Vivendi Bundle
How Did Vivendi Transform from Water to Worldwide Entertainment?
Embark on a journey through the Vivendi SWOT Analysis to uncover the strategic brilliance behind Vivendi's transformation. From its humble beginnings as a water utility, the Vivendi company has remarkably evolved into a global media and content juggernaut. This brief history of Vivendi unveils the pivotal moments and strategic decisions that shaped its remarkable trajectory.
The Vivendi history is a compelling narrative of adaptation and foresight, from its origins as Compagnie Générale des Eaux (CGE) in 1853 to its current status as a media empire. This exploration will delve into the Vivendi timeline, including its significant Vivendi acquisitions and strategic realignments, providing insights into its dynamic Vivendi business model and its lasting impact on the entertainment industry. Discover how Vivendi navigated through industry changes and continues to thrive in the digital age.
What is the Vivendi Founding Story?
The brief history Vivendi begins on December 14, 1853. This was when Compagnie Générale des Eaux (CGE) was established by an Imperial Decree of Napoleon III. The company's initial focus was on managing public services, specifically water distribution in French municipalities.
The primary problem CGE addressed was the need for reliable water supply systems in rapidly growing urban areas. This was a crucial public health and infrastructure concern at the time. CGE's business model involved securing concessions from local authorities to provide water services, which included building and maintaining water networks.
While there wasn't a single 'founder' in the modern sense, CGE's creation was a strategic initiative. It was supported by prominent financial and political figures of the Second French Empire. This reflected the era's emphasis on large-scale infrastructure development. Initial funding came from investors, including the Rothschild family. This indicated a substantial capital base from its inception.
Compagnie Générale des Eaux, or CGE, was founded to manage water distribution. The company faced challenges like the need for significant capital investment and securing long-term concessions.
- The company's name, Compagnie Générale des Eaux, directly reflected its core business: a general company for waters.
- The cultural and economic context of mid-19th century France, characterized by industrialization and urban growth, heavily influenced the company's creation.
- Reliable public services were essential for societal progress and economic development.
- Early challenges included significant capital investment, technical complexities, and securing long-term concessions.
The company's early challenges included the substantial capital investment needed for infrastructure. There were also the technical complexities of water management and securing long-term concessions from various municipalities. The cultural and economic context of mid-19th century France, marked by industrialization and urban growth, significantly influenced the company's creation. Reliable public services were essential for societal progress and economic development.
For more insights into the company's strategic positioning, consider exploring the Target Market of Vivendi.
Vivendi SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
What Drove the Early Growth of Vivendi?
The early growth and expansion of the Vivendi company began with Compagnie Générale des Eaux (CGE), which initially focused on public services, particularly water distribution. This period marked the company's strategic expansion into various essential services, including gas, electricity, and waste management. This diversification laid the foundation for its future ventures, solidifying its presence in the utilities sector.
In the late 19th and early 20th centuries, CGE expanded beyond water, entering gas distribution and electricity generation. This strategic move was a response to the growing needs of industrializing Europe. The company secured numerous municipal contracts across France and internationally, establishing a strong base in utilities. This expansion included acquiring smaller local utility companies, consolidating its market position and extending its reach.
The latter half of the 20th century saw a significant strategic shift for CGE, driven by leaders like Guy Dejouany and Jean-Marie Messier. The company ventured into media and telecommunications, recognizing opportunities in these sectors. This transformation gained momentum in the 1980s and 1990s. CGE launched Canal+ in 1984, a pay-television channel, and entered mobile telephony with SFR in 1987.
By the late 1990s, CGE had largely divested its water utility assets, rebranding as Vivendi in 1998 to reflect its new focus. This period was marked by aggressive Vivendi acquisitions, including stakes in Universal Studios and Seagram. This demonstrated a clear intent to become a global media conglomerate. The company's vision was a converged media and technology future, as discussed in Mission, Vision & Core Values of Vivendi.
Market reception to these strategic shifts was mixed, with some analysts questioning the rapid diversification. The company's leadership remained committed to its vision of a converged media and technology future. This period of expansion set the stage for Vivendi's future, including its involvement in music, entertainment, and telecommunications. The move from utilities to media represented a significant transformation in Vivendi's business model.
