GameStop Bundle
Who Really Controls GameStop?
Ever wondered who pulls the strings at GameStop? The company, once a simple retail chain, became a cultural phenomenon, sparking a dramatic shift in the stock market. Understanding the GameStop SWOT Analysis is just the beginning; the company's ownership structure is a key to unlocking its future. The story of GameStop is a captivating tale of retail investors, institutional giants, and the ever-evolving landscape of modern finance.

Delving into the details of GameStop ownership provides crucial insights into the company's strategic direction and its susceptibility to market forces. Examining the current GameStop owners, including the influence of GameStop shareholders and the role of the GameStop CEO, is vital. This analysis will explore the evolution of GameStop's ownership, highlighting the impact of the meme stock saga and its implications for the GameStop stock.
Who Founded GameStop?
The story of GameStop begins with Babbage's, founded in 1984. James McCurry and Gary M. Kusin were the visionaries behind the initial concept. Information on the exact equity split among the founders during the company's inception is not readily available in public records.
Babbage's started by selling software for home computers. As the video game console market evolved, the company adapted, expanding its retail presence. Details about early angel investors or initial friends and family who acquired stakes aren't widely publicized.
Early agreements, such as vesting schedules or buy-sell clauses, from this private phase of the company are not publicly available. Initial ownership disputes or buyouts among the founders during the early stages are also not highlighted in public records. The founding team's focus was on creating a specialized retail experience for gaming and software, which guided the company's early expansion.
Babbage's, the precursor to GameStop, was established in 1984. The founders were James McCurry and Gary M. Kusin.
The initial business of Babbage's revolved around selling software for home computers. This was the company's primary offering in its early years.
Babbage's adapted to the evolving video game console market. The company expanded its retail footprint to capitalize on the growing demand for video games.
There is a lack of publicly available information regarding early angel investors. Details of initial investments from friends and family are also not widely publicized.
Early agreements, like vesting schedules or buy-sell clauses, are not detailed in public records. These details remain private.
Public records do not highlight initial ownership disputes or buyouts among the founders during the very early stages of the company.
Understanding GameStop's growth strategy also helps to understand its ownership. The company's evolution from Babbage's to its current form reflects its ability to adapt to the changing landscape of the gaming industry. Information on current GameStop owners and the impact of the GameStop stock on ownership is crucial for investors. As of late 2024, the company's market capitalization fluctuates, influencing the value of shares held by GameStop shareholders and other major stakeholders. The identity of the current GameStop CEO also plays a significant role in the company's direction.
Early ownership details of GameStop are not extensively documented in public records.
- The founders of Babbage's, the precursor to GameStop, were James McCurry and Gary M. Kusin.
- Babbage's initially focused on selling software for home computers.
- Information on early investors and specific ownership agreements is limited.
- The company adapted to the video game market, expanding its retail presence.
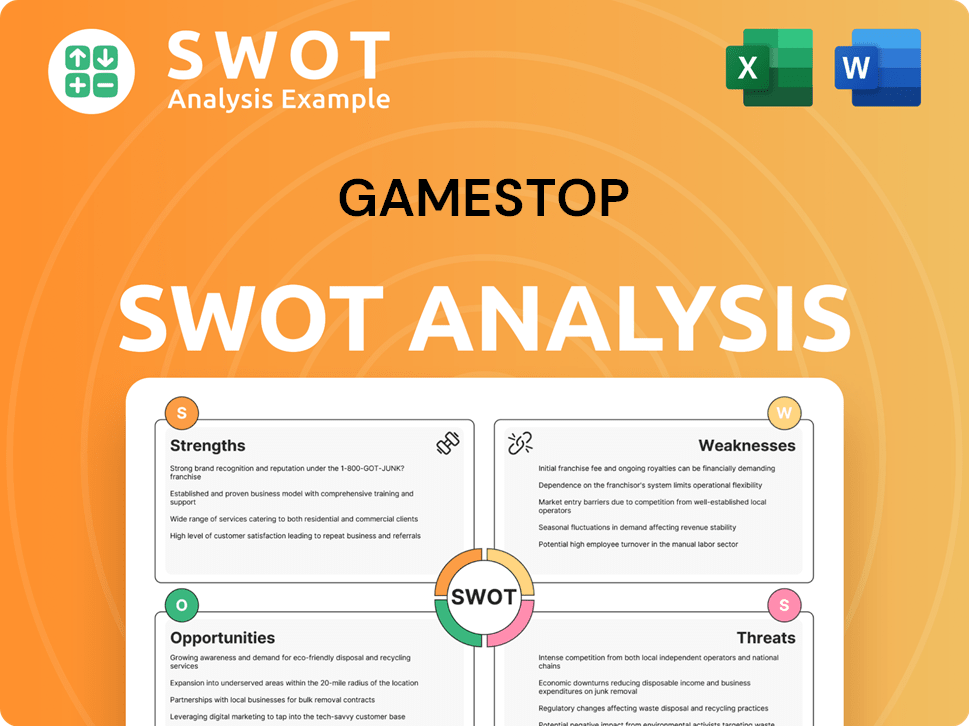
GameStop SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
How Has GameStop’s Ownership Changed Over Time?
