Samsung Electronics Bundle
How did Samsung Rise to Global Tech Dominance?
From humble beginnings to a global technology behemoth, the Samsung Electronics SWOT Analysis reveals a compelling story of innovation and strategic prowess. This South Korean giant has redefined the electronics landscape, constantly pushing boundaries and setting new industry standards. Delve into the Samsung history and uncover the remarkable journey of a company that transformed itself from a local trading business into a worldwide leader.
The Samsung Electronics company origin story is a testament to vision and adaptability. This article will explore the Samsung timeline, from its early days focused on black-and-white televisions to its current status as a leader in semiconductors, mobile devices, and home appliances. Discover the Samsung evolution, its key milestones, and the strategic decisions that propelled it to the forefront of the tech industry, examining how Samsung's first products shaped its future and its Samsung founder, Lee Byung-chull's initial ambition.
What is the Samsung Electronics Founding Story?
The story of Samsung Electronics began on March 1, 1938, in Taegu (now Daegu), Korea, with its founder, Lee Byung-chull. Initially, the company was a grocery trading store. The name 'Samsung' in Korean, meaning 'three stars', reflected Lee's vision for the company's lasting strength.
The early days of Samsung involved trading noodles and other locally produced goods, exporting them to China. The company started with a small team of only 40 employees. This marked the humble beginnings of what would become a global technology giant.
Following the Korean War, Lee Byung-chull expanded Samsung's operations into textiles. The company benefited from protectionist policies by the Korean government. In the late 1950s, Samsung diversified into various sectors, including banking and insurance.
Samsung's early years were marked by diversification and strategic moves.
- The company expanded into textiles, establishing a large woolen mill.
- Acquired major commercial banks and an insurance company in the late 1950s.
- Further diversified into cement, fertilizer, and other industries.
- Acquired more insurance companies, an oil refinery, a nylon company, and a department store in the 1960s.
Samsung's entry into the electronics industry occurred on January 13, 1969, with the establishment of Samsung Electric Industries in Suwon, South Korea. This marked a pivotal shift from trading and manufacturing into the technology sector. The company's first products were black-and-white televisions, laying the foundation for its future in consumer electronics. If you want to know more about the company, here is the Target Market of Samsung Electronics.
Samsung Electronics SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
What Drove the Early Growth of Samsung Electronics?
The early growth of Samsung Electronics, or Samsung, marked a pivotal period in the company's Samsung history. Starting in 1969, with its initial focus on black-and-white televisions, Samsung quickly expanded into various electronics. This expansion laid the foundation for its future dominance in the tech industry.
Samsung's journey began with the establishment of Samsung Electric Industries in 1969. The company's first products were black-and-white televisions, which hit the market in 1970. By the 1970s, Samsung diversified its product line to include radios and color televisions, marking significant Samsung evolution.
A crucial step in Samsung's early growth was its entry into the semiconductor industry. This occurred in 1974 with the acquisition of a 50% stake in Korea Semiconductor. This move was a precursor to Samsung's later success in memory chip manufacturing.
The 1980s were transformative for Samsung, particularly in semiconductors. The launch of its first DRAM chip in 1983 was a major milestone. By the late 1990s, Samsung became the world's largest producer of memory chips, a testament to its strategic focus on this sector.
In 1985, Samsung established Samsung SDS (Samsung Data Systems) to capitalize on the rising demand for systems development. Following the death of Samsung founder Lee Byung-Chull in 1987, his son, Lee Kun-Hee, took over, reorganizing Samsung into five companies. This change set the stage for Samsung's future growth and global expansion.
Lee Kun-Hee initiated a 'new management' concept in the 1990s, focusing on product quality. Despite initial challenges, Samsung's mobile division improved its products. By 2003, Samsung had become the world's largest mobile phone vendor.
Strategic investments in research and development and global market expansion were key. These moves, along with strategic alliances, helped position Samsung at the forefront of the technology industry. For more insights, explore the Competitors Landscape of Samsung Electronics.
Samsung Electronics PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
What are the key Milestones in Samsung Electronics history?