Vivendi PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
What are the key Milestones in Vivendi history?
The Vivendi history includes several key milestones that have shaped its evolution into a major player in the media and entertainment industry. From its origins to its current structure, Vivendi has navigated significant changes and strategic shifts to adapt to the evolving market landscape.
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 1984 | Launch of Canal+, revolutionizing pay-television in France. |
| 1987 | Pioneering mobile telecommunications with SFR, contributing to early mobile service adoption. |
| 2000 | Acquisition of Seagram, including Universal Studios and Universal Music Group, expanding into global entertainment. |
| 2002 | Jean-René Fourtou replaced Jean-Marie Messier as CEO, marking a leadership change during a financial crisis. |
| 2013 | Vivendi completed the separation of its telecommunications business, creating a new company, and refocusing on media. |
| 2024 | Vivendi explores strategic options for Canal+ and Havas, potentially including listings, to unlock further value. |
Innovations at Vivendi have included pioneering content delivery and early adoption of mobile services. The company has consistently adapted its strategies to leverage new technologies and market opportunities.
The launch of Canal+ in 1984 was a groundbreaking innovation, establishing a successful model for premium content delivery in France. This initiative significantly impacted the pay-television market, setting a precedent for future content distribution models.
SFR's early involvement in mobile telecommunications in 1987 played a crucial role in the early adoption of mobile services in France. This initiative positioned Vivendi as a key player in the burgeoning telecommunications sector.
Vivendi has made significant investments in the digital realm, particularly in video games through Gameloft and advertising through Havas. These strategic moves reflect the company's adaptation to the digital transformation of media and entertainment.
Focusing on content creation and distribution across various platforms has been a key innovation. This strategy allows Vivendi to adapt to evolving consumer habits and maintain a strong presence in the media landscape.
Vivendi has formed strategic partnerships to expand its reach and capabilities, such as the acquisition of Seagram. These alliances have been crucial for Vivendi's growth and market positioning.
The company has undertaken major restructuring efforts, including divesting assets to reduce debt and refocus operations. This has helped Vivendi to stabilize its financial position and adapt to market changes.
The Vivendi company has faced several challenges, including financial crises and intense competition. These challenges have prompted strategic shifts and a focus on sustainable growth.
The early 2000s saw Vivendi facing a severe financial crisis due to excessive debt from rapid acquisitions and downturns in the technology and media sectors. This period tested the company's resilience and required significant restructuring.
Intense competition from streaming services and tech giants poses a constant challenge. Vivendi must continually adapt its strategies to maintain its market position in the evolving media landscape.
Changing consumer habits, such as the shift towards streaming and on-demand content, require Vivendi to adapt its content creation and distribution models. This necessitates continuous innovation and strategic adjustments.
Vivendi faces regulatory scrutiny, which impacts its strategic decisions and operational flexibility. Navigating complex regulatory environments requires careful planning and compliance.
The company has had to manage significant debt levels at various points, leading to restructuring efforts and asset sales. This has been a recurring challenge, requiring careful financial management.
Vivendi has been impacted by market downturns, particularly in the technology and media sectors, which affected its financial performance. These downturns have necessitated strategic adjustments and cost-cutting measures.
Vivendi Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What is the Timeline of Key Events for Vivendi?
The Vivendi history is a story of transformation, beginning as a water management company and evolving into a global media and entertainment leader. This journey includes strategic shifts, acquisitions, and divestitures that have shaped its current structure. From its early focus on infrastructure to its current emphasis on content creation and distribution, the Vivendi company has consistently adapted to the changing media landscape, making it a fascinating case study in corporate evolution. Understanding the brief history Vivendi provides crucial context for its present and future endeavors.
