company focus on providing accessible pharmacy services and a wide array of retail products. The company aims to create and deliver value through convenience and personalized care, serving individuals and families with prescription medications, over-the-counter drugs, health and beauty aids, personal care items, and general merchandise. As of May 2025, Rite Aid operates approximately 1,240 stores across 15 U.S. states, primarily on the East and West coasts.
Rite Aid's operational processes involve sourcing a comprehensive selection of products and managing a complex supply chain. The company has emphasized enhancing pharmacy services, which are central to its mission of delivering healthcare solutions. This includes providing personalized care through trained pharmacists who offer expert advice and guidance. Rite Aid also offers convenient services such as online prescription refills and medication management tools to improve customer access and ease of managing healthcare needs.
A significant part of Rite Aid's operational strategy has involved its pharmacy benefit management (PBM) services, Elixir. However, Rite Aid sold its Elixir PBM business to MedImpact Healthcare Systems in February 2024 as part of its restructuring efforts. This divestiture highlights a shift in its operational focus. Compared to competitors, Rite Aid has emphasized its network of physical pharmacies, which allows for convenient access to medications and healthcare products across diverse geographical areas, from urban centers to rural communities. Its core capabilities translate into customer benefits through trusted, accessible healthcare and a broad product offering, although its operational effectiveness has been challenged by recent financial difficulties and a shrinking store footprint. To understand more about the people Rite Aid serves, you can read about the Target Market of Rite Aid.
Rite Aid pharmacies offer a range of services, including prescription fulfillment, medication counseling, and immunizations. They aim to provide convenient access to healthcare services and products. The focus is on delivering personalized care and expert advice through trained pharmacists.
Rite Aid stores carry a wide variety of retail products, including over-the-counter medications, health and beauty aids, personal care items, and general merchandise. This diversified product selection aims to meet the everyday needs of customers. The goal is to provide a one-stop shopping experience.
Rite Aid offers online prescription refills and medication management tools to improve customer access and convenience. These digital services aim to enhance the overall customer experience. The company focuses on providing accessible and user-friendly healthcare solutions.
Rite Aid manages a complex supply chain to ensure the availability of products in its stores. This includes sourcing a wide range of products and efficient distribution. Effective supply chain management is crucial for maintaining inventory levels and meeting customer demand.
Rite Aid faces several operational challenges, including financial difficulties and a shrinking store footprint. The sale of Elixir PBM indicates a strategic shift and restructuring efforts. These challenges impact the company's ability to compete effectively in the market.
- Financial Restructuring: Rite Aid has been undergoing financial restructuring, including debt reduction and cost-cutting measures.
- Store Closures: The company has closed numerous stores as part of its restructuring plan, reducing its overall store count.
- Market Competition: Rite Aid faces intense competition from larger pharmacy chains, discount retailers, and online pharmacies.
- Operational Efficiency: Improving operational efficiency and streamlining processes are critical for Rite Aid's long-term success.
Rite Aid SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
How Does Rite Aid Make Money?
The Rite Aid company's revenue streams primarily originate from its retail pharmacy operations and its pharmacy services segment. These segments contribute to the overall financial performance of the Rite Aid business model. The company generates revenue through prescription sales, front-end merchandise sales, and services offered through its pharmacy benefits management (PBM) business, Elixir (now sold).
In fiscal year 2023, Rite Aid reported total revenues of approximately $24.1 billion. For fiscal year 2024, the company projected revenues to be between $22.6 billion and $23.0 billion, indicating a slight decrease. This projection reflects changes in the company's structure and market conditions.
The retail pharmacy segment is a significant revenue driver for Rite Aid, with prescription sales being a crucial component. The company's monetization strategies also involve expanding its own brand products and collaborating with suppliers to boost revenue. However, the company faces challenges like low generic prescription prices and unfavorable margins on brand-name drugs that affect revenue.