The Samsung history is marked by significant milestones, from its early days to its current status as a global technology leader. The Samsung Electronics company origin can be traced back to its beginnings as a trading company, eventually evolving into a powerhouse in electronics and beyond. This evolution showcases the Samsung evolution from a small business to a multinational corporation.
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 1969 | Founded as Samsung Electronics Industry. |
| 1983 | Developed its first 64K DRAM chip, marking its entry into the semiconductor industry. |
| 2010 | Launched the Galaxy smartphone series, becoming a key driver of revenue and market dominance. |
| 2024 | Maintained its position as the global leader in the TV market for 19 consecutive years. |
| Q1 2025 | Led global smartphone shipments with 60.5 million units and held a 22.88% share of the global smartphone market. |
Samsung has consistently pushed the boundaries of technology, driving innovation across various sectors. The company's commitment to R&D is evident in its substantial investments, with a highest-ever annual R&D expenditure allocated for 2024, and a 16% increase in R&D expenditure to 9 trillion won in Q1 2025 compared to the same period last year.
Samsung's early development of the 64K DRAM chip was a pivotal moment. This laid the groundwork for its later dominance in the memory chip market.
The launch of the Galaxy smartphone series in 2010 transformed the company. The Galaxy became a critical driver of revenue and established its dominance in the global smartphone market.
Samsung leads the global TV market with innovations in premium and ultra-large screens. This includes QLED and OLED technologies, solidifying its market share.
Recent advancements include AI-powered displays with Samsung Vision AI. The company is also integrating AI into new products, like the Galaxy Z Fold6.
The Galaxy Buds3 Pro with real-time translation showcases Samsung's commitment to enhancing user experience through innovative features.
Samsung is exploring new product segments like XR. The upcoming Galaxy S25 series will feature cutting-edge AI capabilities.
Despite its successes, Samsung has faced significant challenges throughout its history. The company has grappled with market downturns and competitive threats. The company is also facing a 'crisis' regarding its 'fundamental technological competitiveness' in the memory-chip market.
In Q4 2024, Samsung's operating profit decreased quarter-on-quarter due to soft market conditions. This was especially true for IT products.
Samsung faces competition in the memory-chip market, particularly in high-bandwidth memory (HBM) chips. The company lags behind rivals like SK Hynix and Micron.
In the mid-1990s, the mobile phone division struggled with poor quality. This led to discussions about exiting the sector.
Samsung is working to regain dominance in the AI semiconductor HBM market. They aim to achieve this by Q2 2025.
Samsung is actively pursuing mergers and acquisitions (M&A) in areas like AI, robotics, and meditech. This is to secure new growth engines.
The company is adapting its chip production strategy. They are fast-tracking R&D in HBM and 3nm process nodes.
To understand more about Samsung's strategies, you can read about the Marketing Strategy of Samsung Electronics.
Samsung Electronics Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What is the Timeline of Key Events for Samsung Electronics?
The Samsung Electronics company has a rich Samsung history, marked by significant innovations and strategic expansions. From its humble beginnings as a trading company in 1938, founded by Lee Byung-chull, to its current status as a global technology leader, Samsung's evolution is a testament to its adaptability and vision. The company's journey includes pivotal moments in the electronics, semiconductor, and mobile phone industries, establishing its position as a key player in the global market. Here's a look at the Samsung timeline.