| Year | Key Event |
|---|---|
| 1853 | Compagnie Générale des Eaux (CGE) is founded, initially concentrating on water management. |
| 1984 | Launch of Canal+, a pioneering pay-television channel, marks a significant entry into the media sector. |
| 1987 | Entry into mobile telecommunications with SFR expands its business portfolio. |
| 1998 | CGE rebrands as Vivendi, signaling its strategic shift towards media and communications. |
| 2000 | Acquisition of Seagram, including Universal Studios and Universal Music Group, forms Vivendi Universal. |
| 2002 | Financial crisis and leadership change lead to major asset divestitures. |
| 2006 | Sale of Vivendi Universal Entertainment to NBC, resulting in the formation of NBC Universal. |
| 2013 | Sale of its stake in Activision Blizzard, focusing on core media assets. |
| 2014 | Sale of SFR, completing its exit from telecommunications operations. |
| 2017 | Acquisition of Gameloft strengthens its position in the video game industry. |
| 2020 | Increased stake in Lagardère expands its presence in publishing and travel retail. |
| 2024-2025 | Strategic considerations for potential listings of Canal+ and Havas to unlock value. |
Vivendi is focused on consolidating its position as a global media and content leader. Its strategic initiatives include further developing its premium content offerings through Canal+ and expanding its advertising and communications capabilities via Havas.
Vivendi plans to grow its presence in publishing with Lagardère. The company is poised to capitalize on industry trends such as the continued rise of streaming services and the increasing demand for diverse content. Analysts predict further acquisitions and partnerships to enhance its content library.
The potential listings of Canal+ and Havas are being actively explored to maximize their potential. Leadership is committed to creating value for shareholders through organic growth and structural adjustments. Vivendi aims to be a premier provider of cultural and entertainment content worldwide.
The convergence of media and technology will significantly impact Vivendi's future. Vivendi's extensive portfolio of strong brands and its global reach position it well. For additional insights, consider exploring the history of media empires.
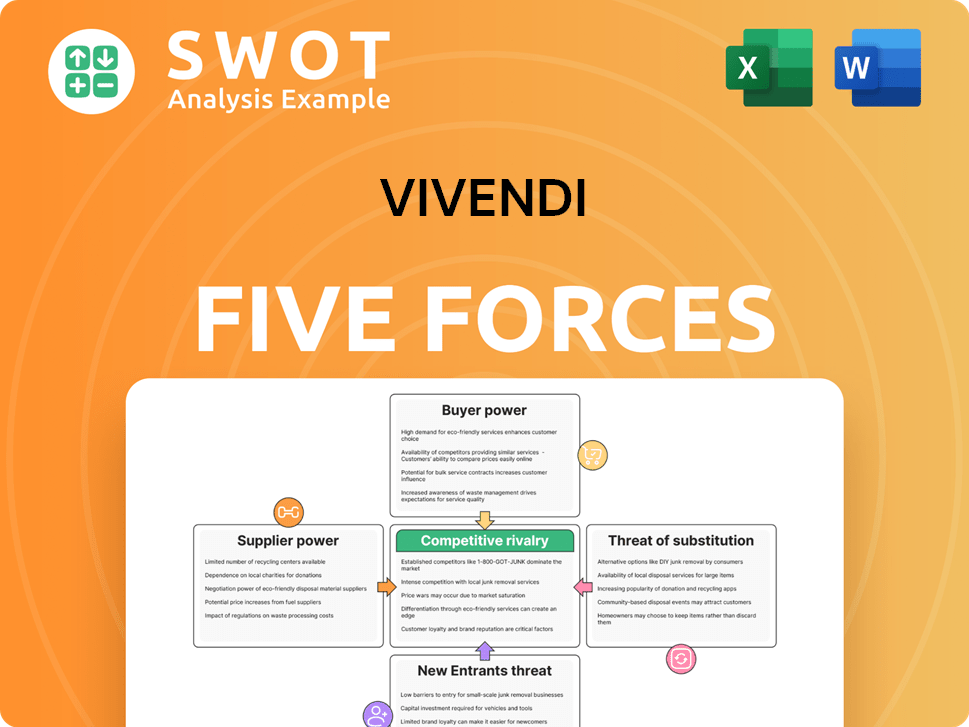
Vivendi Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What is Competitive Landscape of Vivendi Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Vivendi Company?
- How Does Vivendi Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Vivendi Company?
- What is Brief History of Vivendi Company?
- Who Owns Vivendi Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Vivendi Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.