Uber Bundle
How Does Uber Navigate the Global Marketplace?
Uber, a titan of the on-demand economy, has revolutionized how we move and receive goods. From its inception as a ride-sharing service, Uber has expanded its reach, becoming a global transportation service and logistics powerhouse. The ubiquitous Uber app has redefined consumer expectations, making instant access to transportation and delivery a modern necessity.
This exploration of Uber's operations will dissect its core components, from its innovative Uber SWOT Analysis to its diverse revenue streams. Understanding the Uber business model is crucial for anyone seeking to grasp the intricacies of on-demand transportation and the competitive landscape. We'll examine how Uber driver make money, its Uber car requirements, and other key aspects of this influential company.
What Are the Key Operations Driving Uber’s Success?
The core operations of Uber center on its technology platform, which connects users with independent service providers. This platform facilitates ride-hailing (Uber), food delivery (Uber Eats), and freight transportation (Uber Freight). These services are designed to serve various customer segments, from individuals needing convenient transportation to businesses requiring efficient logistics solutions.
The operational processes are driven by mobile applications and data analytics. When a user requests a ride or places a food order, the Uber app dispatches the request to nearby independent drivers or delivery persons. The platform manages matching, routing, fare calculation, and payment processing, using algorithms to optimize efficiency and reduce wait times. This approach allows for scalability and adaptability, resulting in widespread availability and quick service delivery.
Uber's value proposition emphasizes convenience, accessibility, and efficiency. For riders, it offers on-demand transportation, often more convenient than traditional taxis. Drivers benefit from a flexible income opportunity. Uber Eats provides restaurants with a wider customer base and a streamlined delivery infrastructure, while consumers gain access to various food options delivered to their doorstep. Uber Freight aims to digitize and optimize the trucking industry, providing transparency for shippers and carriers. The company's supply chain is largely digital, relying on its network of independent contractors and proprietary technology. For more insights, you can check out Owners & Shareholders of Uber.
Uber's ride-sharing operations involve connecting riders with drivers through its app. The app uses GPS to locate available drivers and calculate fares. The platform handles payments and provides a rating system for both riders and drivers.
Uber Eats facilitates food delivery by connecting customers with restaurants and delivery partners. Customers place orders via the Uber Eats app, and the platform dispatches the order to a nearby delivery person. The process includes order tracking and payment processing.
Uber Freight is designed to streamline freight transportation. It connects shippers with carriers, providing tools for booking, tracking, and managing shipments. This platform aims to improve efficiency and transparency in the trucking industry.
The Uber app is central to the company's operations. It provides features like ride-hailing, food ordering, and freight management. The app includes functionalities such as real-time tracking, fare estimation, and payment processing, enhancing the user experience.
Uber's business model is characterized by its asset-light approach, relying on independent contractors. This model allows for rapid scaling and adaptability. In 2024, Uber reported over 130 million monthly active platform consumers.
- Ride-sharing: Offers on-demand transportation services.
- Food delivery: Provides a platform for restaurants and consumers.
- Freight transportation: Connects shippers and carriers.
- Technology platform: Leverages mobile apps and data analytics.
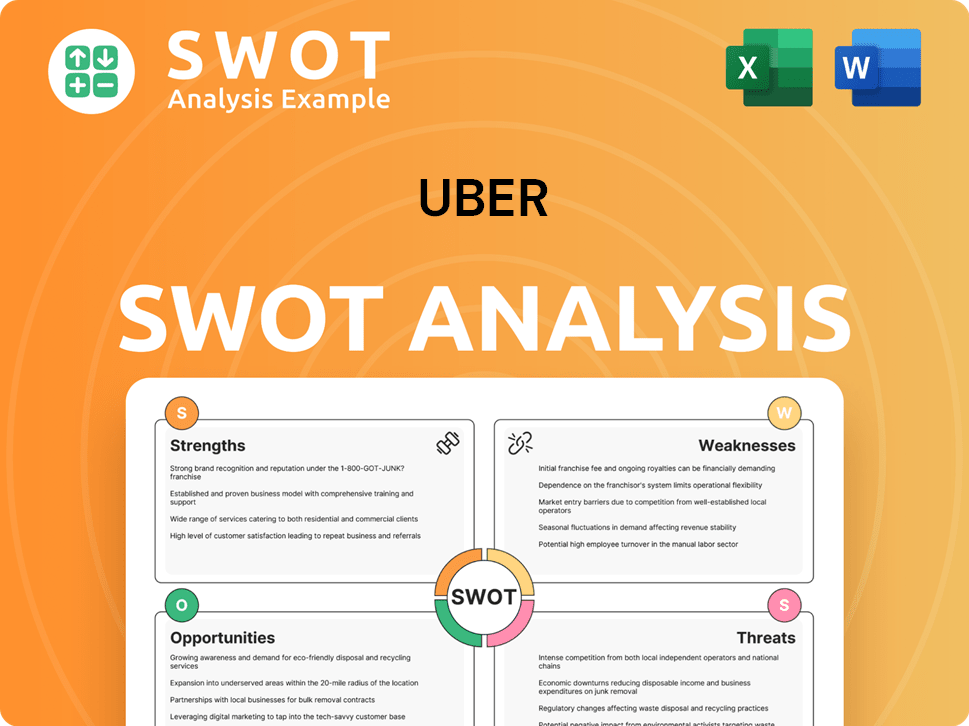
Uber SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
How Does Uber Make Money?