| Year | Key Event |
|---|---|
| March 1, 1938 | Lee Byung-chull founded Samsung as a trading company in Taegu, Korea, marking the early days of Samsung. |
| January 13, 1969 | Samsung Electronics was established, signifying the company's entry into the electronics industry and its company origin. |
| 1970 | Samsung released its first black-and-white televisions, showcasing Samsung's first products. |
| 1974 | Samsung entered the semiconductor business by acquiring a 50% stake in Korea Semiconductor. |
| 1983 | Samsung launched its first 64K DRAM chip, a significant milestone in its semiconductor development. |
| 1985 | Samsung SDS was established, broadening its IT services. |
| 1988 | Samsung launched its first mobile phone in South Korea, marking its entry into the mobile market. |
| 1992 | Samsung launched its first mobile phone, expanding its presence in the mobile phone market. |
| 1995 | Samsung SDI was established, focusing on display screens and batteries. |
| Late 1990s | Samsung became the world's largest producer of memory chips, highlighting its growth over time. |
| 2003 | Samsung became the world's largest mobile phone vendor, demonstrating its global expansion. |
| 2010 | Samsung launched the Galaxy smartphone series, revolutionizing the mobile phone market. |
| 2024 | Samsung achieved a 28.3% global TV market share, leading for the 19th consecutive year. |
| Q1 2025 | Samsung Electronics posted KRW 79.14 trillion in consolidated revenue, an all-time quarterly high. |
| January 22, 2025 | Samsung plans to unveil the Galaxy S25 series with cutting-edge AI capabilities at Galaxy Unpacked 2025, showing its innovation history. |
Samsung is prioritizing AI and robotics to drive future growth and secure industry leadership, increasing R&D investments in artificial intelligence, quantum computing, and next-generation 5G/6G telecommunications.
Strategic expansion in semiconductors and displays aims to boost market position, capitalizing on demand for high-density products like HBM and AI server memory, with Samsung Display expanding OLED product lines and the Foundry business ramping up advanced node production.
Samsung plans to sustain flagship-centric sales with the Galaxy S25 Edge and expand its AI smartphone lineup through 'Awesome Intelligence' in the Galaxy A series, while strengthening its foldable lineup with differentiated AI user experiences.
Analysts project Samsung Electronics' revenue to grow by 6.3% annually over the next three years, with profit margins expected to increase from 11.2% to 12.2%, despite macroeconomic uncertainties and global trade tensions.
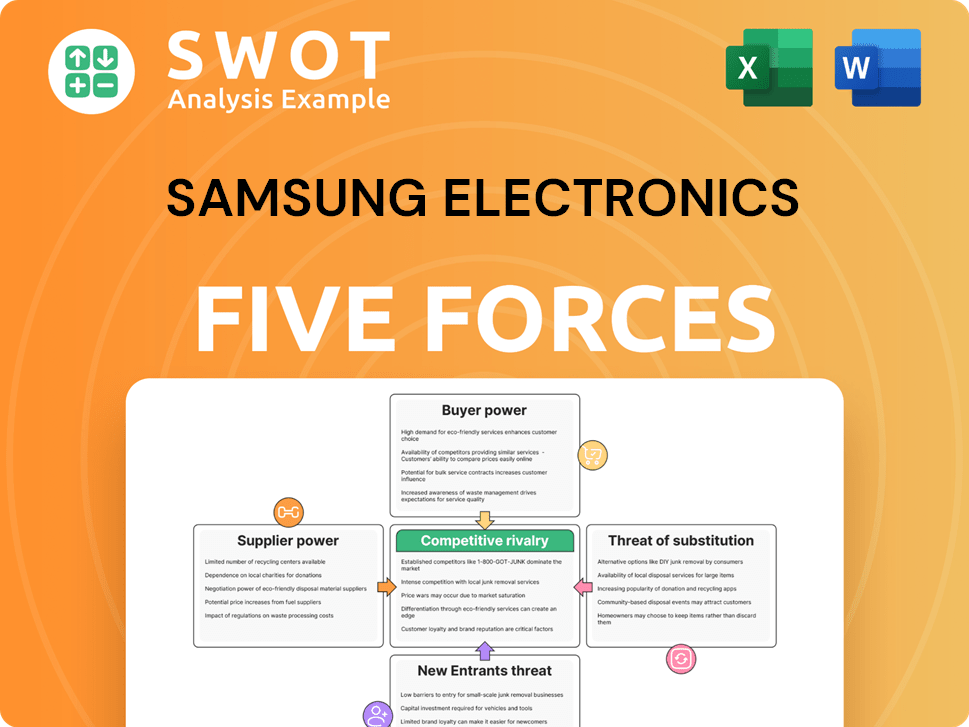
Samsung Electronics Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What is Competitive Landscape of Samsung Electronics Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Samsung Electronics Company?
- How Does Samsung Electronics Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Samsung Electronics Company?
- What is Brief History of Samsung Electronics Company?
- Who Owns Samsung Electronics Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Samsung Electronics Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.