Intel Bundle
How Does the Intel Company Operate in Today's Market?
Intel, a cornerstone of the semiconductor industry, is at the forefront of shaping our digital world with its innovative Intel SWOT Analysis. Its influence stretches across personal computing, data centers, and cutting-edge technologies, cementing its place as a key player in the global tech ecosystem. Given its crucial role in powering the digital infrastructure of modern society, understanding how Intel operates and generates revenue is essential for investors, customers, and industry watchers.
Intel designs, manufactures, and sells essential computer components, primarily microprocessors, chipsets, and other semiconductor devices. These components are vital for everything from everyday personal computers to complex server farms and the expanding Internet of Things (IoT) devices. As of early 2024, the Intel company remains a dominant force in the CPU market, though facing increasing competition. This article will explore the core value propositions, revenue streams, strategic moves, and competitive positioning of Intel to provide a comprehensive understanding of its market leadership and technological advancements, including insights on Intel processor features and Intel's manufacturing process explained.
What Are the Key Operations Driving Intel’s Success?
The core operations of the Intel company center around the design, manufacturing, and sale of advanced semiconductor products. The company's primary focus is on microprocessors and chipsets, serving a diverse customer base. This includes original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) of personal computers, cloud service providers, enterprise IT departments, and developers of IoT solutions.
The value proposition of Intel lies in delivering high-performance, energy-efficient, and reliable computing solutions. These solutions power a vast array of digital experiences. The operational process is vertically integrated, encompassing research and development, chip design, fabrication, assembly, testing, and packaging.
This integrated device manufacturing (IDM) model has been a cornerstone of Intel's operational uniqueness, providing tight control over the entire production cycle. This comprehensive operational framework translates into customer benefits such as superior processing power, enhanced security features, and a broad ecosystem of compatible software and hardware, differentiating Intel from competitors who may rely solely on fabless models or less integrated supply chains.
Intel's operational strengths include its extensive intellectual property portfolio, advanced manufacturing capabilities, and a robust global supply chain. The company's partnerships with software developers, system integrators, and channel partners are crucial for ensuring broad adoption and compatibility of its products. For example, Intel’s close collaboration with PC manufacturers ensures its processors are optimized for new laptop and desktop designs.
Customers benefit from superior processing power, enhanced security features, and a broad ecosystem of compatible software and hardware. This is a key differentiator against competitors. This approach allows the company to maintain a strong position in the market and continue to innovate.
In 2024, Intel reported revenue of approximately $52.2 billion. The company's commitment to innovation is reflected in its R&D spending, which reached roughly $18.5 billion in 2024. Intel's market share in the CPU market has fluctuated, with the company holding a significant portion but facing competition from AMD and others. For more insights, check out the Marketing Strategy of Intel.
- Intel's focus remains on high-performance computing solutions.
- Investments in advanced manufacturing processes are ongoing.
- The company is expanding its presence in emerging markets.
- Intel continues to adapt to the changing demands of the semiconductor market.
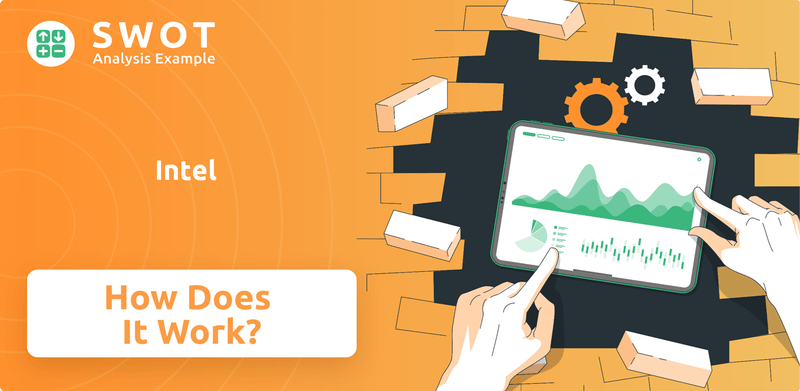
Intel SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
How Does Intel Make Money?
The primary revenue streams for the Intel company are centered around the sale of its semiconductor products. These products are crucial components in various devices, from personal computers to data center servers. The Intel processor is a key product, and the company's financial performance heavily relies on its sales across different market segments.
Intel generates revenue through a mix of direct sales and a global network of distributors. Its monetization strategies involve tiered pricing based on product performance and features. This approach allows Intel to capture value across different market segments, ensuring profitability and competitiveness.
Intel's business model has evolved to include diverse revenue sources beyond traditional PC processors. This strategic diversification is essential for adapting to the dynamic semiconductor landscape and addressing new growth opportunities. The company's ability to innovate and expand its product offerings is crucial for its long-term success.
