GCC Bundle
Who Really Owns GCC Company?
Unraveling the ownership of GCC Company is key to understanding its strategic moves and market dominance in the construction materials sector. From major acquisitions to shifts in shareholder dynamics, the company's ownership structure is a dynamic force. Founded in 1941, GCC, formerly known as Grupo Cementos de Chihuahua, has grown into a significant player in North America.

This deep dive into GCC SWOT Analysis will explore the evolution of GCC Company's ownership, from its founders to today's key investors. We'll examine the impact of its public shareholdings and any changes in control, providing crucial insights for investors and analysts. Understanding the GCC Company Structure and its management is vital for anyone seeking to navigate the complexities of this leading building materials provider. Learn about Who owns GCC and the influence of its major shareholders.
Who Founded GCC?
The story of GCC Company Ownership begins in 1941, when it was founded as Grupo Cementos de Chihuahua S.A.B. de C.V. The initial goal was to supply essential building materials, setting the stage for what the company is today. While specific details about the original founders' equity splits aren't readily available, understanding the early ownership structure is key to grasping the company's evolution.
Early ownership likely involved a group of local entrepreneurs and business figures who pooled their resources. These individuals, often with backgrounds in commerce, industry, or finance, established the initial cement production facilities. This early phase was crucial in shaping the company's direction and laying the groundwork for future growth. Understanding the founders and early shareholders provides insight into the company's initial vision and values.
Early ownership would have included the initial investors, possibly with angel investors or family members providing seed capital. The agreements would have outlined share distribution, responsibilities, and decision-making authority. Early companies often have vesting schedules or buy-sell clauses to manage potential founder exits, although specific details for the early days of GCC aren't publicly itemized. Any initial ownership disputes or buyouts would have been resolved internally, shaping the company's foundational control. The founding team’s vision for a reliable and high-quality building materials supplier would have been intrinsically linked to how control was distributed, ensuring alignment with the company's long-term objectives.
Understanding the GCC Company Structure is important for investors and stakeholders. Key aspects include the initial founders, early investors, and the evolution of ownership over time. This also involves the management structure and how decisions are made within the company. For more insights, read about the Growth Strategy of GCC.
- The initial ownership structure was typical of industrial companies of the time, involving local entrepreneurs.
- Early investors, potentially including angel investors, provided crucial seed capital.
- Initial agreements would have detailed share distribution, responsibilities, and decision-making processes.
- Vesting schedules and buy-sell clauses were likely used to manage founder commitments.
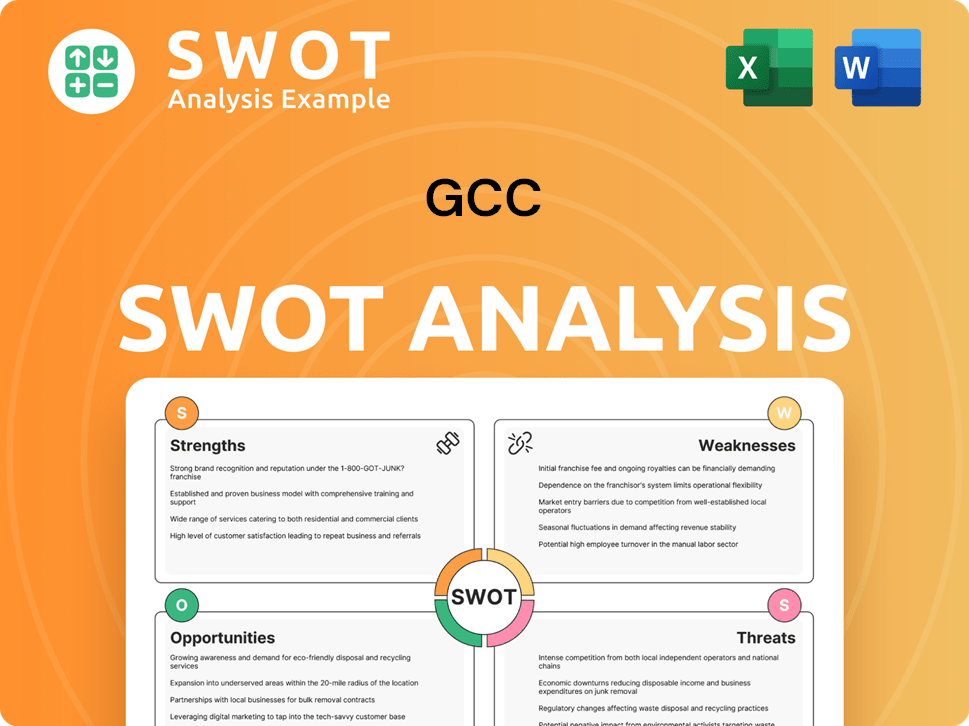
GCC SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
How Has GCC’s Ownership Changed Over Time?
