Kimberly-Clark Bundle
Who Really Calls the Shots at Kimberly-Clark?
Ever wondered who truly steers the ship at a global giant like Kimberly-Clark? Understanding the Kimberly-Clark SWOT Analysis is vital for any investor or strategist. From its humble beginnings, Kimberly-Clark's ownership has evolved, shaping its strategic direction and market dominance. This exploration delves into the fascinating story behind Kimberly-Clark ownership.

Knowing who owns Kimberly-Clark is more than just a question of curiosity; it's key to understanding its future. The Kimberly-Clark parent company structure directly influences its financial performance, governance, and long-term strategy. As a publicly traded entity, Kimberly-Clark corporation's ownership dynamics are a critical aspect of its profile, impacting everything from dividend policies to its response to market challenges. This deep dive will uncover the major shareholders, board composition, and recent trends that define the company's ownership landscape.
Who Founded Kimberly-Clark?
The story of Kimberly-Clark's origins begins in 1872, with four founders coming together to establish what would become a global leader in consumer goods. These individuals, John A. Kimberly, Havilah Babcock, Charles B. Clark, and Frank C. Shattuck, each brought unique skills to the table, forming the initial ownership structure of the company.
The early days of the Kimberly-Clark corporation were marked by the collaborative efforts of its founders. While specific equity breakdowns from the company's inception are not publicly available, the ownership was undoubtedly shared among the four partners. This arrangement reflected their shared investment and commitment to the success of the venture.
The founders' vision was instrumental in shaping the company's early direction and setting the stage for its future growth. Their combined expertise in finance, paper production, operations, and sales laid the foundation for Kimberly-Clark's expansion and diversification into the consumer products market.
John A. Kimberly, Havilah Babcock, Charles B. Clark, and Frank C. Shattuck were the founders of the company.
The company initially focused on paper manufacturing.
Ownership was divided among the four founders, reflecting their shared investment.
The company faced challenges common to early industrial enterprises, including securing capital and establishing efficient production processes.
The company expanded its paper production capabilities, eventually diversifying into consumer products.
The initial ownership structure remained relatively stable, allowing the company to focus on industrial growth.
Understanding the early ownership of Kimberly-Clark provides context to its evolution. The founders' commitment and diverse skills were critical to the company's initial success. The absence of external investors in the early stages suggests that the founders themselves provided the necessary capital. The focus on industrial growth and product development during this period laid the groundwork for Kimberly-Clark's future as a global consumer goods leader. The company's early ownership structure and its evolution over time are essential aspects of its history, influencing its strategic decisions and market position.
- The company was founded in 1872.
- The founders were John A. Kimberly, Havilah Babcock, Charles B. Clark, and Frank C. Shattuck.
- Early ownership agreements were likely informal, based on trust.
- The founders provided the primary capital and resources.
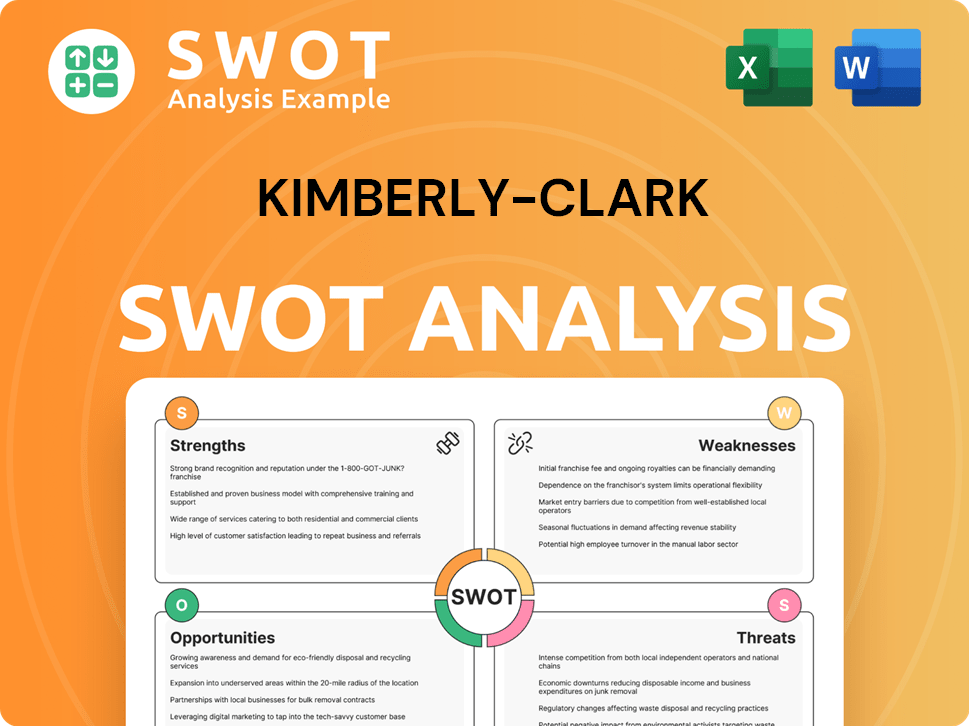
Kimberly-Clark SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
How Has Kimberly-Clark’s Ownership Changed Over Time?