The core of [Company Name]'s financial strategy revolves around generating revenue through its diverse services. This includes ride-hailing, delivery services, and freight operations. The company leverages transaction fees and commissions to monetize its platform, ensuring a steady flow of income from both riders and drivers, as well as from restaurants and shippers.
In the fourth quarter of 2024, [Company Name] demonstrated strong performance, with gross bookings reaching $37.6 billion. The Mobility segment, encompassing ride-sharing, contributed $19.3 billion, while the Delivery segment, which includes [Company Name] Eats, generated $17.0 billion in gross bookings. This illustrates the significant impact of ride-sharing and delivery services on the company's overall revenue.
The primary revenue stream for [Company Name] comes from taking a percentage of each transaction. For instance, in ride-hailing, the company charges service fees to drivers and, in some cases, booking fees to riders. [Company Name] Eats operates on a commission model with restaurants and may also charge delivery fees to customers. This approach ensures that the company benefits from every transaction facilitated through its platform.
To maximize revenue and adapt to market dynamics, [Company Name] employs several innovative monetization strategies. Dynamic pricing, also known as surge pricing, is implemented during periods of high demand, balancing supply and demand while increasing revenue. For [Company Name] Eats, subscription services such as [Company Name] One provide benefits like discounts and waived delivery fees, fostering customer loyalty and recurring revenue. The freight operations, which connect shippers with carriers, operate on a commission model, taking a cut of the transportation fee.
- Surge Pricing: During peak hours or high-demand events, [Company Name] increases prices to encourage more drivers to work, ensuring availability for riders. This strategy is a key component of the on-demand transportation model.
- Subscription Services: [Company Name] One offers subscribers benefits like free delivery and discounts, creating a recurring revenue stream and enhancing customer loyalty.
- Commission-Based Model: [Company Name] takes a percentage of each transaction, whether it's a ride-hailing fare, a delivery order, or a freight shipment.
- Advertising: [Company Name] is exploring advertising opportunities on its platform, providing another avenue for revenue generation.
While Mobility and Delivery consistently account for the majority of [Company Name]'s revenue, the freight segment is experiencing growth. The company is also exploring new revenue streams, such as advertising, to optimize profitability and adapt to market demands. For more insights, you can read about the Growth Strategy of Uber.
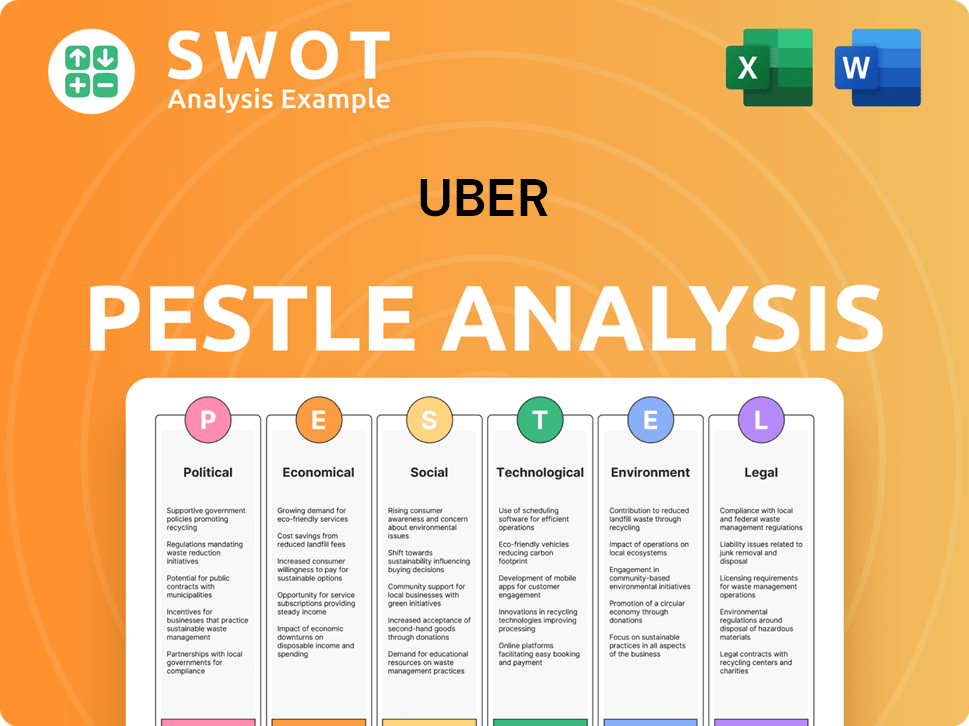
Uber PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
Which Strategic Decisions Have Shaped Uber’s Business Model?