The ownership structure of GCC has evolved significantly since its inception. Key events, such as its initial public offering (IPO), have reshaped its shareholder base. While specific dates and initial market capitalization figures are historical, the company's ownership has seen shifts. Institutional investors, mutual funds, and index funds now hold a substantial portion of GCC's shares. For instance, as of early 2025, major institutional holders often include large asset management firms and investment funds, with their stakes regularly disclosed through SEC filings. These filings reveal the percentages held by these entities, influencing company strategy and governance through their voting power and engagement with management. If you are interested in the Competitors Landscape of GCC, you might find more insights.
Beyond institutional investors, significant individual shareholders, potentially including members of founding families or long-term strategic investors, also hold notable stakes. While specific names and percentages for individual shareholders are less frequently highlighted in general public reports unless they cross certain disclosure thresholds, their collective influence can be substantial. Changes in equity allocation also occur through strategic investments, mergers, and acquisitions, which can introduce new major stakeholders or alter the proportionate ownership of existing ones. These shifts directly impact company strategy, particularly regarding capital allocation, expansion initiatives, and long-term growth plans, as major shareholders often have a significant voice in board appointments and key strategic decisions.
Understanding GCC Company Ownership involves examining its shareholder base, including institutional and individual investors. Major shareholders influence company strategy and governance through voting power. Changes in ownership occur through strategic investments and acquisitions.
- Institutional investors often hold a significant portion of shares.
- Individual shareholders can have substantial influence.
- Changes in equity allocation impact company strategy.
- Major shareholders influence board appointments.
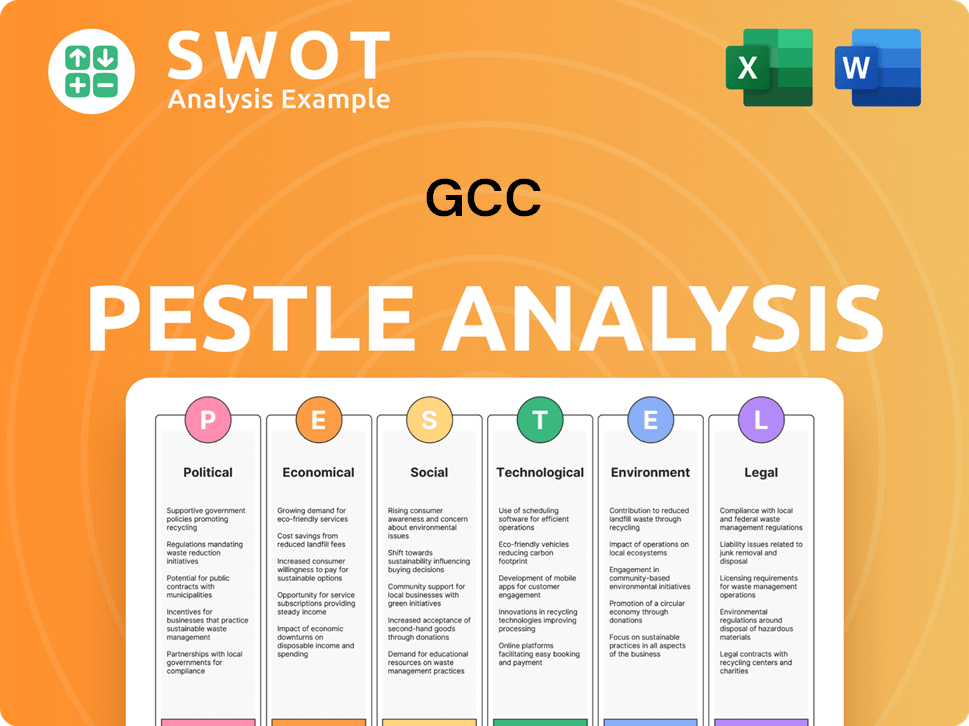
GCC PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
Who Sits on GCC’s Board?
The Board of Directors of GCC plays a critical role in the company's governance, representing the interests of its diverse ownership base. As of late 2024 and early 2025, the board typically includes a mix of individuals representing major shareholders, independent directors, and potentially executive members. Accessing the latest annual reports or proxy statements is necessary to get a specific list of all current board members and their affiliations. It's common for large institutional investors to have a voice, directly or indirectly, in appointing board members who align with their investment strategies. Independent directors are essential for ensuring objective oversight and adherence to corporate governance best practices. Understanding the board's composition is crucial to understanding the company's direction. For more insights into the company's strategic approach, consider reading about the Marketing Strategy of GCC.