The ownership structure of the company has changed dramatically since its inception. Initially, the company operated as a privately held partnership. A significant shift occurred when it went public on the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) on July 23, 1928. This initial public offering (IPO) marked a transition, broadening the ownership base beyond the founding families and early investors. Although specific market capitalization data from the 1928 IPO isn't readily accessible, this event was a pivotal moment in the company's history, allowing for wider public investment.
Today, the company (NYSE: KMB) is primarily owned by institutional investors. This is a common pattern for large, publicly traded corporations. As of early 2025, major institutional shareholders include prominent asset management firms and mutual funds. The Vanguard Group, BlackRock, and State Street Corporation are consistently among the top holders, collectively controlling a significant portion of the company's outstanding shares. Vanguard Group, Inc. holds approximately 9.3% of the shares, BlackRock, Inc. holds around 7.8%, and State Street Corp holds approximately 4.5%, according to early 2025 data. These figures are subject to change based on market conditions and investment strategies.
| Shareholder | Approximate Percentage of Shares (Early 2025) | Type |
|---|---|---|
| The Vanguard Group, Inc. | 9.3% | Institutional |
| BlackRock, Inc. | 7.8% | Institutional |
| State Street Corp | 4.5% | Institutional |
Individual insiders, including board members and executive officers, also hold shares. Their collective ownership typically represents a small percentage compared to institutional holdings. This alignment of interests between insiders and shareholders is a key aspect of corporate governance. The shift towards institutional ownership has significantly impacted the company's strategy and governance, as these large investors actively engage with management on various issues, including financial performance and ESG initiatives. The company's annual reports and SEC filings, such as 10-K forms, provide detailed breakdowns of major shareholders, reflecting the evolving nature of its ownership. For more insights into the company's strategic direction, you can explore the Growth Strategy of Kimberly-Clark.
The company's ownership has evolved from a private partnership to a publicly traded entity, primarily held by institutional investors.
- Institutional investors like Vanguard, BlackRock, and State Street hold significant stakes.
- Insider ownership, though smaller, aligns interests with broader shareholders.
- Institutional influence shapes company strategy and governance, including ESG initiatives.
- Annual reports and SEC filings provide detailed ownership breakdowns.
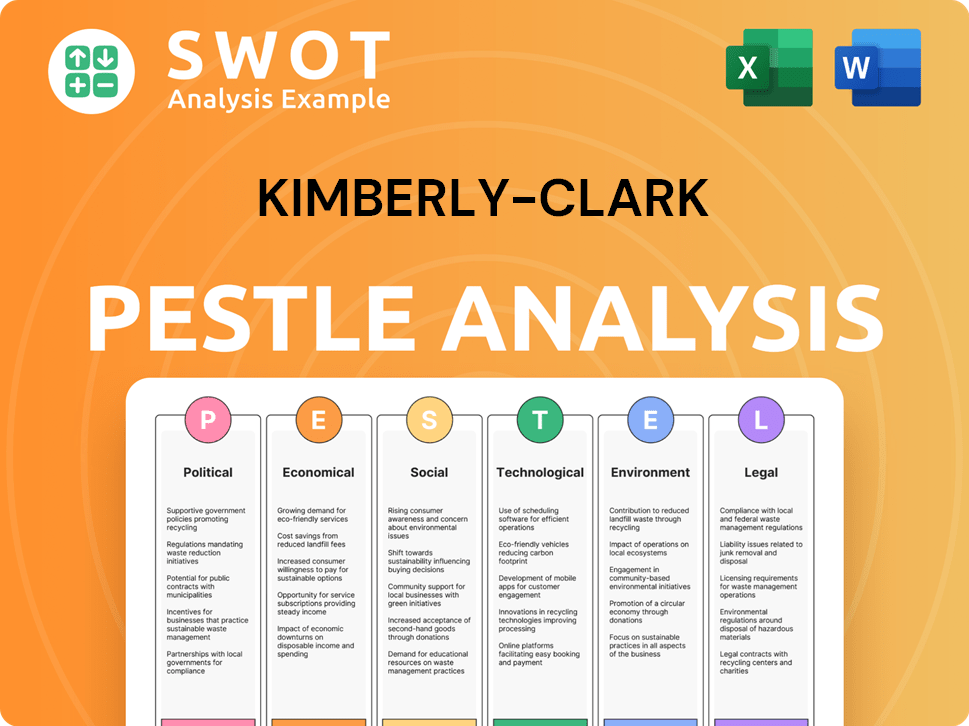
Kimberly-Clark PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
Who Sits on Kimberly-Clark’s Board?