This segment includes processors for laptops and desktops. Revenue from this group fluctuates based on market demand and product cycles. In Q1 2024, CCG revenue was reported at $7.5 billion.
This segment focuses on server processors and solutions for data centers and artificial intelligence. It is a critical growth area for Intel. Q1 2024 revenue for DCAI reached $3.0 billion.
NEX is a growing revenue stream for Intel, focusing on network infrastructure and edge computing solutions. This segment is vital for the company's expansion in the evolving tech landscape.
IFS represents Intel's foray into contract chip manufacturing for external customers. This is a strategic move to capitalize on the growing demand for semiconductor manufacturing. IFS reported Q1 2024 revenue of $4.4 billion.
Intel uses direct sales to large OEMs and enterprises, as well as sales through distributors and resellers. This multi-channel approach ensures broad market coverage. This strategy helps Intel reach a wide range of customers effectively.
Tiered pricing based on product performance and features allows Intel to capture value across different market segments. This approach helps the company maximize profitability. The company optimizes its revenue by matching prices with product capabilities.
Intel is expanding its revenue sources beyond traditional PC processors. This includes solutions for artificial intelligence, autonomous driving, and network infrastructure. This diversification is crucial for Intel's long-term growth. To learn more about Intel's strategic direction, consider reading about the Growth Strategy of Intel.
- Focus on high-growth areas such as AI and data centers.
- Investment in advanced manufacturing processes.
- Expansion of Intel's foundry services to attract external customers.
- Strategic partnerships to enhance market reach and innovation.
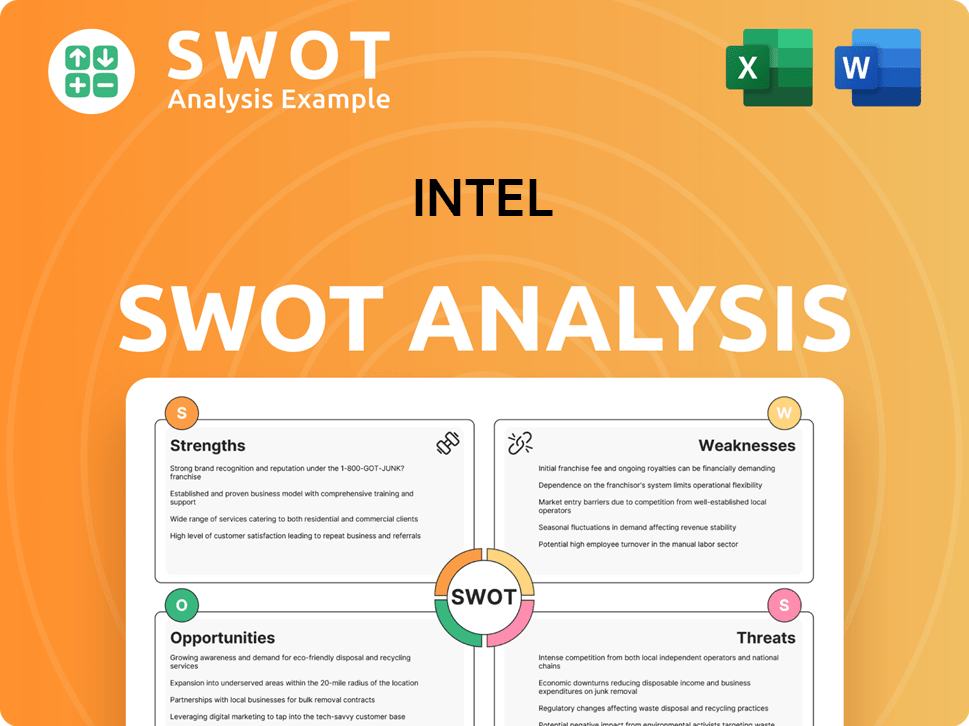
Intel PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
Which Strategic Decisions Have Shaped Intel’s Business Model?
The operational and financial performance of the Intel company has been significantly shaped by key milestones and strategic initiatives over the years. A major recent shift is the 'IDM 2.0' strategy, announced in 2021, which combines internal manufacturing with increased use of third-party foundries. This move aims to enhance agility and competitiveness in the rapidly evolving semiconductor industry. The Intel company's ability to adapt and innovate has been crucial to its long-term success.