The structure of the board and the voting power dynamics are central to understanding who ultimately steers the company's direction. The board's composition and the underlying voting power dynamics are central to understanding who ultimately steers the company's direction. While specific details on the exact board members and their affiliations require reviewing the most recent annual reports or proxy statements, it is typical for large institutional investors to have representation. Independent directors are vital for ensuring objective oversight and adherence to corporate governance best practices. The voting structure at GCC, like many publicly traded companies, generally operates on a one-share-one-vote basis for common shares, meaning that the number of shares held directly correlates with voting power.
| Board Member Category | Typical Representation | Role in Governance |
|---|---|---|
| Major Shareholders | Representatives from significant institutional investors, such as investment funds or other large holders. | Influence strategic decisions and ensure alignment with shareholder interests. |
| Independent Directors | Individuals with no material relationship with the company or its management. | Provide objective oversight, ensure compliance, and represent the interests of all shareholders. |
| Executive Members | CEO, CFO, and other top-level executives. | Provide operational expertise and represent the management's perspective. |
It's essential to review the company's bylaws and articles of incorporation for any potential dual-class share structures, special voting rights, or 'golden shares' that could grant outsized control to certain individuals or entities. While recent proxy battles or activist investor campaigns for GCC specifically in 2024-2025 are not broadly reported as major public controversies, such events can significantly reshape decision-making by challenging current management or advocating for specific strategic changes. For example, in 2024, activist investors targeted several large companies, leading to board changes and shifts in strategy. The board's composition and the underlying voting power dynamics are central to understanding who ultimately steers the company's direction.
The board of directors and voting power are key aspects of GCC Company Ownership. Understanding the composition of the board and the voting structure is crucial for investors and stakeholders.
- Board members often represent major shareholders and independent directors.
- Voting typically follows a one-share-one-vote system.
- Reviewing bylaws is essential to identify any special voting rights.
- Understanding the ownership structure helps in assessing control and influence.
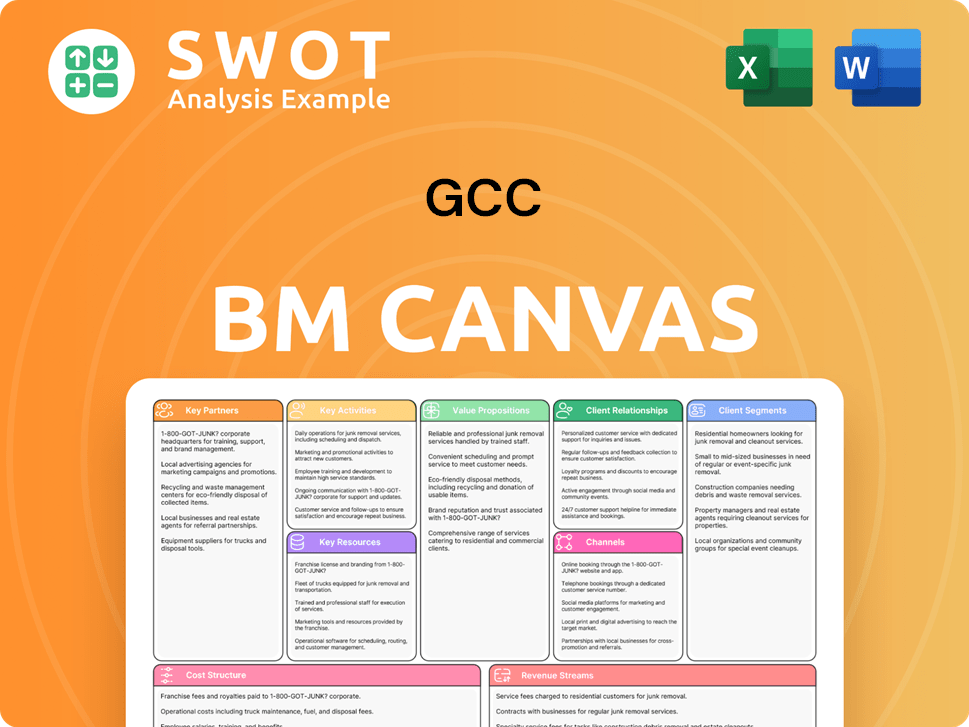
GCC Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What Recent Changes Have Shaped GCC’s Ownership Landscape?
Over the past few years, the ownership structure of GCC Company has likely been influenced by industry-wide trends and specific company actions. Share buybacks, if implemented, would have reduced the number of outstanding shares, potentially increasing the proportionate ownership of remaining shareholders and boosting earnings per share. Secondary offerings, conversely, would dilute existing shareholders but provide capital for strategic initiatives. Mergers and acquisitions, such as the company's continued focus on strengthening its presence in key North American markets, can lead to substantial shifts in ownership by integrating new entities or divesting non-core assets.