The Rite Aid company's financial performance is influenced by several key factors, including prescription sales, front-end merchandise, and pharmacy services. The sale of the Elixir PBM business has significantly altered its revenue composition. To understand more about the company's origins, you can explore the Brief History of Rite Aid.
- In the first quarter of fiscal year 2024, prescription sales accounted for 73.9% of total drugstore sales.
- Rite Aid projected filling about 125 million prescriptions in fiscal year 2024, with a gross margin from retail prescriptions estimated at 19.6%.
- The Retail Pharmacy Segment revenue was expected to be between $18.0 billion and $18.3 billion for fiscal year 2024.
- The Pharmacy Services Segment revenue was anticipated to be between $4.6 billion and $4.7 billion, net of intercompany revenues, for fiscal year 2024.
Rite Aid PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
Which Strategic Decisions Have Shaped Rite Aid’s Business Model?
The Rite Aid company has navigated significant challenges and strategic shifts in recent years. A major turning point was the Chapter 11 bankruptcy filing in October 2023, driven by substantial debt, legal liabilities from opioid-related lawsuits, and a difficult retail pharmacy environment. This restructuring aimed to reduce debt and secure new financing.
Operationally, the Rite Aid business model has involved a significant reduction in its store footprint. The company closed numerous locations, with the store count decreasing from around 2,500 in 2018 to approximately 1,300 by September 2024. Further downsizing occurred, with the store count reaching approximately 1,240 by May 2025. These actions included selling or winding down underperforming stores and divesting its Elixir PBM business.
Despite these efforts, Rite Aid filed for a second Chapter 11 protection in May 2025. This second filing indicates a potential orderly wind-down and sale of the company's remaining assets, as it seeks to address its $2.5 billion debt. The company's competitive edge has historically been its wide range of products, personalized care through its pharmacists, and convenient locations.
The initial Chapter 11 bankruptcy filing in October 2023 was a critical event, aiming to reduce debt and restructure the business. The company emerged as a private entity in September 2024, with ownership shifting to creditors. This restructuring was intended to stabilize the company's financial position.
Aggressive store closures have been a key strategy, with the store count significantly reduced. The sale of the Elixir PBM business in February 2024 for $575 million was another strategic move. The company has also sought to adapt by investing in technology to enhance pharmacy services.
Historically, Rite Aid pharmacy has competed on the basis of product variety, pharmacist-provided personalized care, and convenient locations. The company has tried to leverage technology to improve its services, such as enhancing pharmacy services. Despite these efforts, the company faced continued financial pressures.
The second Chapter 11 filing in May 2025 signals further challenges, indicating the company's inability to secure additional financing. This filing suggests a potential wind-down and sale of remaining assets. The Rite Aid stores continue to operate, but their future remains uncertain.
The company's financial performance has been significantly impacted by debt and legal liabilities. The initial bankruptcy aimed to reduce debt by approximately $2 billion. Store closures have accelerated, reflecting efforts to streamline operations and reduce costs.
- The store count decreased to approximately 1,300 by September 2024.
- The Elixir PBM business was sold for $575 million in February 2024.
- The second Chapter 11 filing in May 2025 reflects ongoing financial difficulties.
- The company's ability to secure additional financing was a key factor in the second filing.
Rite Aid Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
How Is Rite Aid Positioning Itself for Continued Success?
The Rite Aid company's industry position has shifted dramatically. Once a major player, it has experienced a significant decline, particularly after its 2023 bankruptcy. This evolution has reshaped its market presence and competitive dynamics within the retail pharmacy sector.
The company faces substantial risks, including ongoing opioid litigation and a challenging retail environment. High debt, operational inefficiencies, and changing consumer behaviors further complicate its future. The company's future outlook is uncertain as it navigates its second Chapter 11 bankruptcy filing as of May 2025.
Rite Aid's industry standing has diminished significantly. Before bankruptcy, it was the third-largest drugstore chain in the United States, and now it operates approximately 1,240 stores across 15 states as of May 2025. This reduction reflects a major shift from its peak of over 5,000 stores in 2008.