The story of GameStop's ownership is a tale of mergers, acquisitions, and a dramatic shift in shareholder influence. Initially, the company emerged from the merger of Babbage's and Software Etc. in 1999, forming NeoStar Retail Group. This entity was then acquired by Barnes & Noble, which later spun off GameStop as a public company in 2002. This initial public offering (IPO) marked the beginning of GameStop's journey as an independent entity, setting the stage for the evolving ownership dynamics we see today. Finding out GameStop ownership is a complex process.
The ownership structure of GameStop has seen significant changes, especially in recent years. The 'meme stock' phenomenon of early 2021, driven by retail investors, led to a substantial short squeeze. This event temporarily diluted the influence of institutional investors. However, as of early 2025, institutional investors still hold a significant portion of GameStop shares. Major stakeholders include Vanguard Group Inc., BlackRock Inc., and State Street Corp. These firms hold shares through various investment vehicles, influencing the company's stock performance.
| Ownership Category | Stakeholders | Approximate Shareholding (as of March 2025) |
|---|---|---|
| Institutional Investors | Vanguard Group Inc., BlackRock Inc., State Street Corp. | Significant, millions of shares each |
| Retail Investors | Individual shareholders | Variable, but a substantial portion |
| Other | Various investment firms | Varies |
The current landscape of GameStop ownership reflects a balance between institutional and retail investors. While institutional investors like Vanguard and BlackRock hold considerable stakes, the influence of retail investors remains a crucial factor. This dynamic impacts the GameStop stock performance and puts pressure on the company's strategy and governance. Understanding who the GameStop shareholders are is key to understanding the company's direction.
The ownership of GameStop is a blend of institutional and retail investors, with significant shifts in recent years. The 'meme stock' event of 2021 highlighted the power of retail investors.
- Institutional investors hold a substantial portion.
- Retail investors remain a significant influence.
- The ownership structure impacts company strategy.
- Understanding the stakeholders is key.
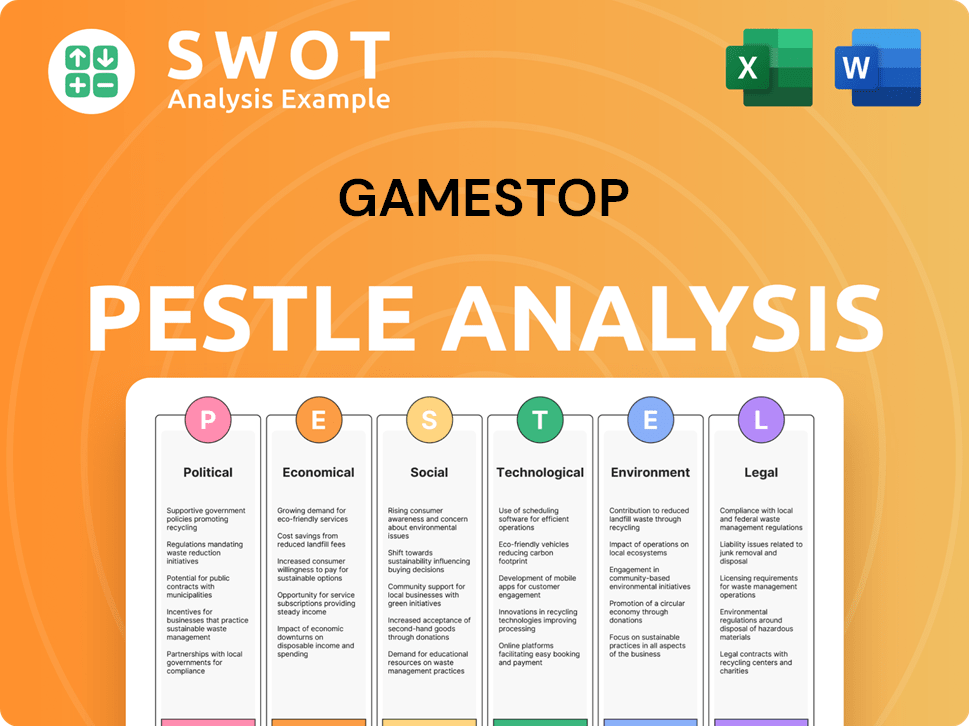
GameStop PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
Who Sits on GameStop’s Board?