The Board of Directors of Kimberly-Clark Corporation, as of mid-2025, is responsible for overseeing the company's strategic direction and representing shareholder interests. The board includes a mix of independent directors and executive management, ensuring diverse perspectives and robust oversight. The CEO typically holds a seat on the board, representing executive management. While specific board members representing major shareholders are not explicitly identified in public disclosures, the large institutional holdings indirectly influence board composition through proxy voting and engagement with the company's nominating committee. The board's composition reflects a commitment to diversity and independent oversight, with a significant number of independent directors who are not employees of the company.
The board's structure supports effective corporate governance and accountability to the broad base of public shareholders. The company actively engages with shareholders, with discussions around executive compensation and environmental impact being regular topics at annual shareholder meetings. This structure helps to ensure that the company is managed in a way that is beneficial to all shareholders. The board plays a crucial role in setting the company's long-term goals and ensuring that management is held accountable for achieving them. For further insights into the growth strategy of the company, you can explore the Growth Strategy of Kimberly-Clark.
| Board Member | Title | Affiliation |
|---|---|---|
| Mike Hsu | Chairman and CEO | Kimberly-Clark Corporation |
| Maria S. Henry | Lead Independent Director | Former CEO, Hologic, Inc. |
| Chris A. Brake | Director | Former EVP and CFO, Colgate-Palmolive Company |
The voting structure for Kimberly-Clark shares follows a one-share-one-vote system, common for most publicly traded companies. Each common share entitles its holder to one vote on matters such as director elections and executive compensation. There are no indications of dual-class shares or special voting rights that would grant outsized control to any specific individual or entity. This democratic structure ensures that control is distributed proportionally to ownership. This structure helps to maintain a fair and transparent voting process.
The Board of Directors oversees strategic direction and represents shareholder interests. The voting structure is one-share-one-vote, ensuring proportional control. The company actively engages with shareholders on key issues.
- The board includes independent directors and executive management.
- The CEO of the company typically holds a seat on the board.
- Shareholders vote on key issues such as director elections.
- No special voting rights exist that would grant outsized control.
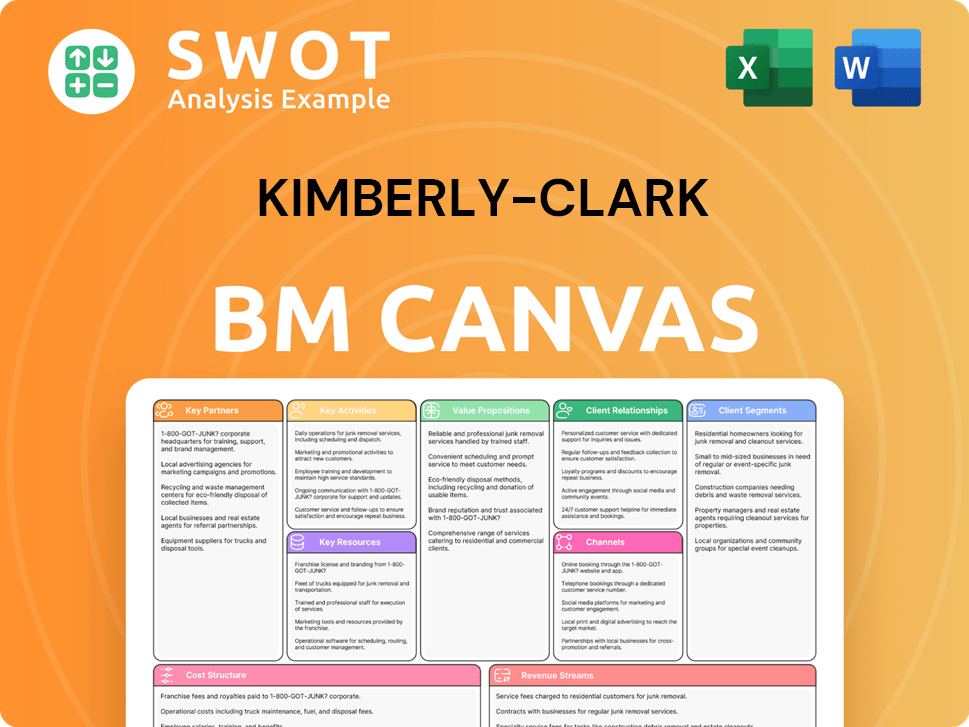
Kimberly-Clark Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What Recent Changes Have Shaped Kimberly-Clark’s Ownership Landscape?