Leadership changes, while not always directly altering ownership percentages, can signal shifts in strategic vision and may be followed by changes in significant shareholdings. New strategic investors, whether private equity firms or corporate partners, can inject capital and expertise, often acquiring substantial stakes. Industry trends in ownership, such as the increasing influence of institutional ownership, are evident for companies like GCC, as large investment funds seek stable, established players in essential industries. Founder dilution is a natural progression as companies grow and raise capital, diversifying the ownership base. Consolidation within the construction materials sector can also lead to ownership changes through mergers and acquisitions.
| Ownership Aspect | Likely Impact | Relevant Data (2022-2025) |
|---|---|---|
| Share Buybacks | Increased ownership for remaining shareholders, EPS boost | Dependent on specific actions; financial reports would show changes in outstanding shares. |
| Secondary Offerings | Dilution of existing shareholders, capital for initiatives | Capital raised and use of proceeds detailed in financial statements. |
| Mergers and Acquisitions | Shifts in ownership through integration or divestiture | Impact reflected in consolidated financial statements and ownership percentages. |
The dynamic ownership landscape of GCC Company is responsive to market conditions and growth opportunities. While specific public statements about future ownership changes or planned succession for GCC in 2025 are not widely disseminated, the company's ongoing strategic growth and market positioning suggest a dynamic ownership landscape responsive to market conditions and growth opportunities. For more in-depth information, you can consult the company's annual reports and investor relations materials. This information can help you understand the GCC Company Ownership and GCC Company Owners.
Increased institutional ownership is a significant trend, reflecting the attractiveness of established companies like GCC to large investment funds.
Mergers and acquisitions within the construction materials sector can lead to shifts in GCC Company Structure and GCC Company Management.
The company's strategic moves to optimize its asset portfolio often involve capital restructuring that impacts ownership and GCC Company Shareholders.
Founder dilution is a natural progression as companies grow and raise capital, diversifying the ownership base, which is important for Who owns GCC.
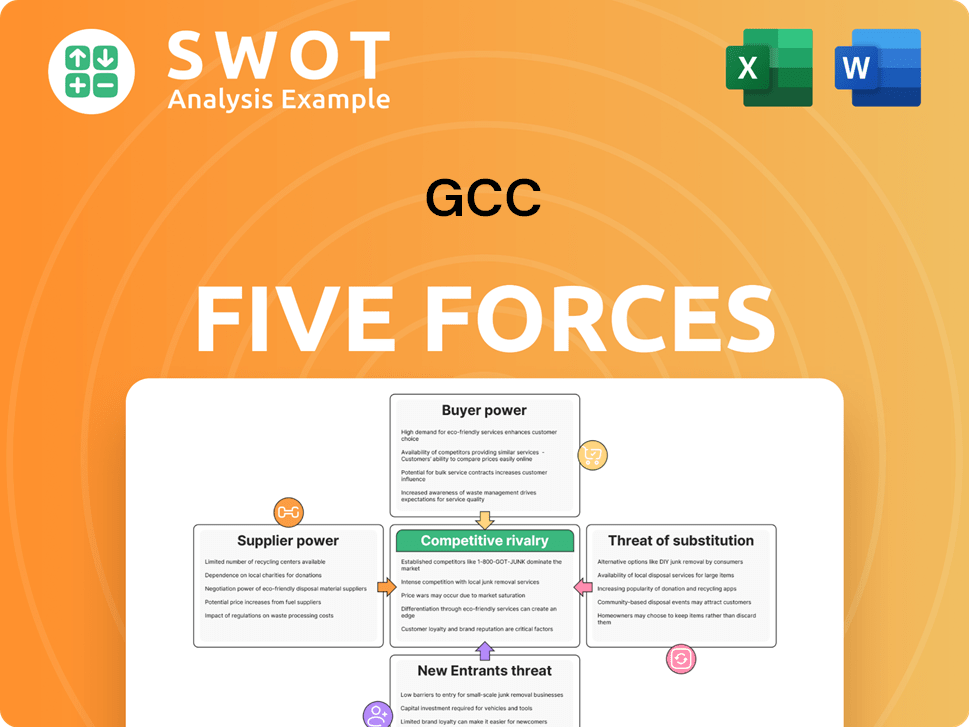
GCC Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of GCC Company?
- What is Competitive Landscape of GCC Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of GCC Company?
- How Does GCC Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of GCC Company?
- What is Brief History of GCC Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of GCC Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.