As of early 2025, understanding the current GameStop ownership structure is crucial for investors. The Board of Directors at GameStop plays a pivotal role in the company's governance. The board includes a mix of independent members and those representing significant interests. Key figures include Ryan Cohen, who is also the company's CEO and a major individual shareholder through RC Ventures LLC. Other board members typically have backgrounds in e-commerce, technology, and finance. It's essential to consult the latest proxy statements for the most current list of board members, as the composition frequently changes.
The composition of the board has evolved, particularly with the influence of activist investors. The involvement of Ryan Cohen and RC Ventures significantly altered the company's strategic direction and leadership. These campaigns, supported by retail investors, have shaped decision-making, pushing for a transformation towards e-commerce and a more digital-centric business model. This dynamic interplay between institutional investors, activist shareholders, and the influential retail investor base highlights the evolving nature of GameStop's corporate governance.
| Board Member | Role | Shareholder Affiliation |
|---|---|---|
| Ryan Cohen | CEO & Chairman | RC Ventures LLC (Significant Shareholder) |
| Alan Attal | Director | Independent |
| Kareem Daniel | Director | Independent |
GameStop operates with a one-share-one-vote voting structure. This means each common share typically grants one vote. There are no known special voting rights or golden shares that would give outsized control to specific individuals beyond their proportional shareholding. The influence of Ryan Cohen and other board members representing significant shareholder interests is derived from their substantial ownership stakes and their positions on the board. For those interested in how GameStop stacks up against its rivals, you can explore the Competitors Landscape of GameStop.
The Board of Directors at GameStop is crucial for governance, with a mix of independent members and those representing major interests. Ryan Cohen, as CEO and a significant shareholder, holds considerable influence.
- Board composition changes; check proxy statements for updates.
- One-share-one-vote voting structure is in place.
- Activist investor campaigns have shaped the company's strategic direction.
- Retail investor support plays a significant role in decision-making.
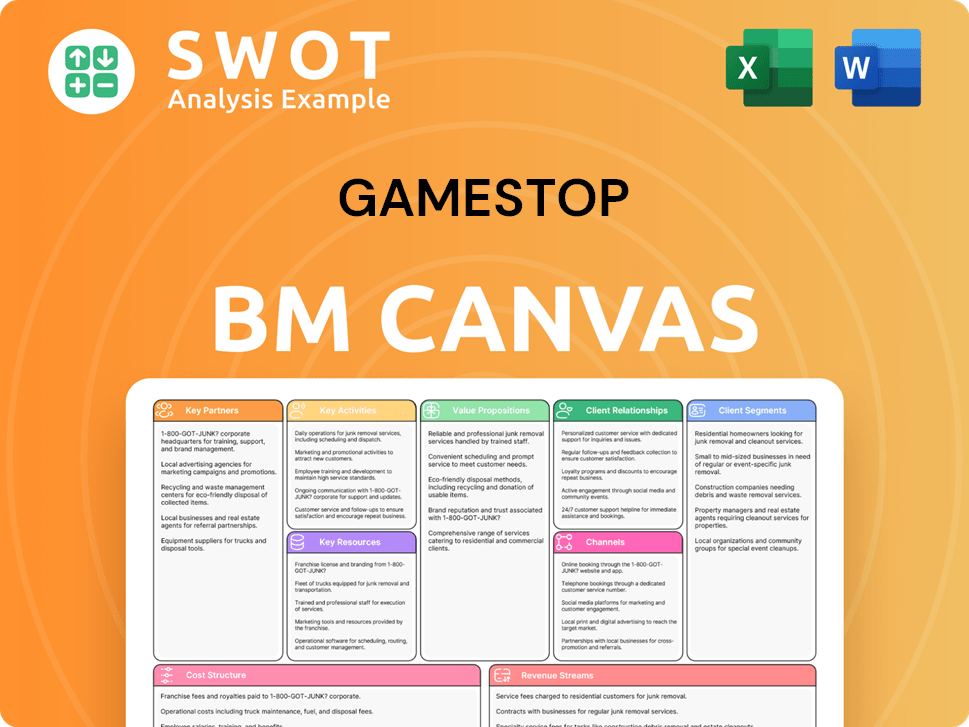
GameStop Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What Recent Changes Have Shaped GameStop’s Ownership Landscape?