In recent years, shifts in the Kimberly-Clark ownership structure have been subtle but consistent, largely influenced by institutional investment trends and the company's financial strategies. Share buyback programs have been a key feature, aimed at returning value to shareholders and reducing outstanding shares. For example, the Q1 2024 earnings report highlighted share repurchases as part of its capital allocation strategy. While there have been no major acquisitions or mergers that drastically altered ownership, the company continually assesses its portfolio, which may lead to divestitures or smaller acquisitions that affect asset distribution.
The Kimberly-Clark corporation is heavily influenced by industry trends, such as the increasing dominance of institutional investors and the rise of passive investing through index funds. These trends often lead to a more concentrated ownership among a few large asset managers, potentially increasing their influence on corporate governance and Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) matters. The company's focus on organic growth, strategic acquisitions, and efficient capital deployment indirectly influences its ownership profile by attracting and retaining investors. To delve deeper into the company's strategic approach, consider exploring the Marketing Strategy of Kimberly-Clark.
The Kimberly-Clark history shows that the company has remained committed to maintaining its current public ownership structure. The focus is on delivering consistent returns to its diverse shareholder base. The company's ongoing investor relations activities suggest this commitment. The company's financial strategies and market dynamics indirectly affect its ownership profile.
Share buybacks are a key strategy to return value to shareholders. They also reduce the number of outstanding shares, increasing earnings per share. In Q1 2024, share repurchases were highlighted as part of the capital allocation strategy.
Institutional investors have a significant impact on Kimberly-Clark ownership. Their increasing dominance and the rise of passive investing lead to concentrated ownership among large asset managers. This can influence corporate governance and ESG matters.
The company operates in a competitive consumer goods market. Public statements and analyst reports often focus on growth strategies, cost management, and market share. These factors indirectly influence the company's ownership profile.
Is Kimberly-Clark a public company? Yes, it is. The company is committed to maintaining its public ownership structure. This involves focusing on delivering consistent returns to its diverse shareholder base. Investor relations are key.
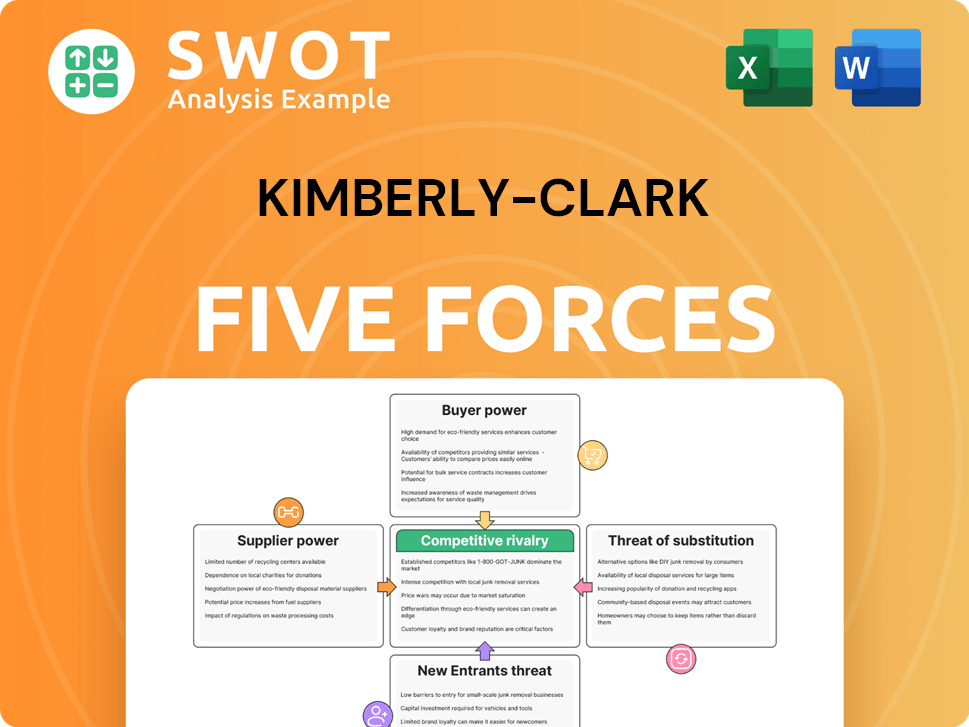
Kimberly-Clark Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of Kimberly-Clark Company?
- What is Competitive Landscape of Kimberly-Clark Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Kimberly-Clark Company?
- How Does Kimberly-Clark Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Kimberly-Clark Company?
- What is Brief History of Kimberly-Clark Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Kimberly-Clark Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.