The evolution of Uber has been marked by significant milestones and strategic shifts. A key initial move was its rapid global expansion in the early 2010s, which quickly established its dominance in the ride-sharing market. The launch of Uber Eats in 2014 was another critical strategic decision, diversifying its service offerings and tapping into the growing food delivery sector.
Operational challenges have included navigating regulatory scrutiny and adapting to market downturns. The company has responded by engaging with policymakers, adjusting its operating models, and investing in safety features. Market downturns, such as the initial impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on ride-hailing, prompted a strategic pivot towards strengthening its delivery services, which ultimately cushioned the financial blow.
Uber's competitive advantages are multi-faceted, including strong brand recognition and a global network effect. Its technology leadership, particularly in matching algorithms and payment systems, provides an operational edge. The company continues to adapt to new trends by investing in autonomous vehicle technology and exploring new mobility solutions, aiming to maintain its competitive edge in a rapidly evolving landscape.
Uber's journey includes aggressive global expansion and diversification. The launch of Uber Eats in 2014 was a pivotal strategic move. The acquisition of Postmates in 2020 further solidified its position in the food delivery sector.
Strategic moves include diversifying services and responding to market changes. Adapting to regulatory scrutiny and market downturns has been crucial. Investing in autonomous vehicle technology is a forward-looking strategy.
Uber benefits from strong brand recognition and network effects. Its technology leadership in matching algorithms and payment systems provides an advantage. Economies of scale allow for heavy investment in technology and marketing.
Operational challenges include regulatory scrutiny and market volatility. Driver classification, pricing, and safety are key areas of focus. Responding to the COVID-19 pandemic required strategic adaptation.
In Q1 2024, Uber's revenue grew by 15% year-over-year to reach $10.1 billion, with Mobility revenue up 29% and Delivery revenue up 8%. Uber's Monthly Active Platform Consumers (MAPC) reached 150 million. The company continues to invest in autonomous vehicle technology, aiming to maintain its competitive edge. Uber's focus on ride-sharing and delivery services has allowed it to navigate economic fluctuations and maintain a strong market presence.
- Uber's gross bookings were $37.7 billion in Q1 2024.
- Adjusted EBITDA for Q1 2024 was $1.4 billion.
- Uber operates in over 70 countries worldwide.
- The company continues to explore new mobility solutions.
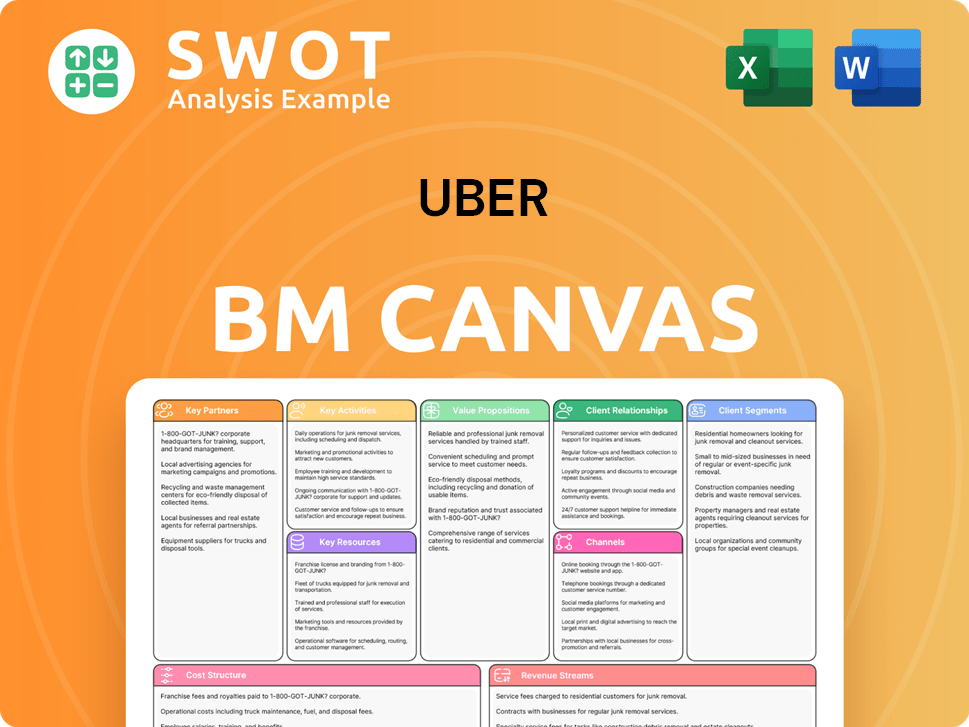
Uber Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
How Is Uber Positioning Itself for Continued Success?