Intel Foundry Services (IFS) is a crucial part of IDM 2.0, allowing Intel to offer its manufacturing capabilities to other chip designers. The company has also invested substantially in new fabrication plants, such as those planned for Ohio and Germany, to expand its manufacturing capacity and geographical footprint. This expansion is vital for meeting the growing global demand for semiconductors and maintaining its competitive edge in the market. The company’s strategic focus on advanced manufacturing technologies and global expansion underscores its commitment to leading the semiconductor industry.
Challenges have included supply chain disruptions, especially during the global chip shortage, and intense competition from rivals like AMD and NVIDIA. Intel has responded by diversifying its product portfolio, focusing on high-growth areas like AI and accelerated computing, and investing heavily in research and development to maintain its technological edge. To learn more about the ownership and financial structure, check out the information on Owners & Shareholders of Intel.
Key milestones include the development of the first microprocessor, the 4004, in 1971. Another significant milestone was the introduction of the x86 architecture, which became the standard for personal computers. Intel has consistently pushed the boundaries of semiconductor technology, leading to innovations in CPU design and manufacturing processes.
Strategic moves include the IDM 2.0 strategy, which integrates internal and external manufacturing. Investments in new fabrication plants in the US and Europe are also key. The company is also focusing on expanding its presence in high-growth areas like AI and data centers. These strategic moves are aimed at increasing Intel's market share and profitability.
Intel's competitive advantages include its strong brand recognition and extensive intellectual property portfolio. The company has deep relationships with key customers and partners. Its long-standing expertise in x86 architecture and its integrated device manufacturing capabilities provide significant barriers to entry. Intel's commitment to innovation and its ability to adapt to market changes are also key.
In Q1 2024, Intel reported revenue of approximately $12.7 billion. The company's gross margin was around 45.1%. Intel's focus on cost-cutting measures and strategic investments is aimed at improving profitability. The company's financial performance reflects its ongoing efforts to navigate the competitive landscape and capitalize on growth opportunities.
Intel plans to continue investing in advanced manufacturing technologies and expanding its foundry services. The company aims to increase its market share in the AI and data center markets. Intel's future plans also include the development of new product lines and strategic partnerships. The company is focused on innovation and adapting to the evolving needs of its customers.
- Expansion of manufacturing capacity in the US and Europe.
- Development of new CPU and GPU architectures.
- Increased focus on AI and data center solutions.
- Strategic partnerships to enhance its market position.
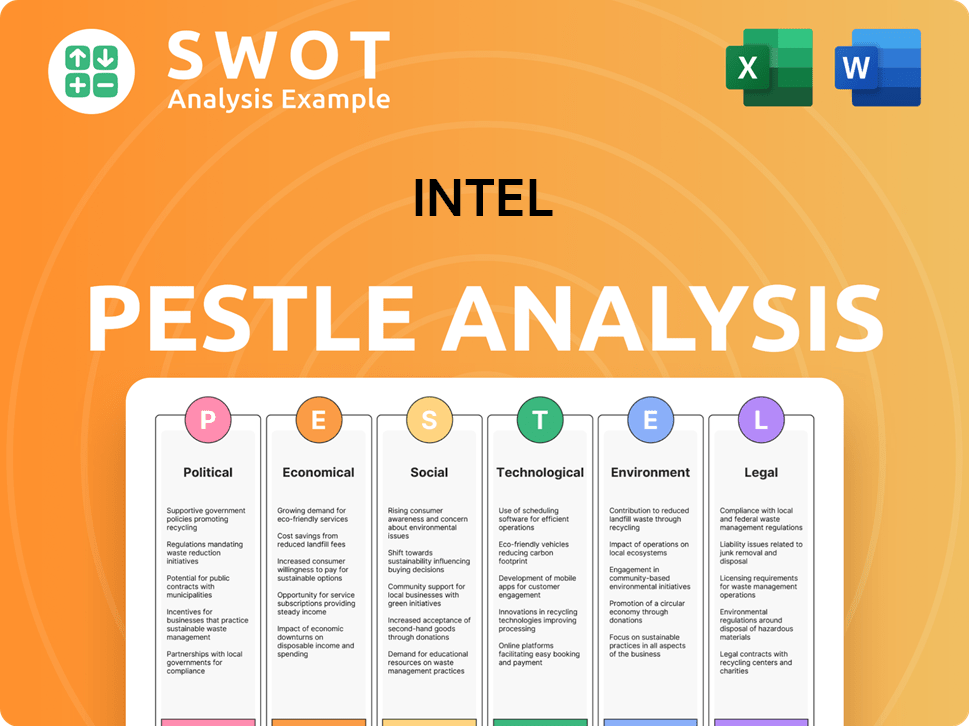
Intel Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
How Is Intel Positioning Itself for Continued Success?