Key risks include ongoing opioid litigation, which has resulted in substantial settlement costs. The company is also challenged by low generic prescription prices and unfavorable margins on brand-name drugs. Rite Aid's high debt load, which stood at $2.5 billion in May 2025, continues to be a significant challenge.
The future of Rite Aid is uncertain, with the company in its second Chapter 11 bankruptcy filing as of May 2025. It seeks to wind down operations and sell its assets. Strategic initiatives now focus on ensuring uninterrupted pharmacy services and preserving jobs through asset sales.
The company faces intense competition from major players like CVS and Walgreens. These competitors have also reduced store counts but remain financially more stable due to their diversified healthcare services. For more information on the competitive environment, consider reading about the Competitors Landscape of Rite Aid.
Rite Aid faces numerous challenges, including operational inefficiencies and changing consumer preferences. The company is focused on maintaining pharmacy services during this transition. The company is in talks with multiple potential buyers, and analysts express skepticism about long-term viability without quick asset sales.
- Rite Aid's market share has declined, with a 15% drop in prescription fills since 2020.
- EBITDA margins hovered around -1% in 2024, highlighting profitability pressures.
- The company secured $1.94 billion in new debtor-in-possession financing to maintain operations.
- Significant job cuts, particularly at corporate offices, have been announced.
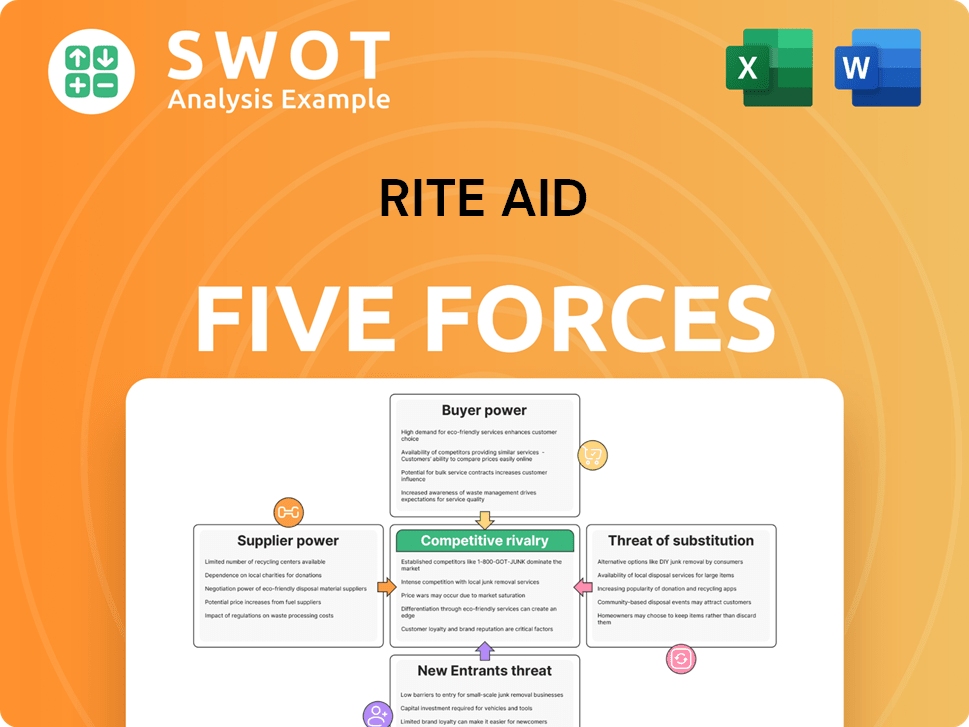
Rite Aid Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of Rite Aid Company?
- What is Competitive Landscape of Rite Aid Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Rite Aid Company?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Rite Aid Company?
- What is Brief History of Rite Aid Company?
- Who Owns Rite Aid Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Rite Aid Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.