Uber has a strong position in the global ride-hailing and food delivery markets. It often holds the largest market share in many regions, despite facing significant competition. Its wide global presence, operating in over 70 countries and 10,000 cities, gives it a big advantage. Customers stay loyal because of the convenient platform, competitive prices, and the variety of services offered under one app. For a deeper understanding of who uses Uber, check out this article about Uber's target market.
However, Uber faces several risks. Changes in regulations, particularly regarding how drivers are classified, could increase labor costs. New competitors keep emerging, which intensifies pricing pressure and requires constant innovation. Technological advancements, such as the rise of self-driving cars, could change its cost structure and operations. Consumer preferences, including a shift toward public transportation or other mobility solutions, also present a challenge.
Uber leads in ride-sharing and food delivery globally. Its extensive reach and diverse service offerings solidify its market leadership. The company benefits from a strong brand and network effects, enhancing its competitive advantage.
Regulatory changes, especially regarding driver classification, pose a risk. Competition from both established and new players puts pressure on pricing. Technological shifts, such as autonomous vehicles, could disrupt the business model.
Uber aims to diversify services and leverage AI and data analytics. Strategic partnerships and global expansion are key to navigating market dynamics. The company is focused on achieving sustained profitability and enhancing user experience.
In 2024, Uber reported its first full year of GAAP operating income and positive free cash flow. Revenue growth is driven by increased trip volumes and expansion of services. The company is focused on improving profitability and operational efficiency.
Uber is investing in autonomous vehicle technology to reduce costs. It is expanding into new areas such as grocery and retail delivery. Leadership emphasizes sustainable profitability, global expansion, and enhanced user experience.
- Investment in autonomous vehicle technology through partnerships.
- Expansion into new verticals like grocery and retail delivery.
- Focus on achieving sustainable profitability and expanding its global footprint.
- Enhancing user experience through technological advancements and data analytics.
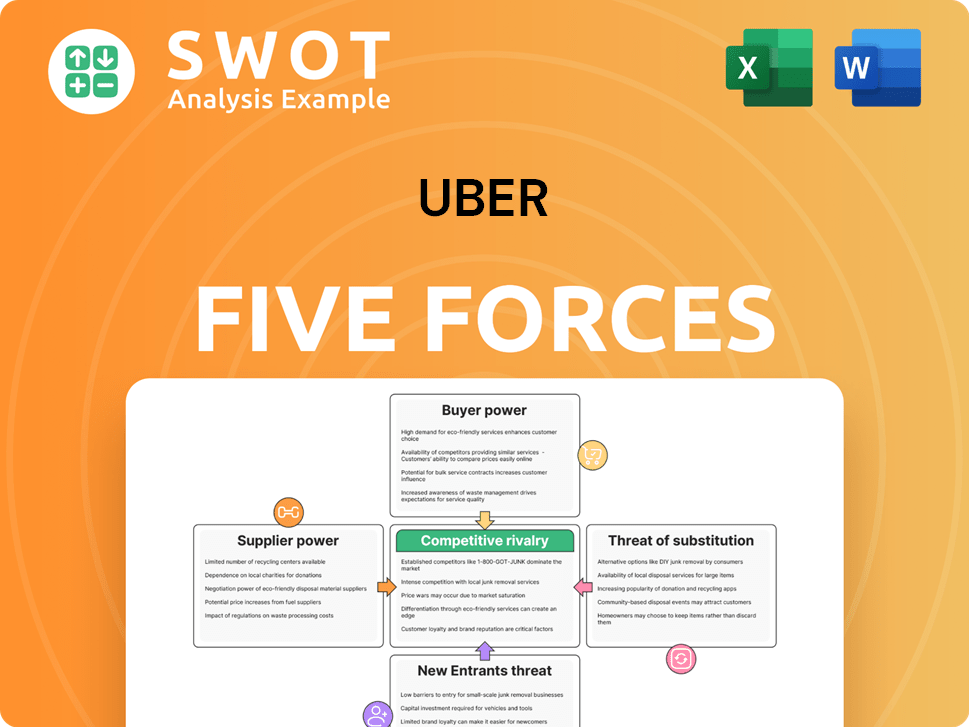
Uber Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of Uber Company?
- What is Competitive Landscape of Uber Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Uber Company?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Uber Company?
- What is Brief History of Uber Company?
- Who Owns Uber Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Uber Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.