The Intel company maintains a significant position in the semiconductor industry, particularly in the CPU market. However, it faces increasing competition from companies like AMD and NVIDIA. Despite these challenges, Intel continues to hold substantial market share and benefits from a loyal customer base in key segments like enterprise and data centers. The company's global reach is extensive, with operations and sales across many countries.
Several risks impact Intel's operations and revenue, including the cyclical nature of the semiconductor industry and intense competition. Geopolitical tensions and trade policies also pose challenges. The rapid pace of technological change requires continuous innovation and significant R&D investment. Intel's future outlook is shaped by its 'IDM 2.0' strategy, aiming to regain process leadership and expand its foundry business.
Intel holds a strong position in the CPU market, though competition from AMD and NVIDIA is increasing. The company benefits from a loyal customer base, especially in enterprise and data centers. Intel has a global presence with operations and sales channels in numerous countries.
Intel faces risks such as the cyclical nature of the semiconductor industry and intense competition. Geopolitical tensions and trade policies can also impact operations. Continuous innovation and significant R&D investment are essential to stay competitive.
Intel's future is shaped by its 'IDM 2.0' strategy, which aims to regain process leadership and expand its foundry business. The company is investing in growth areas like AI and accelerated computing. Intel aims to capitalize on the increasing demand for computing power across various applications.
Intel aims to sustain and expand revenue by leveraging its manufacturing capabilities and fostering a robust ecosystem of partners. The company is focused on regaining process leadership by 2025. For more insights into Intel's target market, read this article: Target Market of Intel.
Intel's revenue in 2023 was approximately $54.2 billion, reflecting the challenges in the PC and server markets. The company's gross margin in Q4 2023 was around 45.8%, showing improvements. Intel continues to invest heavily in R&D, with spending reaching nearly $18 billion in 2023, emphasizing its commitment to innovation.
- Intel faces competition from AMD in the CPU market, with AMD gaining market share.
- NVIDIA leads in GPUs for AI and data centers, impacting Intel's market position.
- Intel is expanding into new growth areas like AI, accelerated computing, and automotive solutions.
- The company is focused on regaining process leadership and expanding its foundry business.
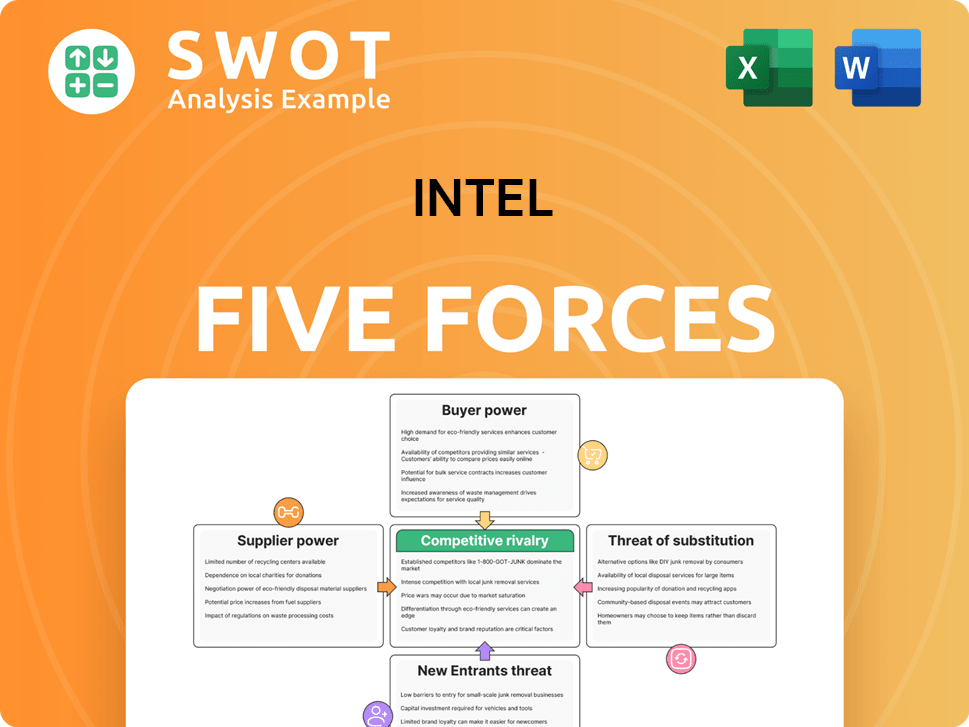
Intel Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of Intel Company?
- What is Competitive Landscape of Intel Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Intel Company?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Intel Company?
- What is Brief History of Intel Company?
- Who Owns Intel Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Intel Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.