Over the past few years, the ownership landscape of GameStop has been significantly influenced by the "meme stock" phenomenon, which has resulted in a higher level of retail investor engagement. While exact figures fluctuate, retail investors continue to represent a substantial portion of the GameStop shareholders base. This contrasts with more traditional ownership structures, where institutional investors typically hold a larger share.
Recent corporate actions, such as occasional equity offerings, have impacted the ownership structure, although less frequently than during the peak of the meme stock frenzy. The appointment of Ryan Cohen as CEO has been a key event, solidifying the influence of a major individual shareholder and aligning with shifts in strategic direction. This dynamic has shaped the GameStop ownership narrative, highlighting the importance of individual investors and activist involvement within the GameStop company.
| Ownership Category | Approximate Percentage (as of Q1 2024) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Institutional Investors | ~30-40% | Includes investment firms, mutual funds, and other institutional entities. |
| Retail Investors | ~35-45% | Estimated based on various filings and analyses; a significant portion. |
| Ryan Cohen (and Affiliates) | ~10-15% | The largest individual shareholder and the current CEO. |
The rise of activist investors, particularly Ryan Cohen, has been a defining theme for GameStop stock. Discussions about the company's transformation efforts indirectly relate to its long-term ownership value. Public statements and analyst reports frequently address the challenges and opportunities presented by this unique ownership structure, especially concerning volatility and strategic flexibility. For additional insights into the business, consider exploring Revenue Streams & Business Model of GameStop.
The GameStop stock has experienced significant volatility, heavily influenced by retail investor sentiment. The company's market capitalization fluctuates considerably. The company's current market capitalization is around $6 billion as of May 2024.
Ryan Cohen, the current GameStop CEO, holds a significant stake and has a strong influence on strategic decisions. His actions and communications are closely watched by investors. His stake is approximately between 9-12% as of May 2024.
Retail investors remain a critical component of GameStop's ownership structure, contributing to high trading volumes and price volatility. Their collective actions can significantly impact the stock's performance. Retail ownership is estimated to be between 35-45%.
Institutional investors have a significant presence, though their influence is often balanced by retail investor activity. Their investment strategies and holdings are essential to monitor. Institutional ownership is around 30-40%.
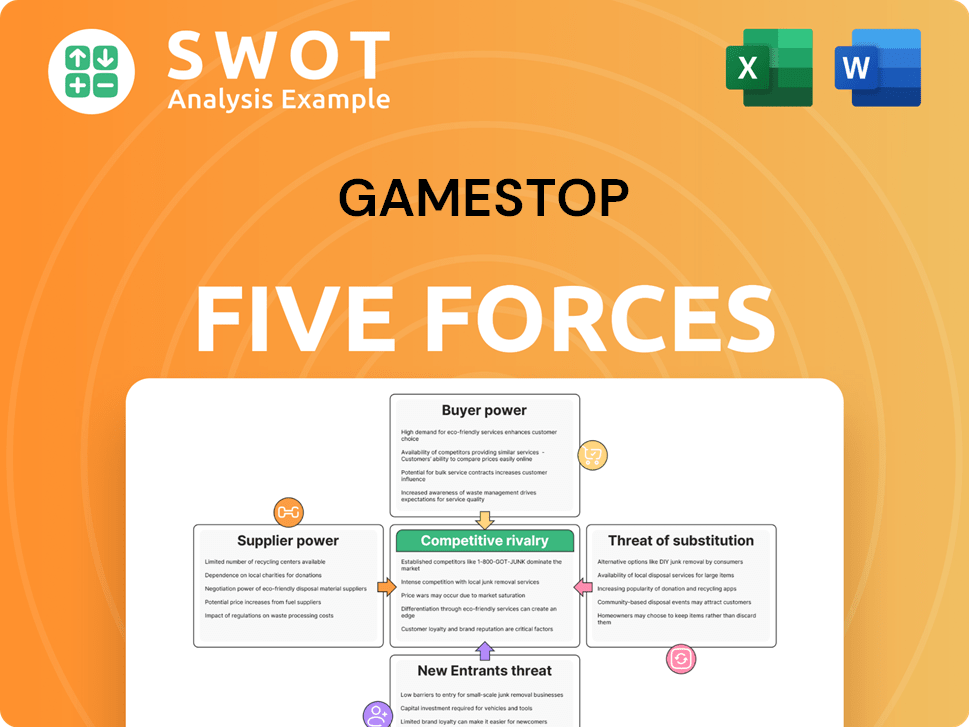
GameStop Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of GameStop Company?
- What is Competitive Landscape of GameStop Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of GameStop Company?
- How Does GameStop Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of GameStop Company?
- What is Brief History of GameStop Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of GameStop Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.